Abstract
Chaotic regimens have been observed experimentally in neurons as well as in deterministic neuronal models. The R15 bursting cell in the abdominal ganglion of Aplysia has been the subject of extensive mathematical modeling. Previously, the model of Plant and Kim has been shown to exhibit both bursting and beating modes of electrical activity. In this report, we demonstrate (a) that a chaotic regime exists between the bursting and beating modes of the model, and (b) that the model approaches chaos from both modes by a period doubling cascade. The bifurcation parameter employed is the external stimulus current. In addition to the period doubling observed in the model-generated trajectories, a period three "window" was observed, power spectra that demonstrate the approaches to chaos were generated, and the Lyaponov exponents and the fractal dimension of the chaotic attractors were calculated. Chaotic regimes have been observed in several similar models, which suggests that they are a general characteristic of cells that exhibit both bursting and beating modes.
Full text
PDF

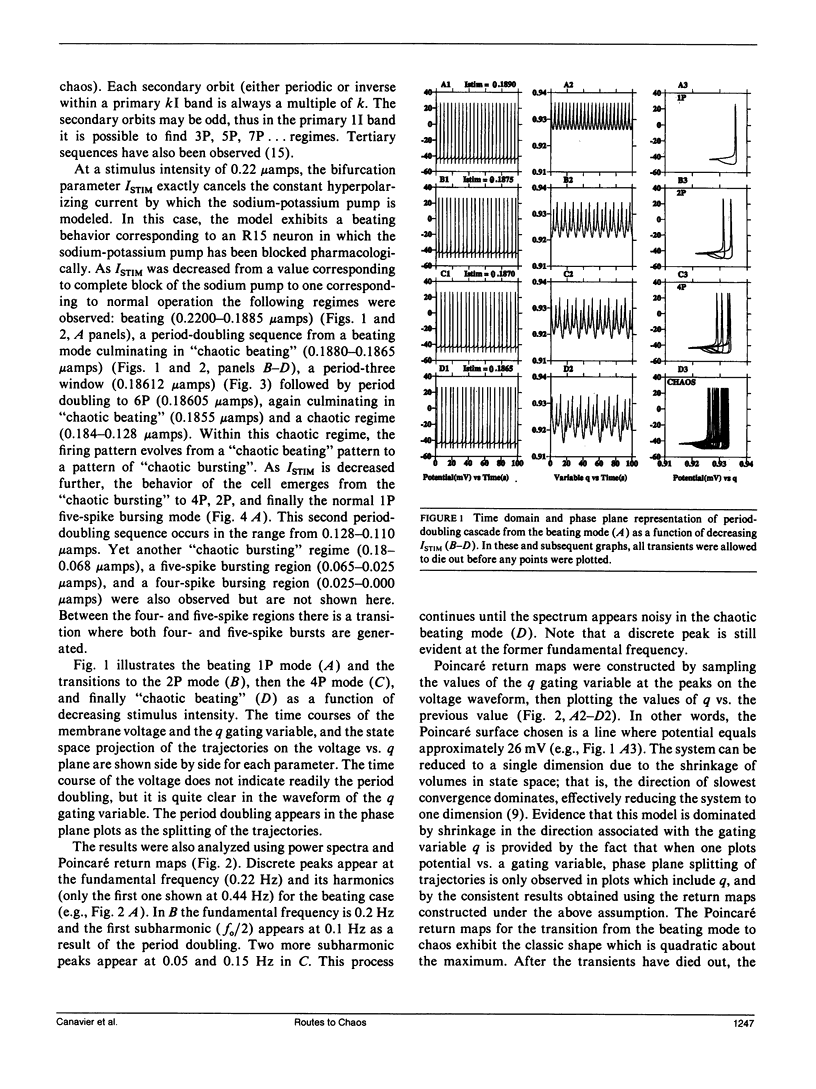
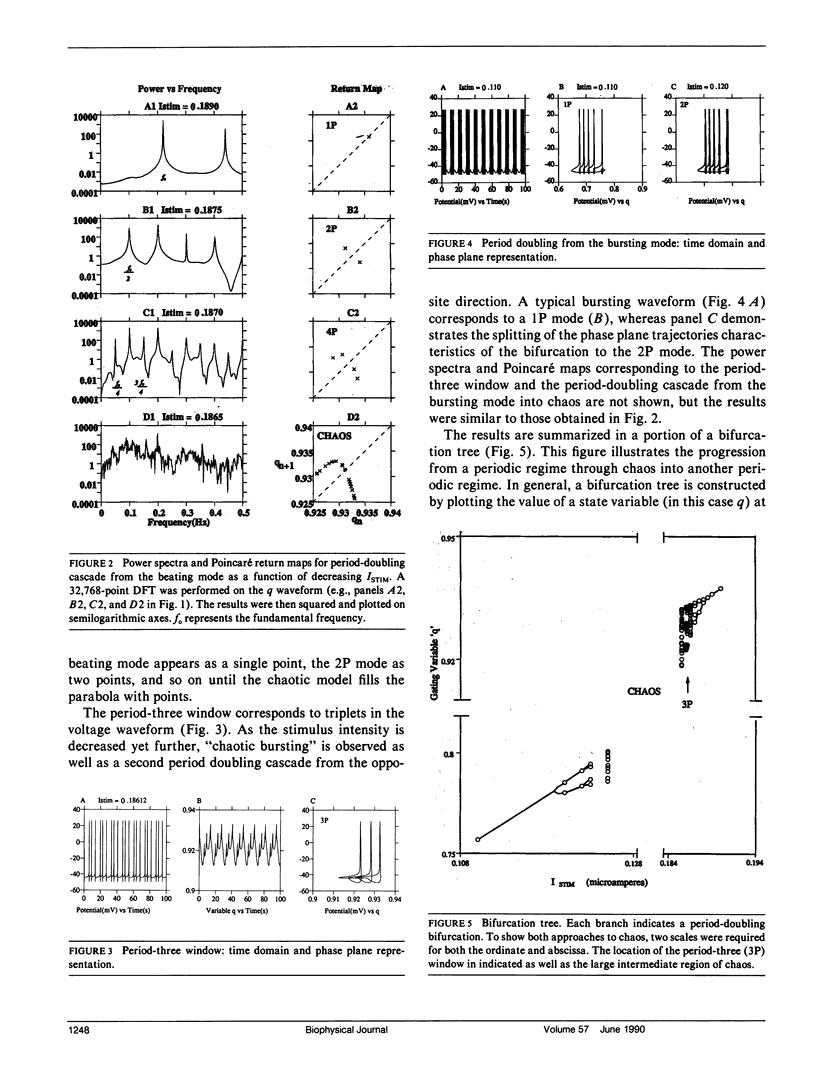



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams W. B., Levitan I. B. Voltage and ion dependences of the slow currents which mediate bursting in Aplysia neurone R15. J Physiol. 1985 Mar;360:69–93. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alving B. O. Spontaneous activity in isolated somata of Aplysia pacemaker naurons. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Jan;51(1):29–45. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chay T. R. Abnormal discharges and chaos in a neuronal model system. Biol Cybern. 1984;50(4):301–311. doi: 10.1007/BF00337079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chay T. R., Rinzel J. Bursting, beating, and chaos in an excitable membrane model. Biophys J. 1985 Mar;47(3):357–366. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83926-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann A., Gorman A. L. Effects of 4-aminopyridine on potassium currents in a molluscan neuron. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Jul;78(1):63–86. doi: 10.1085/jgp.78.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindmarsh J. L., Rose R. M. A model of neuronal bursting using three coupled first order differential equations. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Mar 22;221(1222):87–102. