Abstract
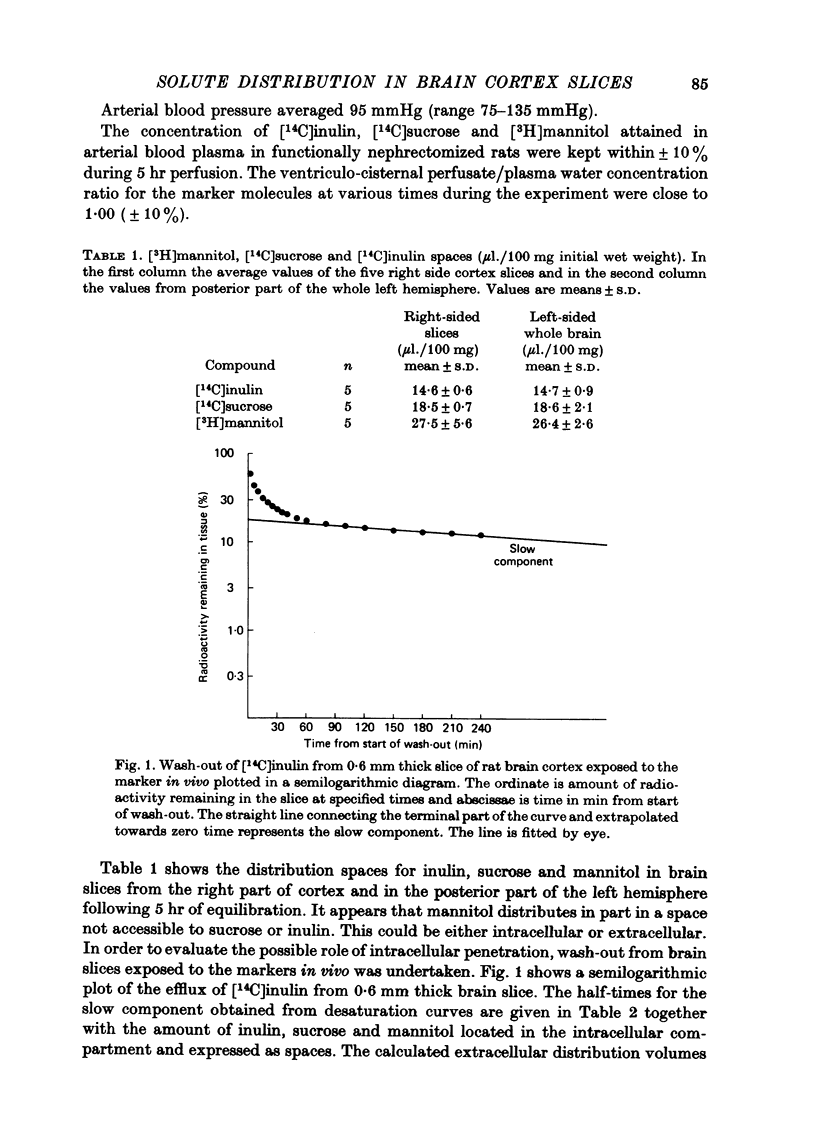
1. The distribution spaces of inulin, sucrose and mannitol in rat brain cortex slices were determined in tracer experiments. Tracer equilibration times of 5 hr were used with combined ventriculo-cisternal perfusion and I.V. infusion of tracers. After 5 hr of equilibration the distribution volumes (expressed as μl./100 mg wet wt.) obtained using the perfusion fluid as reference and after correction of tracer amount in residual blood were obtained. Information on cellular uptake was obtained by examining a slow component of wash-out curves from brain slices after in vivo equilibration. Distribution spaces were corrected for intracellular penetration to obtain the extracellular volumes of distribution. Inulin was found to equilibrate with 13·3 μl. extracellular tissue water per 100 mg initial wet weight, sucrose with 16·6 μl. and mannitol with 19·5 μl.
