Abstract
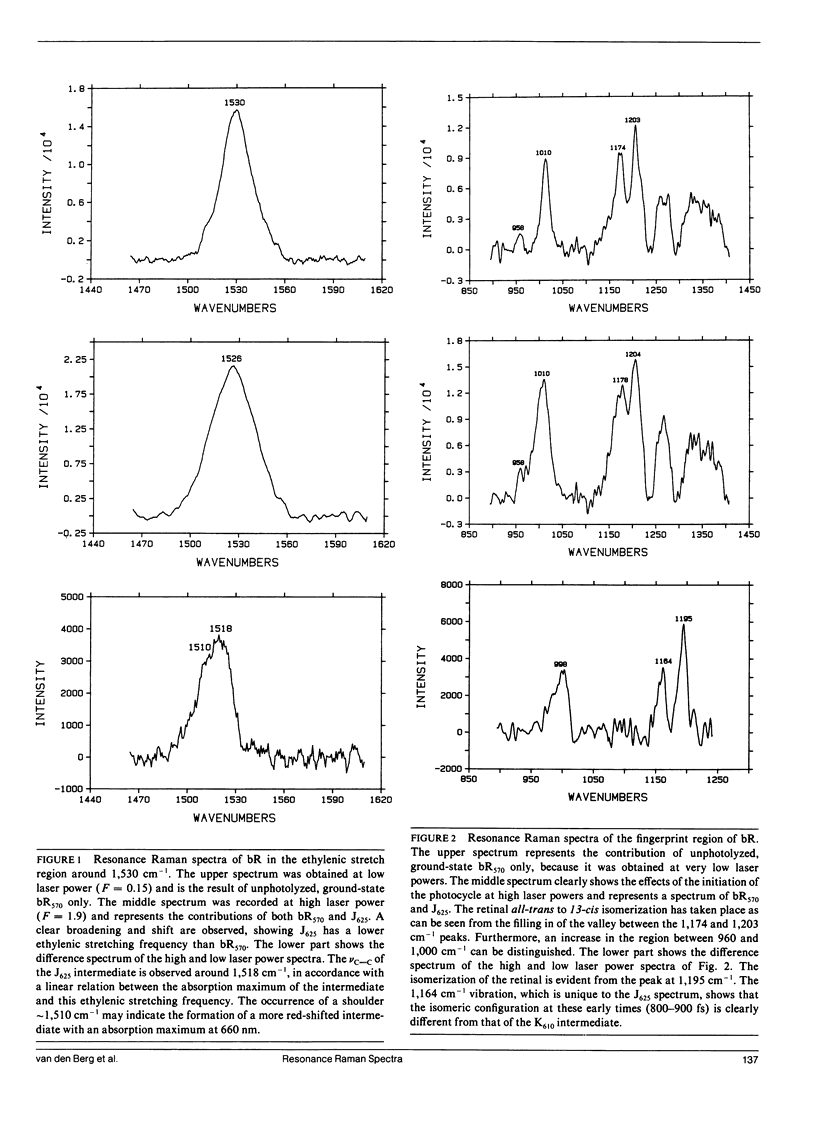
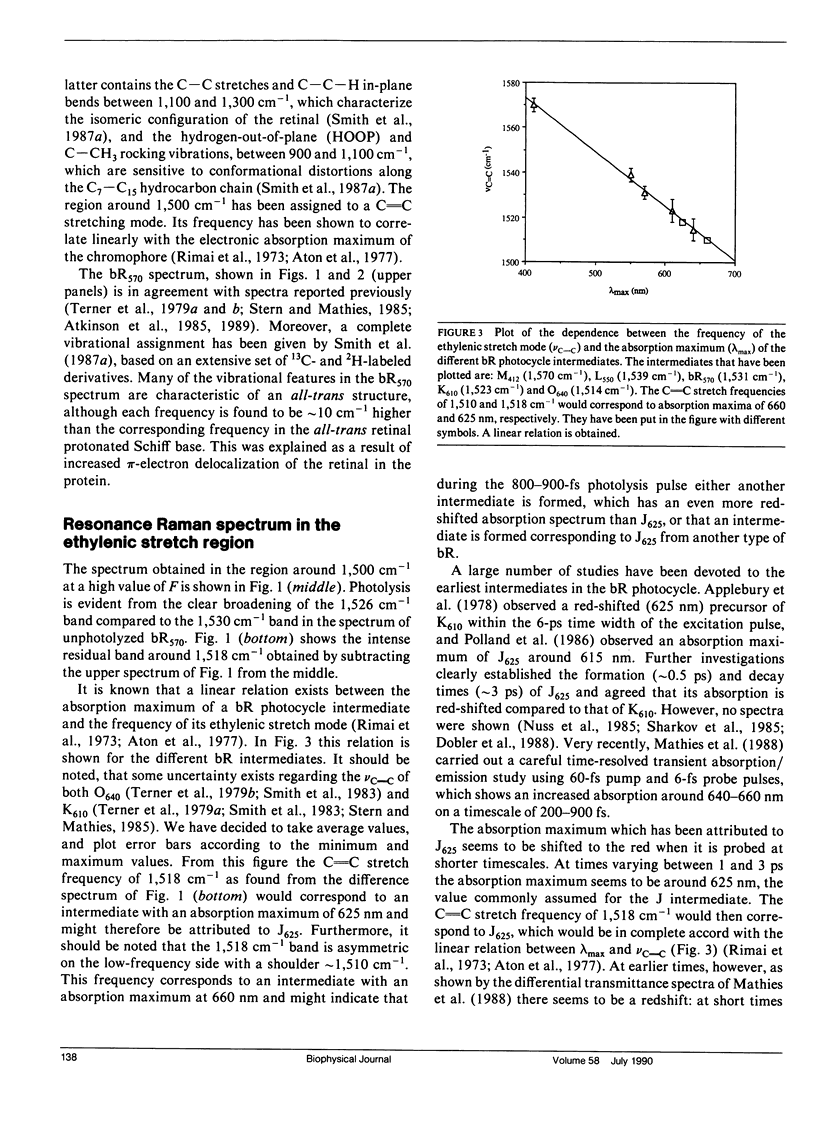
The resonance Raman spectra are presented for the species formed during the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin (bR) on a timescale of 800-900 fs. In the ethylenic stretch region two intermediates were found with frequencies of 1,510 and 1,518 cm-1, corresponding to species with optical absorption maxima at 660 and 625 nm, respectively. This leads to the assignment of the 1,518 cm-1 band to the J625 intermediate. In the fingerprint region, the appearance of a vibration at 1,195 cm-1 strongly suggests that the isomerization indeed has taken place in a time less than the pulsewidth of our laser. This supports the previous proposals made on the basis of the optical spectra. The spectra are compared with those observed in tens of picoseconds up to nanoseconds.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Applebury M. L., Peters K. S., Rentzepis P. M. Primary intermediates in the photochemical cycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1978 Sep;23(3):375–382. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85456-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aton B., Doukas A. G., Callender R. H., Becher B., Ebrey T. G. Resonance Raman studies of the purple membrane. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 28;16(13):2995–2999. doi: 10.1021/bi00632a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becher B. M., Cassim J. Y. Improved isolation procedures for the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Prep Biochem. 1975;5(2):161–178. doi: 10.1080/00327487508061568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M., Mathies R. Resonance Raman evidence for an all-trans to 13-cis isomerization in the proton-pumping cycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5421–5428. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M., Mathies R. Resonance Raman spectra of bacteriorhodopsin's primary photoproduct: evidence for a distorted 13-cis retinal chromophore. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):403–407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanamoto J. H., Dupuis P., El-Sayed M. A. On the protein (tyrosine)-chromophore (protonated Schiff base) coupling in bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7083–7087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann K. J., Rentzepis P. M., Stoeckenius W., Lewis A. Primary photochemical processes in bacteriorhodopsin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 23;68(4):1109–1115. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90310-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A., Stoeckenius W. Bacteriorhodopsin: a light-driven proton pump in Halobacterium Halobium. Biophys J. 1975 Sep;15(9):955–962. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85875-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus M. A., Lewis A. Resonance Raman spectroscopy of the retinylidene chromophore in bacteriorhodopsin (bR570), bR560, M421, and other intermediates: structural conclusions based on kinetics, analogues, models, and isotopically labeled membranes. