Abstract
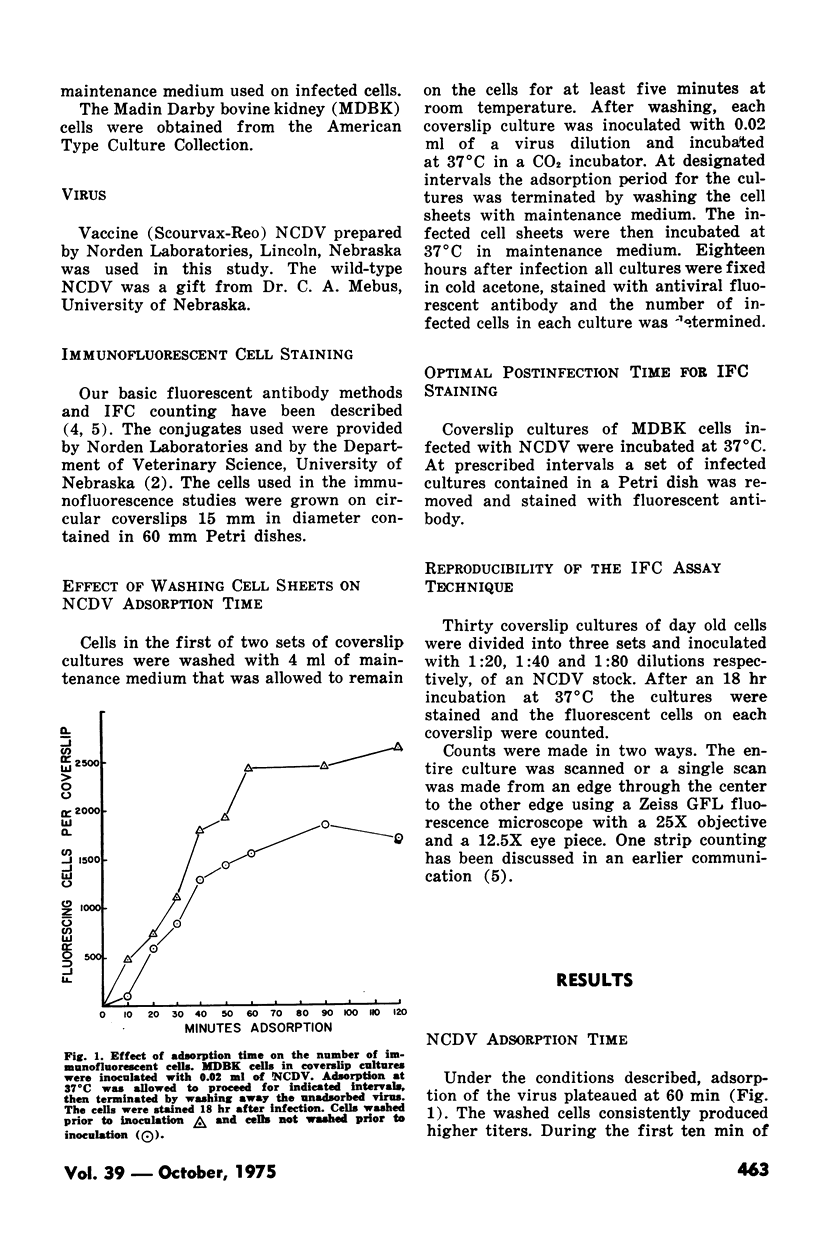
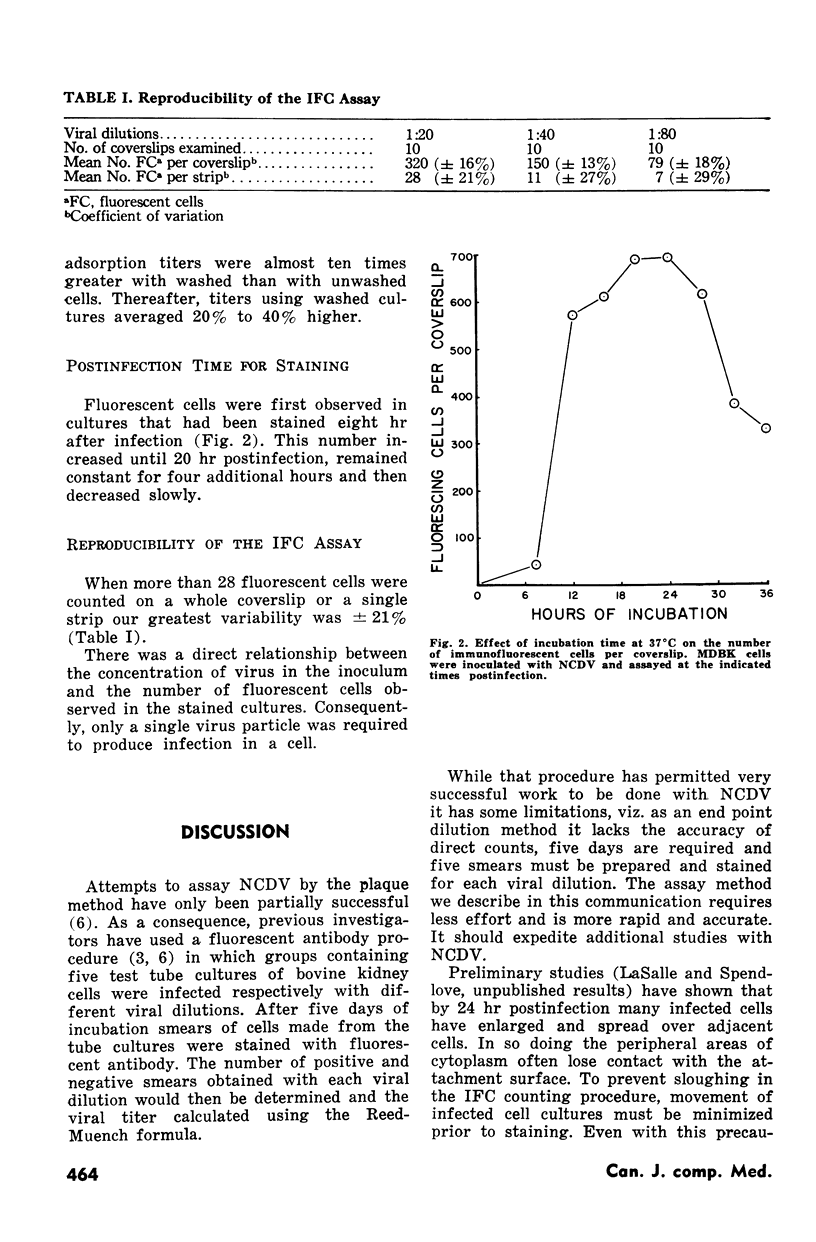
A reliable plaque assay procedure has not yet been described for the neonatal calf diarrhea virus. Therefore, a previously developed immunofluorescent cell counting procedure was adapted to assay this virus. Adsorption of the virus to bovine kidney cells plateaued at 60 minutes. The optimal staining time was between 20 and 24 hours postinfection. Infected cells begun releasing from the coverslips if the cultures were incubated longer than 24 hours. This procedure has proven successful with virus grown in cell culture as well as virus present in fecal samples.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kapikian A. Z., Kim H. W., Wyatt R. G., Rodriguez W. J., Ross S., Cline W. L., Parrott R. H., Chanock R. M. Reoviruslike agent in stools: association with infantile diarrhea and development of serologic tests. Science. 1974 Sep 20;185(4156):1049–1053. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4156.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebus C. A., Kono M., Underdahl N. R., Twiehaus M. J. Cell culture propagation of neonatal calf diarrhea (scours) virus. Can Vet J. 1971 Mar;12(3):69–72. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu K. C., Spendlove R. S., Goede R. W. Immunofluorescent cell assay of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Mar;27(3):593–599. doi: 10.1128/am.27.3.593-599.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch A. B., Twiehaus M. J. Cell culture studies of a neonatal calf diarrhea virus. Can J Comp Med. 1973 Jul;37(3):287–294. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


