Abstract
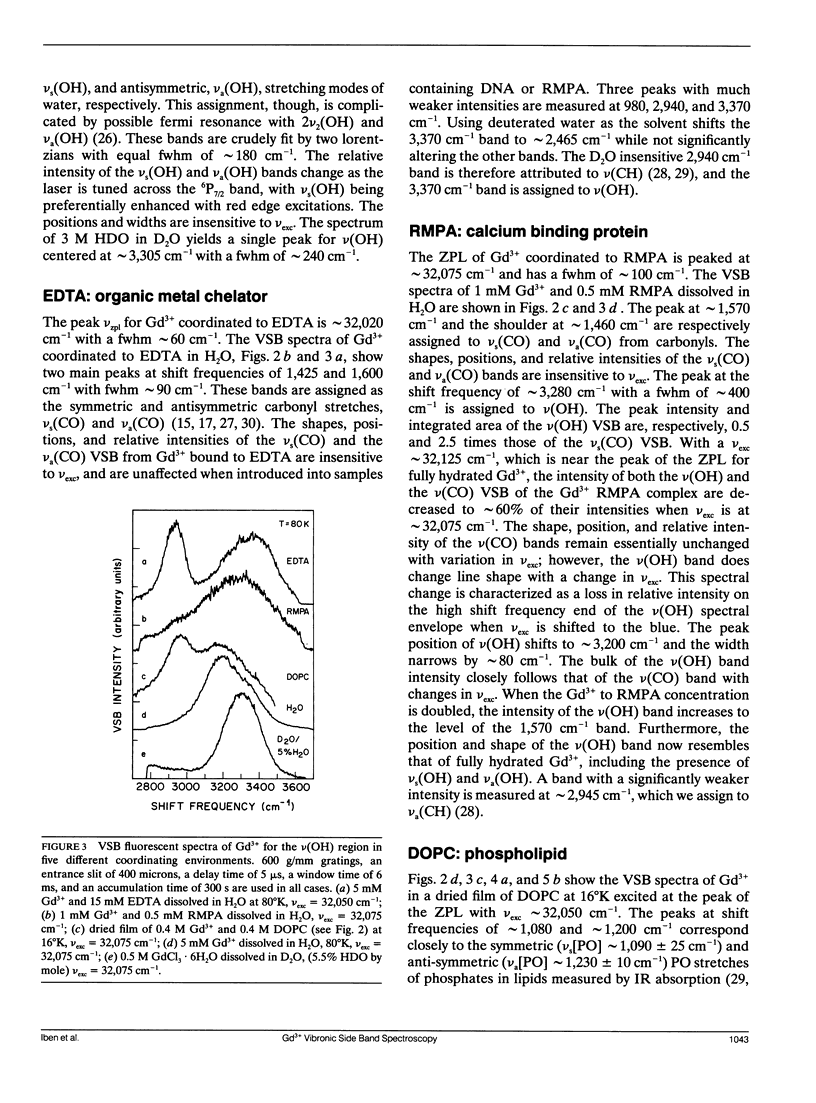
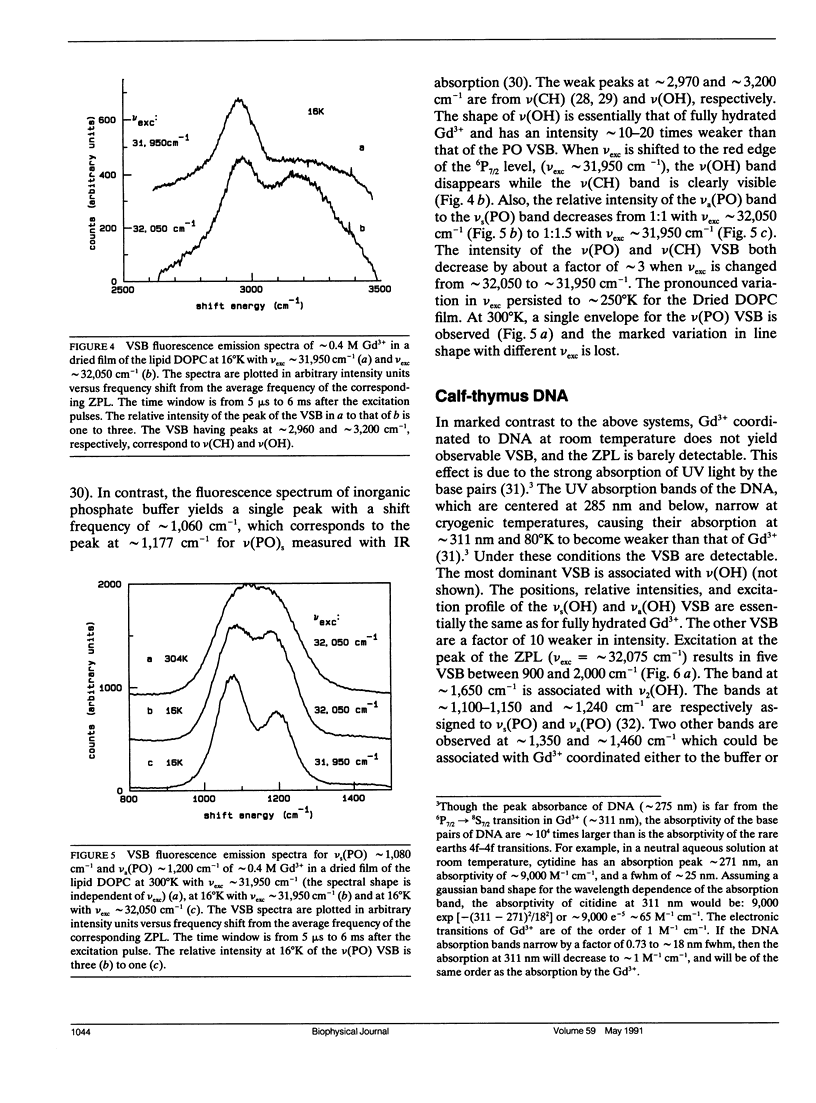
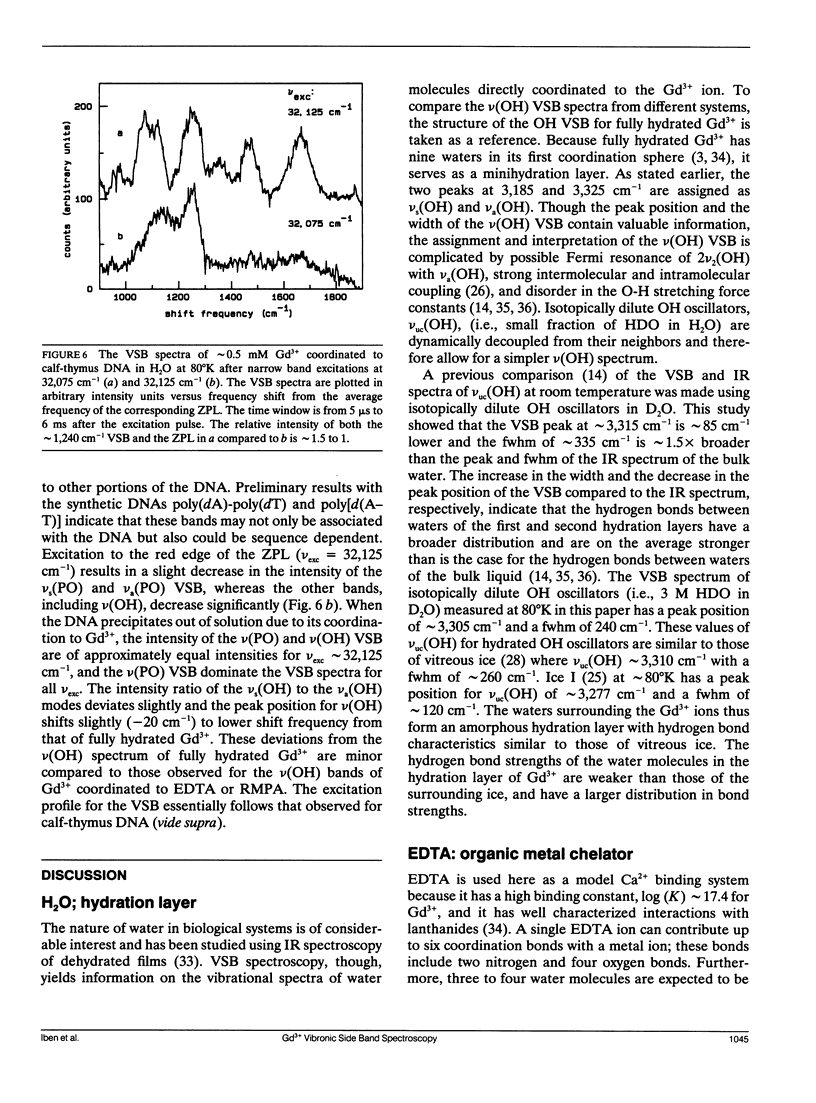
A new spectroscopic technique is presented for obtaining infraredlike spectra of the binding sites of Ca2+ and other metals in biological macromolecules. The technique, based on the Ca(2+)-like binding properties of Gd3+, utilizes vibronic side bands (VSB) that appear in Gd3+ fluorescence. In the fluorescence spectrum of Gd3+, the separation in photon frequency between a VSB and its electronic origin at approximately 32,150 cm-1 (approximately 311 nm) is a direct measure of the vibrational frequency of a ligand coordinated to Gd3+ ion. As a consequence, the VSB are uncomplicated by molecular vibrations distant from the Gd3+ binding site. The vibrational spectra resulting from the VSB of Gd3+ coordinated to a Ca2+ binding protein, a phospholipid, and DNA are presented.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrondo J. L., Goñi F. M., Macarulla J. M. Infrared spectroscopy of phosphatidylcholines in aqueous suspension. A study of the phosphate group vibrations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 6;794(1):165–168. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90310-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin R. H., Stein D. L., Wang J. Terbium luminescence-lifetime heterogeneity and protein equilibrium conformational dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1541–1545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentz J., Alford D., Cohen J., Düzgüneş N. La3+-induced fusion of phosphatidylserine liposomes. Close approach, intermembrane intermediates, and the electrostatic surface potential. Biophys J. 1988 Apr;53(4):593–607. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83138-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breen P. J., Hild E. K., Horrocks W. D., Jr Spectroscopic studies of metal ion binding to a tryptophan-containing parvalbumin. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 10;24(19):4991–4997. doi: 10.1021/bi00340a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cader B. M., Horrocks W. D., Jr A laser-induced europium (III) ion luminescence study of the interaction of this ion with phospholipid bilayer vesicles above and below the gel to liquid-crystalline phase transition temperature. Biophys Chem. 1988 Oct;32(1):97–109. