Abstract
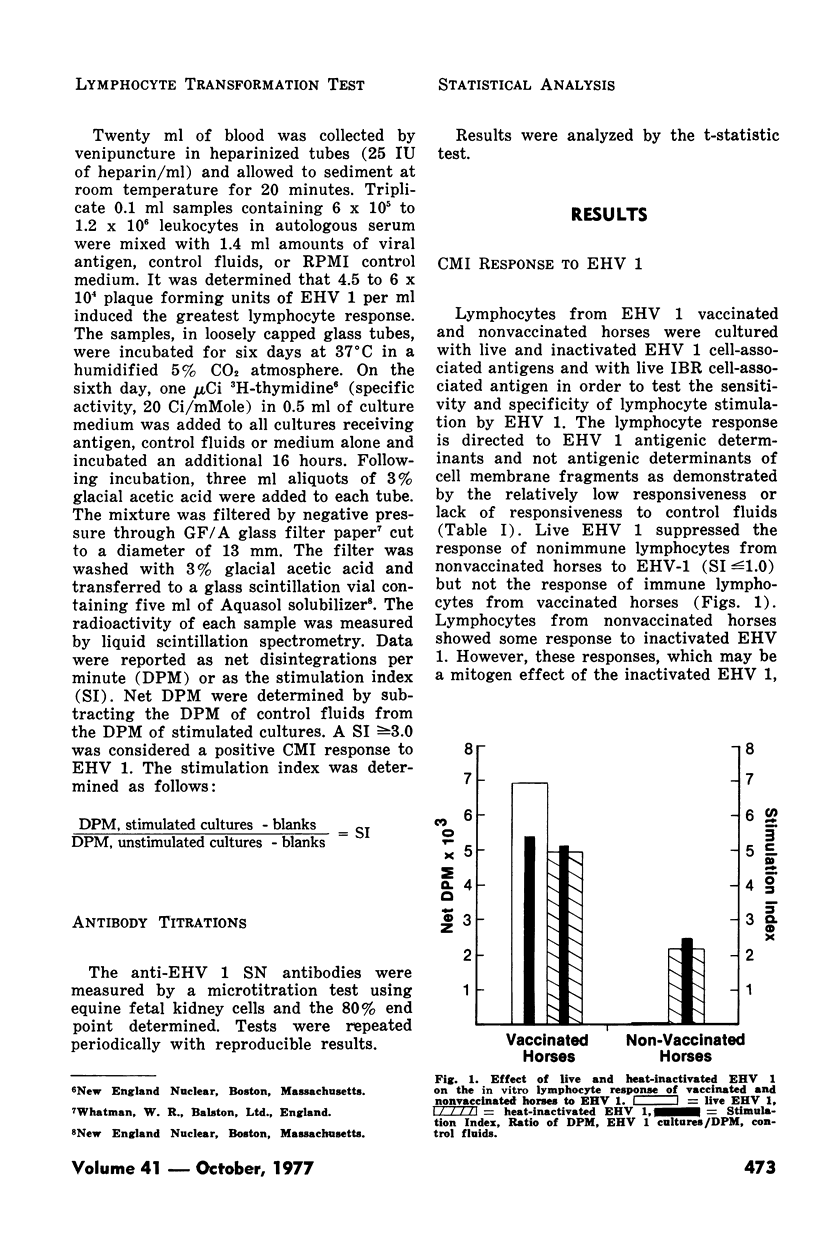
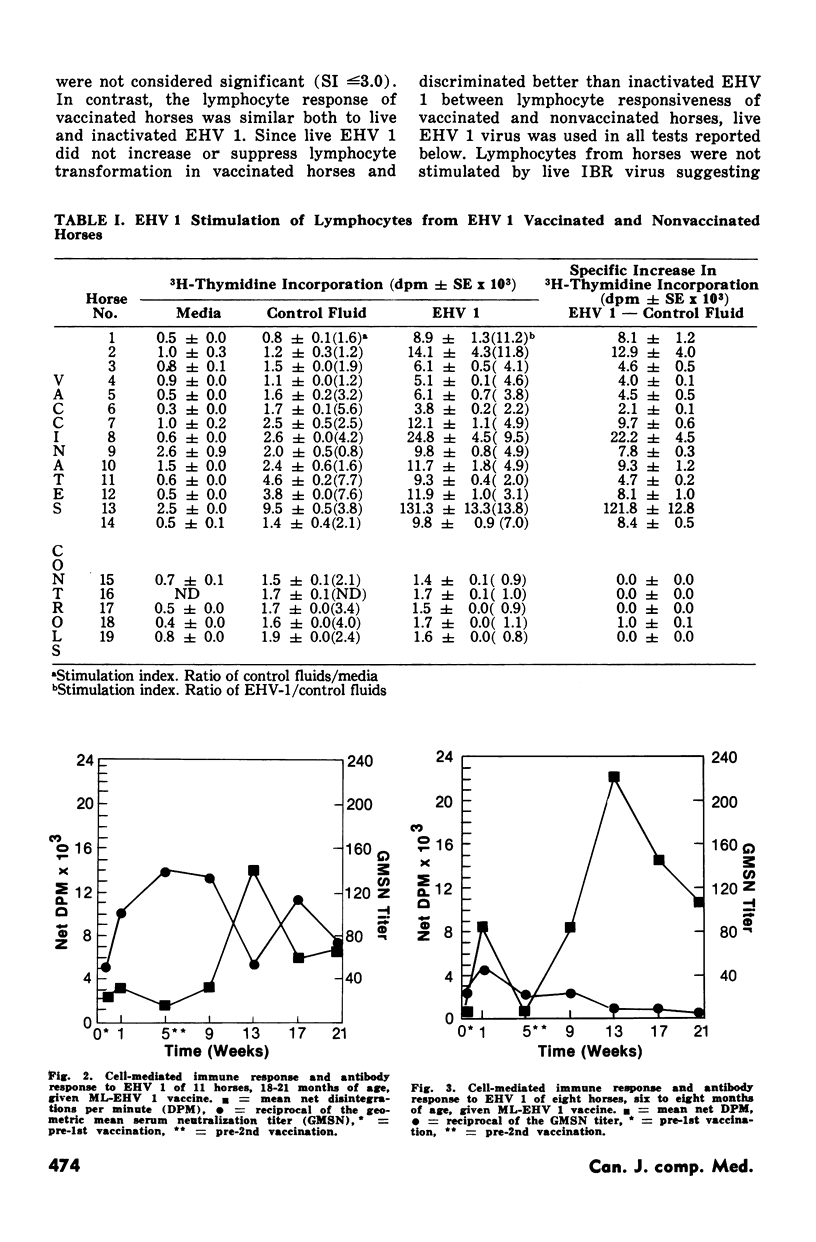
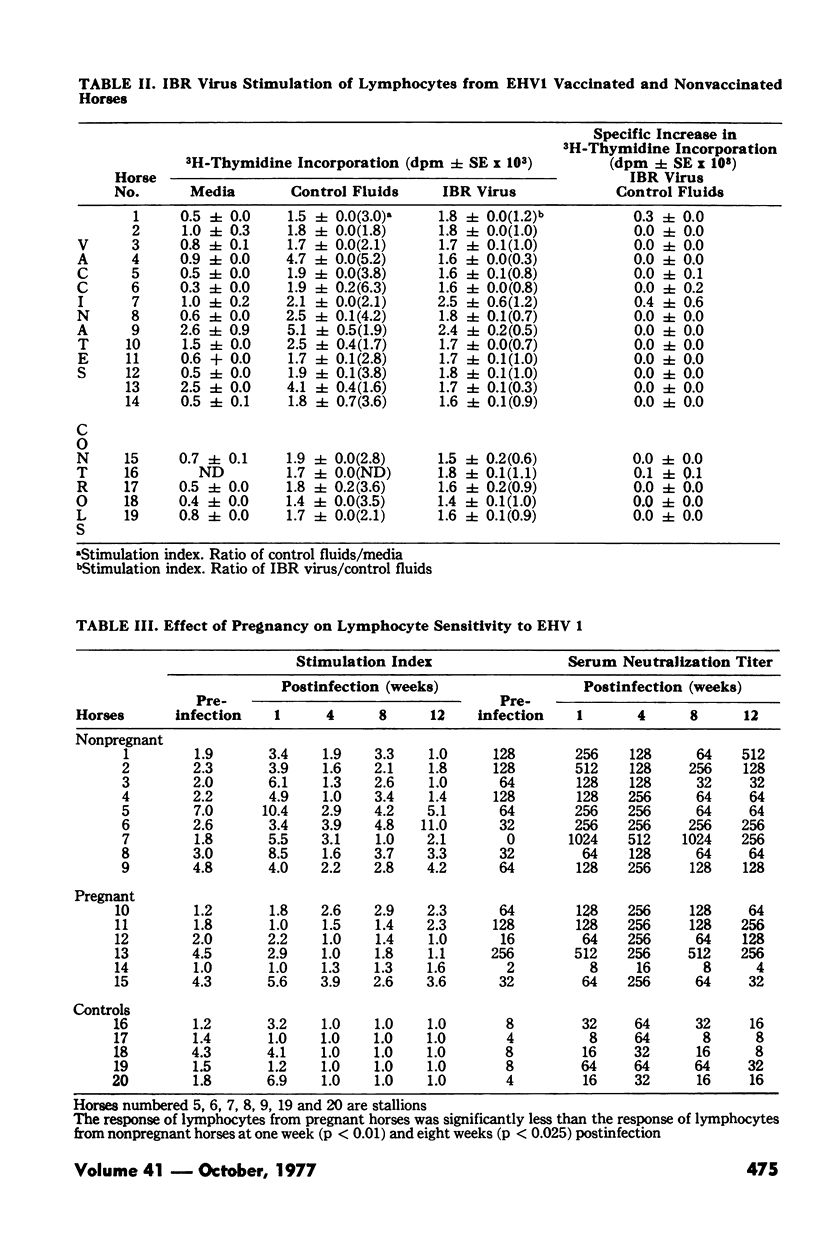
The cell-mediated immune response and antibody response of horses of varying ages and of pregnant horses to equine herpesvirus 1 antigen were examined. Six to eight month old horses showed either no increase or slight increases in anti-equine herpesvirus 1 serum neutralizing antibody following vaccination and revaccination with a modified live equine herpesvirus 1 vaccine. However, these same horses showed a marked increase in the cell-mediated immune response to equine herpesvirus 1 as measured by the lymphocyte transformation test. Eighteen to 21 month old horses showed four to 64-fold increases in anti-equine herpesvirus 1 serum neutralizing antibody titer following vaccination, but the cell-mediated immune response to equine herpesvirus 1 was low or absent. Only after revaccination did they show an increased cell-mediated immune response to equine herpesvirus 1. The cell-mediated immune response of mares in the latter stages of pregnancy to equine herpesivurs 1 was suppressed although antibody titers increased as much as 16-fold following exposure to virulent equine herpesvirus 1.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biesecker J. L., Fitch F. W., Rowley D. A., Stuart F. P. Passive antibody delays development of cell-mediated immunity in rats receiving renal allografts. Transplant Proc. 1973 Mar;5(1):667–669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryans J. T. On immunity to disease caused by equine herpesvirus 1. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1969 Jul 15;155(2):294–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLL E. R., BRYANS J. T. Epizootiology of equine viral rhinopneumonitis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1963 Jan 1;142:31–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLL E. R., BRYANS J. T. Immunization of young horses against viral rhinopneumonitis. Cornell