Full text
PDF










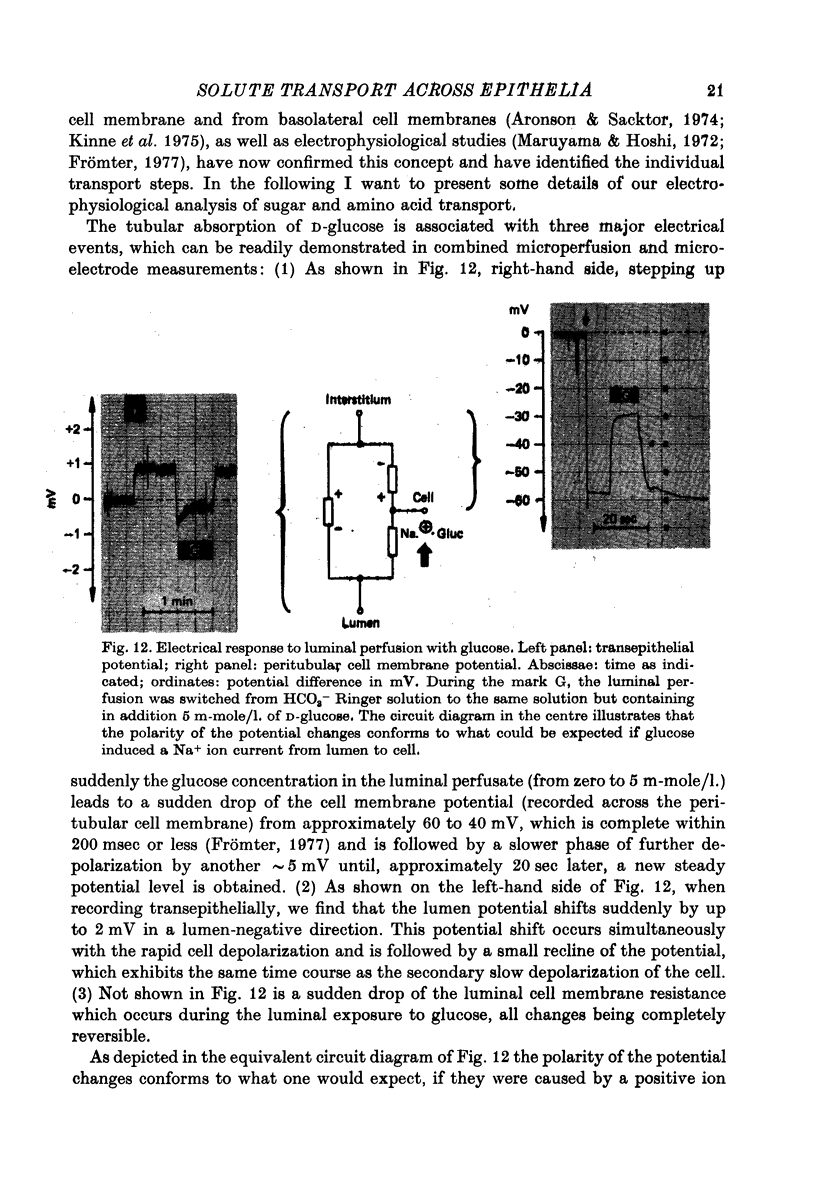
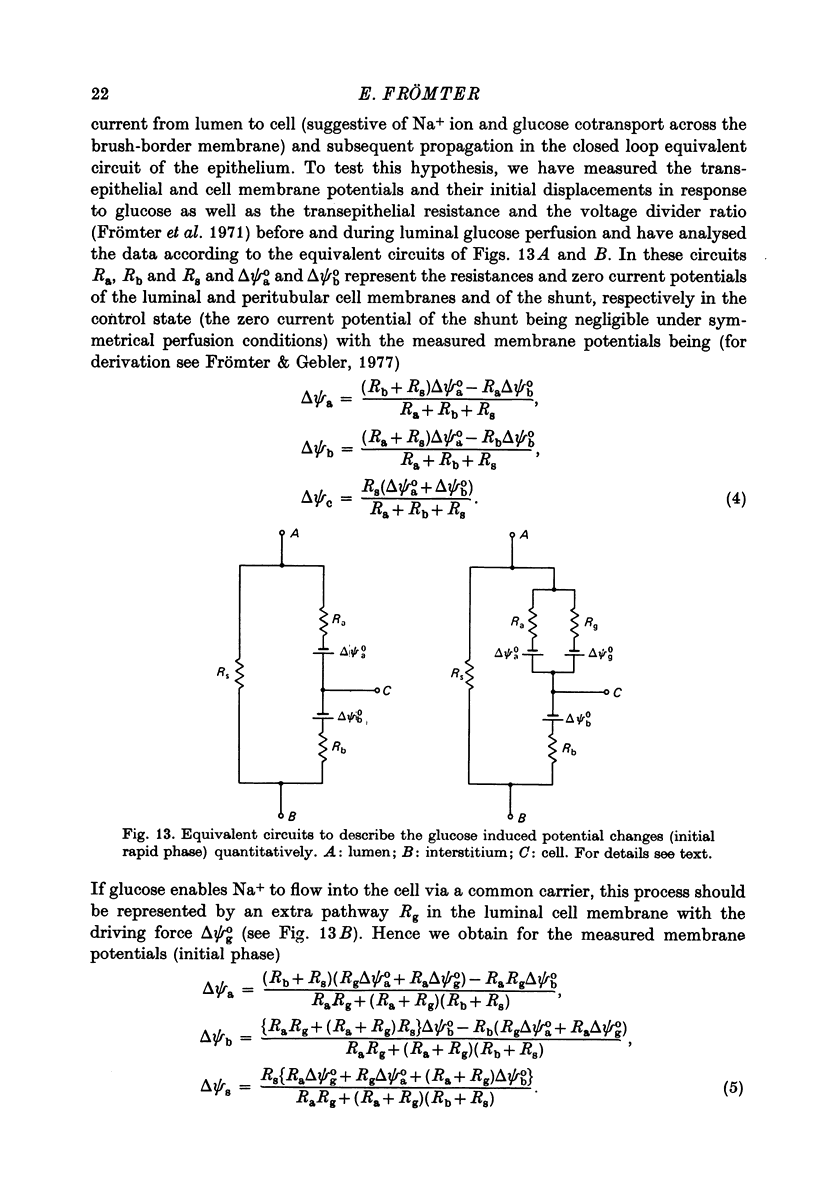

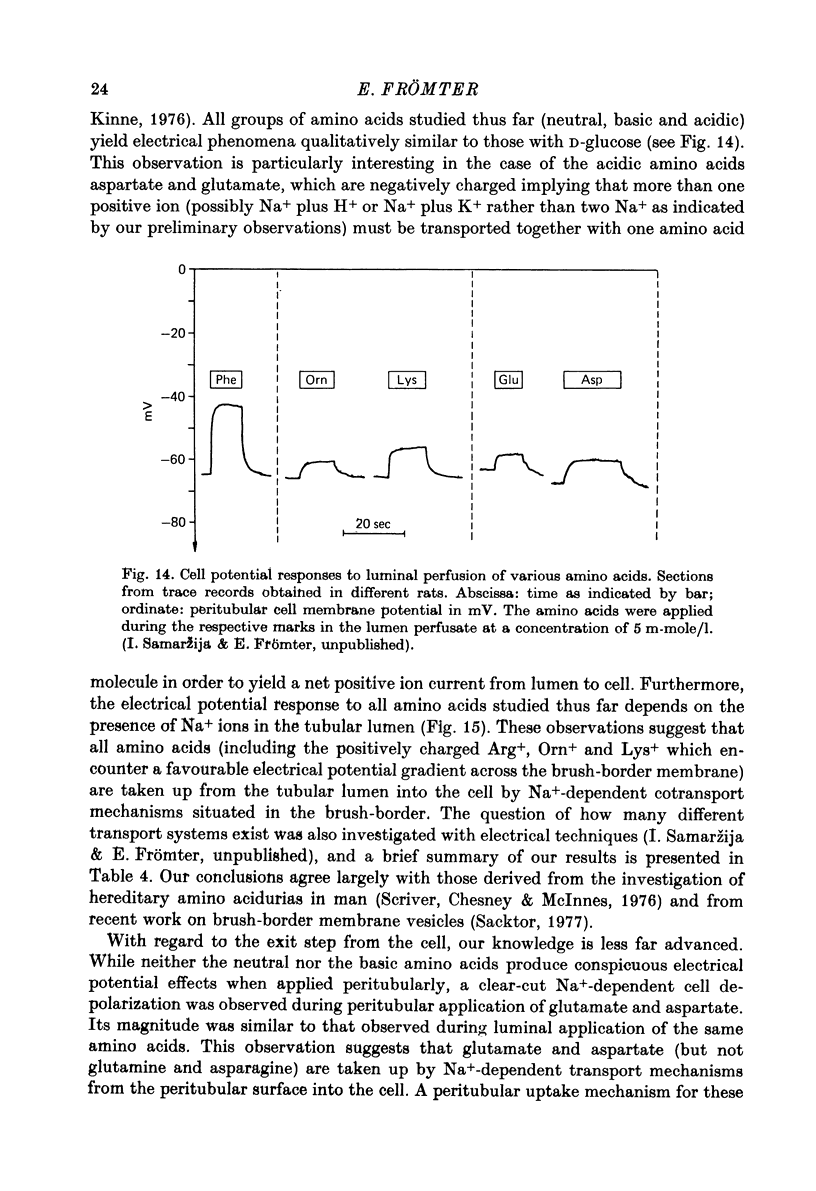
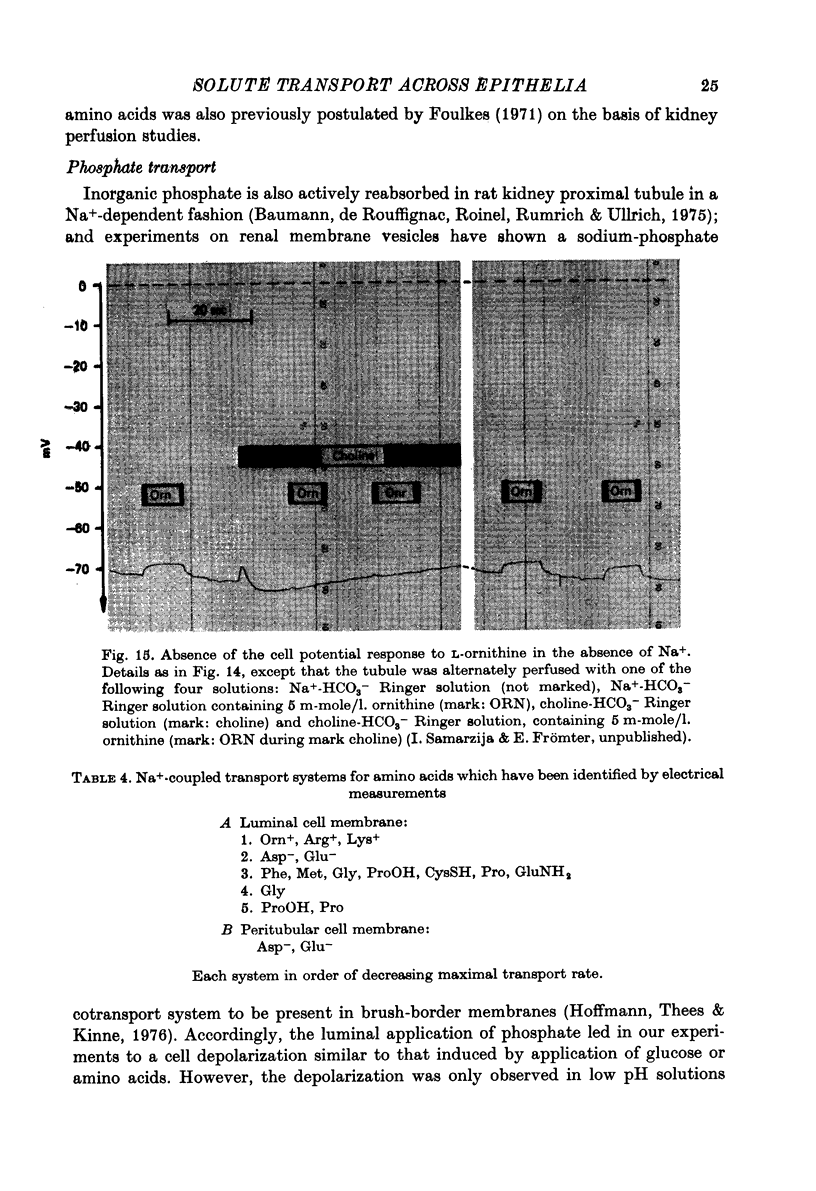
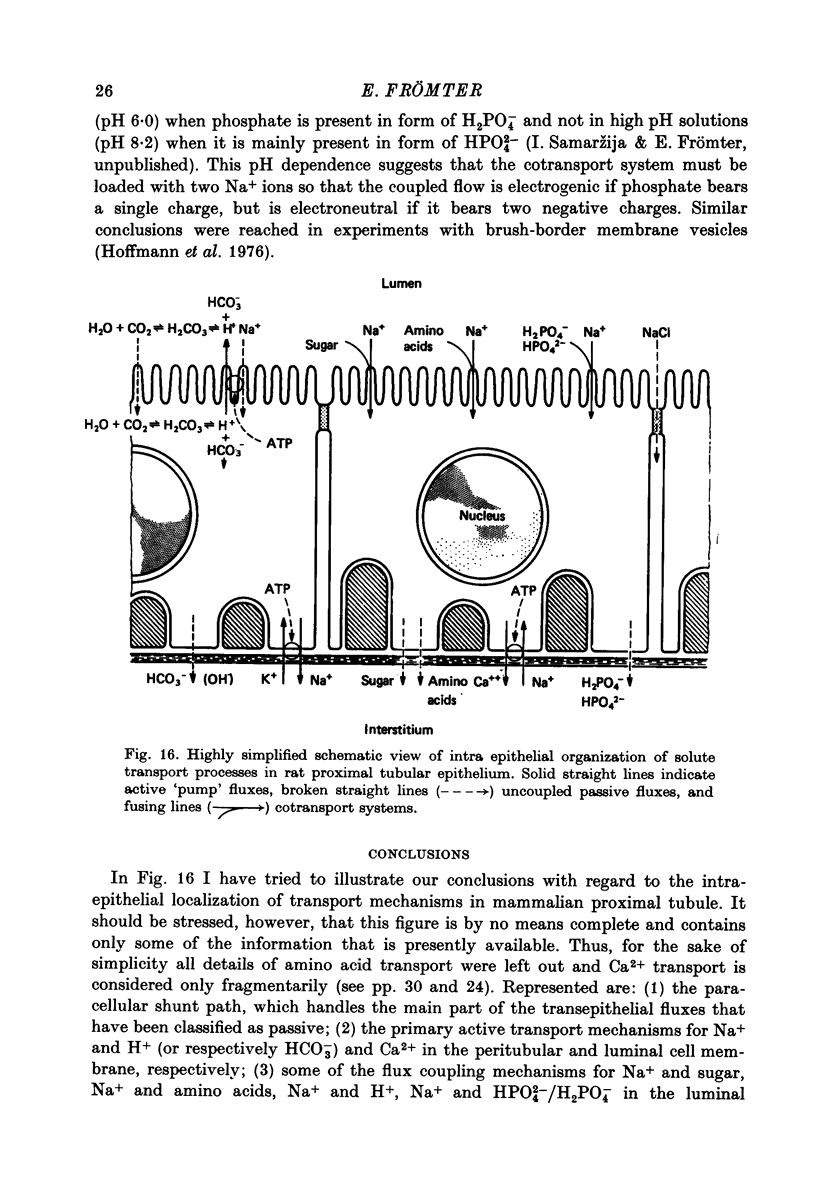





Images in this article
Selected References
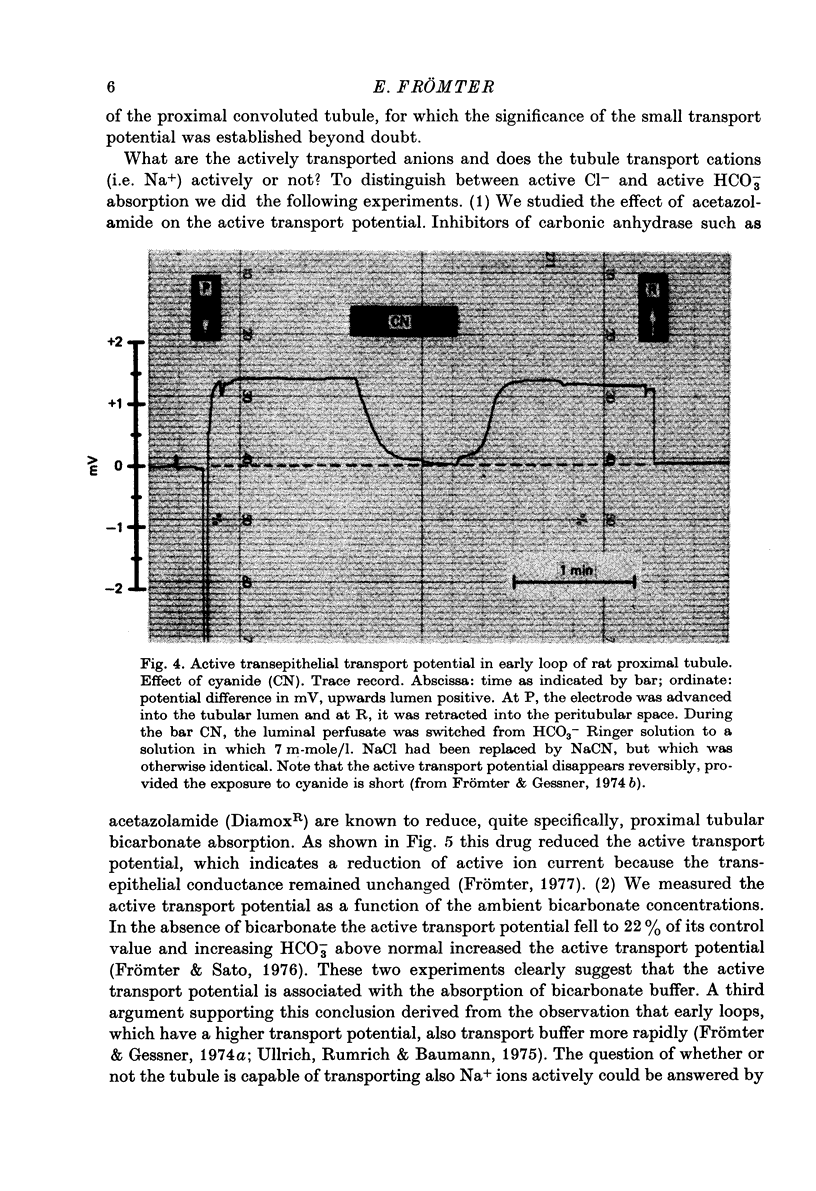
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
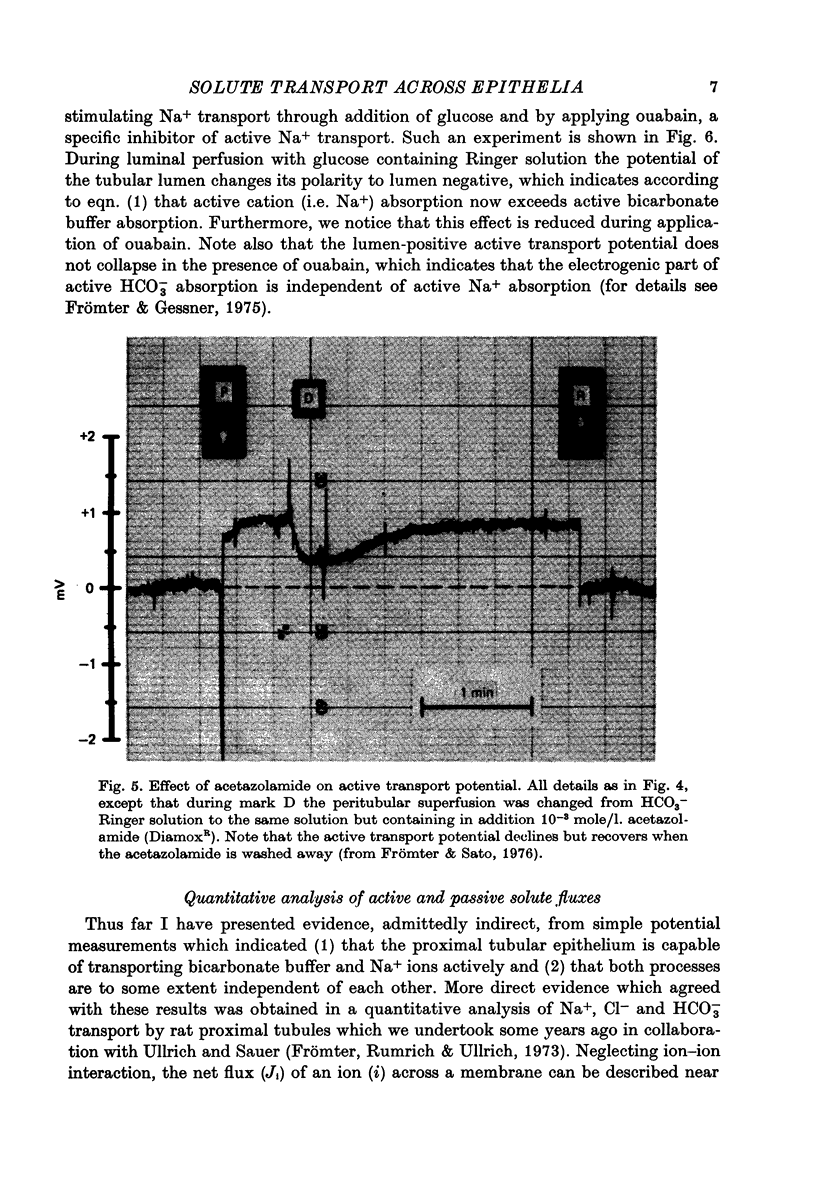
- Aronson P. S., Sacktor B. Transport of D-glucose by brush border membranes isolated from the renal cortex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 31;356(2):231–243. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90286-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
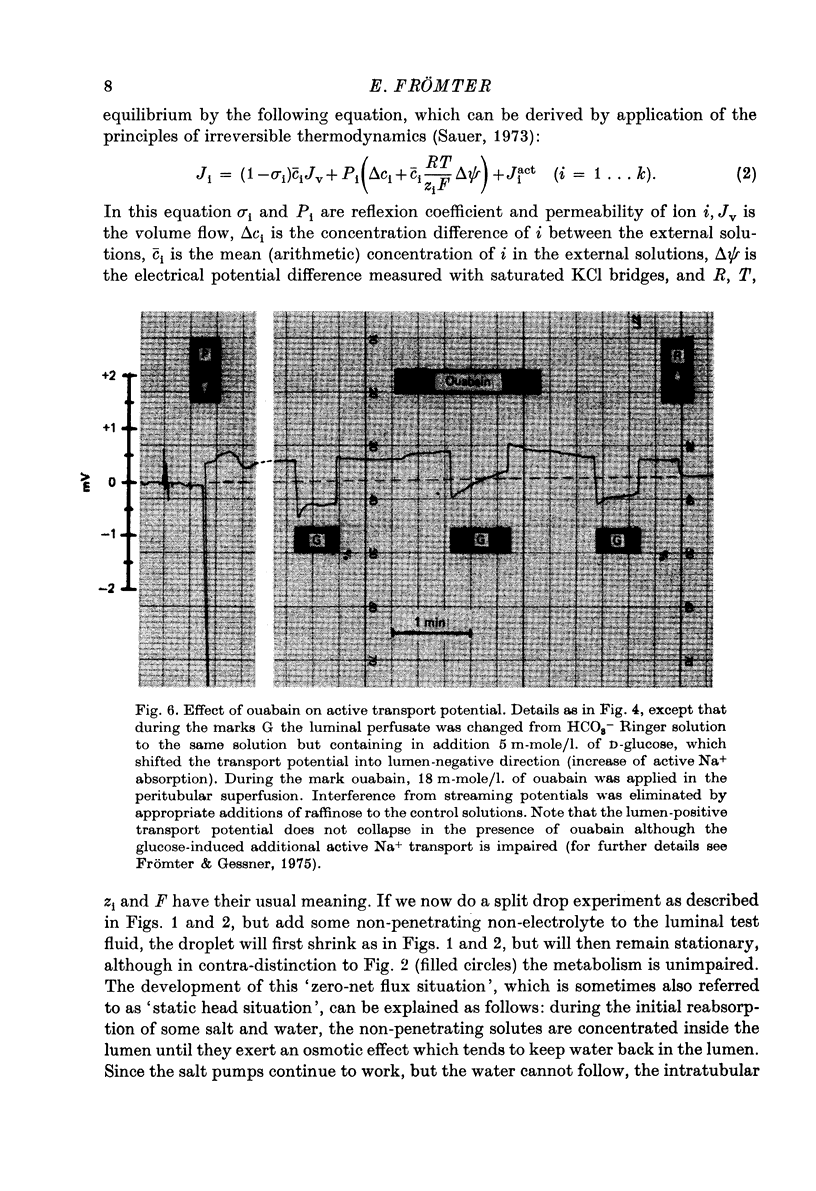
- Barratt L. J., Rector F. C., Jr, Kokko J. P., Seldin D. W. Factors governing the transepithelial potential difference across the proximal tubule of the rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):454–464. doi: 10.1172/JCI107579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
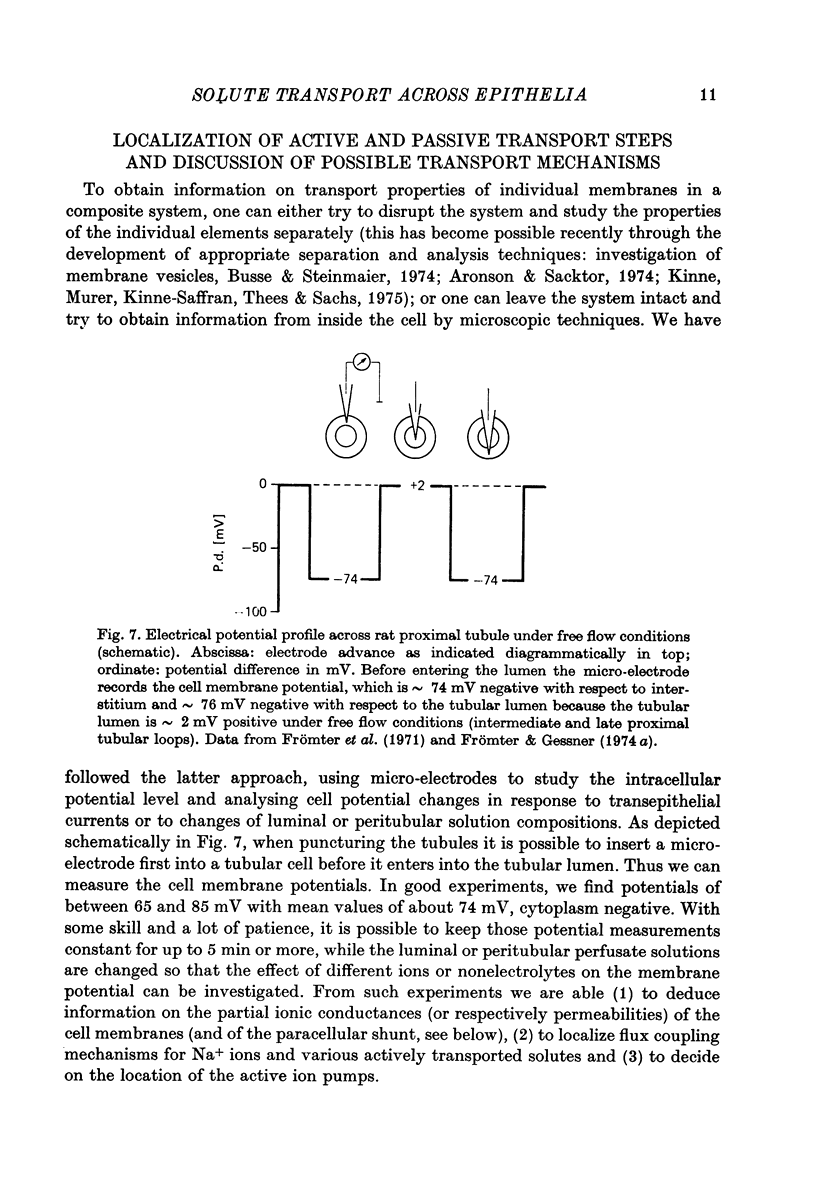
- Baumann K., de Rouffignac C., Roinel N., Rumrich G., Ullrich K. J. Renal phosphate transport: inhomogeneity of local proximal transport rates and sodium dependence. Pflugers Arch. 1975;356(4):287–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00580003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
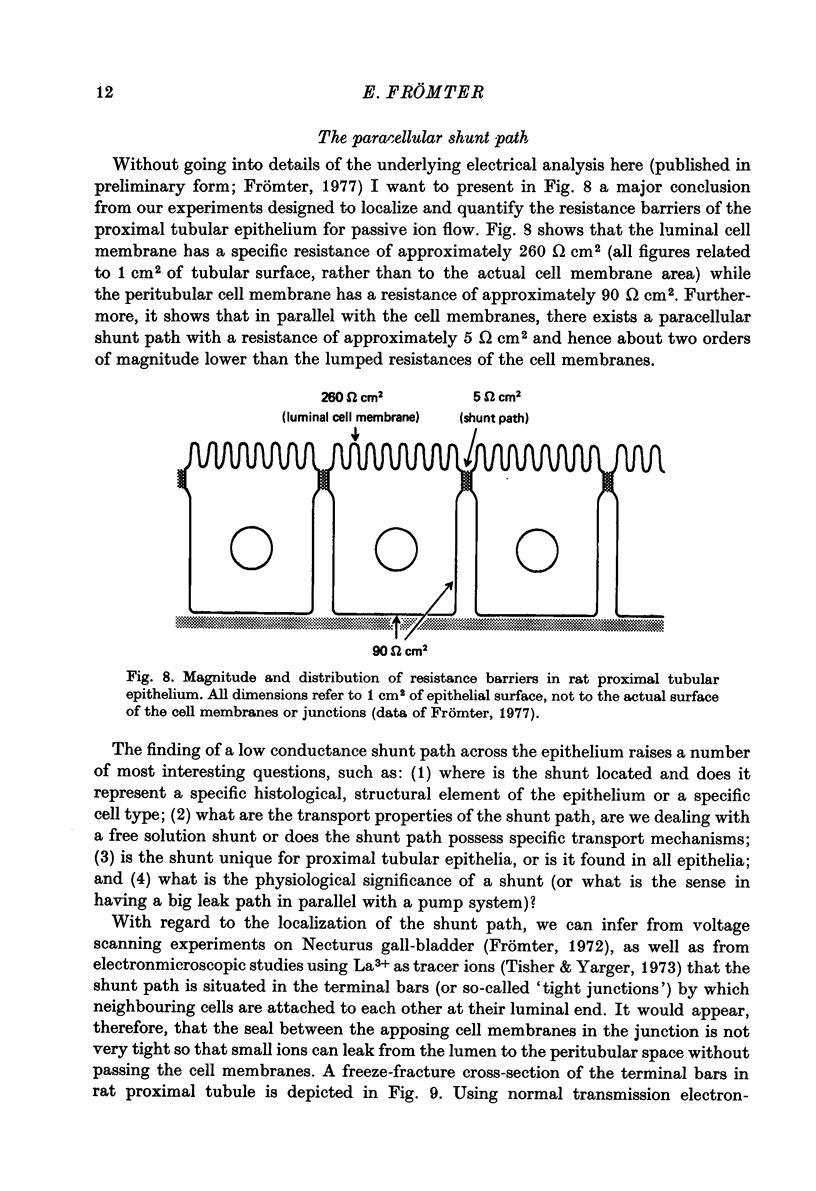
- Boulpaep E. L., Seely J. F. Electrophysiology of proximal and distal tubules in the autoperfused dog kidney. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):1084–1096. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M., Grantham J., Abramow M., Orloff J. Preparation and study of fragments of single rabbit nephrons. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jun;210(6):1293–1298. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.6.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
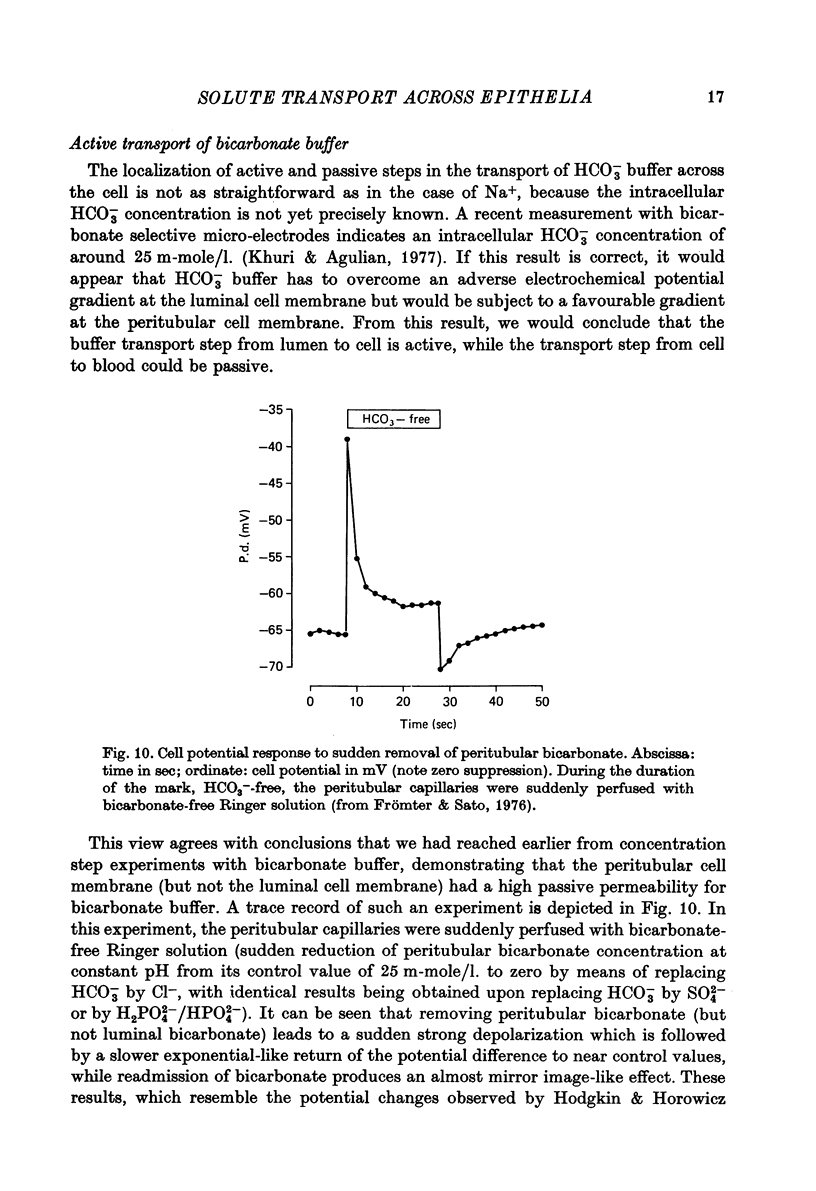