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(88)85038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrzeszczyk A., Wishnia A., Springer C. S., Jr Evidence for cooperative effects in the bind of polyvalent metal ions to pure phosphatidylcholine bilayer vesicle surfaces. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Oct 20;648(1):28–48. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90121-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti J., Halladay H. N., Petersheim M. An ionotropic phase transition in phosphatidylcholine: cation and anion cooperativity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Aug 7;902(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90135-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasdalen H., Göran Eriksson L. E., Westman J., Ehrenberg A. Surface potential effects on metal ion binding to phosphatidylcholine membranes 31P NMR study of lanthanide and calcium ion binding to egg-yolk lecithin vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 5;469(2):151–162. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90177-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann T. R., Jayaweera A. R., Shamoo A. E. Interaction of europium(III) with phospholipid vesicles as monitored by laser-excited europium(III) luminescence. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 23;25(19):5834–5838. doi: 10.1021/bi00367a074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iben IE, Braunstein D, Doster W, Frauenfelder H, Hong MK, Johnson JB, Luck S, Ormos P, Schulte A, Steinbach PJ. Glassy behavior of a protein. Phys Rev Lett. 1989 Apr 17;62(16):1916–1919. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.62.1916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H. Calcium-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:239–266. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.001323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H., Nockolds C. E. Carp muscle calcium-binding protein. II. Structure determination and general description. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):3313–3326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H. Structure and evolution of calcium-modulated proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1980;8(2):119–174. doi: 10.3109/10409238009105467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuntz I. D., Jr, Kauzmann W. Hydration of proteins and polypeptides. Adv Protein Chem. 1974;28:239–345. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60232-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehky P., Blum H. E., Stein E. A., Fischer E. H. Isolation and characterization of parvalbumins from the skeletal muscle of higher vertebrates. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4332–4334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor R. B., Jr Vibrational spectroscopy in the ultraviolet via Gd3+ fluorescence: application to biological systems. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Oct;274(1):312–316. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90444-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. B., Richardson F. S. Lanthanides as probes for calcium in biological systems. Q Rev Biophys. 1979 May;12(2):181–209. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulqueen P., Tingey J. M., Horrocks W. D., Jr Characterization of lanthanide (III) ion binding to calmodulin using luminescence spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1985 Nov 5;24(23):6639–6645. doi: 10.1021/bi00344a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormos P., Ansari A., Braunstein D., Cowen B. R., Frauenfelder H., Hong M. K., Iben I. E., Sauke T. B., Steinbach P. J., Young R. D. Inhomogeneous broadening in spectral bands of carbonmonoxymyoglobin. The connection between spectral and functional heterogeneity. Biophys J. 1990 Feb;57(2):191–199. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82522-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee M. J., Sudnick D. R., Arkle V. K., Horrocks W. D., Jr Lanthanide ion luminescence probes. Characterization of metal ion binding sites and intermetal energy transfer distance measurements in calcium-binding proteins. 1. Parvalbumin. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 9;20(12):3328–3334. doi: 10.1021/bi00515a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg J. M., Seeman N. C., Kim J. J., Suddath F. L., Nicholas H. B., Rich A. Double helix at atomic resolution. Nature. 1973 May 18;243(5403):150–154. doi: 10.1038/243150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowadski J., Cornick G., Kretsinger R. H. Terbium replacement of calcium in parvalbumin. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 5;124(1):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90151-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonuschot G., Mushrush G. W. Terbium as a fluorescent probe for DNA and chromatin. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 22;14(8):1677–1681. doi: 10.1021/bi00679a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


