Abstract
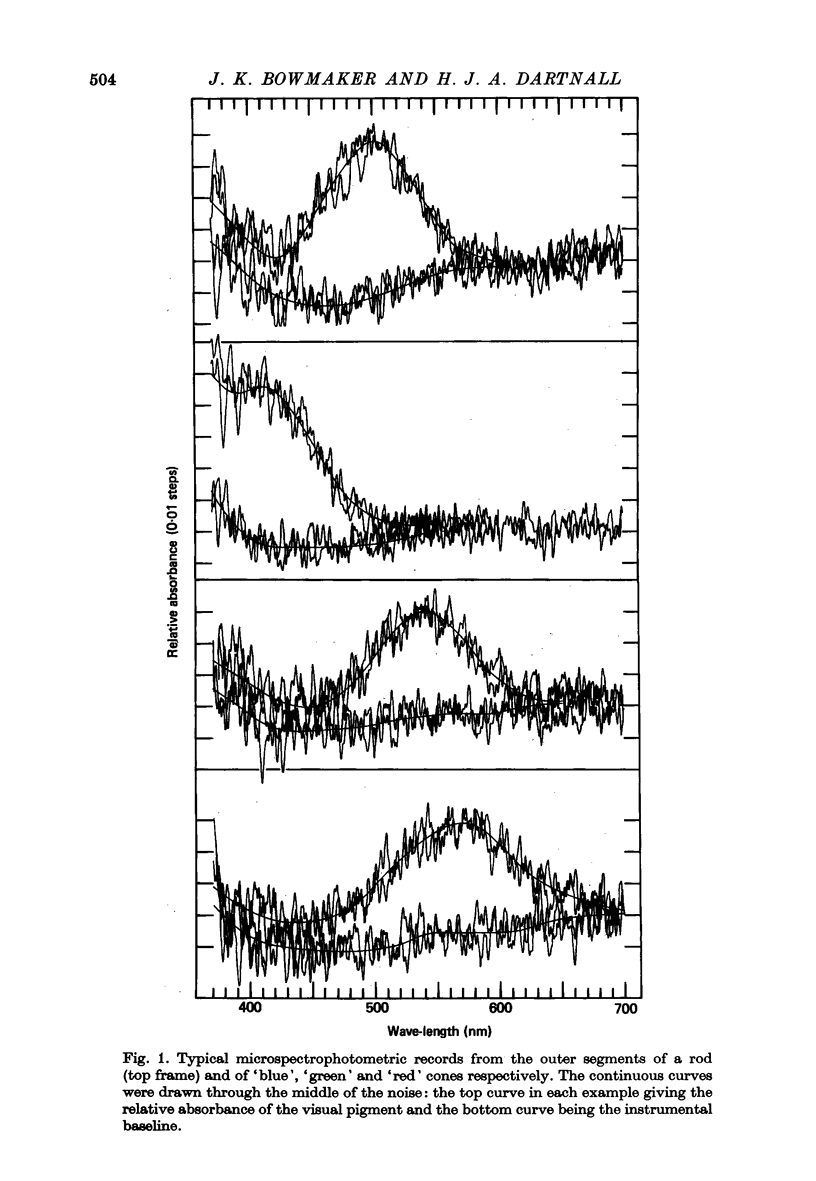
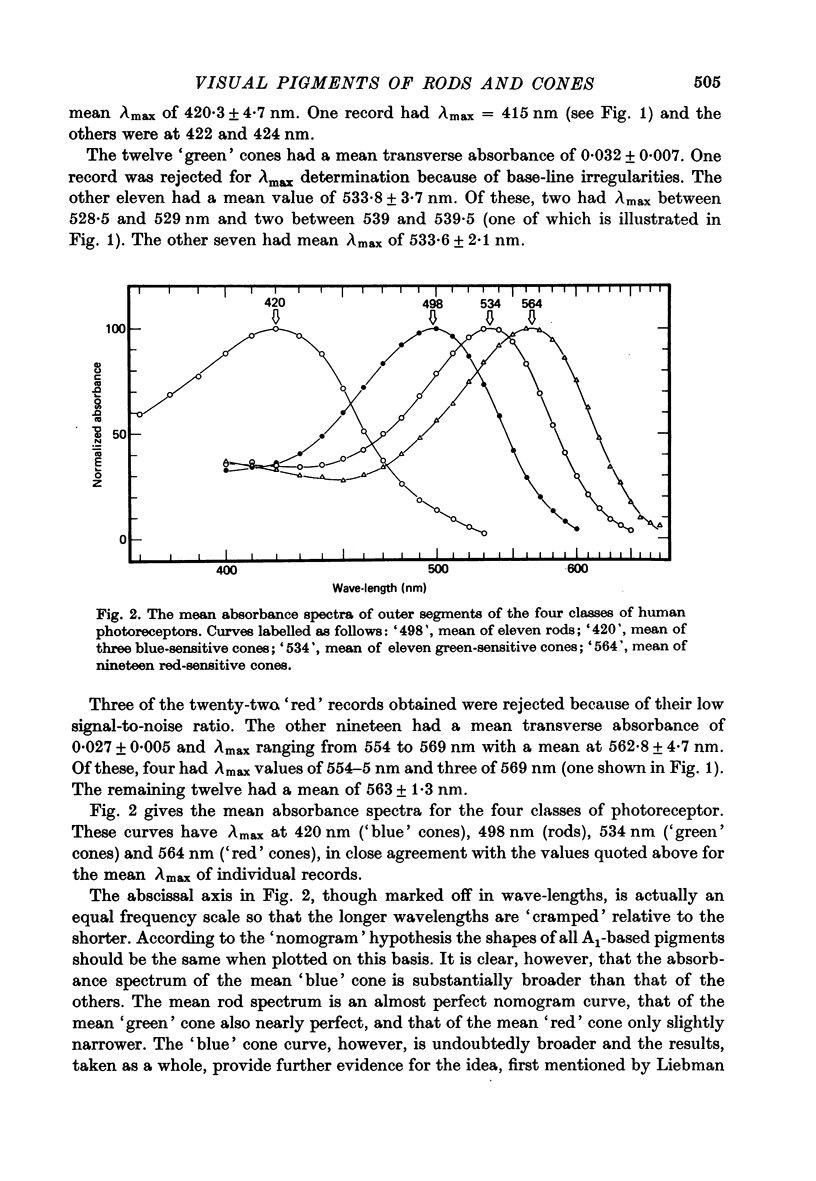
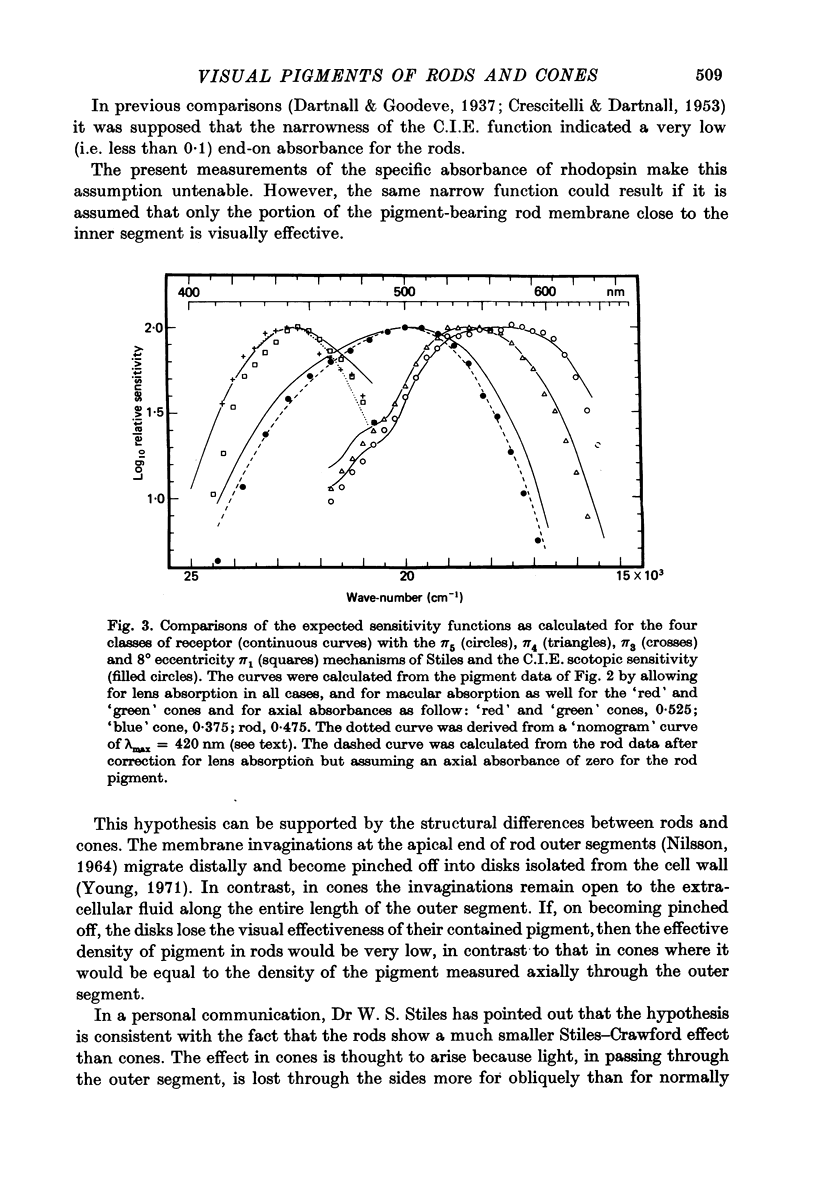
1. Microspectrophotometric measurements have been made of the photopigments of individual rods and cones from the retina of a man. The measuring beam was passed transversely through the isolated outer segments. 2. The mean absorbance spectrum for rods (n = 11) had a peak at 497.6 +/- 3.3 nm and the mean transverse absorbance was 0.035 +/- 0.007. 3. Three classes of cones were identified. The long-wave cones ('red' cones) had a lambda max of 562.8 +/- 4.7 nm (n = 19) with a mean transverse absorbance of 0.027 +/- 0.005. The middle-wave cones ('green' cones) had a lambda max of 533.8 +/- 3.7 nm (n = 11) with a mean transverse absorbance of 0.032 +/- 0.007. The short-wave cones ('blue' cones) had a lambda max of 420.3 +/- 4.7 nm (n = 3) with a mean transverse absorbance of 0.037 +/- 0.011. 4. If assumptions are made about the length of cones and about pre-receptoral absorption, it is possible to derive psychophysical sensitivities for the cones that closely resemble the appropriate pi mechanisms of W. S. Stiles. 5. If assumptions are made about the length of rods and about pre-receptoral absorption, however, the psychophysical sensitivity derived for the rods is considerably broader than the C.I.E. scotopic sensitivity function.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWN P. K., WALD G. VISUAL PIGMENTS IN SINGLE RODS AND CONES OF THE HUMAN RETINA. DIRECT MEASUREMENTS REVEAL MECHANISMS OF HUMAN NIGHT AND COLOR VISION. Science. 1964 Apr 3;144(3614):45–52. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3614.