Abstract
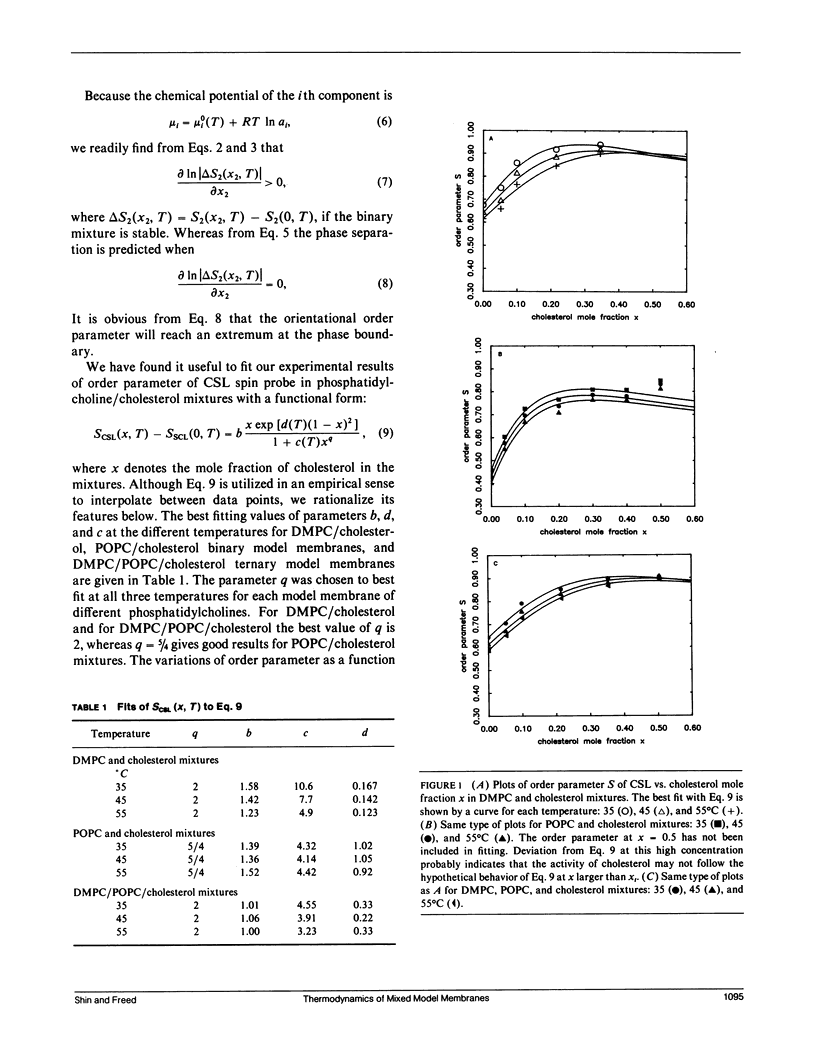
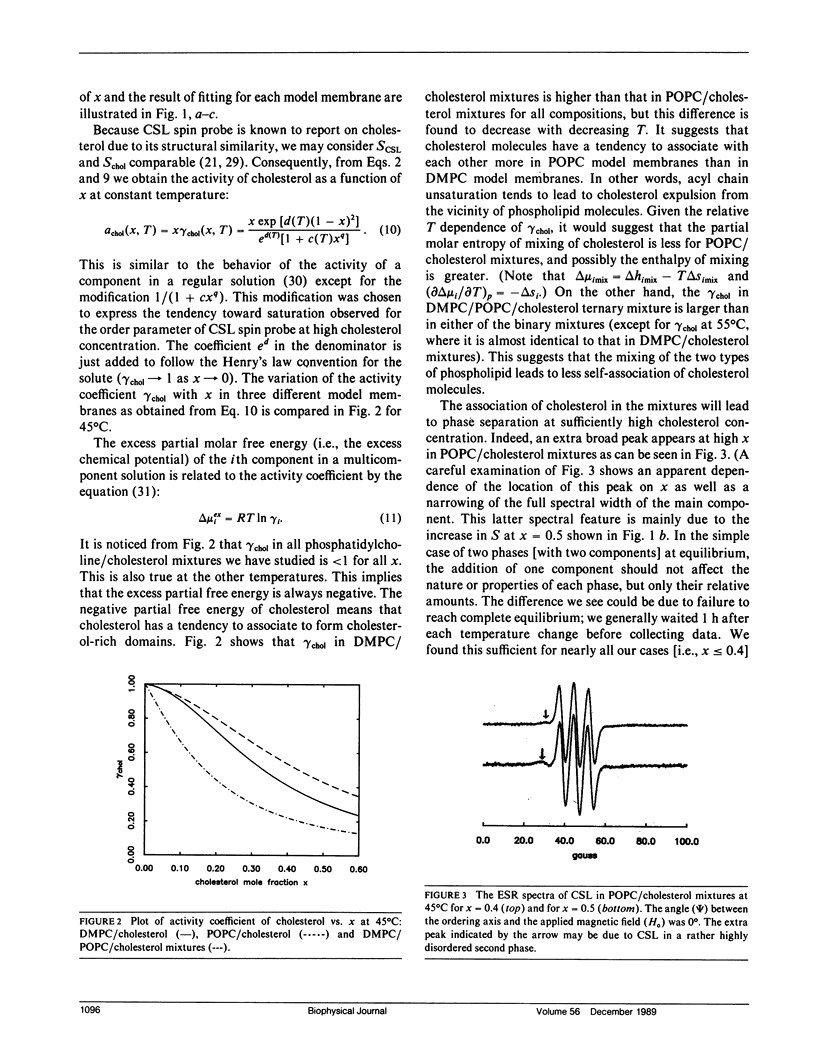
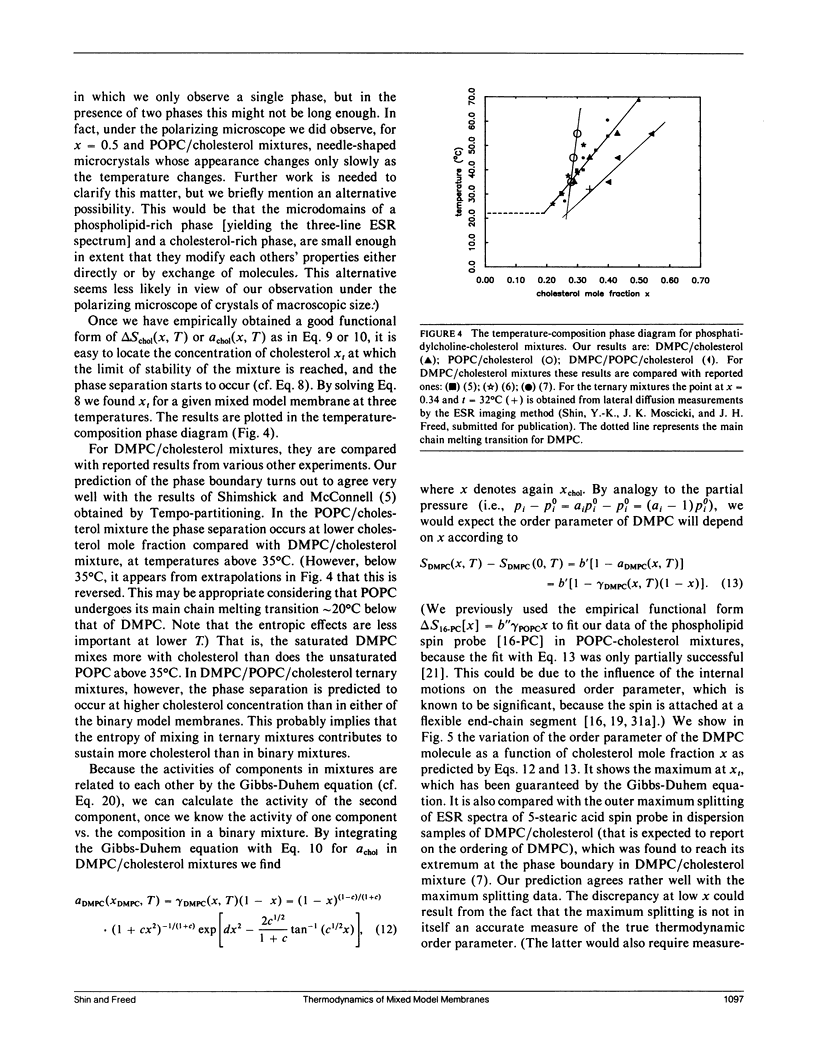
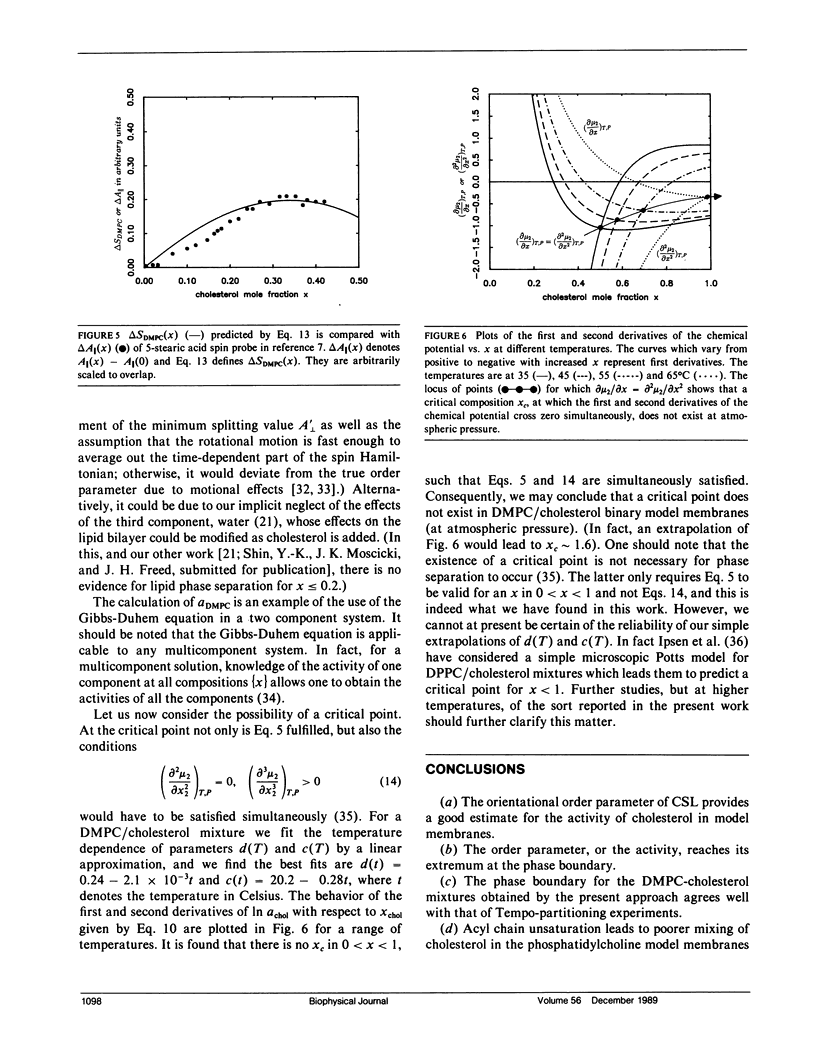
It is shown that good estimates of the activity of cholesterol in phosphatidylcholine-cholesterol mixed model membranes are obtained by examining the orientational order parameter S of cholestane spin probe (CSL) that is obtained from electron spin resonance by spectral simulation. By introducing thermodynamic stability conditions of liquid mixtures, the variation of activity (or S) as a function of cholesterol mole fraction is utilized to predict the concentration at which the phase separation occurs. These results for DMPC and cholesterol binary mixtures agree very well with those of Tempo-partitioning experiments. The comparison of activity coefficients and the phase boundary in DMPC/cholesterol mixtures with those of POPC/cholesterol mixtures suggests that acyl chain unsaturation leads to poorer mixing of cholesterol in phosphatidylcholine model membranes at higher temperatures (i.e., greater than 35 degrees C). In ternary solutions of DMPC, POPC, and cholesterol, it is found that cholesterol shows less deviation from ideality than in either of the two binary mixtures, and this implies that the phase separation occurs at higher cholesterol concentration than in either of the two binary mixtures. The present analysis suggests that there may not be a critical point in DMPC/cholesterol mixtures, even though phase separation does occur.