Abstract
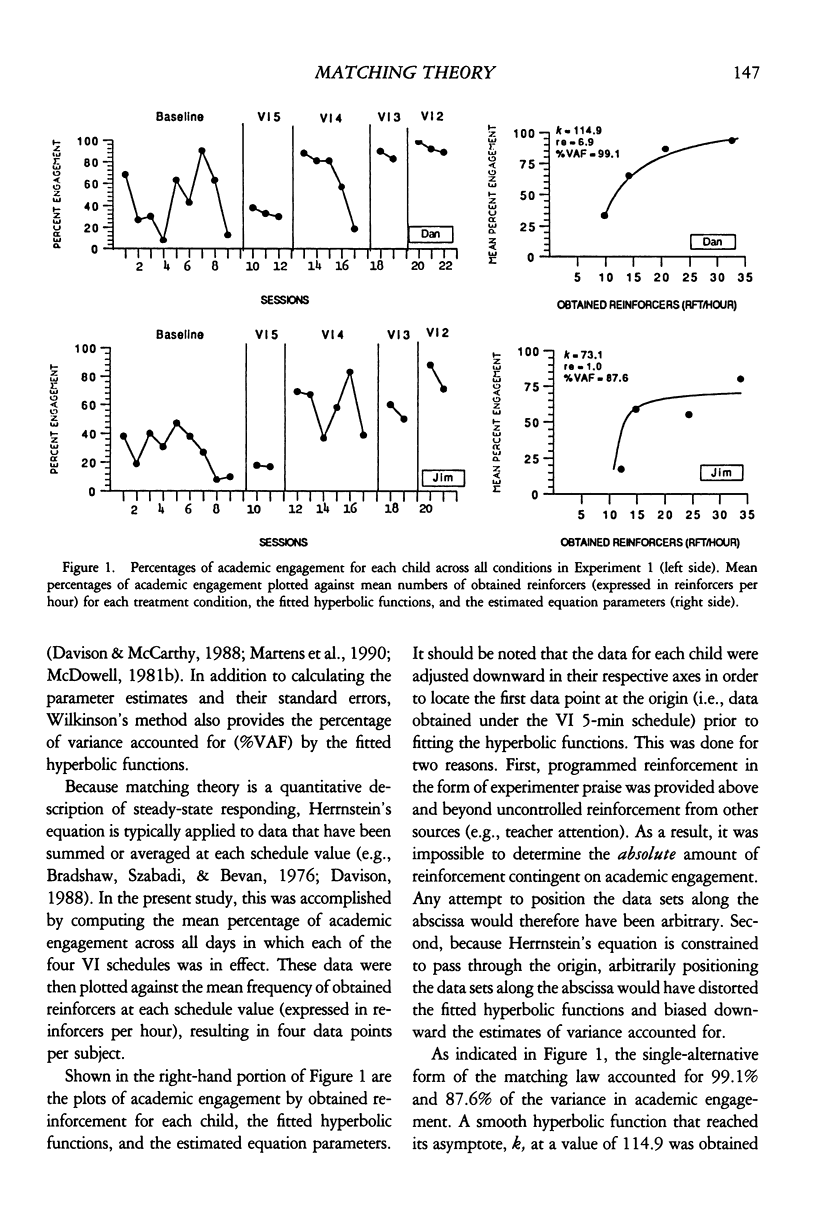
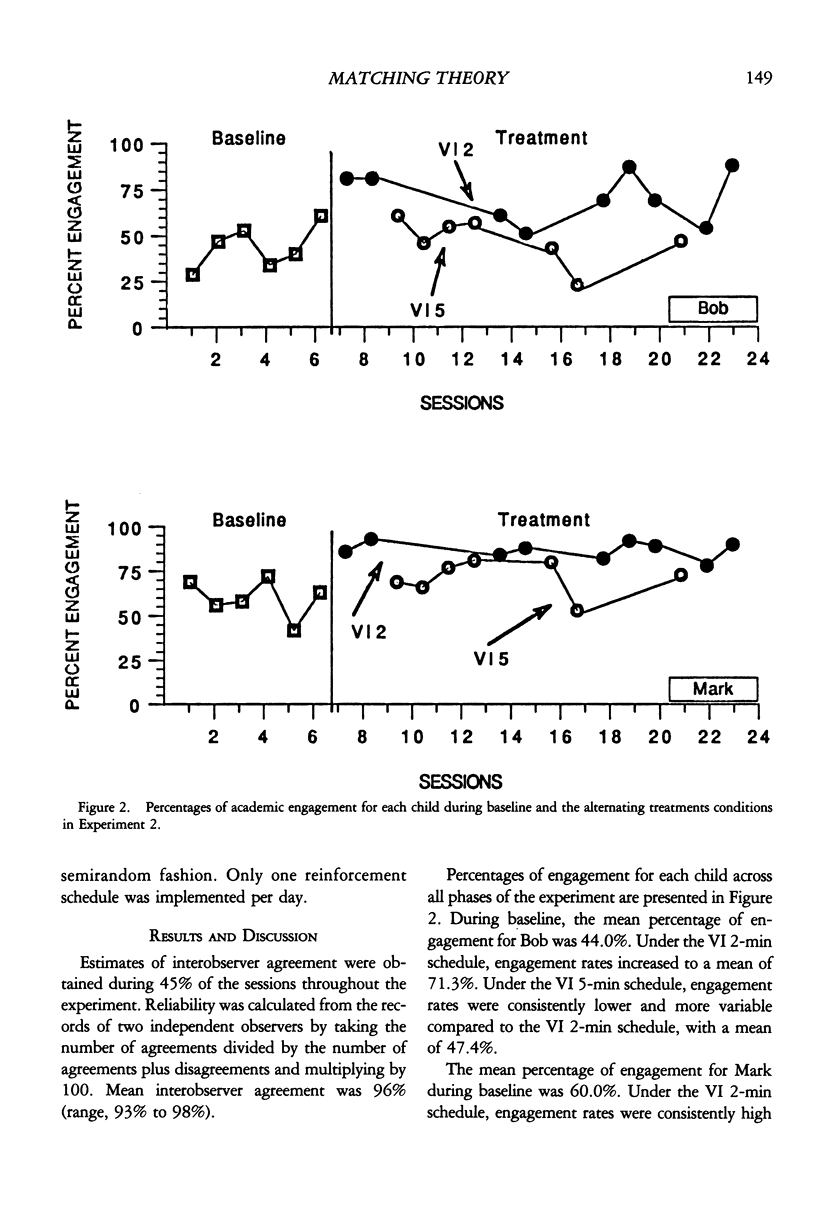
The single-alternative form of the matching law has enjoyed extensive support in laboratory research with both animals and humans. However, few data exist concerning its validity as a description of behavior in applied settings. In Experiment 1, 2 fourth-grade students were exposed to variable-interval schedules of social reinforcement contingent on academic engagement. The data for each subject were then plotted via Herrnstein's equation. The results showed Herrnstein's equation to account for 99.1% and 87.6% of the variance in student engagement, respectively. In Experiment 2, control over student engagement by two of the reinforcement schedules was examined further within an alternating treatments design with similar results. The implications of these findings for linking experimental and applied behavior analysis are discussed.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlow D. H., Hayes S. C. Alternating treatments design: one strategy for comparing the effects of two treatments in a single subject. J Appl Behav Anal. 1979 Summer;12(2):199–210. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1979.12-199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M., Rachlin H. C. Choice as time allocation. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):861–874. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw C. M., Szabadi E., Bevan P. Behavior of humans in variable-interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 Sep;26(2):135–141. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.26-135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATANIA A. C. Concurrent performances: reinforcement interaction and response independence. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:253–263. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison M. Concurrent schedules: Interaction of reinforcer frequency and reinforcer duration. J Exp Anal Behav. 1988 May;49(3):339–349. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1988.49-339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findley J. D. Preference and Switching under Concurrent Scheduling. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Apr;1(2):123–144. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. Relative and absolute strength of response as a function of frequency of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jul;4:267–272. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes S. C. Single case experimental design and empirical clinical practice. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1981 Apr;49(2):193–211. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.49.2.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J. On the law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Mar;13(2):243–266. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mace F. C., Hock M. L., Lalli J. S., West B. J., Belfiore P., Pinter E., Brown D. K. Behavioral momentum in the treatment of noncompliance. J Appl Behav Anal. 1988 Summer;21(2):123–141. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1988.21-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mace F. C., McCurdy B., Quigley E. A. A collateral effect of reward predicted by matching theory. J Appl Behav Anal. 1990 Summer;23(2):197–205. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1990.23-197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen C. H., Becker W. C., Thomas D. R. Rules, praise, and ignoring: elements of elementary classroom control. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Summer;1(2):139–150. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martens B. K., Houk J. L. The application of Herrnstein's law of effect to disruptive and on-task behavior of a retarded adolescent girl. J Exp Anal Behav. 1989 Jan;51(1):17–27. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1989.51-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell J. J. The importance of Herrnstein's mathematical statement of the law of effect for behavior therapy. Am Psychol. 1982 Jul;37(7):771–779. doi: 10.1037//0003-066x.37.7.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell J. J. Wilkinson's method of estimating the parameters of Herrnstein's hyperbola. J Exp Anal Behav. 1981 May;35(3):413–414. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1981.35-413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerson J., Hale S. Practical implications of the matching law. J Appl Behav Anal. 1984 Fall;17(3):367–380. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1984.17-367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrish J. M., Cataldo M. F., Kolko D. J., Neef N. A., Egel A. L. Experimental analysis of response covariation among compliant and inappropriate behaviors. J Appl Behav Anal. 1986 Fall;19(3):241–254. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1986.19-241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