- CRANE R. K. Hypothesis for mechanism of intestinal active transport of sugars. Fed Proc. 1962 Nov-Dec;21:891–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
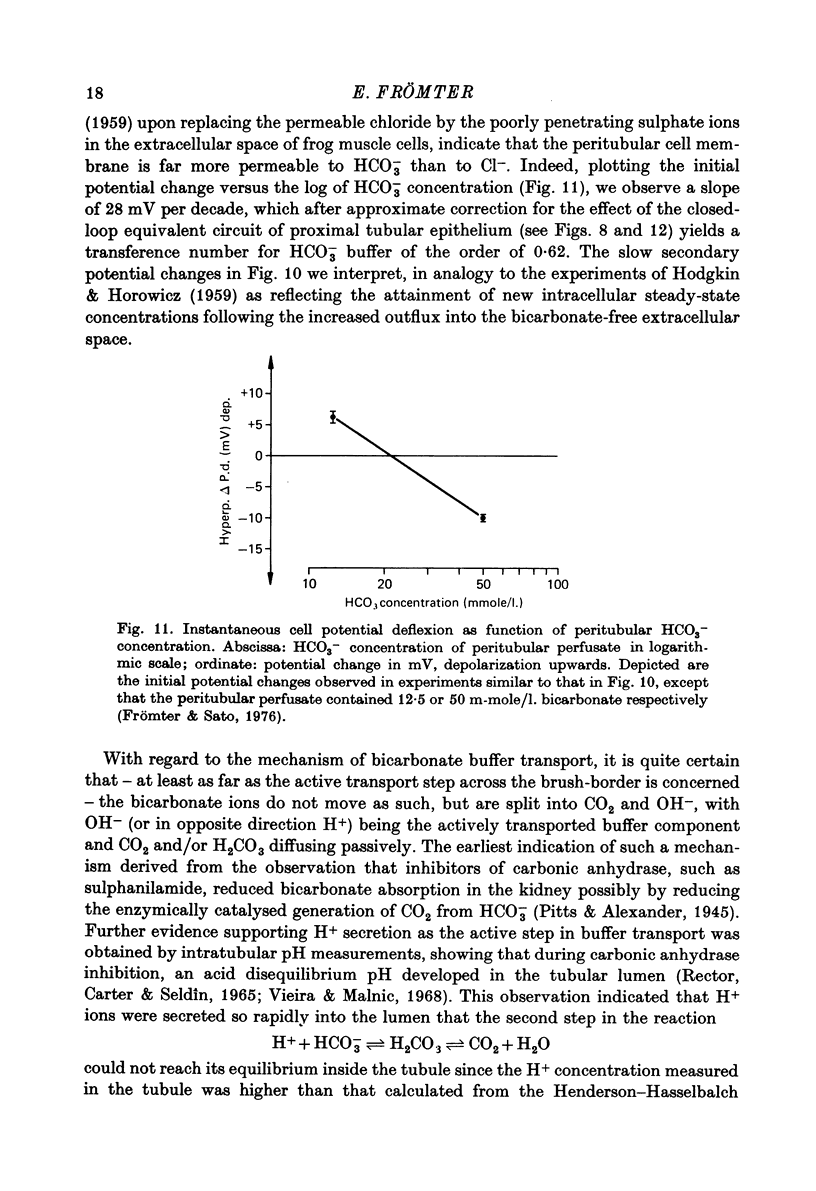
- Cabantchik Z. I., Rothstein A. The nature of the membrane sites controlling anion permeability of human red blood cells as determined by studies with disulfonic stilbene derivatives. J Membr Biol. 1972 Dec 29;10(3):311–330. doi: 10.1007/BF01867863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deetjen P., Boylan J. W. Glucose reabsorption in the rat kidney. Microperfusion studies. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1968;299(1):19–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00362538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M. Tight and leaky junctions of epithelia: a perspective on kisses in the dark. Fed Proc. 1974 Nov;33(11):2220–2224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M., Wright E. M. Biological membranes: the physical basis of ion and nonelectrolyte selectivity. Annu Rev Physiol. 1969;31:581–646. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.31.030169.003053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evers J., Murer H., Kinne R. Phenylalanine uptake in isolated renal brush border vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 5;426(4):598–615. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90124-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARQUHAR M. G., PALADE G. E. Junctional complexes in various epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:375–412. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbarg J., Lim J. J. Role of cations, anions and carbonic anhydrase in fluid transport across rabbit corneal endothelium. J Physiol. 1974 Sep;241(3):647–675. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes E. C. Effects of heavy metals on renal aspartate transport and the nature of solute movement in kidney cortex slices. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 14;241(3):815–822. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A., Schultz S. G. Ionic conductances of extracellular shunt pathway in rabbit ileum. Influence of shunt on transmural sodium transport and electrical potential differences. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Mar;59(3):318–346. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.3.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frömter E., Diamond J. Route of passive ion permeation in epithelia. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 5;235(53):9–13. doi: 10.1038/newbio235009a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frömter E., Gebler B. Electrical properties of amphibian urinary bladder epithelia. III. The cell membrane resistances and the effect of amiloride. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Oct 19;371(1-2):99–108. doi: 10.1007/BF00580777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frömter E., Gessner K. Active transport potentials, membrane diffusion potentials and streaming potentials across rat kidney proximal tubule. Pflugers Arch. 1974;351(1):85–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00603513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frömter E., Gessner K. Effect of inhibitors and diuretics on electrical potential differences in rat kidney proximal tubule. Pflugers Arch. 1975 Jun 26;357(3-4):209–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00585976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frömter E., Gessner K. Free-flow potential profile along rat kidney proximal tubule. Pflugers Arch. 1974;351(1):69–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00603512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frömter E., Rumrich G., Ullrich K. J. Phenomenologic description of Na+, Cl- and HCO-3 absorption from proximal tubules of rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1973 Oct 22;343(3):189–220. doi: 10.1007/BF00586045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frömter E. The