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden A. V., Winlow W., Haydon P. G. The induction of periodic and chaotic activity in a molluscan neurone. Biol Cybern. 1982;43(3):169–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00319976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junge D., Stephens C. L. Cyclic variation of potassium conductance in a burst-generating neurone in Aplysia. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;235(1):155–181. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. H., Zucker R. S. Calcium-induced inactivation of calcium current causes the inter-burst hyperpolarization of Aplysia bursting neurones. J Physiol. 1985 May;362:131–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan E. S., Levitan I. B. A cyclic GMP analog decreases the currents underlying bursting activity in the Aplysia neuron R15. J Neurosci. 1988 Apr;8(4):1162–1171. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-04-01162.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotshaw D. P., Levitan I. B. Reciprocal modulation of calcium current by serotonin and dopamine in the identified Aplysia neuron R15. Brain Res. 1988 Jan 26;439(1-2):64–76. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91462-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May R. M. Simple mathematical models with very complicated dynamics. Nature. 1976 Jun 10;261(5560):459–467. doi: 10.1038/261459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mpitsos G. J., Burton R. M., Jr, Creech H. C., Soinila S. O. Evidence for chaos in spike trains of neurons that generate rhythmic motor patterns. Brain Res Bull. 1988 Sep;21(3):529–538. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(88)90169-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant R. E. Bifurcation and resonance in a model for bursting nerve cells. J Math Biol. 1981 Jan;11(1):15–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00275821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant R. E., Kim M. Mathematical description of a bursting pacemaker neuron by a modification of the Hodgkin-Huxley equations. Biophys J. 1976 Mar;16(3):227–244. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85683-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. J., Thompson S. H. Slow membrane currents in bursting pace-maker neurones of Tritonia. J Physiol. 1987 Jan;382:425–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


