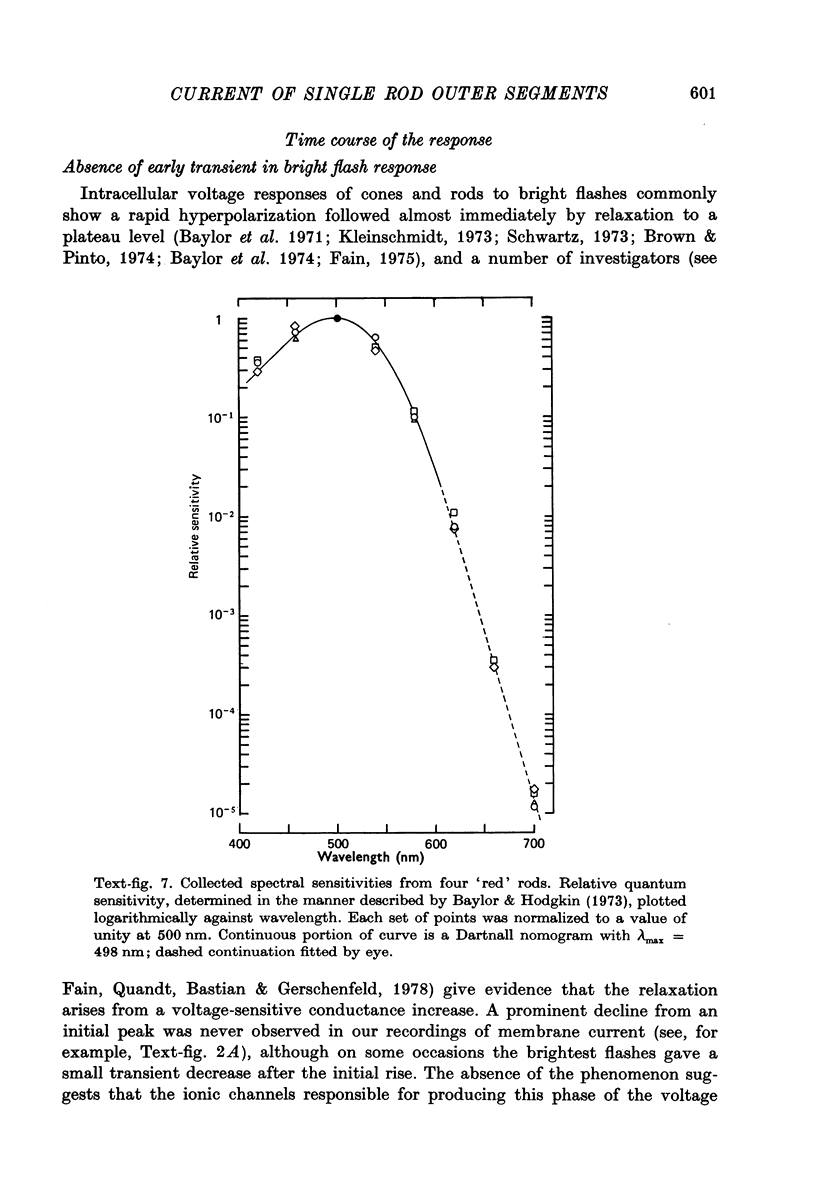
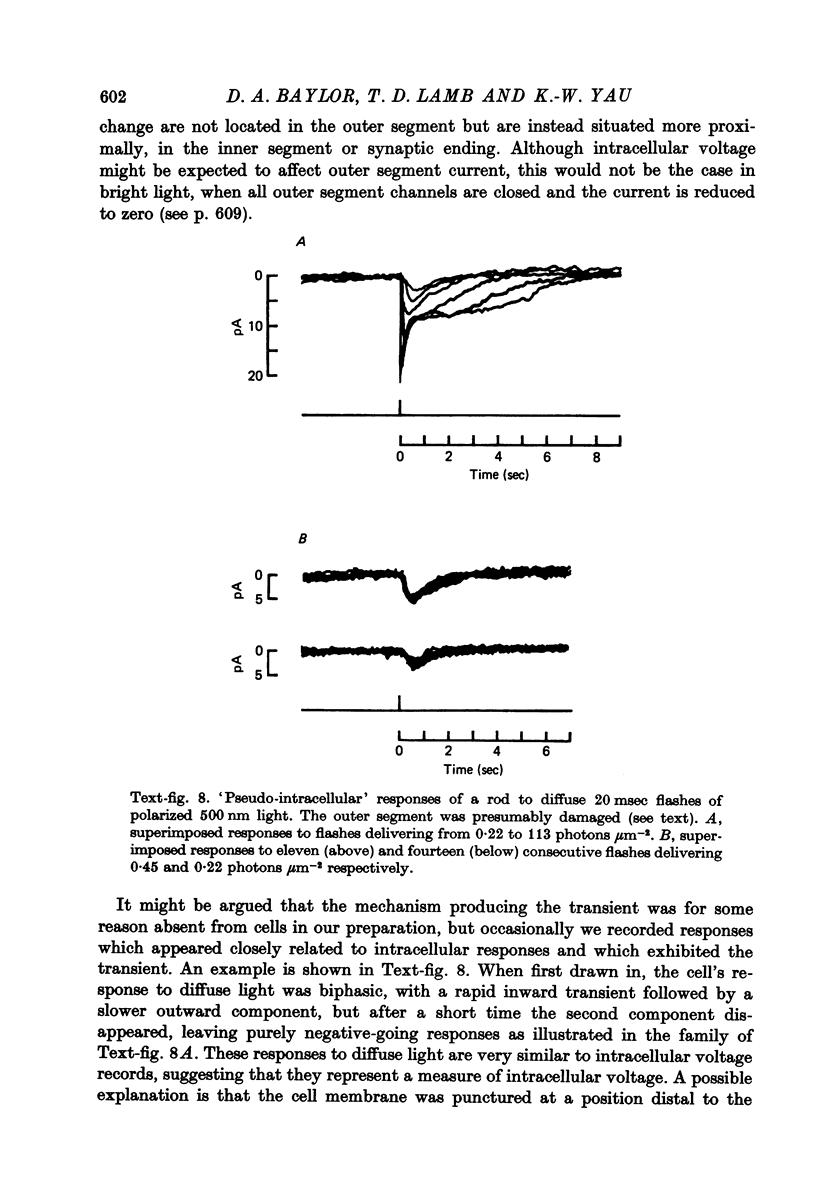
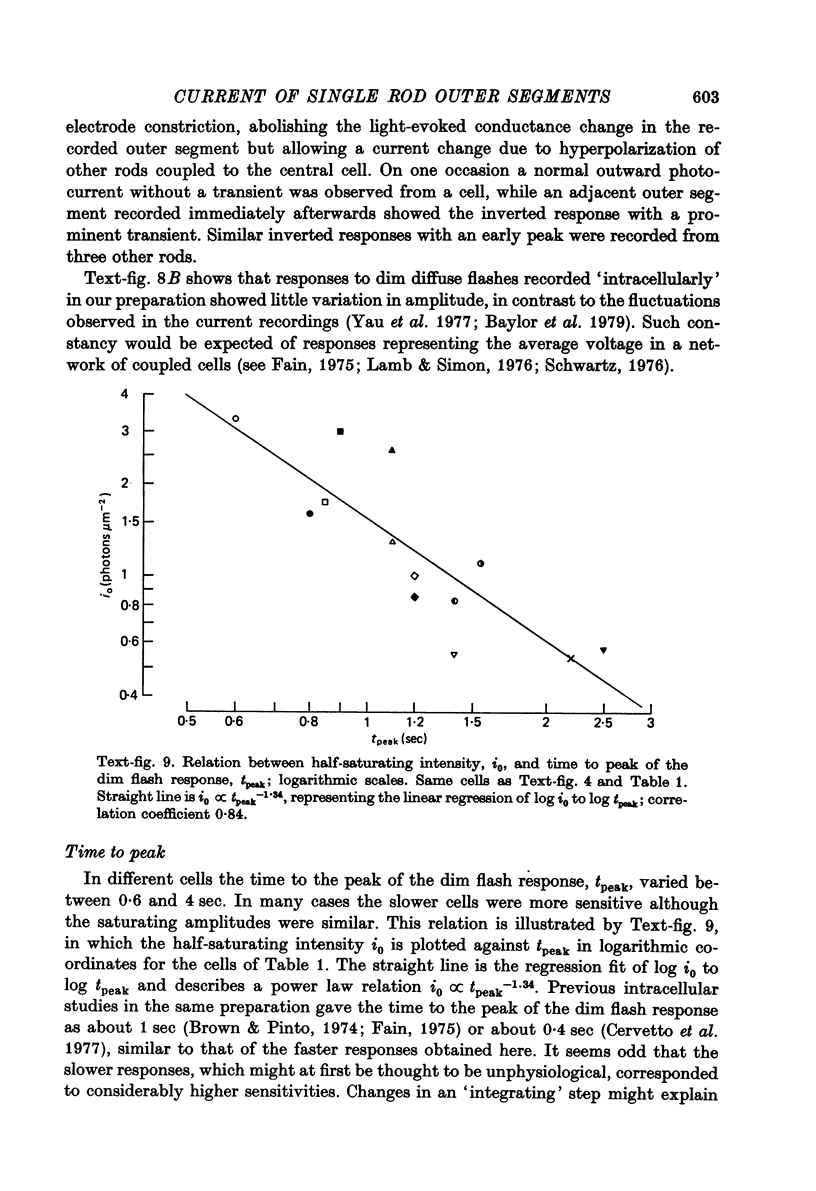
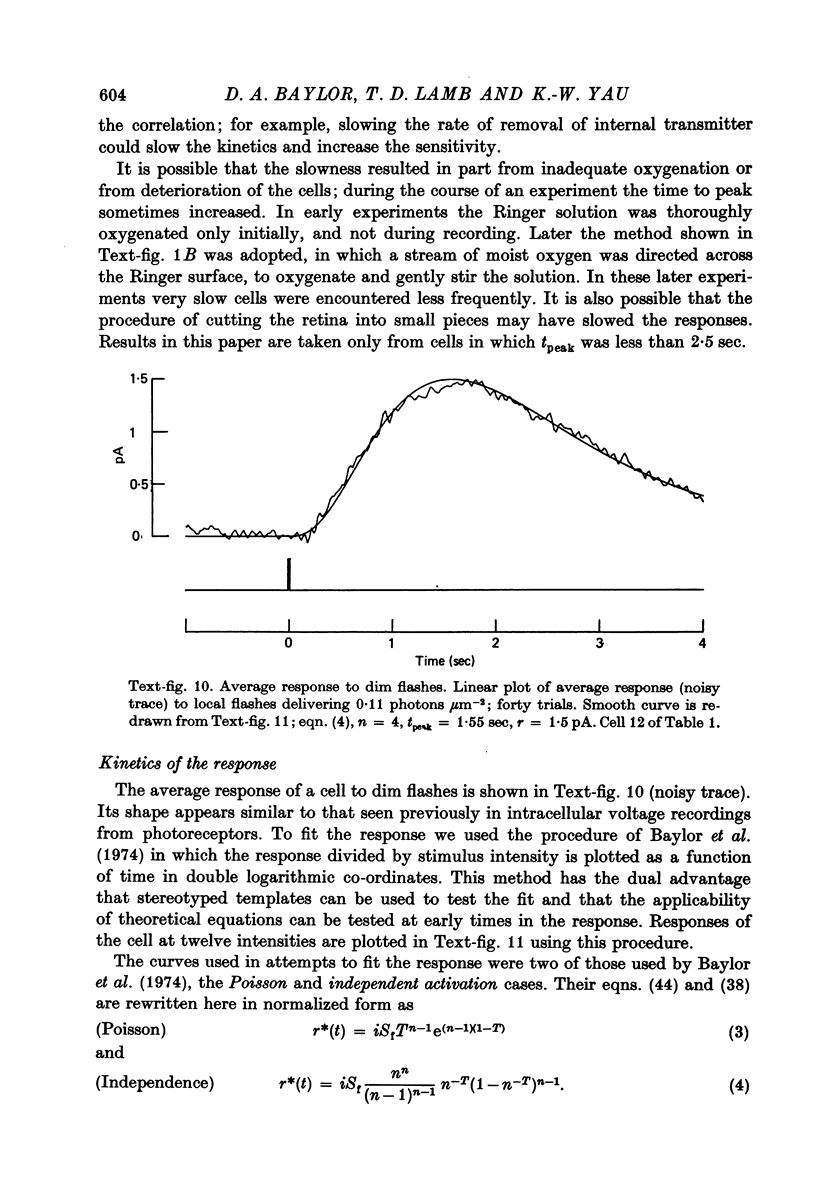
Abstract
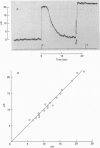
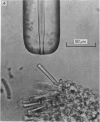
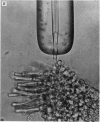
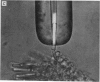
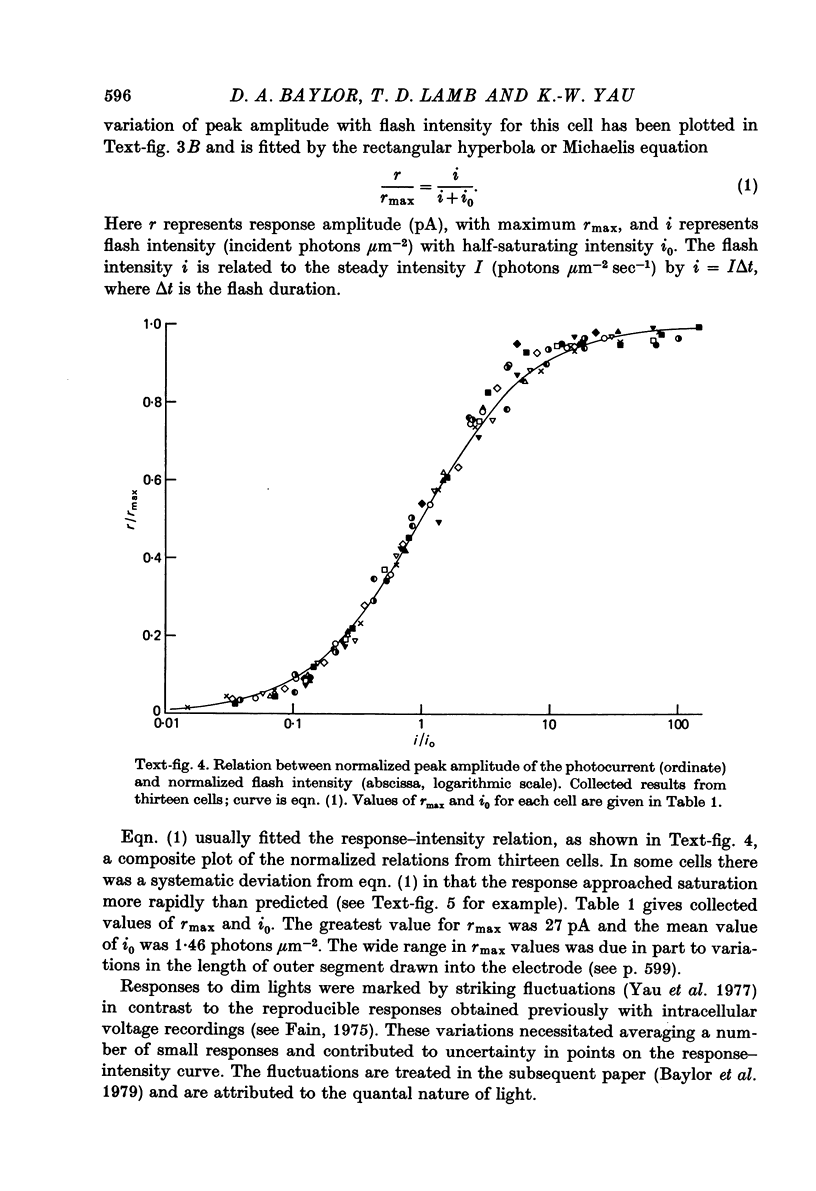
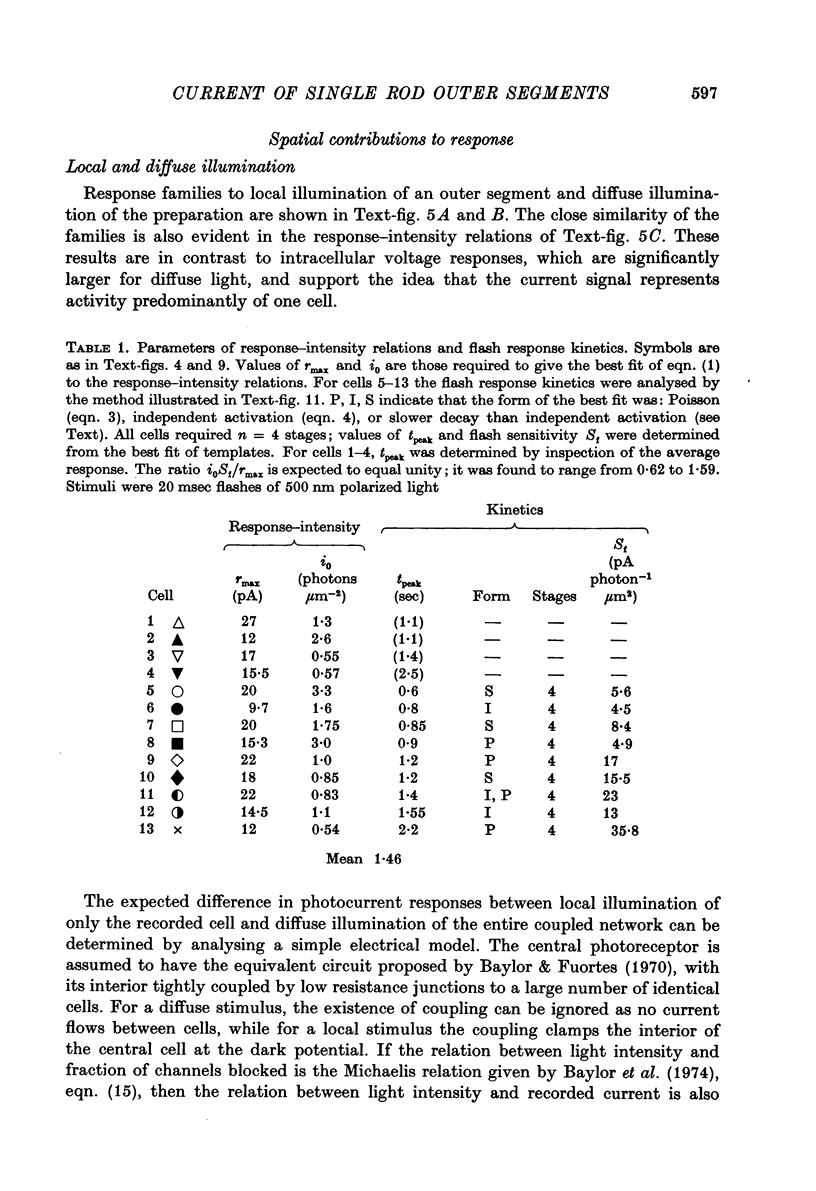
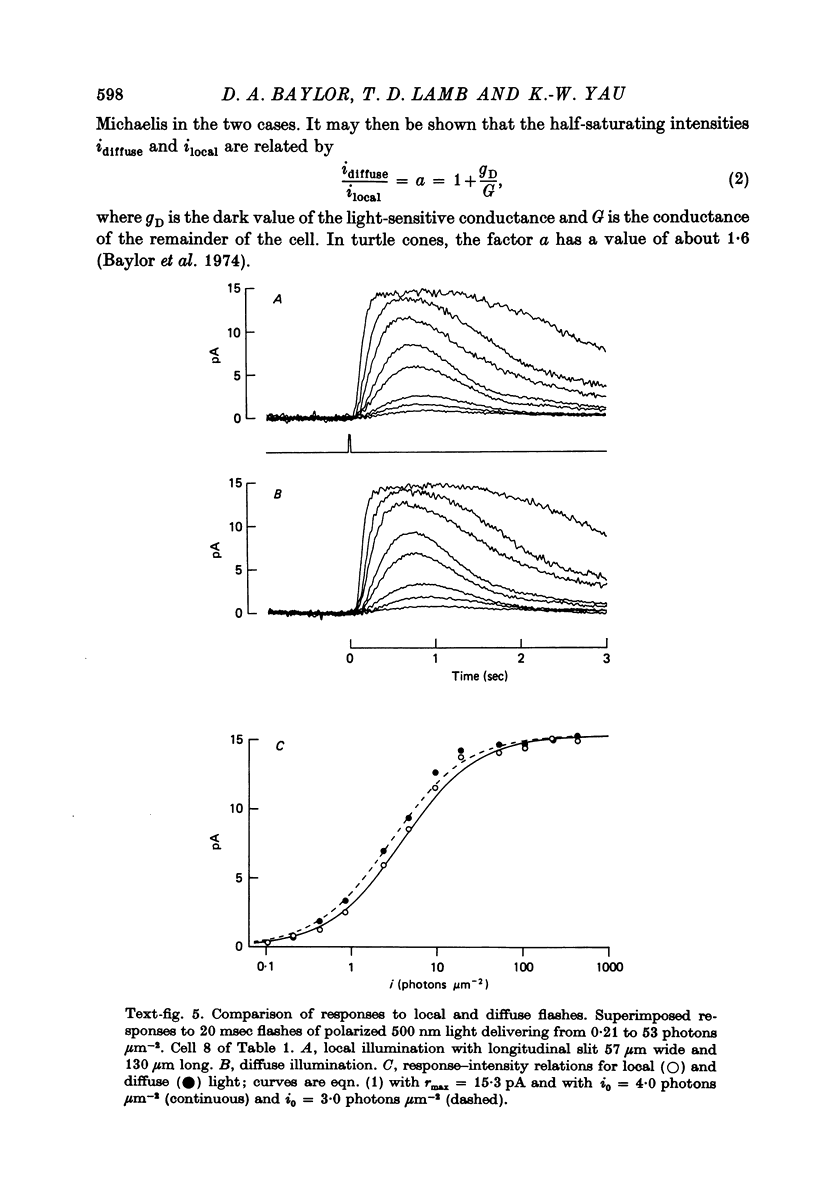
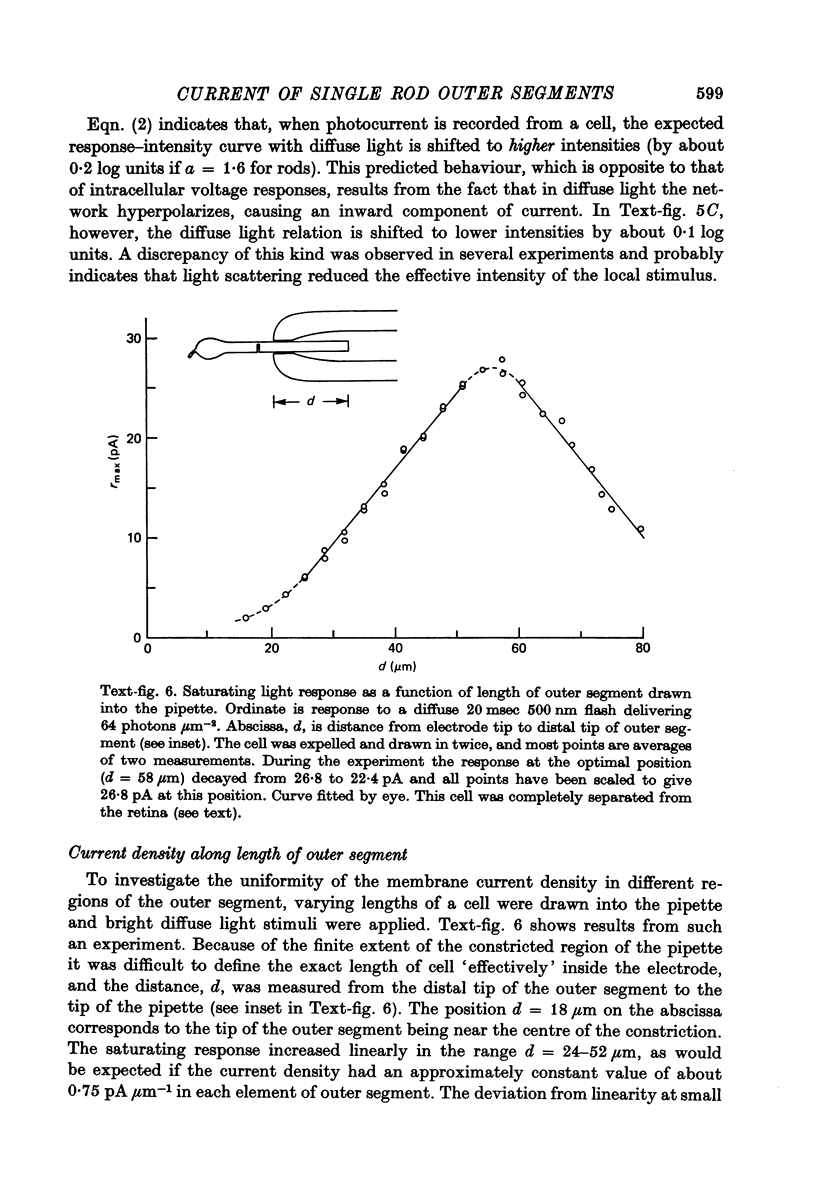
1. Outer segments of individual rods in the retina of the toad, Bufo marinus, were drawn into a glass pipette to record the membrane current. 