Abstract
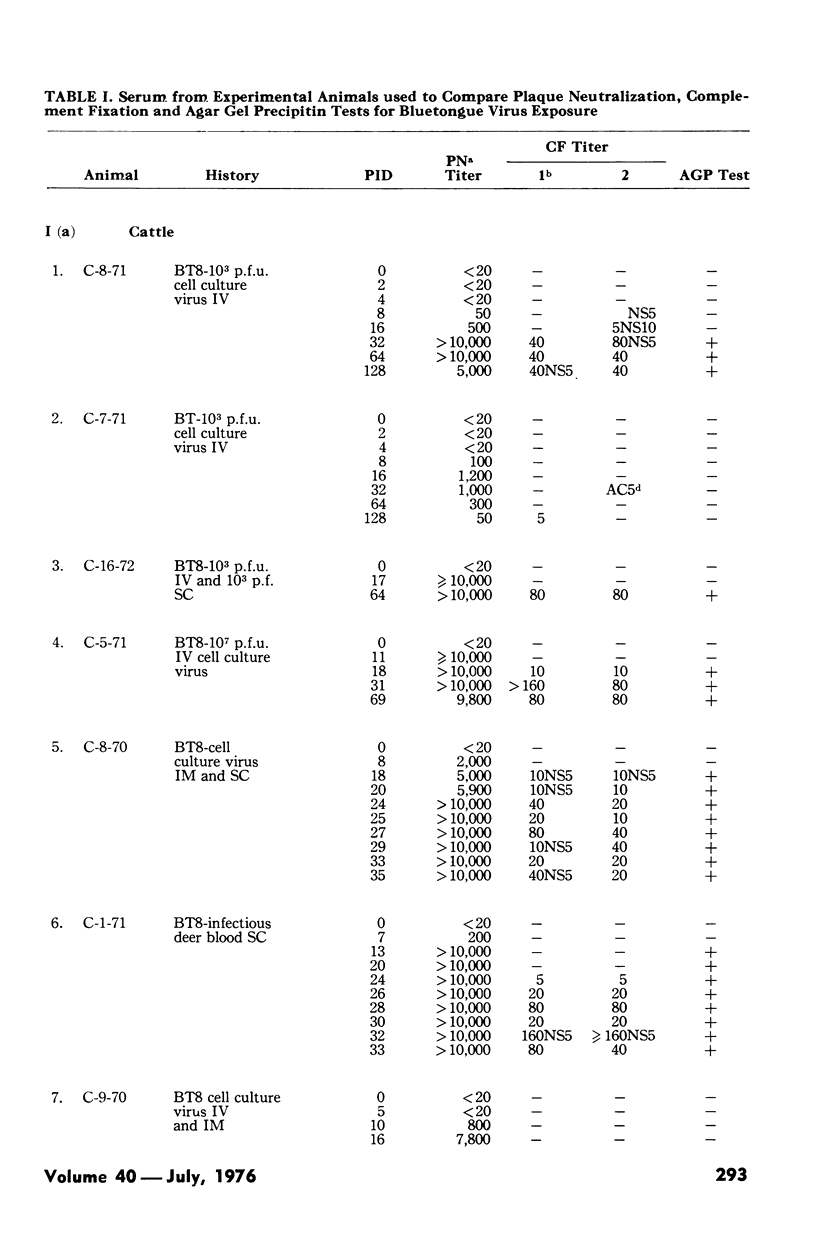
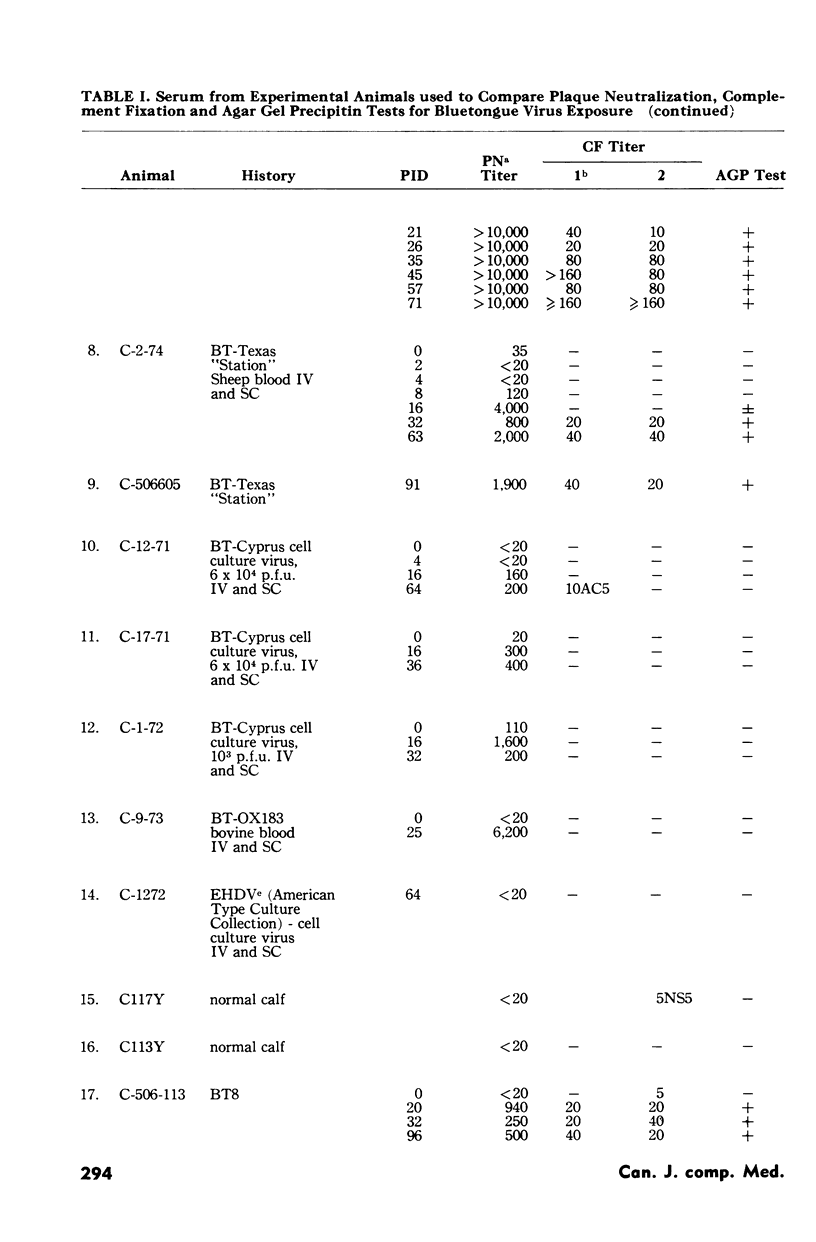
The plaque neutralization, complement fixation, and agar gel precipitin tests were compared by measuring bluetongue virus antibody in 137 serums from experimental animals (cattle and sheep) and suspected field reactors (cattle and deer). In general, the tests agreed well with each other. Plaque neutralization titers began earlier than the other two and went much higher than the complement fixation titers. Plaque neutralization titers usually peaked between two and three weeks after exposure and complement fixation titers from four to six weeks. The greater sensitivity of the plaque neutralization test allowed the detection of all complement fixation and agar gel precipitin reactors whereas occasionally the latter two tests failed to detect plaque neutralization reactors.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boulanger P., Ruckerbauer G. M., Bannister G. L., Gray D. P., Girard A. Studies on bluetongue. 3. Comparison of two complement-fixation methods. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1967 Jul;31(7):166–170. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulanger P. Technique of a Modified Direct Complement-Fixation Test for Viral Antibodies in Heat Inactivated Cattle Serum. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1960 Sep;24(9):262–269. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrier S. P., Boulanger P. Improvements in the modified direct complement fixation test and its application in the detection of bluetongue antibodies in cattle and sheep sera. Can J Comp Med. 1975 Apr;39(2):231–233. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray D. P., Willis N. G., Girard A., Ruckerbauer G. M., Boulanger P., Bannister G. L. Studies on bluetongue. VI. Animal transmission studies. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1967 Jul;31(7):182–188. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell P. G., Kümm N. A., Botha M. J. The application of improved techniques to the identification of strains of bluetongue virus. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 1970 Mar;37(1):59–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jochim M. M., Chow T. L. Immunodiffusion of bluetongue virus. Am J Vet Res. 1969 Jan;30(1):33–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON A., APPEL M., BANNISTER G. L., RUCKERBAUER G. M., BOULANGER P. STUDIES ON BLUETONGUE II. COMPLEMENT-FIXING ACTIVITY OF OVINE AND BOVINE SERA. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1965 May;29:113–117. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P. K., Nisalak A., Sukhavachana P., Vivona S. A plaque reduction test for dengue virus neutralizing antibodies. J Immunol. 1967 Aug;99(2):285–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVEHAG S. E., MANDEL B. THE FORMATION AND PROPERTIES OF POLIOVIRUS-NEUTRALIZING ANTIBODY. I. 19S AND 7S ANTIBODY FORMATION: DIFFERENCES IN KINETICS AND ANTIGEN DOSE REQUIREMENT FOR INDUCTION. J Exp Med. 1964 Jan 1;119:1–19. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seawright G. L., Harding G., Thomas F. C., Hanson R. P. Microculture plaque neutralization test for California group arboviruses. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Nov;28(5):802–806. doi: 10.1128/am.28.5.802-806.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas F. C., Trainer D. O. Bluetongue virus: (1) in pregnant white-tailed deer (2) a plaque reduction neutralization test. J Wildl Dis. 1970 Oct;6(4):384–388. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-6.4.384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas F. C., Trainer D. O. Bluetongue virus: some relationships among North American isolates and further comparisons with EHD virus. Can J Comp Med. 1971 Jul;35(3):187–191. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


