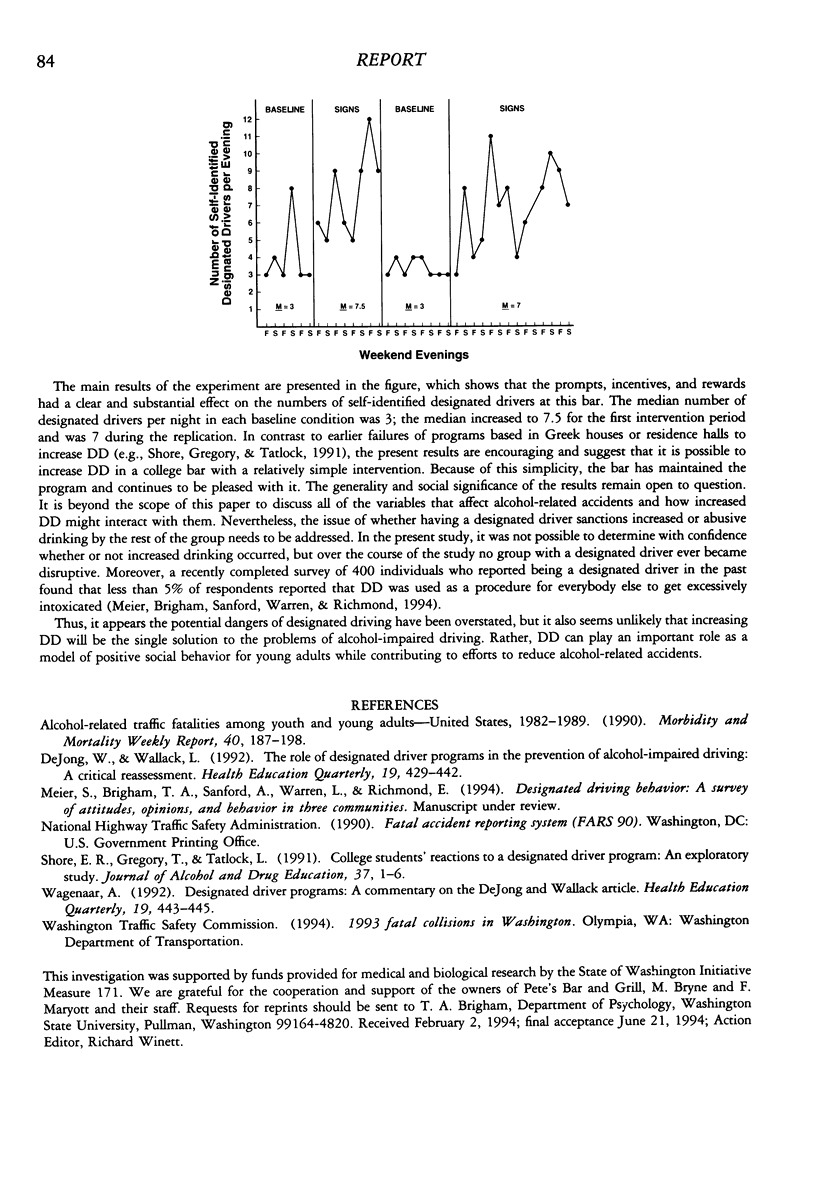
Abstract
Designated driving (DD) is a potentially viable but underutilized component of efforts to reduce driving while intoxicated. A reversal design was used to evaluate the effects of prompts and incentives in a bar on the frequency of DD. The results showed an approximate doubling of the number of designated drivers during the two intervention periods.
Keywords: alcohol-impaired driving, designated driving, prompts, incentives
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DeJong W., Wallack L. The role of designated driver programs in the prevention of alcohol-impaired driving: a critical reassessment. Health Educ Q. 1992 Winter;19(4):429–445. doi: 10.1177/109019819201900407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


