Abstract
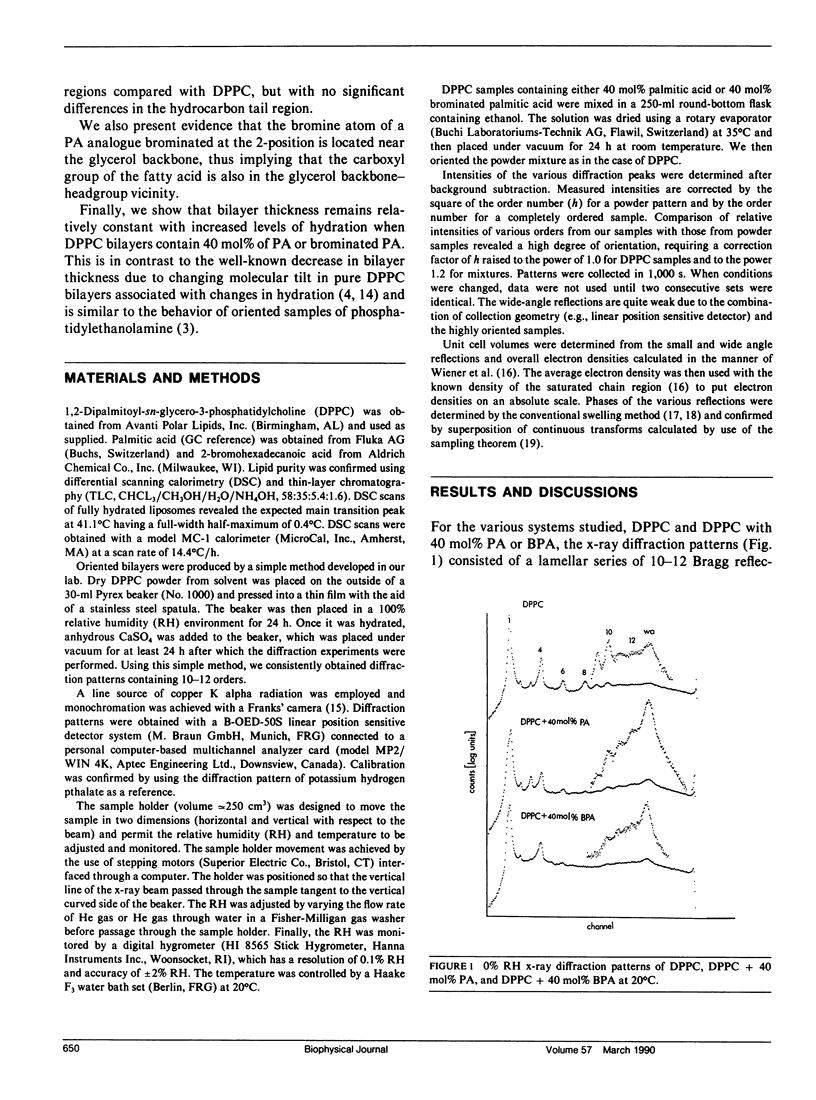
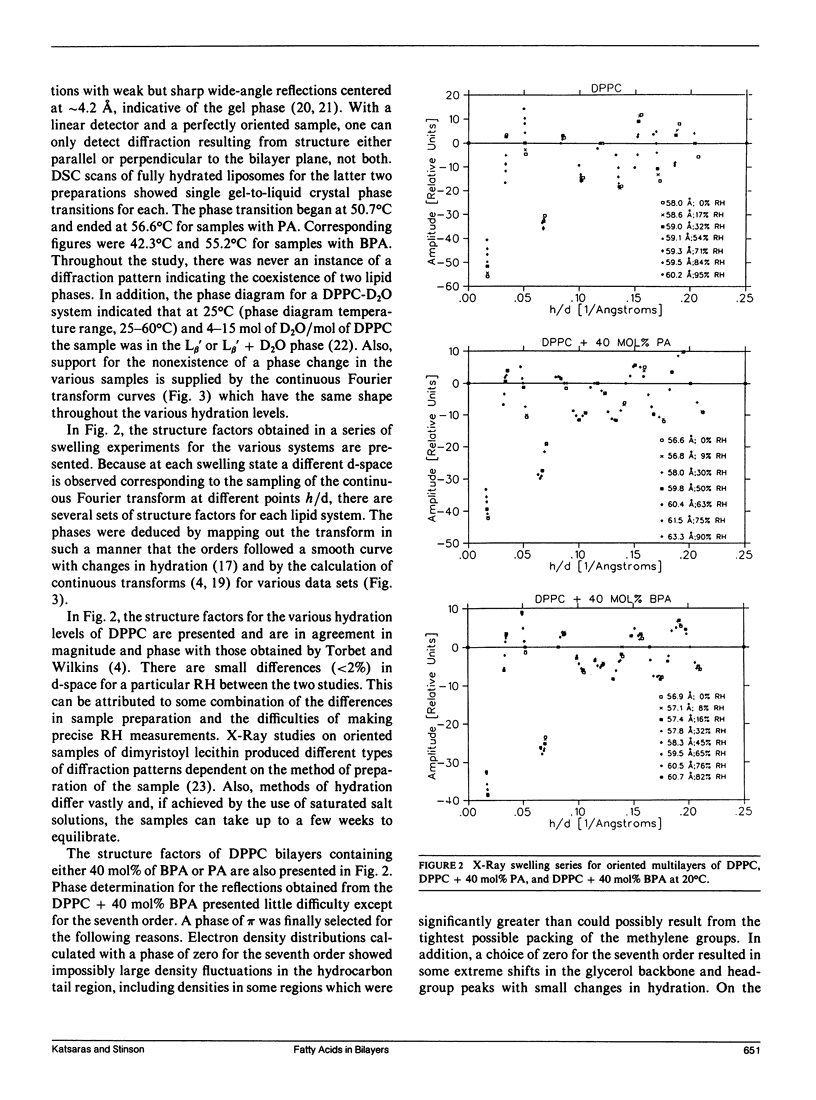
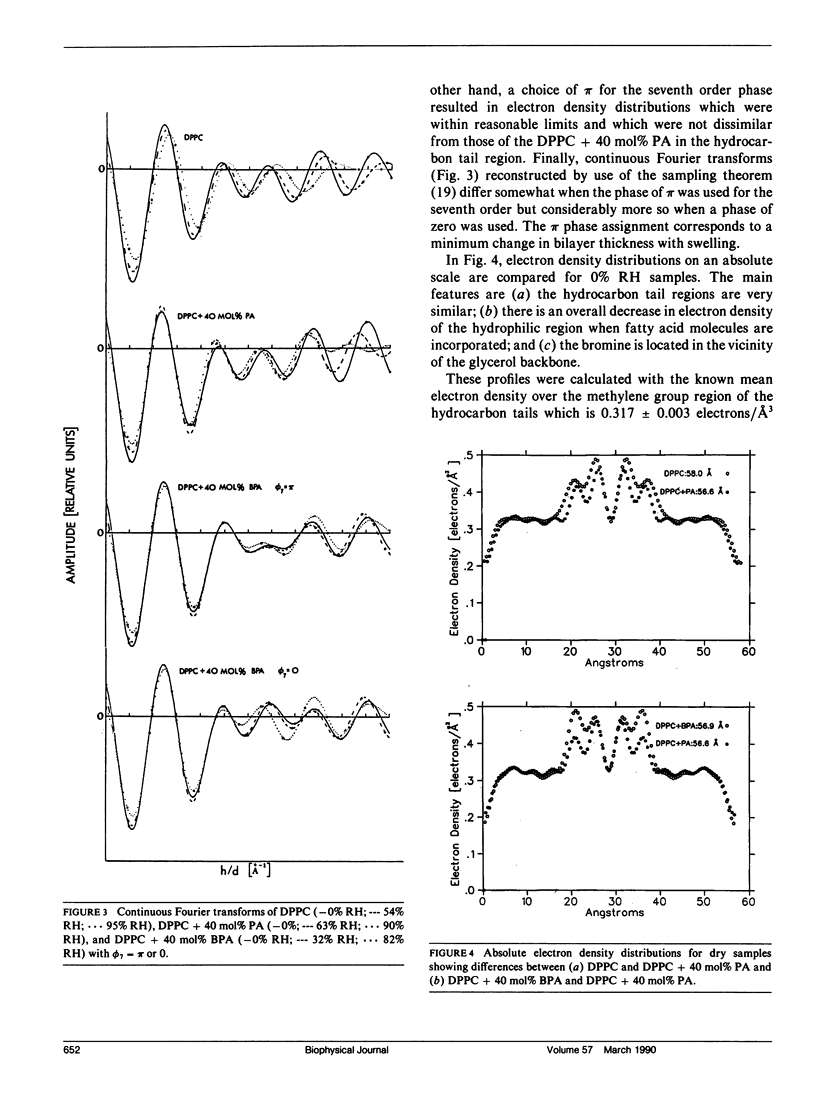
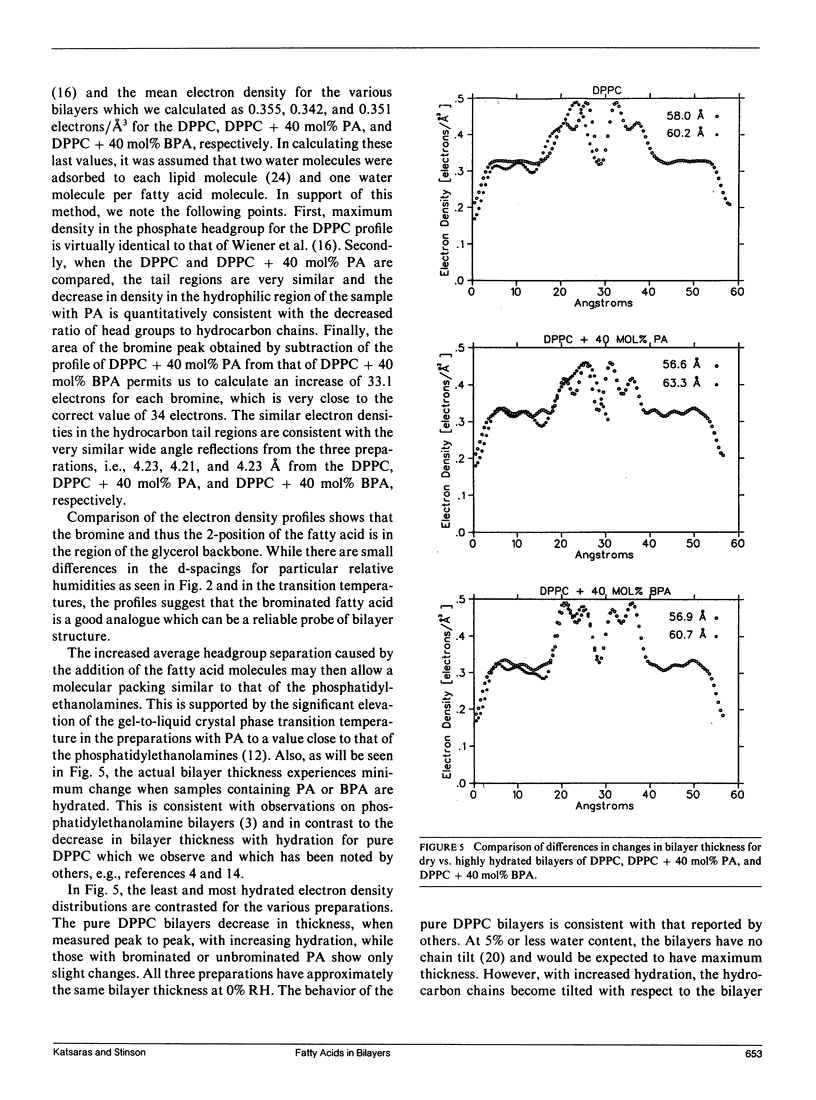
Small-angle x-ray diffraction studies were performed on gel phase-oriented bilayers of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC) and DPPC containing 40 mol% of either palmitic acid (PA) or palmitic acid brominated at the 2-position (BPA). Oriented samples were prepared using a method developed by us, which is as simple as powder sample preparations while offering all the advantages of oriented samples made by traditional methods. Phases were determined using swelling experiments with structure factors plotted in reciprocal space, creating a relatively smooth curve as the amount of water between the bilayers was changed. Continuous Fourier transforms were also calculated to further test the consistency of the phase assignments. The diffraction data were used to calculate absolute electron density profiles for different bilayers to a resolution of 5-6 A. Analysis indicates the following: (a) The electron density profiles for the three preparations are virtually identical in the hydrocarbon chain region. (b) There is a decrease in the electron density of the glycerol backbone-headgroup region and d-space in DPPC-PA compared to DPPC. (c) The bromine of fatty-acid brominated at the 2-position is in the vicinity of the glycerol backbone. (d) The bilayer thickness of DPPC containing either brominated or unbrominated fatty acid remains relatively constant with increased levels of hydration, unlike DPPC bilayers.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chapman D., Urbina J. Biomembrane phase transitions. Studies of lipid-water systems using differential scanning calorimetry. