Abstract
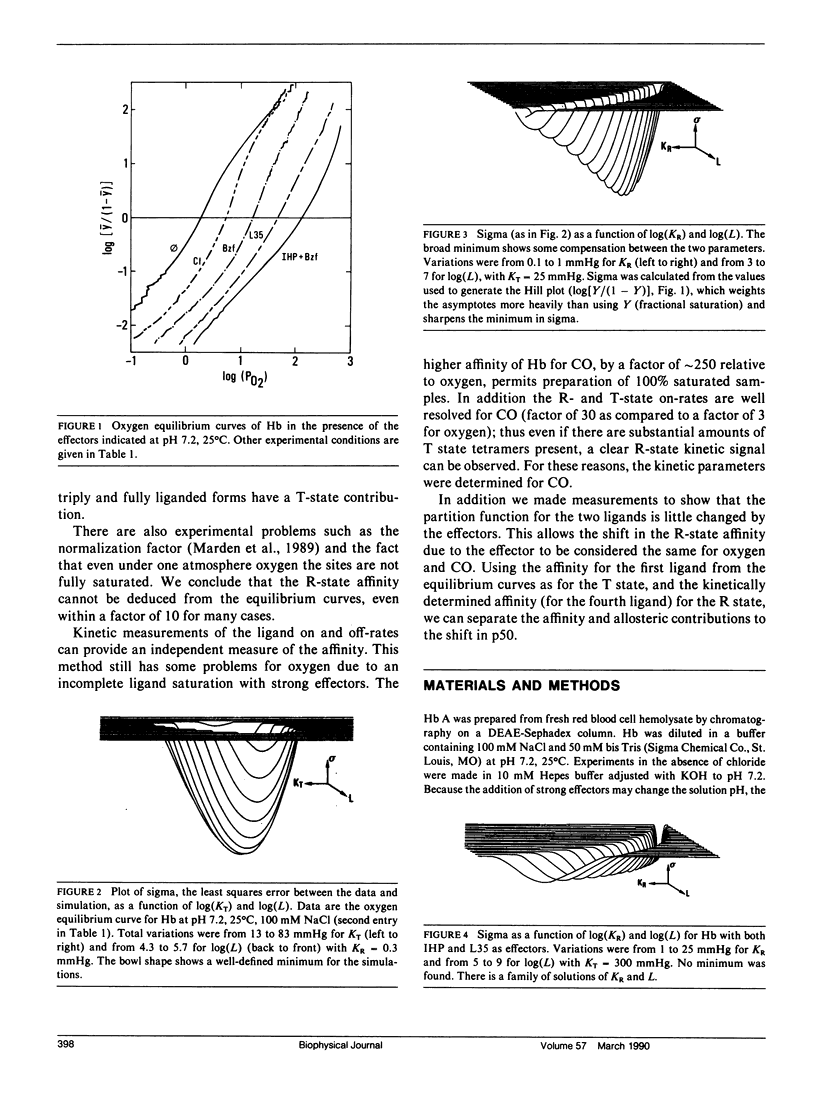
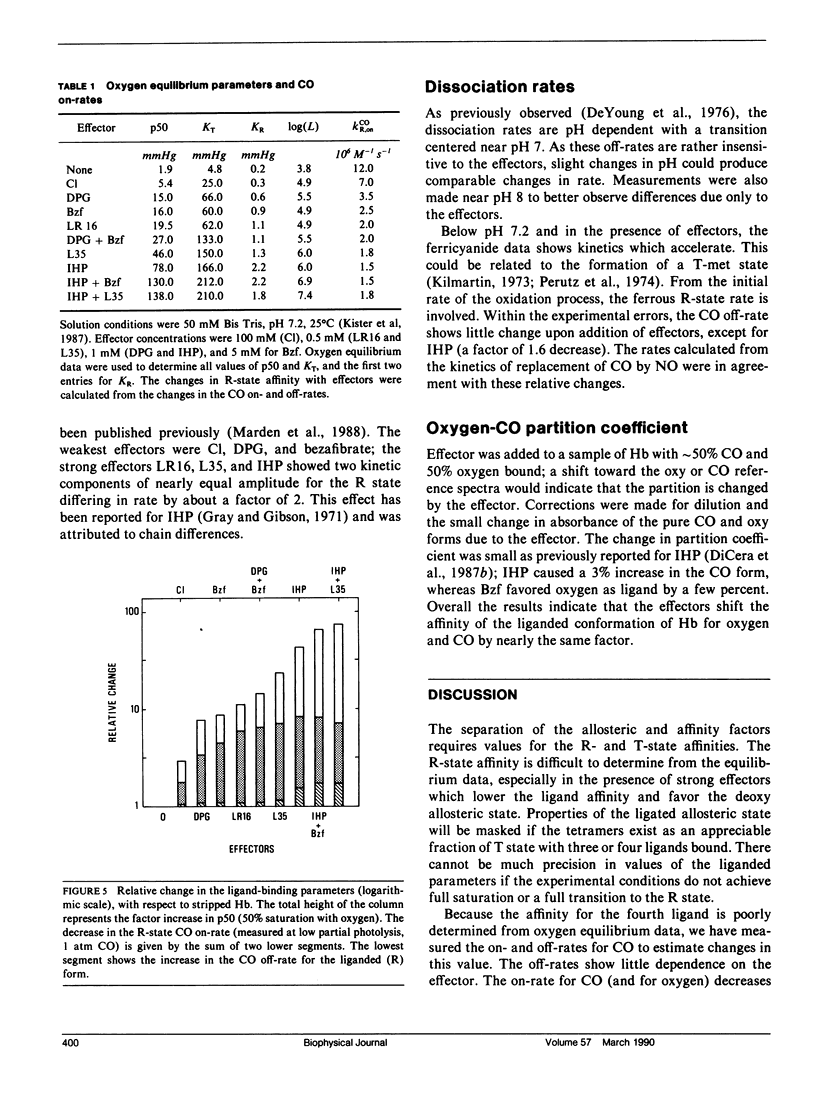
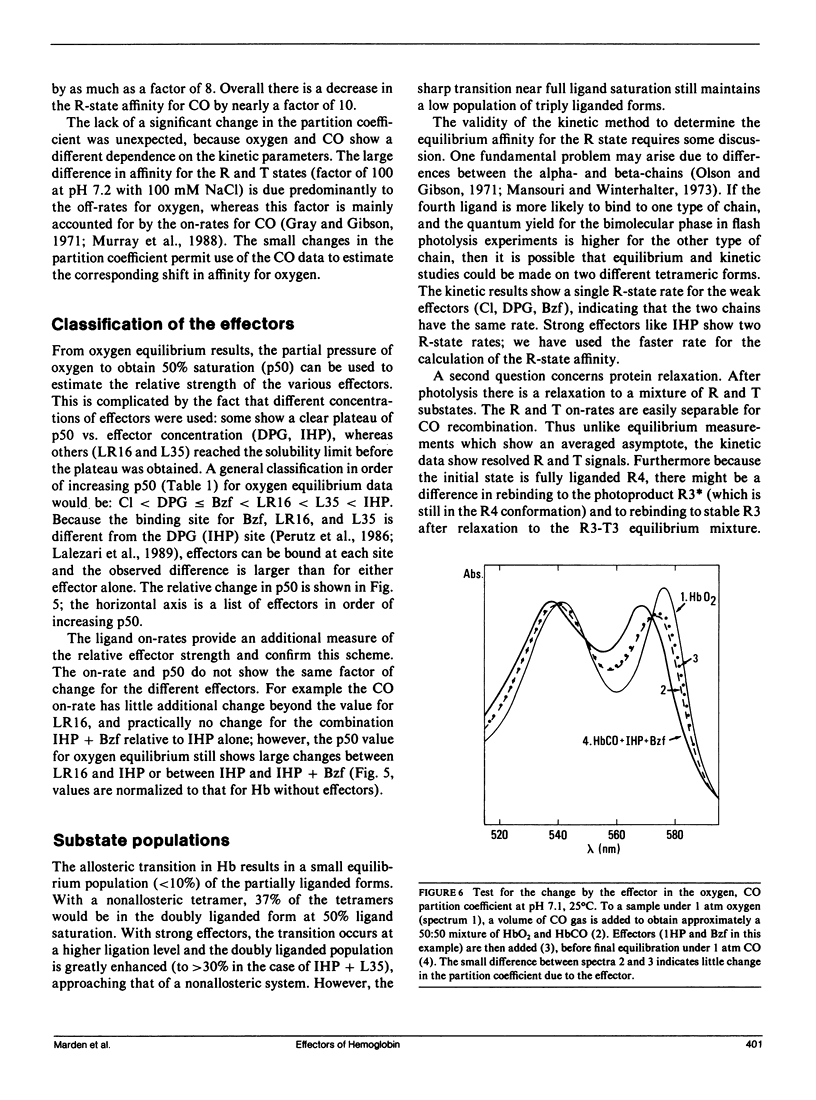
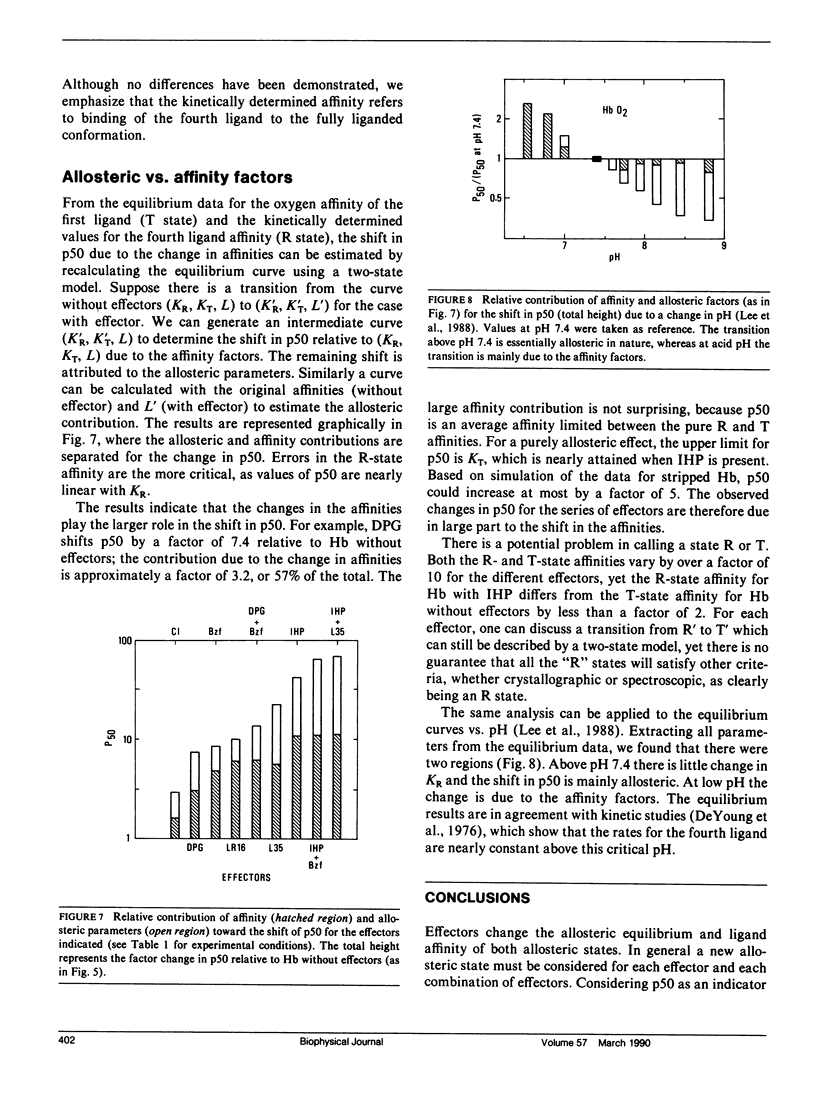
The relative contributions of the allosteric and affinity factors toward the change in p50 have been calculated for a series of effectors of hemoglobin (Hb). Shifts in the ligand affinity of deoxy Hb and the values for 50% ligand saturation (p50) were obtained from oxygen equilibrium data. Because the high-affinity parameters (liganded conformation) are poorly determined from the equilibrium curves, they were determined from kinetic measurements of the association and dissociation rates with CO as ligand. The CO on-rates were obtained by flash photolysis measurements. The off-rates were determined from the rate of oxidation of HbCO by ferricyanide, or by replacement of CO with NO. The partition function of fully liganded hemoglobin for oxygen and CO is only slightly changed by the effectors. Measurements were made in the presence of the effectors 2,3-diphosphoglycerate (DPG), inositol hexakisphosphate (IHP), bezafibrate (Bzf), and two recently synthesized derivatives of Bzf (LR16 and L35). Values of p50 change by over a factor of 60; the on-rates decrease by nearly a factor of 8, with little change in the off-rates for the liganded conformation. The data indicate that both allosteric and affinity parameters are changed by the effectors; the changes in ligand affinity represent the larger contribution toward shifts in p50.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTONINI E., BRUNORI M., WYMAN J. STUDIES ON THE OXIDATION-REDUCTION POTENTIALS OF HEME PROTEINS. IV. THE KINETICS OF OXIDATION OF HEMOGLOBIN AND MYOGLOBIN BY FERRICYANIDE. Biochemistry. 