route of passive ion movement through the epithelium of Necturus gallbladder. J Membr Biol. 1972;8(3):259–301. doi: 10.1007/BF01868106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERTZ K. H. [Transtubular sodium chloride transport and permeability for nonelectrolytes in the proximal and distal convolution of the rat kidney]. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1963;276:336–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK C. W., LASSITER W. E., MYLLE M. Localization of urine acidification in the mammalian kidney. Am J Physiol. 1960 Mar;198:581–585. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.3.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R., Giebisch G. Ionic requirements of proximal tubular sodium transport. I. Bicarbonate and chloride. Am J Physiol. 1975 Nov;229(5):1205–1215. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.5.1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Györy A. Z., Kinne R. Energy source for transepithelial sodium transport in rat renal proximal tubules. Pflugers Arch. 1971;327(3):234–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00586861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:127–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegel U., Frömter E., Wick T. Der elektrische Wandwiderstand des proximalen Konvolutes der Rattenniere. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1967;294(4):274–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidrich H. G., Kinne R., Kinne-Saffran E., Hannig K. The polarity of the proximal tubule cell in rat kidney. Different surface charges for the brush-border microvilli and plasma membranes from the basal infoldings. J Cell Biol. 1972 Aug;54(2):232–245. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.2.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann N., Thees M., Kinne R. Phosphate transport by isolated renal brush border vesicles. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Mar 30;362(2):147–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00583641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi T., Sakai F. A comparison of the electrical resistances of the surface cell membrane and cellular wall in the proximal tubule of the newt kidney. Jpn J Physiol. 1967 Dec 15;17(6):627–637. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.17.627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinne-Saffran E., Kinne R. Localization of a calcium-stimulated ATPase in the basal-lateral plasma membranes of the proximal tubule of rat kidney cortex. J Membr Biol. 1974 Jul 12;17(3):263–274. doi: 10.1007/BF01870187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinne-Saffran E., Kinne R. Presence of bicarbonate stimulated ATPase in the brush border microvillus membranes of the proximal tubule. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Jul;146(3):751–753. doi: 10.3181/00379727-146-38186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITCHFIELD J. B., BOTT P. A. Micropuncture study of renal excretion of water, K, Na, and Cl in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1962 Oct;203:667–670. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.203.4.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Eaton D. C., Diamond J. M. The mechanism of Na+ transport by rabbit urinary bladder. J Membr Biol. 1976 Aug 27;28(1):41–70. doi: 10.1007/BF01869690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeschke K., Baumann K. Kinetische Studien der D-Glucoseresorption im proximalen Konvolut der Rattenniere. Pflugers Arch. 1969;305(2):139–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00585841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeschke K., Baumann K., Renschler H., Ullrich K. J. Differenzierung zwischen aktiver und passiver Komponente des D-Glucosetrnsports am proximalen Konvolut der Rattenniere. Pflugers Arch. 1969;305(2):118–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00585840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama T., Hoshi T. The effect of D-glucose on the electrical potential profile across the proximal tubule of newt kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 1;282(1):214–225. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90327-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maude D. L. Mechanism of salt transport and some permeability properties of rat proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1970 Jun;218(6):1590–1595. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.6.1590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murer H., Hopfer U., Kinne R. Sodium/proton antiport in brush-border-membrane vesicles isolated from rat small intestine and kidney. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 15;154(3):597–604. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann K. H., Rector F. C., Jr Mechanism of NaCl and water reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule of rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1110–1118. doi: 10.1172/JCI108563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECTOR F. C., Jr, CARTER N. W., SELDIN D. W. THE MECHANISM OF BICARBONATE REABSORPTION IN THE PROXIMAL AND DISTAL TUBULES OF THE KIDNEY. J Clin Invest. 1965 Feb;44:278–290. doi: 10.1172/JCI105142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuss L., Finn A. L. Electrical properties of the cellular transepithelial pathway in Necturus gallbladder. I. Circuit analysis and steady-state effects of mucosal solution ionic substitutions. J Membr Biol. 1975 Dec 4;25(1-2):115–139. doi: 10.1007/BF01868571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuss L., Finn A. L. Passive electrical properties of toad urinary bladder epithelium. Intercellular electrical coupling and transepithelial cellular and shunt conductances. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Jul;64(1):1–25. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEN A. K., POST R. L. STOICHIOMETRY AND LOCALIZATION OF ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE-DEPENDENT SODIUM AND POTASSIUM TRANSPORT IN THE ERYTHROCYTE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:345–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt U., Dubach U. C. Na K stimulated adenosinetriphosphatase: intracellular localisation within the proximal tubule of the rat nephron. Pflugers Arch. 1971;330(3):265–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00588617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scriver C. R., Chesney R. W., McInnes R. R. Genetic aspects of renal tubular transport: diversity and topology of carriers. Kidney Int. 1976 Feb;9(2):149–171. doi: 10.1038/ki.1976.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seely J. F., Chirito E. Studies of the electrical potential difference in rat proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jul;229(1):72–80. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin L. A., Mukherjee T. M., Williams A. W. Freeze-etch appearance of the tight junctions in the epithelium of small and large intestine of mice. Protoplasma. 1969;67(2):165–184. doi: 10.1007/BF01248737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struyvenberg A., Morrison R. B., Relman A. S. Acid-base behavior of separated canine renal tubule cells. Am J Physiol. 1968 May;214(5):1155–1162. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.5.1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisher C. C., Yarger W. E. Lanthanum permeability of the tight junction (zonula occludens) in the renal tubule of the rat. Kidney Int. 1973 Apr;3(4):238–250. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tune B. M., Burg M. B. Glucose transport by proximal renal tubules. Am J Physiol. 1971 Aug;221(2):580–585. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.2.580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich K. J., Capasso G., Rumrich G., Papavassiliou F., Klöss S. Coupling between proximal tubular transport processes. Studies with ouabain, SITS and HCO3-free solutions. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Apr 25;368(3):245–252. doi: 10.1007/BF00585203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich K. J., Radtke H. W., Rumrich G. The role of bicarbonate and other buffers on isotonic fluid absorption in the proximal convolution of the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1971;330(2):149–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00643031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich K. J., Rumrich G., Baumann K. Renal proximal tubular buffer-(glycodiazine) transport. Inhomogeneity of local transport rate, dependence on sodium, effect of inhibitors and chronic adaptation. Pflugers Arch. 1975 Jun 26;357(3-4):149–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00585971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich K. J., Rumrich G., Klöss S. Active Ca2+ reabsorption in the proximal tubule of the rat kidney. Dependence on sodium- and buffer transport. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Aug 24;364(3):223–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00581759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich K. J., Rumrich G., Klöss S. Sodium dependence of the amino acid transport in the proximal convolution of the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1974;351(1):49–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00603510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich K. J., Rumrich G., Klöss S. Specificity and sodium dependence of the active sugar transport in the proximal convolution of the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1974;351(1):35–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00603509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira F. L., Malnic G. Hydrogen ion secretion by rat renal cortical tubules as studied by an antimony microelectrode. Am J Physiol. 1968 Apr;214(4):710–718. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.4.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]