Vet. 1963 Jan;53:24–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLL E. R., MCCOLLUM W. H., WALLACE M. E., BRYANS J. T., RICHARDS M. G. Complement-fixation reactions in equine virus abortion. Am J Vet Res. 1953 Jan;14(50):40–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eardley D. D., Sercarz E. E. Modulation of help and suppression in a hapten-carrier system. J Immunol. 1976 Mar;116(3):600–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn R., St Hill C. A., Govan A. J., Ralfs I. G., Gurney F. J., Denye V. Immunological responses in pregnancy and survival of fetal homograft. Br Med J. 1972 Jul 15;3(5819):150–152. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5819.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon R. K., Cohen P., Hencin R., Liebhaber S. A. Suppressor T cells. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):586–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand T. L., Ceglowski W. S., Damrongsak D., Friedman H. Development of antibody-forming cells in neonatal mice: stimulation and inhibition by calf thymus fractions. J Immunol. 1970 Aug;105(2):442–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson T., Kendrick J. W. Paralysis of horses associated with equine herpesvirus 1 infection. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1971 Apr 15;158(8):1351–1357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasakura S. A factor in maternal plasma during pregnancy that suppresses the reactivity of mixed leukocyte cultures. J Immunol. 1971 Nov;107(5):1296–1301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B., Lagrange P. H., Miller T. E., Ishibashi T. Feedback inhibition of specifically sensitized lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1974 Mar 1;139(3):543–559. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.3.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar K. G., Mills P., Baines M. G. A study of the influence of pregnancy on the thymus gland of the mouse. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1973 Dec 1;117(7):913–918. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(73)90061-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton H., Hegh V., Clunie G. J. Immunosuppression detected in pregnant mice by rosette inhibition test. Nature. 1974 May 31;249(456):459–460. doi: 10.1038/249459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notkins A. L. Immune mechanisms by which the spread of viral infections is stopped. Cell Immunol. 1974 Mar 30;11(1-3):478–483. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter V., Schlesinger M., Kalderon R., Trainin N. Response of human lymphocytes to PHA and Con A, dependent on and regulated by THF, a thymic hormone. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1927–1932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig M. J. Demonstration of suppressor T cells in a population of 'educated' T cells. Nature. 1974 Mar 15;248(445):236–238. doi: 10.1038/248236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thong Y. H., Steele R. W., Vincent M. M., Hensen S. A., Bellanti J. A. Impaired in vitro cell-mediated immunity to rubella virus during pregnancy. N Engl J Med. 1973 Sep 20;289(12):604–606. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197309202891203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman B. H., Namba Y. On soluble mediators of immunologic regulation. Cell Immunol. 1976 Jan;21(1):161–176. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90337-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks C. R., Coggins L. Immunity to equine herpesvirus type 1 (rhinopneumonitis): in vitro lymphocyte response. Am J Vet Res. 1976 May;37(5):486–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks C. R. In vitro cytotoxicity of serum and peripheral blood leukocytes for equine herpesvirus type 1-infected target cells. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Jan;38(1):117–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