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Copeland B. R., McConnel H. M. The rippled structure in bilayer membranes of phosphatidylcholine and binary mixtures of phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 20;599(1):95–109. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curatolo W., Sears B., Neuringer L. J. A calorimetry and deuterium NMR study of mixed model membranes of 1-palmitoyl-2-oleylphosphatidylcholine and saturated phosphatidylcholines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jul 25;817(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui S. W., He N. B. Molecular organization in cholesterol-lecithin bilayers by X-ray and electron diffraction measurements. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 1;22(5):1159–1164. doi: 10.1021/bi00274a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ipsen J. H., Karlström G., Mouritsen O. G., Wennerström H., Zuckermann M. J. Phase equilibria in the phosphatidylcholine-cholesterol system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 27;905(1):162–172. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kar L., Ney-Igner E., Freed J. H. Electron spin resonance and electron-spin-echo study of oriented multilayers of L alpha-dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine water systems. Biophys J. 1985 Oct;48(4):569–595. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83814-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll W., Schmidt G., Ibel K., Sackmann E. Small-angle neutron scattering study of lateral phase separation in dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine-cholesterol mixed membranes. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 10;24(19):5240–5246. doi: 10.1021/bi00340a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korstanje L. J., Van Faassen E. E., Levine Y. K. Slow-motion ESR study of order and dynamics in oriented lipid multibilayers: effects of unsaturation and hydration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Apr 14;980(2):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusumi A., Subczynski W. K., Pasenkiewicz-Gierula M., Hyde J. S., Merkle H. Spin-label studies on phosphatidylcholine-cholesterol membranes: effects of alkyl chain length and unsaturation in the fluid phase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 29;854(2):307–317. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcelja S. Lipid-mediated protein interaction in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 11;455(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owicki J. C., McConnell H. M. Theory of protein-lipid and protein-protein interactions in bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4750–4754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presti F. T., Chan S. I. Cholesterol-phospholipid interaction in membranes. 1. Cholestane spin-label studies of phase behavior of cholesterol-phospholipid liposomes. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 3;21(16):3821–3830. doi: 10.1021/bi00259a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recktenwald D. J., McConnell H. M. Phase equilibria in binary mixtures of phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 21;20(15):4505–4510. doi: 10.1021/bi00518a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein J. L., Smith B. A., McConnell H. M. Lateral diffusion in binary mixtures of cholesterol and phosphatidylcholines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):15–18. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J. Deuterium magnetic resonance: theory and application to lipid membranes. Q Rev Biophys. 1977 Aug;10(3):353–418. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimshick E. J., McConnell H. M. Lateral phase separation in phospholipid membranes. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 5;12(12):2351–2360. doi: 10.1021/bi00736a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimshick E. J., McConnell H. M. Lateral phase separations in binary mixtures of cholesterol and phospholipids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jul 17;53(2):446–451. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90682-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin Y. K., Freed J. H. Dynamic imaging of lateral diffusion by electron spin resonance and study of rotational dynamics in model membranes. Effect of cholesterol. Biophys J. 1989 Mar;55(3):537–550. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82847-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


