Abstract
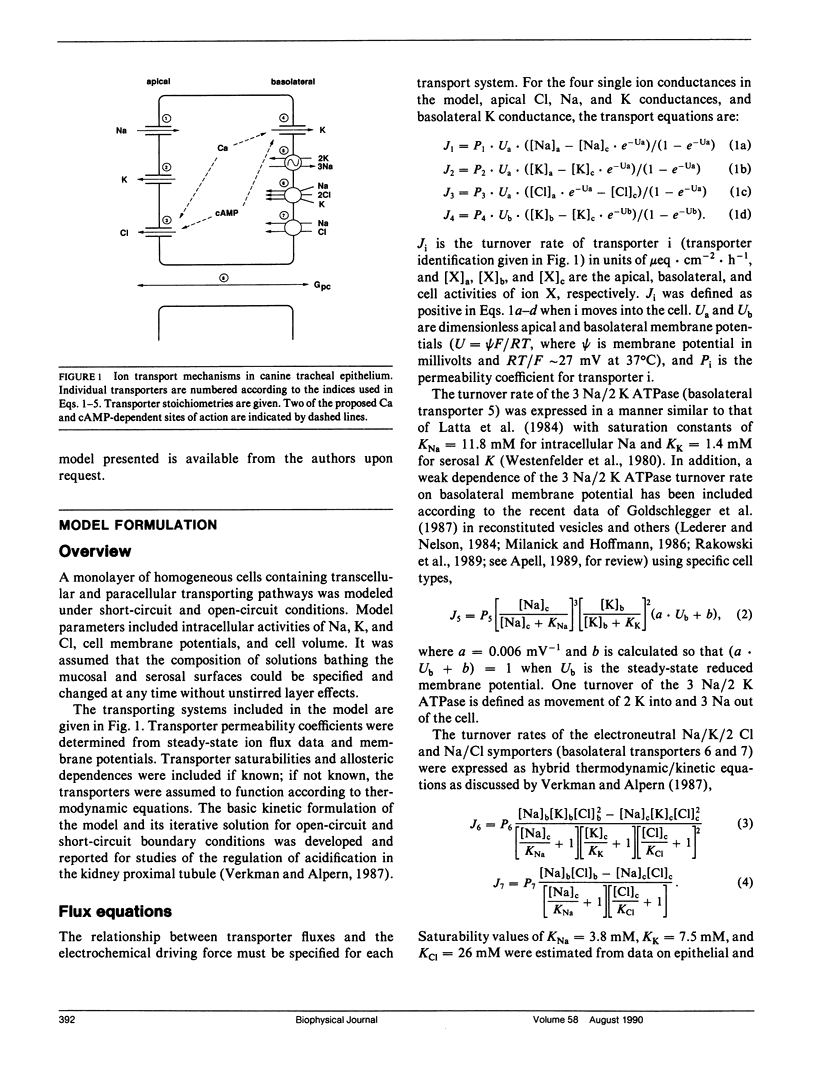
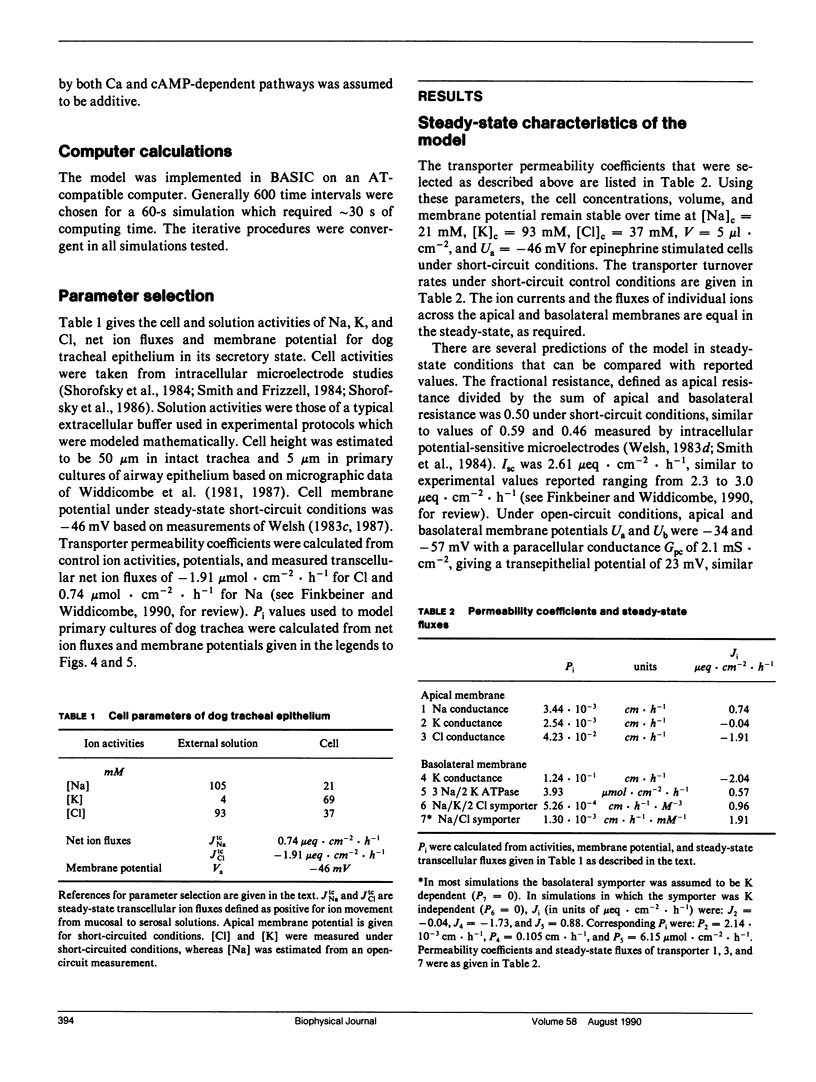
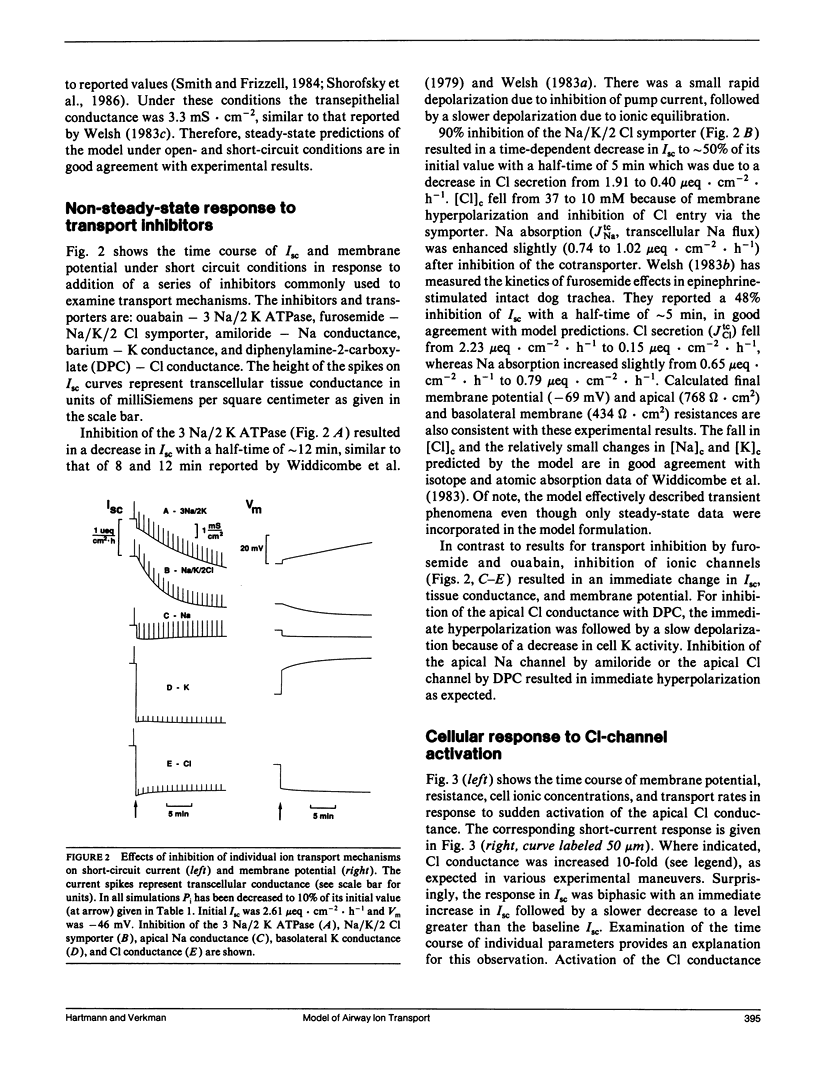
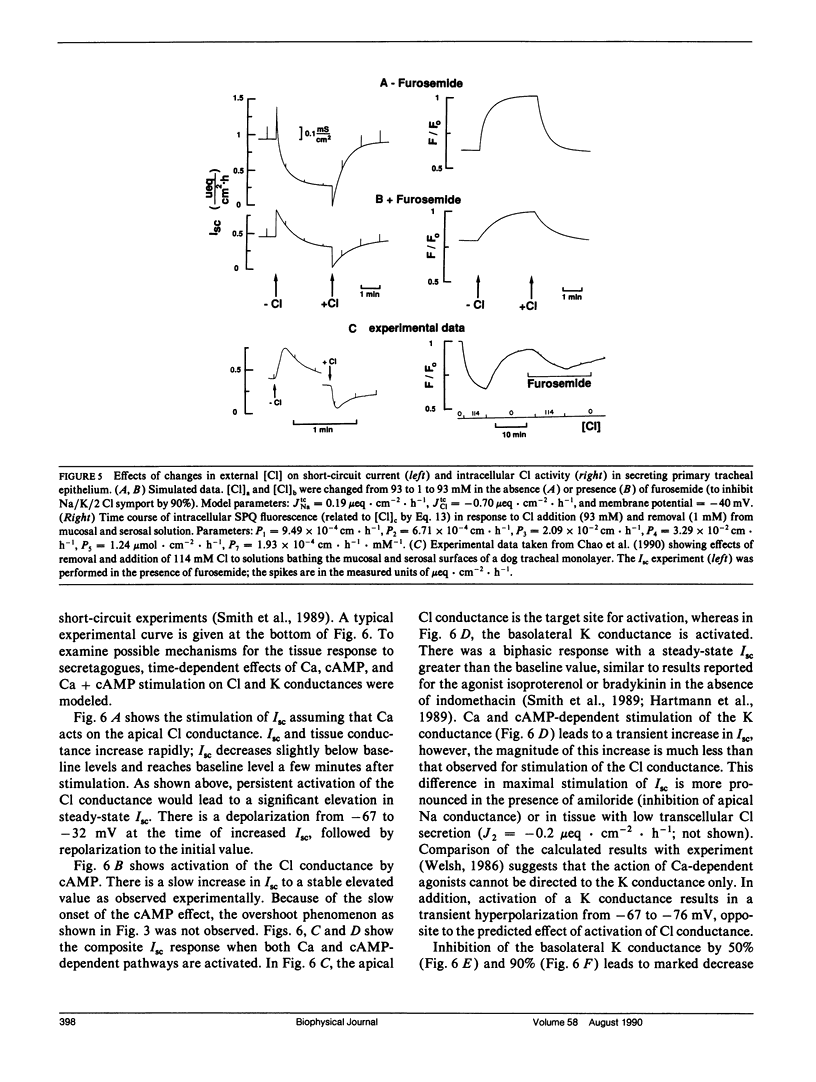
An electrokinetic model was developed to calculate the time course of electrical parameters, ion fluxes, and intracellular ion activities for experiments performed in airway epithelial cells. Model variables included cell [Na], [K], [Cl], volume, and membrane potentials. The model contained apical membrane Cl, Na, and K conductances, basolateral membrane K conductance, Na/K/2 Cl and Na/Cl symport, and 3 Na/2 K ATPase, and a paracellular conductance. Transporter permeabilities and ion saturabilities were determined from reported ion flux data and membrane potentials in intact canine trachea. Without additional assumptions, the model predicted accurately the measured short-circuit current (Isc), cellular conductances, voltage-divider ratios, open-circuit potentials, and the time course of cell ion composition in ion substitution experiments. The model was used to examine quantitatively: (a) the effect of transport inhibitors on Isc and membrane potentials, (b) the dual role of apical Cl and basolateral K conductance in cell secretion, (c) whether the basolateral symporter requires K, and (d) the regulation of apical Cl conductance by cAMP and Ca-dependent signaling pathways. Model predictions gave improved understanding of the interrelations among transporting systems and in many cases gave surprising predictions that were not obvious without a detailed model. The model developed here has direct application to secretory or absorptive epithelial cells in the kidney thick ascending limb, cornea, sweat duct, and intestine in normal and pathophysiological states such as cystic fibrosis and cholera.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apell H. J. Electrogenic properties of the Na,K pump. J Membr Biol. 1989 Sep;110(2):103–114. doi: 10.1007/BF01869466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierman A. J., Cragoe E. J., Jr, de Laat S. W., Moolenaar W. H. Bicarbonate determines cytoplasmic pH and suppresses mitogen-induced alkalinization in fibroblastic cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15253–15256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher R. C., Stutts M. J., Gatzy J. T. Regional differences in bioelectric properties and ion flow in excised canine airways. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Sep;51(3):706–714. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.51.3.706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao A. C., Widdicombe J. H., Verkman A. S. Chloride conductive and cotransport mechanisms in cultures of canine tracheal epithelial cells measured by an entrapped fluorescent indicator. J Membr Biol. 1990 Feb;113(3):193–202. doi: 10.1007/BF01870071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L., Tuet I. K., Widdicombe J. H. Electrical properties of dog tracheal epithelial cells grown in monolayer culture. Am J Physiol. 1984 Mar;246(3 Pt 1):C355–C359. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1984.246.3.C355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. I., Young J. A. Effect of K+ channels in the apical plasma membrane on epithelial secretion based on secondary active Cl- transport. J Membr Biol. 1989 Sep;110(2):139–146. doi: 10.1007/BF01869469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen J. J., Welsh M. J. Regulation of sodium absorption by canine tracheal epithelium. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):73–79. doi: 10.1172/JCI112811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz M. B., Boyarsky G., Sterzel R. B., Boron W. F. Arginine vasopressin enhances pHi regulation in the presence of HCO3- by stimulating three acid-base transport systems. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):648–651. doi: 10.1038/337648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldshlegger R., Karlish S. J., Rephaeli A., Stein W. D. The effect of membrane potential on the mammalian sodium-potassium pump reconstituted into phospholipid vesicles. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:331–355. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latta R., Clausen C., Moore L. C. General method for the derivation and numerical solution of epithelial transport models. J Membr Biol. 1984;82(1):67–82. doi: 10.1007/BF01870733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederer W. J., Nelson M. T. Sodium pump stoicheiometry determined by simultaneous measurements of sodium efflux and membrane current in barnacle. J Physiol. 1984 Mar;348:665–677. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leikauf G. D., Ueki I. F., Nadel J. A., Widdicombe J. H. Bradykinin stimulates Cl secretion and prostaglandin E2 release by canine tracheal epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jan;248(1 Pt 2):F48–F55. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.1.F48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann J. D., Bhalla R. C., Welsh M. J. Release of intracellular calcium by two different second messengers in airway epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 1):L116–L124. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1989.257.2.L116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRoberts J. A., Erlinger S., Rindler M. J., Saier M. H., Jr Furosemide-sensitive salt transport in the Madin-Darby canine kidney cell line. Evidence for the cotransport of Na+, K+, and Cl-. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2260–2266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H. Effects of growth factors on intracellular pH regulation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:363–376. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.002051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musch M. W., Field M. K-independent Na-Cl cotransport in bovine tracheal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 1):C658–C665. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.3.C658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Grady S. M., Musch M. W., Field M. Stoichiometry and ion affinities of the Na-K-Cl cotransport system in the intestine of the winter flounder (Pseudopleuronectes americanus). J Membr Biol. 1986;91(1):33–41. doi: 10.1007/BF01870212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen N. E., Prastein M. L. Na/K/Cl cotransport in cultured human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1445–1451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakowski R. F., Gadsby D. C., De Weer P. Stoichiometry and voltage dependence of the sodium pump in voltage-clamped, internally dialyzed squid giant axon. J Gen Physiol. 1989 May;93(5):903–941. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.5.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorofsky S. R., Field M., Fozzard H. A. Changes in intracellular sodium with chloride secretion in dog tracheal epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1986 Apr;250(4 Pt 1):C646–C650. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.4.C646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorofsky S. R., Field M., Fozzard H. A. Mechanism of Cl secretion in canine trachea: changes in intracellular chloride activity with secretion. J Membr Biol. 1984;81(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF01868804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. L., Frizzell R. A. Chloride secretion by canine tracheal epithelium: IV. Basolateral membrane K permeability parallels secretion rate. J Membr Biol. 1984;77(3):187–199. doi: 10.1007/BF01870568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki J., Ueki I. F., Widdicombe J. H., Nadel J. A. Stimulation of Cl secretion by neurokinin A and neurokinin B in canine tracheal epithelium. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Apr;137(4):899–902. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.4.899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkman A. S., Alpern R. J. Kinetic transport model for cellular regulation of pH and solute concentration in the renal proximal tubule. Biophys J. 1987 Apr;51(4):533–546. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83379-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J. Adrenergic regulation of ion transport by primary cultures of canine tracheal epithelium: cellular electrophysiology. J Membr Biol. 1986;91(2):121–128. doi: 10.1007/BF01925789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J. Electrolyte transport by airway epithelia. Physiol Rev. 1987 Oct;67(4):1143–1184. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.4.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J. Energetics of chloride secretion in canine tracheal epithelium. Comparison of the metabolic cost of chloride transport with the metabolic cost of sodium transport. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):262–268. doi: 10.1172/JCI111410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J. Evidence for basolateral membrane potassium conductance in canine tracheal epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1983 May;244(5):C377–C384. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.244.5.C377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J. Inhibition of chloride secretion by furosemide in canine tracheal epithelium. J Membr Biol. 1983;71(3):219–226. doi: 10.1007/BF01875463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J. Intracellular chloride activities in canine tracheal epithelium. Direct evidence for sodium-coupled intracellular chloride accumulation in a chloride-secreting epithelium. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1392–1401. doi: 10.1172/JCI110892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J., McCann J. D. Intracellular calcium regulates basolateral potassium channels in a chloride-secreting epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8823–8826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J., Smith P. L., Frizzell R. A. Chloride secretion by canine tracheal epithelium: III. Membrane resistances and electromotive forces. J Membr Biol. 1983;71(3):209–218. doi: 10.1007/BF01875462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westenfelder C., Earnest W. R., Al-Bazzaz F. Characterization of Na-K-ATPase in dog tracheal epithelium: enzymatic and ion transport measurements. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Jun;48(6):1008–1019. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.48.6.1008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdicombe J. H., Coleman D. L., Finkbeiner W. E., Friend D. S. Primary cultures of the dog's tracheal epithelium: fine structure, fluid, and electrolyte transport. Cell Tissue Res. 1987 Jan;247(1):95–103. doi: 10.1007/BF00216551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdicombe J. H., Nathanson I. T., Highland E. Effects of "loop" diuretics on ion transport by dog tracheal epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1983 Nov;245(5 Pt 1):C388–C396. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.5.C388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdicombe J. H., Ueki I. F., Bruderman I., Nadel J. A. The effects of sodium substitution and ouabain on ion transport by dog tracheal epithelium. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Aug;120(2):385–392. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.2.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdicombe J. H., Welsh M. J. Ion transport by dog tracheal epithelium. Fed Proc. 1980 Nov;39(13):3062–3066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