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Lamb T. D., Yau K. W. The membrane current of single rod outer segments. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:589–611. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowmaker J. K., Dartnall H. J., Lythgoe J. N., Mollon J. D. The visual pigments of rods and cones in the rhesus monkey, Macaca mulatta. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:329–348. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowmaker J. K., Loew E. R., Liebman P. A. Variation in the lambdamax of rhodopsin from individual frogs. Vision Res. 1975 Aug-Sep;15:997–1003. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(75)90242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowmaker J. K. The visual pigments, oil droplets and spectral sensitivity of the pigeon. Vision Res. 1977;17(10):1129–1138. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(77)90147-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges C. D. Spectroscopic properties of porphyropsins. Vision Res. 1967 May;7(5):349–369. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(67)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESCITELLI F., DARTNALL H. J. Human visual purple. Nature. 1953 Aug 1;172(4370):195–197. doi: 10.1038/172195a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dartnall H. J., Lythgoe J. N. The spectral clustering of visual pigments. Vision Res. 1965 Apr;5(3):81–100. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(65)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hárosi F. I. Absorption spectra and linear dichroism of some amphibian photoreceptors. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Sep;66(3):357–382. doi: 10.1085/jgp.66.3.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman P. A., Entine G. Sensitive low-light-level microspectrophotometer: detection of photosensitive pigments of retinal cones. J Opt Soc Am. 1964 Dec;54(12):1451–1459. doi: 10.1364/josa.54.001451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman P. A., Entine G. Visual pigments of frog and tadpole (Rana pipiens). Vision Res. 1968 Jul;8(7):761–775. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(68)90128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKS W. B., DOBELLE W. H., MACNICHOL E. F., Jr VISUAL PIGMENTS OF SINGLE PRIMATE CONES. Science. 1964 Mar 13;143(3611):1181–1183. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3611.1181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NILSSON S. E. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC CLASSIFICATION OF THE RETINAL RECEPTORS OF THE LEOPARD FROG (RANA PIPIENS). J Ultrastruct Res. 1964 Jun;10:390–416. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(64)80018-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn R. D., Hagins W. A. Signal transmission along retinal rods and the origin of the electroretinographic a-wave. Nature. 1969 Jul 12;223(5202):201–204. doi: 10.1038/223201a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald G., Brown P. K. Human color vision and color blindness. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1965;30:345–361. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1965.030.01.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. W. An hypothesis to account for a basic distinction between rods and cones. Vision Res. 1971 Jan;11(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(71)90201-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