1965 Mar;4:545–551. doi: 10.1021/bi00879a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiancone E., Norne J. E., Forsén S., Bonaventura J., Brunori M., Antonini E., Wyman J. Identification of chloride-binding sites in hemoglobin by nuclear-magnetic-resonance quadrupole-relaxation studies of hemoglobin digests. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jul 1;55(2):385–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02173.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeYoung A., Pennelly R. R., Tan-Wilson A. L., Noble R. W. Kinetic studies on the binding affinity of human hemoglobin for the 4th carbon monoxide molecule, L4. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6692–6698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Cera E., Doyle M. L., Connelly P. R., Gill S. J. Carbon monoxide binding to human hemoglobin A0. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 6;26(20):6494–6502. doi: 10.1021/bi00394a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Cera E., Robert C. H., Gill S. J. Allosteric interpretation of the oxygen-binding reaction of human hemoglobin tetramers. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 30;26(13):4003–4008. doi: 10.1021/bi00387a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray R. D., Gibson Q. H. The effect of inositol hexaphosphate on the kinetics of CO and O 2 binding by human hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 10;246(23):7168–7174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilmartin J. V. The interaction of inositol hexaphosphate with methaemoglobin. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;133(4):725–733. doi: 10.1042/bj1330725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kister J., Poyart C., Edelstein S. J. An expanded two-state allosteric model for interactions of human hemoglobin A with nonsaturating