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4722–4735. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathies R. A., Brito Cruz C. H., Pollard W. T., Shank C. V. Direct observation of the femtosecond excited-state cis-trans isomerization in bacteriorhodopsin. Science. 1988 May 6;240(4853):777–779. doi: 10.1126/science.3363359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathies R., Oseroff A. R., Stryer L. Rapid-flow resonance Raman spectroscopy of photolabile molecules: rhodopsin and isorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):1–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogi T., Marti T., Khorana H. G. Structure-function studies on bacteriorhodopsin. IX. Substitutions of tryptophan residues affect protein-retinal interactions in bacteriorhodopsin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14197–14201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Isolation of the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium and its fractionation into red and purple membrane. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:667–678. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polland H. J., Franz M. A., Zinth W., Kaiser W., Kölling E., Oesterhelt D. Early picosecond events in the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1986 Mar;49(3):651–662. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83692-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimai L., Heyde M. E., Gill D. Vibrational spectra of some carotenoids and related linear polyenes. A Raman spectroscopic study. J Am Chem Soc. 1973 Jul 11;95(14):4493–4501. doi: 10.1021/ja00795a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockburger M., Klusmann W., Gattermann H., Massig G., Peters R. Photochemical cycle of bacteriorhodopsin studied by resonance Raman spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 30;18(22):4886–4900. doi: 10.1021/bi00589a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and related pigments of halobacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:587–616. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terner J., Hsieh C. L., Burns A. R., El-Sayed M. A. Time-resolved resonance Raman characterization of the bO640 intermediate of bacteriorhodopsin. Reprotonation of the Schiff base. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 7;18(16):3629–3634. doi: 10.1021/bi00583a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terner J., Hsieh C. L., Burns A. R., El-Sayed M. A. Time-resolved resonance Raman spectroscopy of intermediates of bacteriorhodopsin: The bK(590) intermediate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3046–3050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terner J., Hsieh C. L., El-Sayed M. A. Time-resolved resonance Raman characterization of the bL550 intermediate and the two dark-adapted bRDA/560 forms of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1979 Jun;26(3):527–541. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85269-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


