Abstract
1. Experiments were conducted in isolated perfused rat kidneys to determine the effect of raising perfusate albumin concentration on renin release.
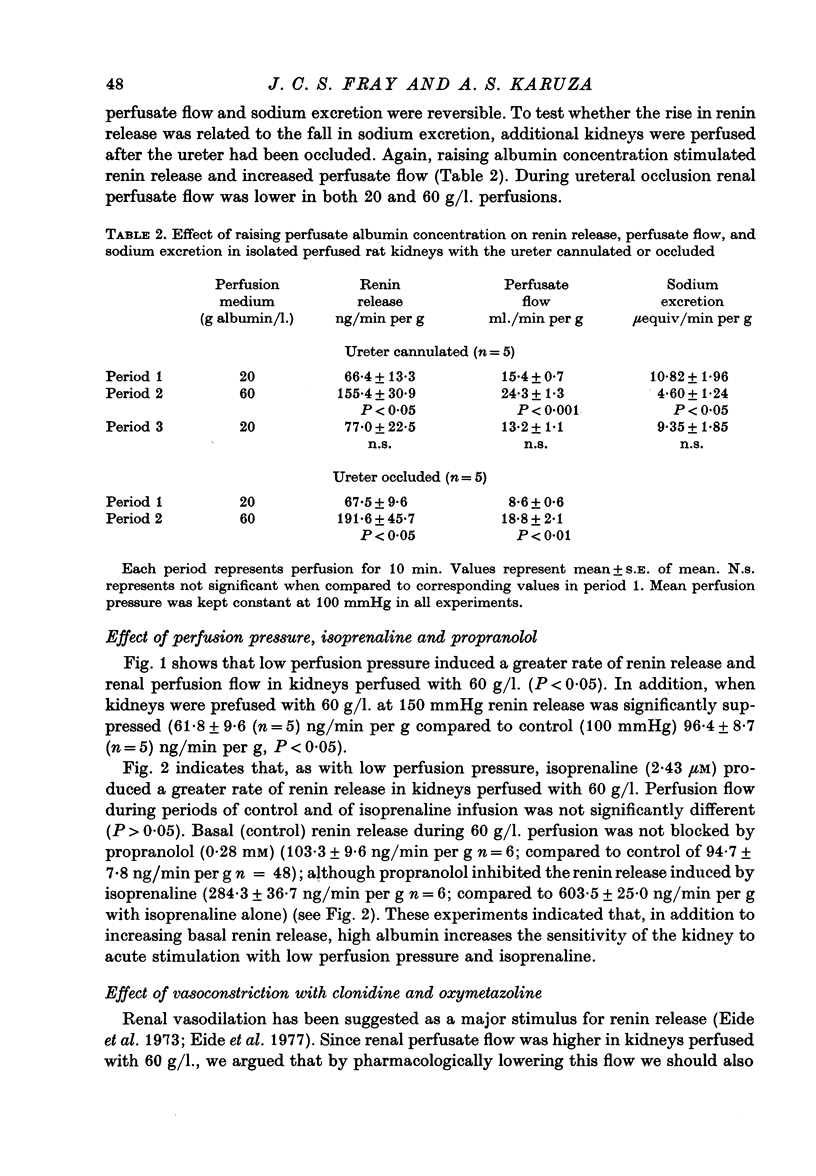
2. Raising albumin concentration in the perfusion fluid from 20 g/l. to 60 g/l. (high albumin concentration) increased renin release and renal perfusate flow rate. The effect was reversible.
3. Ureteral occlusion did not prevent the rise in renin release and renal perfusate flow induced by high albumin concentration.