concentrations of 2,3-diphosphoglycerate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12085–12091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kister J., Poyart C., Edelstein S. J. Oxygen-organophosphate linkage in hemoglobin A. The double hump effect. Biophys J. 1987 Oct;52(4):527–535. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83242-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalezari I., Rahbar S., Lalezari P., Fermi G., Perutz M. F. LR16, a compound with potent effects on the oxygen affinity of hemoglobin, on blood cholesterol, and on low density lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6117–6121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanir A., Caughey W. S., Charache S. Oxidation of carbonyl hemoglobins by ferricyanide. Hemoglobins A, Osler (beta 145 Tyr replaced by Asp) and Zurich (beta 63 His replaced by Arg). Eur J Biochem. 1982 Nov 15;128(2-3):521–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. W., Karplus M., Poyart C., Bursaux E. Analysis of proton release in oxygen binding by hemoglobin: implications for the cooperative mechanism. Biochemistry. 1988 Feb 23;27(4):1285–1301. doi: 10.1021/bi00404a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., WYMAN J., CHANGEUX J. P. ON THE NATURE OF ALLOSTERIC TRANSITIONS: A PLAUSIBLE MODEL. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:88–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansouri A., Winterhalter K. H. Nonequivalence of chains in hemoglobin oxidation. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 20;12(24):4946–4949. doi: 10.1021/bi00748a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marden M. C., Kister J., Bohn B., Poyart C. T-state hemoglobin with four ligands bound. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 8;27(5):1659–1664. doi: 10.1021/bi00405a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marden M. C., Kister J., Poyart C., Edelstein S. J. Analysis of hemoglobin oxygen equilibrium curves. Are unique solutions possible? J Mol Biol. 1989 Jul 20;208(2):341–345. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90393-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minton A. P., Imai K. The three-state model: a minimal allosteric description of homotropic and heterotropic effects in the binding of ligands to hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1418–1421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray L. P., Hofrichter J., Henry E. R., Ikeda-Saito M., Kitagishi K., Yonetani T., Eaton W. A. The effect of quaternary structure on the kinetics of conformational changes and nanosecond geminate rebinding of carbon monoxide to hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2151–2155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. S., Gibson Q. H. The reaction of n-butyl isocyanide with human hemoglobin. I. Determination of the kinetic parameters involved in the last step in ligand binding. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 10;246(17):5241–5253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F., Fersht A. R., Simon S. R., Roberts G. C. Influence of globin structure on the state of the heme. II. Allosteric transitions in methemoglobin. Biochemistry. 1974 May 7;13(10):2174–2186. doi: 10.1021/bi00707a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu K., Bucci E. Allosteric effectors of hemoglobin. Interaction of human adult and fetal hemoglobins with poly(carboxylic acids). Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 12;13(4):809–814. doi: 10.1021/bi00701a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


