Abstract
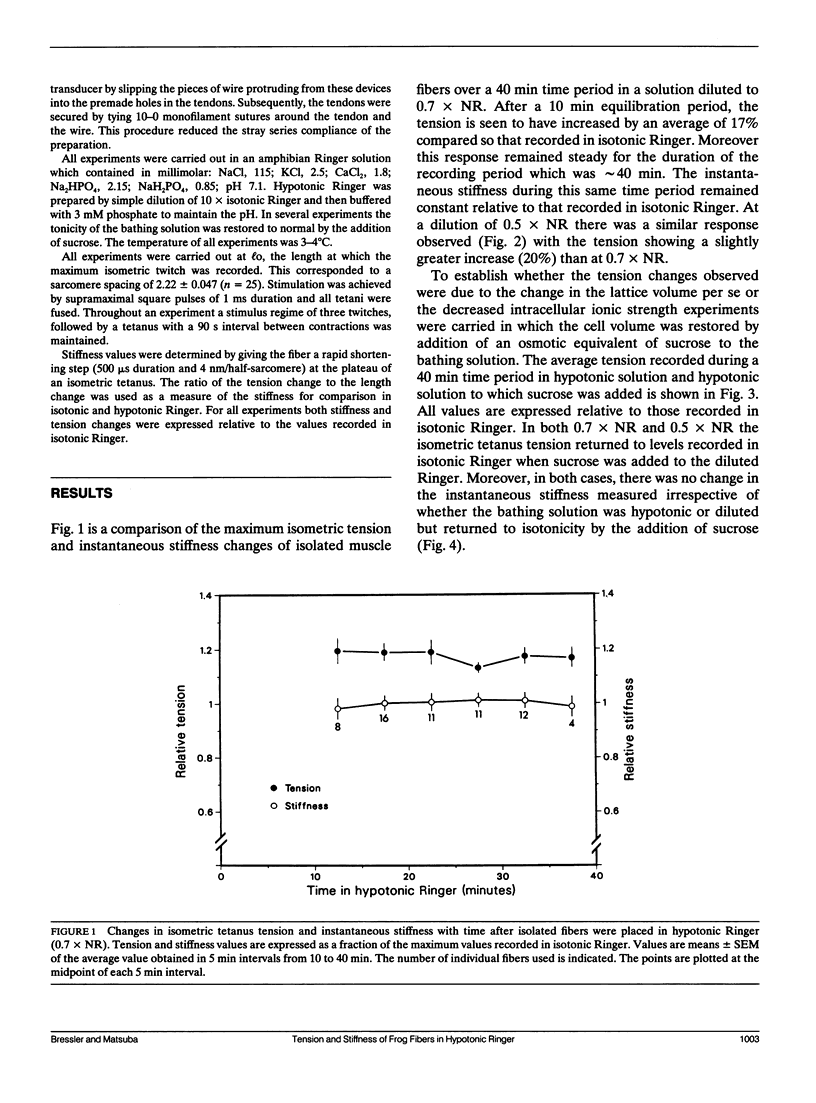
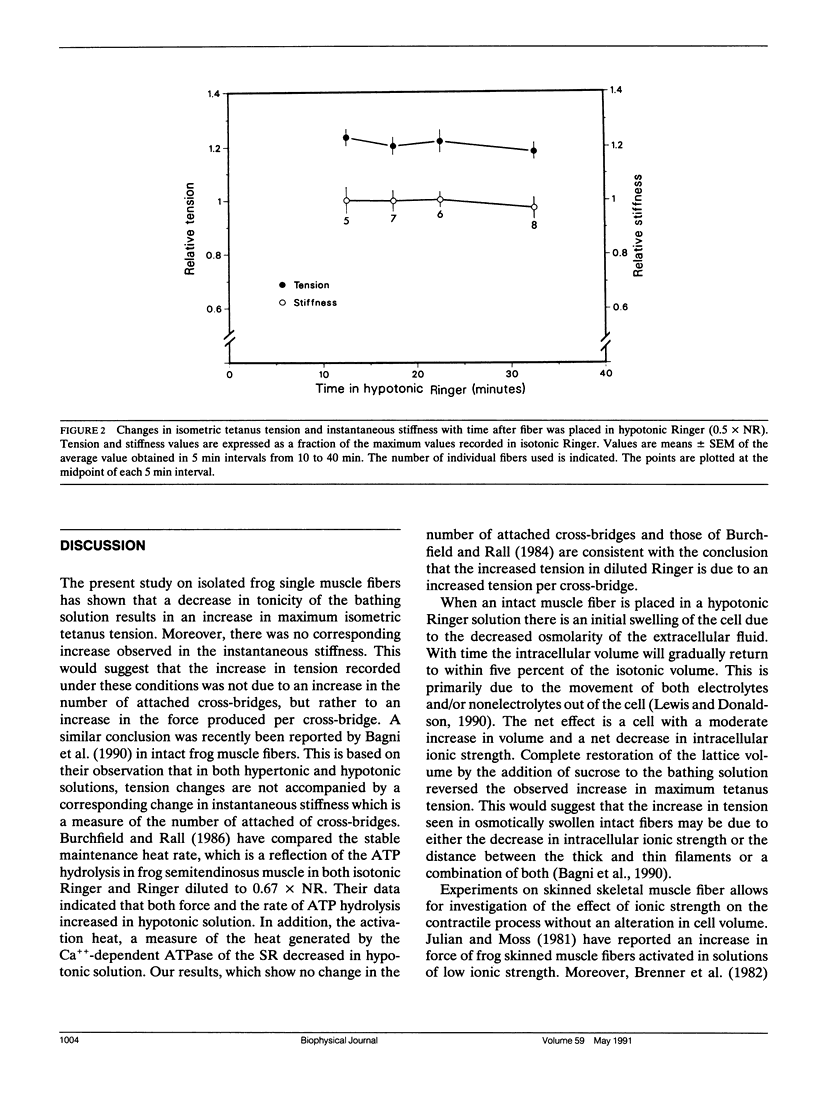
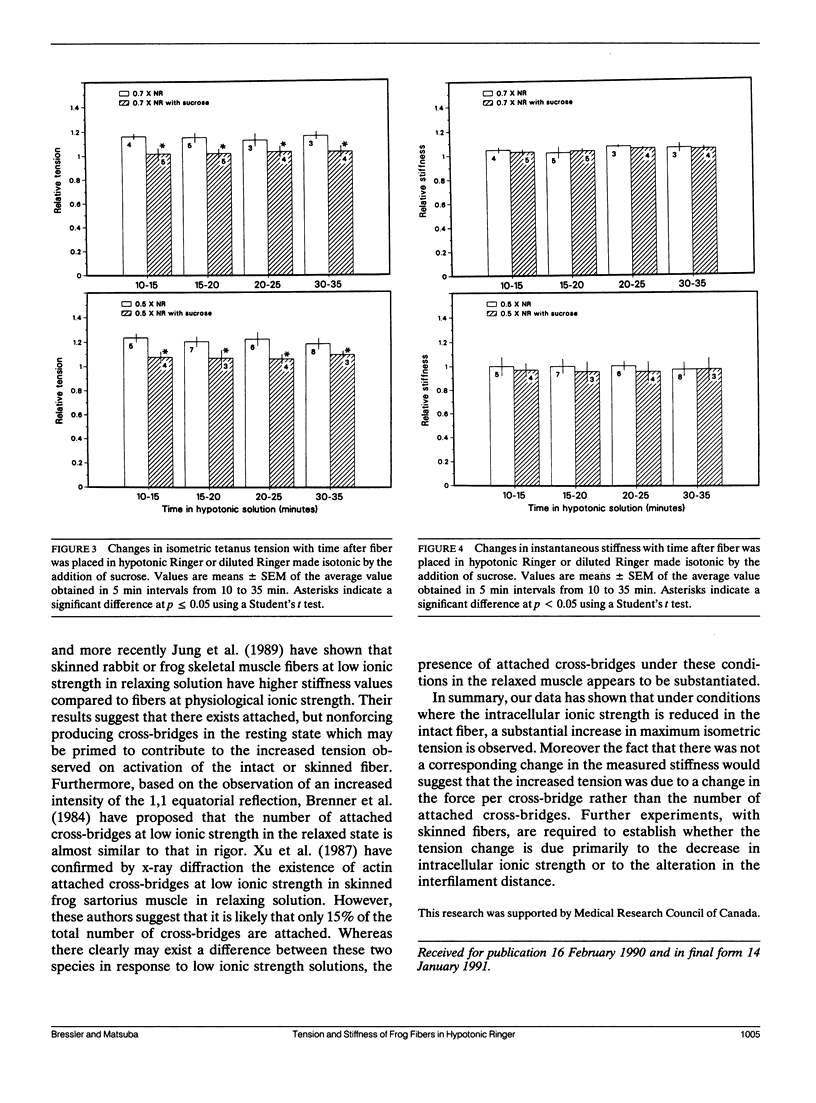
Isometric tension and instantaneous stiffness were measured in frog semitendinosus single muscle fibers in both isotonic and hypotonic Ringer solution. In 0.7 and 0.5 x normal Ringer tension increased 17 and 20%, respectively. There was no corresponding increase in the measured stiffness. The increase in tension in hypotonic Ringer could be reversed by the addition of an osmotic equivalent of sucrose to the bathing solution. These findings suggest that the potentiated tension observed in hypotonic Ringer is due to an increased tension per cross-bridge and not to an increase in the number of attached cross-bridges.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagni M. A., Cecchi G., Colomo F. Myofilament spacing and force generation in intact frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1990 Nov;430:61–75. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B., Schoenberg M., Chalovich J. M., Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Evidence for cross-bridge attachment in relaxed muscle at low ionic strength. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7288–7291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressler B. H., Clinch N. F. The compliance of contracting skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(3):477–493. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressler B. H., Dusik L. A., Menard M. R. Tension responses of frog skeletal muscle fibres to rapid shortening and lengthening steps. J Physiol. 1988 Mar;397:631–641. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressler B. H. Isometric tension and instantaneous stiffness in amphibian skeletal muscle exposed to solutions of increased tonicity. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;55(5):1208–1210. doi: 10.1139/y77-166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchfield D. M., Rall J. A. Energetics and mechanics of frog skeletal muscle in hypotonic solution. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jul;251(1 Pt 1):C66–C71. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.1.C66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman K. A., Hwang J. C. The force-velocity relationship in vertebrate muscle fibres at varied tonicity of the extracellular medium. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(2):255–272. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. The relation between stiffness and filament overlap in stimulated frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:219–249. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARTH J. V. The behaviour of frog muscle in hypertonic solutions. J Physiol. 1958 Nov 10;144(1):167–175. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian F. J., Moss R. L. Effects of calcium and ionic strength on shortening velocity and tension development in frog skinned muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:179–199. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung D. W., Blangé T., de Graaf H., Treijtel B. W. Weakly attached cross-bridges in relaxed frog muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1989 Apr;55(4):605–619. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82858-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada R. D., Gordon A. M. Excitation, contraction, and excitation-contraction coupling of frog muscles in hypotonic solutions. Life Sci I. 1972 May 1;11(9):449–460. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(72)90117-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan P. C., Bressler B. H., Dusik L. A., Trotter M. J. Hypertonicity and force development in frog skeletal muscle fibres. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1983 Aug;61(8):847–856. doi: 10.1139/y83-130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu S. G., Kress M., Huxley H. E. X-ray diffraction studies of the structural state of crossbridges in skinned frog sartorius muscle at low ionic strength. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1987 Feb;8(1):39–54. doi: 10.1007/BF01767263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