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 25;249(8):2512–2521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cistola D. P., Atkinson D., Hamilton J. A., Small D. M. Phase behavior and bilayer properties of fatty acids: hydrated 1:1 acid-soaps. Biochemistry. 1986 May 20;25(10):2804–2812. doi: 10.1021/bi00358a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark N. A., Rothschild K. J., Luippold D. A., Simon B. A. Surface-induced lamellar orientation of multilayer membrane arrays. Theoretical analysis and a new method with application to purple membrane fragments. Biophys J. 1980 Jul;31(1):65–96. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85041-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janiak M. J., Small D. M., Shipley G. G. Nature of the Thermal pretransition of synthetic phospholipids: dimyristolyl- and dipalmitoyllecithin. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 19;15(21):4575–4580. doi: 10.1021/bi00666a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jendrasiak G. L., Hasty J. H. The hydration of phospholipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jan 23;337(1):79–91. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(74)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn A. B., Schullery S. E. Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine-palmitic acid phase diagram studied by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance. Chem Phys Lipids. 1985 May;37(2):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(85)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabrey S., Sturtevant J. M. Incorporation of saturated fatty acids into phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 25;486(3):444–450. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNaughtan W., Snook K. A., Caspi E., Franks N. P. An X-ray diffraction analysis of oriented lipid multilayers containing basic proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Aug 27;818(2):132–148. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90556-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J. Differences in hydrocarbon chain tilt between hydrated phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine bilayers. A molecular packing model. Biophys J. 1980 Feb;29(2):237–245. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85128-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J., Holloway P. W. Determination of the depth of bromine atoms in bilayers formed from bromolipid probes. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 24;26(6):1783–1788. doi: 10.1021/bi00380a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz A., Gómez-Fernández J. C. A differential scanning calorimetry study of the interaction of free fatty acids with phospholipid membranes. Chem Phys Lipids. 1987 Oct;45(1):75–91. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(87)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand R. P., Chapman D., Larsson K. Tilted hydrocarbon chains of dipalmitoyl lecithin become perpendicular to the bilayer before melting. Biophys J. 1975 Nov;15(11):1117–1124. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85888-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schullery S. E., Seder T. A., Weinstein D. A., Bryant D. A. Differential thermal analysis of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine--fatty acid mixtures. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 24;20(24):6818–6824. doi: 10.1021/bi00527a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suwalsky M., Knight E. X-ray studies on phospholipid bilayers. II. Polymorphic forms of dipalmitoyl phosphatidylethanolamine. Z Naturforsch C. 1982 Nov-Dec;37(11-12):1157–1160. doi: 10.1515/znc-1982-11-1218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suwalsky M., Tapia J. X-ray studies on phospholipid bilayers. I. Polymorphic forms of dimyristoyl lecithin. Z Naturforsch C. 1981 Sep-Oct;36(9-10):875–879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieu A., Luzzati V., Reman F. C. Structure and polymorphism of the hydrocarbon chains of lipids: a study of lecithin-water phases. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 25;75(4):711–733. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torbet J., Wilkins M. H. X-ray diffraction studies of lecithin bilayers. J Theor Biol. 1976 Oct 21;62(2):447–458. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(76)90129-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmius J., Wennerström H., Lindblom G., Arvidson G. Deuteron nuclear magnetic resonance studies of phase equilibria in a lecithin-water system. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 27;16(26):5742–5745. doi: 10.1021/bi00645a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener M. C., Suter R. M., Nagle J. F. Structure of the fully hydrated gel phase of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine. Biophys J. 1989 Feb;55(2):315–325. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82807-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worthington C. R., McIntosh T. J. Direct determination of the electron density profile of nerve myelin. Nat New Biol. 1973 Sep 26;245(143):97–99. doi: 10.1038/newbio245097a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


