Abstract
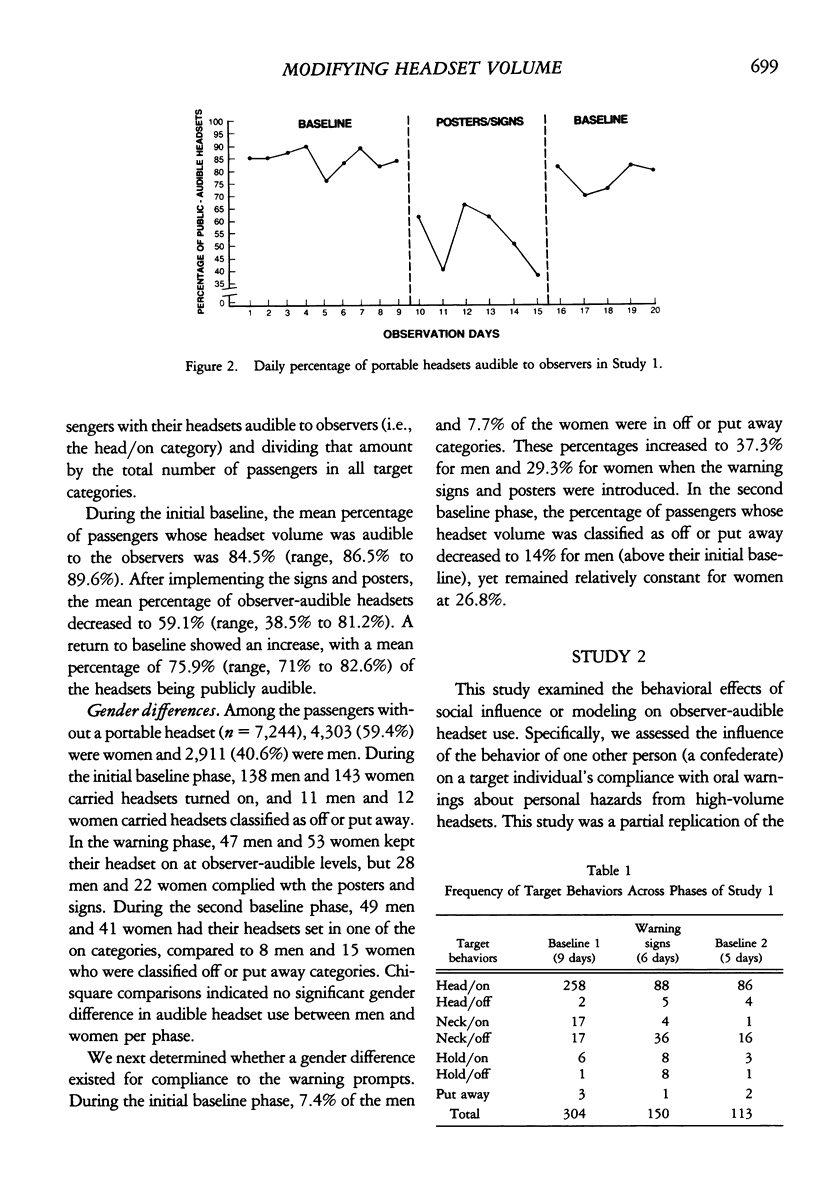
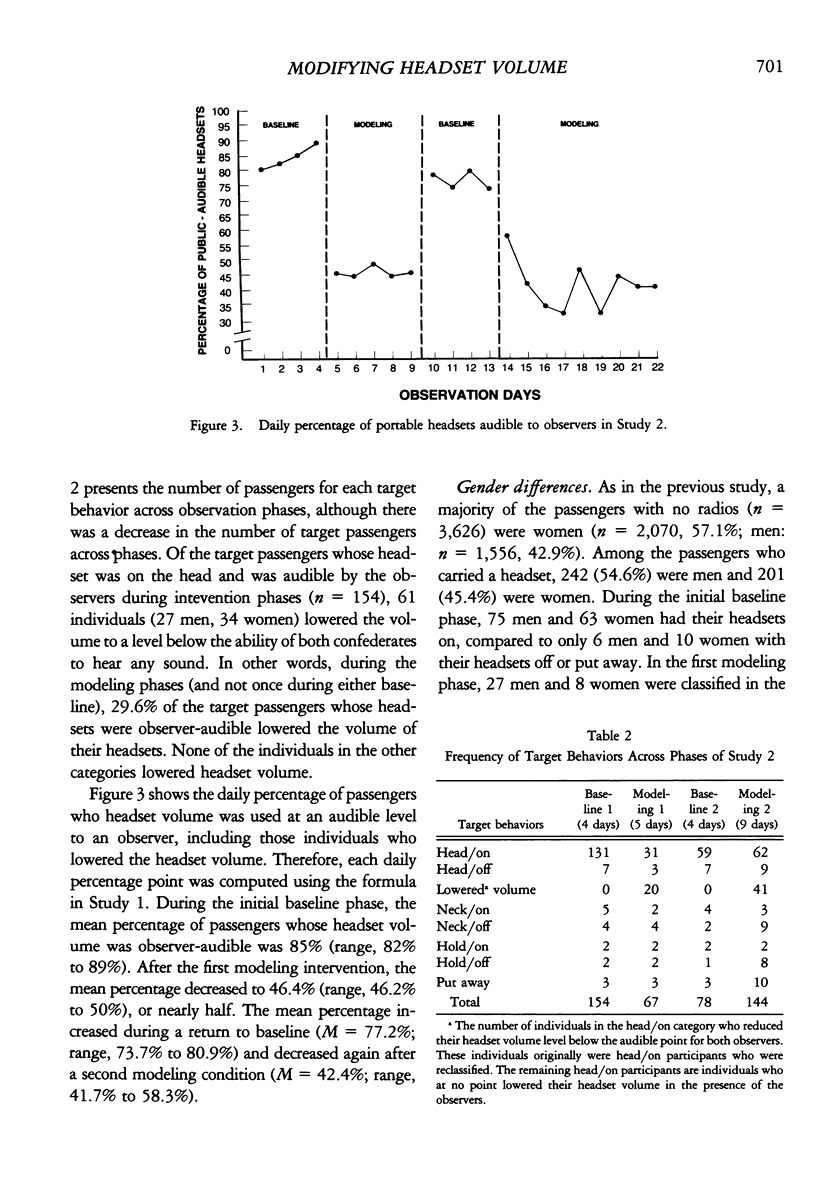
Two studies examined effects of interventions to reduce noise levels from portable stereo headphones. Study 1 examined the effectiveness of warning signs posted in and nearby public elevators with 567 passengers possessing a portable headphone (total N = 7,811). During a 9-day baseline, the mean percentage of headphones played at an observer-audible level was 85%. During a subsequent 6-day warning sign phase, the mean percentage of audible headphones declined to 59%, which increased to a mean of 76% during a second baseline phase (5 days). Study 2 assessed the impact of a student confederate who lowered his or her observer-audible headphone volume at the polite request of a second student confederate. Of the 4,069 elevator passengers, 433 possessed a portable headset. The mean percentage of observer-audible headphones during a 4-day baseline was 85%. Subsequently, a 5-day modeling intervention reduced audible volumes to a mean of 46%. During a second baseline phase of 4 days, the mean level was 77%, and during reintroduction of the modeling phase (9 days) the mean level was 42%. The modeling intervention was significantly more effective with women (53% compliance) than men (29% compliance).
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ferrari J. R., Baldwin C. H. From cars to carts. Increasing safety belt usage in shopping carts. Behav Modif. 1989 Jan;13(1):51–64. doi: 10.1177/01454455890131003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari J. R., Barone R. C., Jason L. A., Rose T. The effects of a personal phone call prompt on blood donor commitment. J Community Psychol. 1985 Jul;13(3):295–298. doi: 10.1002/jcop.2290130307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari J. R., Barone R. C., Jason L. A., Rose T. The use of incentives to increase blood donations. J Soc Psychol. 1985 Dec;125(6):791–793. doi: 10.1080/00224545.1985.9713559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. T., Kazdin A. E., Haney J. I. Social validation and training of emergency fire safety skills for potential injury prevention and life saving. J Appl Behav Anal. 1981 Fall;14(3):249–260. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1981.14-249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. C., Senders C. W., Gantz B. J., Otto S. R. Transient sensorineural hearing loss after overuse of portable headphone cassette radios. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1985 Oct;93(5):622–625. doi: 10.1177/019459988509300510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. G., Breslin M., Roper R. G. Sound levels from personal cassette players. Br J Audiol. 1987 Nov;21(4):273–278. doi: 10.3109/03005368709076419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. G., Rossi G., Olina M. Damage risk from personal cassette players. Br J Audiol. 1987 Nov;21(4):279–288. doi: 10.3109/03005368709076420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twardosz S., Cataldo M. F., Risley T. R. Open environment design for infant and toddler day care. J Appl Behav Anal. 1974 Winter;7(4):529–546. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1974.7-529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