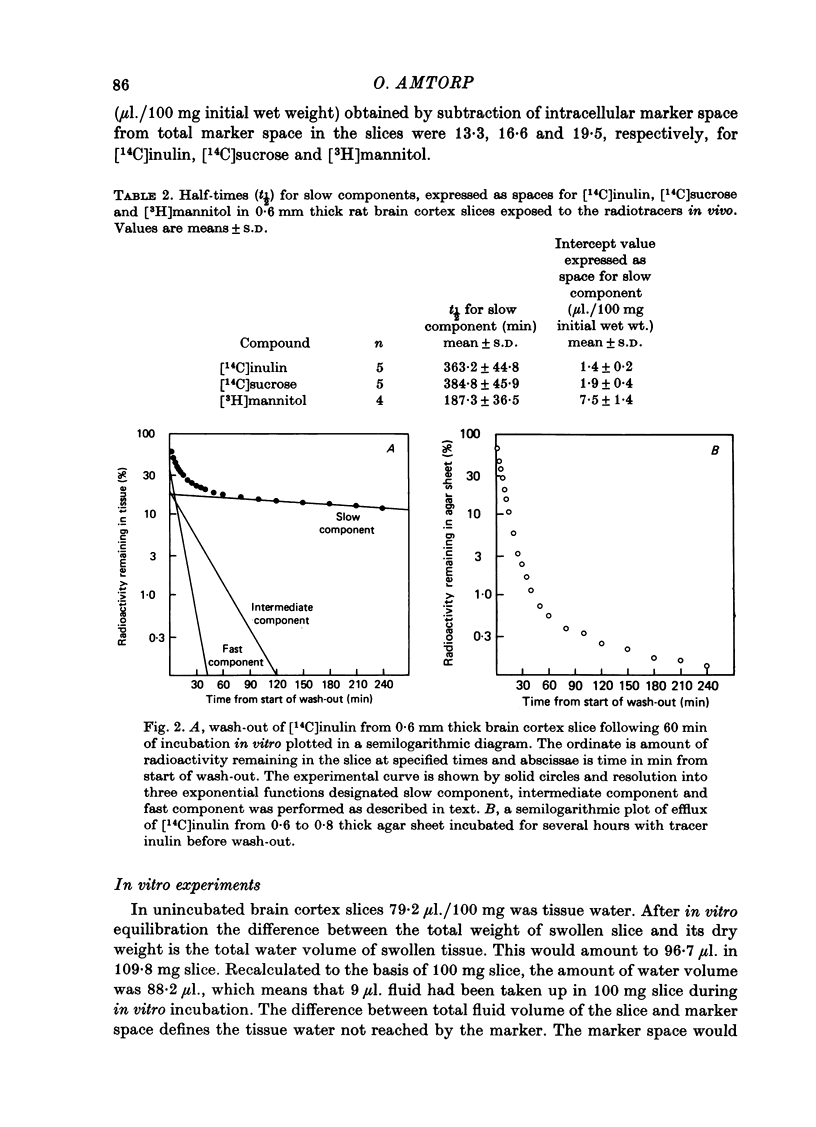
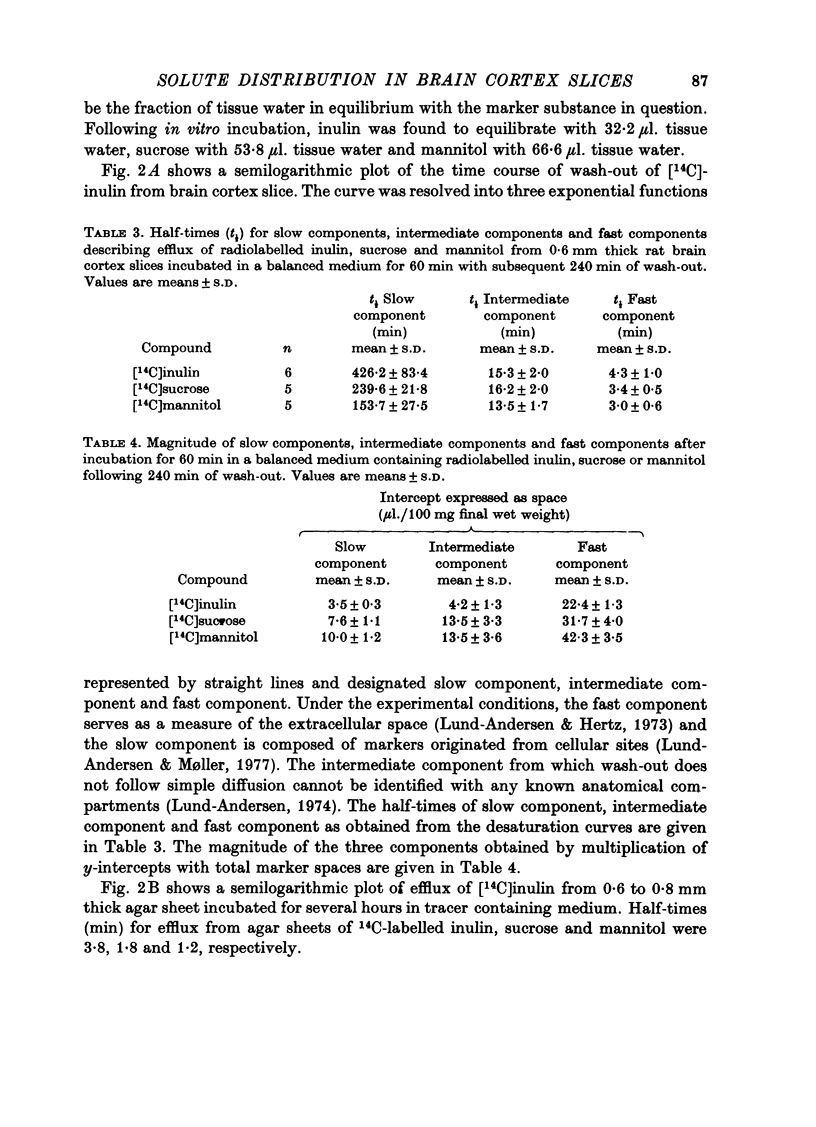
2. Marker spaces in rat brain cortex slices were also analysed by compartmental analysis of efflux of tracer inulin, sucrose and mannitol following in vitro incubation in a balanced medium for 60 min. Following in vitro equilibration, inulin was found to equilibrate with 22·4 μl. extracellular tissue water per 100 mg of final wet weight, sucrose to equilibrate with 31·7 μl. extracellular tissue water and mannitol with 42·3 μl.
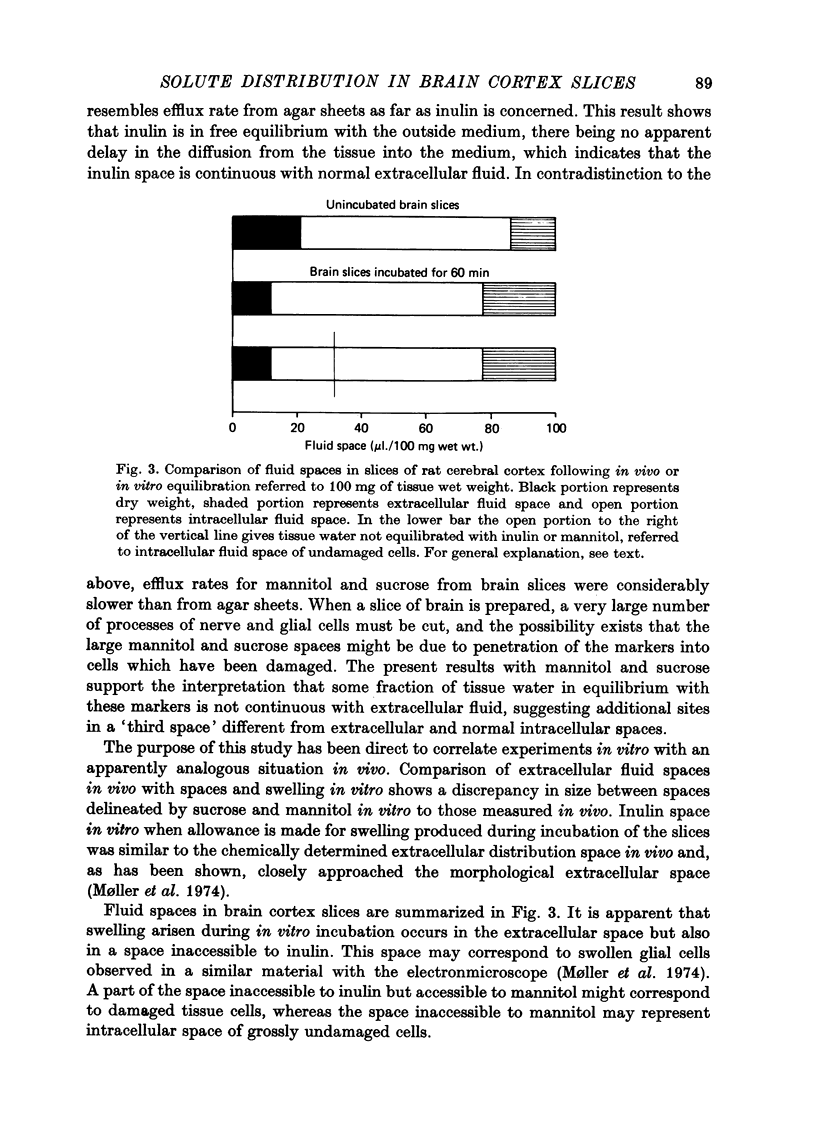
3. Inulin space in vitro when allowance is made for swelling produced during incubation of the slice was similar to the chemically delineated extracellular distribution volume in vivo. Sucrose and mannitol spaces in vitro, however, did not accord with in vivo determinations, most likely due to access of markers to areas of cell damage in the slice arisen during incubation.
4. Comparison of fluid spaces delineated by inulin in slices of rat cerebral cortex following in vivo and in vitro equilibration indicated that swelling produced during incubation in vitro mainly occurred in the extracellular space. Swollen glial cells may account for the small, but significant intracellular swelling in incubated slices.