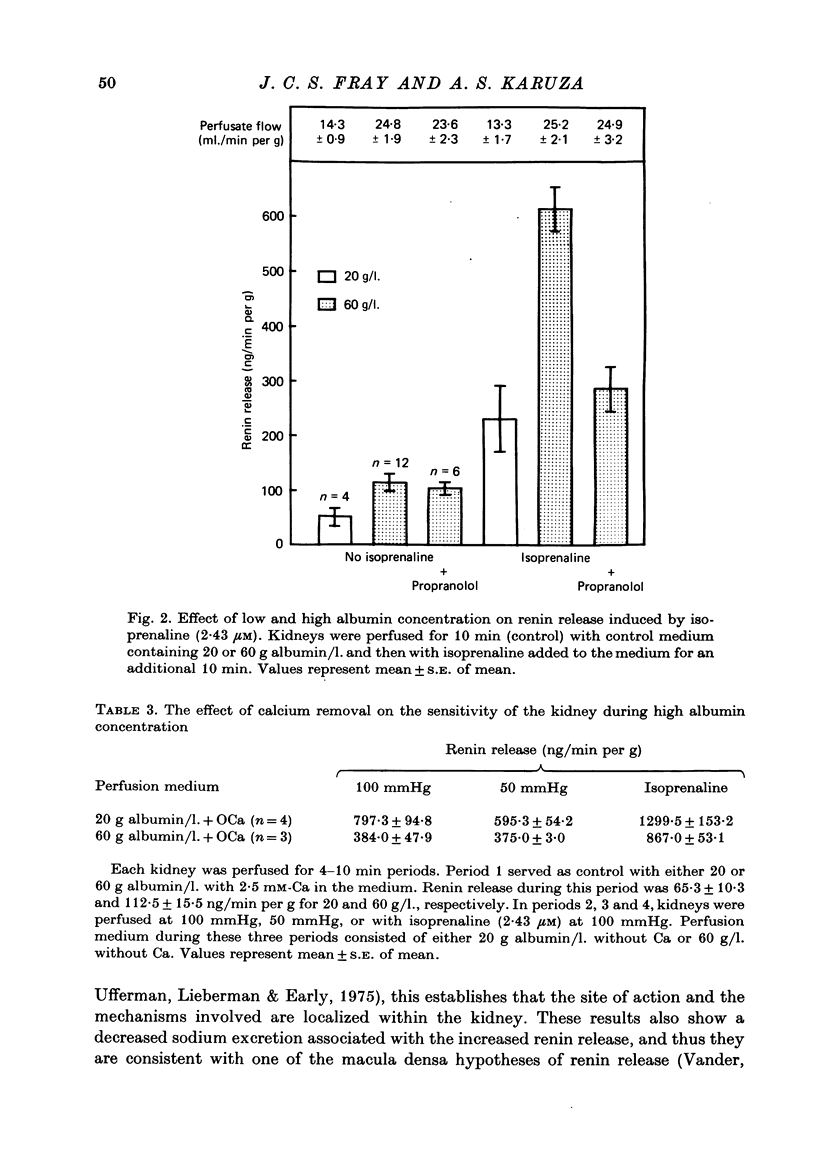
4. Propranolol (0·28 mM) did not block the renin release stimulated by high albumin concentration, but it inhibited the release stimulated by isoprenaline (2·43 μM).
5. Clonidine (10 μM) and oxymetazoline (10 μM) constricted the renal vasculature and stimulated renin release during high perfusate albumin concentration providing perfusion pressure was kept constant.
6. Low renal perfusion pressure (50 mmHg) and isoprenaline (2·43 μM) stimulated renin release in perfusion experiments with both 20 and 60 g/l., but the rate of renin release was substantially greater with 60 g/l.
7. On the other hand, perfusion fluid deprived of calcium induced a greater increase in renin release in kidneys perfused with 20 g/l. than in those with 60 g/l.
8. We conclude that high albumin concentration stimulates renin release in isolated perfused rat kidneys by a mechanism which does not involve the renal nerve, direct renal vasodilation or sodium excretion. High albumin concentration may increase the sensitivity of the kidney to acute stimulation by a mechanism involving calcium.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer P. G., Navar L. G. Renal vasodilation and uncoupling of blood flow and filtration rate autoregulation. Kidney Int. 1973 Jul;4(1):12–21. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullivant M. Autoregulation of plasma flow in the isolated perfused rat kidney. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:141–153. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunag R. D., Page I. H., McCubbin J. W. Influence of dietary sodium on stimuli causing renin release. Am J Physiol. 1966 Dec;211(6):1383–1386. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.6.1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. O., Freeman R. H. Mechanisms regulating renin release. Physiol Rev. 1976 Jan;56(1):1–56. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eide I., Loyning E., Kiil F. Evidence for hemodynamic autoregulation of renin release. Circ Res. 1973 Feb;32(2):237–245. doi: 10.1161/01.res.32.2.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eide I., Loyning E., Langård O., Kiil F. Mechanism of renin release during acute ureteral constriction in dogs. Circ Res. 1977 Mar;40(3):293–299. doi: 10.1161/01.res.40.3.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eide I., Löyning E., Kill F. Potentiation of renin release by combining renal arterial constriction and beta-adrenergic stimulation. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1974 Dec;34(4):301–310. doi: 10.3109/00365517409049884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faucheux B., Buu N. T., Kuchel O. Effects of saline and albumin on plasma and urinary catecholamines in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1977 Feb;232(2):F123–F127. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.232.2.F123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fray J. C., Mayer P. V. Decreased plasma renin activity and renin release in rats with phaeochromocytoma. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1977 Nov;53(5):447–452. doi: 10.1042/cs0530447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fray J. C. Mechanism of increased renin release during sodium deprivation. Am J Physiol. 1978 May;234(5):F376–F380. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.234.5.F376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fray J. C., Park C. S. Influence of potassium, sodium, perfusion pressure, and isoprenaline on renin release induced by acute calcium deprivation. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:363–372. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fray J. C. Stretch receptor control of renin release in perfused rat kidney: effect of high perfusate potassium. J Physiol. 1978 Sep;282:207–217. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fray J. C. Stretch receptor model for renin release with evidence from perfused rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1976 Sep;231(3):936–944. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.3.936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fray J. S. Stimulation of renin release in perfused kidney by low calcium and high magnesium. Am J Physiol. 1977 Apr;232(4):F377–F382. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.232.4.F377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb S., Bosanac M., Goldberg M., Agus Z. S. Effects of calcium on renal tubular phosphate reabsorption. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jan;234(1):F22–F28. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.234.1.F22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. E., Guyton A. C. Changes in renal hemodynamics and renin release caused by increased plasma oncotic pressure. Am J Physiol. 1976 Nov;231(5 Pt 1):1550–1556. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.5.1550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada E., Rubin R. P. Stimulation of renin secretion and calcium efflux from the isolated perfused cat kidney by noradrenaline after prolonged calcium deprivation. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:367–379. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys M. H., Reid I. A., Ufferman R. C., Lieberman R. A., Earley L. E. The relationship between sodium excretion and renin secretion by the perfused kidney. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Dec;150(3):728–734. doi: 10.3181/00379727-150-39115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiil F. Influence of autoregulation on renin release and sodium excretion. Kidney Int Suppl. 1975 Sep;:S208–S218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox F. G., Willis L. R., Strandhoy J. W., Schneider E. G., Navar L. G., Ott C. E. Role of peritubule Starling forces in proximal reabsorption following albumin infusion. Am J Physiol. 1972 Oct;223(4):741–749. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.4.741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester G. E., Rubin R. P. The role of calcium in renin secretion from the isolated perfused cat kidney. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(1):93–108. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan A. G., Tenyi I., Peart W. S., Breathnach A. S., Martin B. G. The effect of lanthanum on renin secretion and renal vasoconstriction. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Jan 14;195(1120):327–342. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez G. A., Reid I. A., Rose J. C., Ganong W. F. Effect of norepinephrine on renin release and the cyclic AMP content of rat kidney slices: modification by sodium deficiency and alpha-adrenergic blockade. Neuroendocrinology. 1978;27(1-2):63–73. doi: 10.1159/000122832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navar L. G., Baer P. G., Wallace S. L., McDaniel J. K. Reduced intrarenal resistance and autoregulatory capacity after hyperoncotic dextran. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jul;221(1):329–334. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.1.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan P. L., Reid I. A. Mechanism of suppression of renin secretion by clonidine in the dog. Circ Res. 1978 Feb;42(2):206–211. doi: 10.1161/01.res.42.2.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. L., Noordewier B., Hook J. B., Bailie M. D. Mechanism of prostaglandin E(2) stimulation of renin secretion. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Nov;159(2):249–252. doi: 10.3181/00379727-159-40325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peart W. S. The kidney as an endocrine organ. Lancet. 1977 Sep 10;2(8037):543–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagawa H., Vander A. J. Effect of acetylcholine on renin secretion in salt-depleted dogs. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Dec;132(3):1087–1090. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dongen R., Peart W. S. Calcium dependence of the inhibitory effect of angiotensin on renin secretion in the isolated perfused kidney of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Jan;50(1):125–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09599.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J. Control of renin release. Physiol Rev. 1967 Jul;47(3):359–382. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1967.47.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WURZEL M., BACON R. C., KALT R. B., ZWEIFACH B. W. VASOACTIVE PROPERTIES OF PLASMA PROTEIN FRACTIONS. Am J Physiol. 1964 Apr;206:923–925. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.4.923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witty R. T., Davis J. O., Shade R. E., Johnson J. A., Prewitt R. L. Mechanisms regulating renin release in dogs with thoracic caval constriction. Circ Res. 1972 Sep;31(3):339–347. doi: 10.1161/01.res.31.3.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