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnfred T., Hertz L., Lolle L., Lund-Andersen H. An improved holder for transfer of brain slices during in vitro incubation. Exp Brain Res. 1970 Nov 26;11(4):373–375. doi: 10.1007/BF00237910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosain F., McIntyre P. A., Poulose K., Stern H. S., Wagner H. N., Jr Binding of trace amounts of ionic indium-113m to plasma transferrin. Clin Chim Acta. 1969 Apr;24(1):69–75. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(69)90142-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E., Sisson W. B. The penetration of radiolabeled substances into rabbit brain from subarachnoid space. Brain Res. 1972 Jun 8;41(1):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90622-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund-Andersen H. Extracellular and intracellular distribution of inulin in rat brain cortex slices. Brain Res. 1974 Jan 11;65(2):239–254. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund-Andersen H., Hertz L. Effects of potassium content in brain-cortex slices from adult rats. Exp Brain Res. 1970;11(2):199–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00234323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund-Andersen H., Moller M. Uptake of inulin by cells in rat brain cortex. Exp Brain Res. 1977 May 23;28(1-2):37–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00237084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moller M., Mollgård K., Lund-Andersen H., Hertz L. Concordance between morphological and biochemical estimates of fluid spaces in rat brain cortex slices. Exp Brain Res. 1974;21(3):299–314. doi: 10.1007/BF00235749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappius H. M. The distribution of water in brain tissues swollen in vitro and in vivo. Prog Brain Res. 1965;15:135–154. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)60944-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANHARREVELD A., CROWELL J. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY AFTER RAPID FREEZING ON A METAL SURFACE AND SUBSTITUTION FIXATION. Anat Rec. 1964 Jul;149:381–385. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091490307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANHARREVELD A., CROWELL J., MALHOTRA S. K. A STUDY OF EXTRACELLULAR SPACE IN CENTRAL NERVOUS TISSUE BY FREEZE-SUBSTITUTION. J Cell Biol. 1965 Apr;25:117–137. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