2. Light flashes evoked transient outward currents. The peak response amplitude was related to flash intensity by a Michaelis equation with half-saturating intensity about 1 photon mum-2. 3. The saturating response amplitude ranged up to 27 pA and corresponded closely to complete suppression of the steady inward current present in darkness. 4. For a given cell the saturating response amplitude varied linearly with the length of outer segment within the pipette. This is consistent with a uniform density of light-sensitive channels and negligible gradient of membrane potential along the outer segment. 5. Responses to bright flashes never showed the relaxation from an initial peak seen previously in intracellular voltage recordings, suggesting that the conductance change responsible for the relaxation does not occur in the outer segment. 6. Responses to local illumination of only the recorded outer segment were very similar to those obtained with diffuse light at the same intensity, indicating that peripheral rods made little contribution to the responses. 7. The spectral sensitivity of 'red' rods was consistent with a retinal1-based pigment with lambda max = 498 +/- 2 nm. 8. The kinetics of the response were consistent with four stages of delay affecting action of the internal transmitter. Responses were faster at the basal end of the outer segment than at the distal tip. 9. Background light reduced the sensitivity to a superposed dim test flash and shortened the time course of the response, indicating that adapting light modifies the kinetics and gain of the transduction mechanism within the outer segment. 10. Responses to dim lights exhibited pronounced fluctuations which are attributed in the succeeding paper (Baylor, Lamb & Yau, 1979) to the quantal nature of light.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Fuortes M. G. Electrical responses of single cones in the retina of the turtle. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;207(1):77–92. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Fuortes M. G. Electrical responses of single cones in the retina of the turtle. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;207(1):77–92. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Fuortes M. G., O'Bryan P. M. Receptive fields of cones in the retina of the turtle. J Physiol. 1971 Apr;214(2):265–294. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Hodgkin A. L. Changes in time scale and sensitivity in turtle photoreceptors. J Physiol. 1974 Nov;242(3):729–758. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Hodgkin A. L. Detection and resolution of visual stimuli by turtle photoreceptors. J Physiol. 1973 Oct;234(1):163–198. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Hodgkin A. L. Detection and resolution of visual stimuli by turtle photoreceptors. J Physiol. 1973 Oct;234(1):163–198. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Hodgkin A. L., Lamb T. D. The electrical response of turtle cones to flashes and steps of light. J Physiol. 1974 Nov;242(3):685–727. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Hodgkin A. L., Lamb T. D. The electrical response of turtle cones to flashes and steps of light. J Physiol. 1974 Nov;242(3):685–727. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Lamb T. D., Yau K. W. Responses of retinal rods to single photons. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:613–634. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Pinto L. H. Ionic mechanism for the photoreceptor potential of the retina of Bufo marinus. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;236(3):575–591. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONE R. A. THE RAT ELECTRORETINOGRAM. II. BLOCH'S LAW AND THE LATENCY MECHANISM OF THE B-WAVE. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Jul;47:1107–1116. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.6.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervetto L., Pasino E., Torre V. Electrical responses of rods in the retina of Bufo marinus. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(1):17–51. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copenhagen D. R., Owen W. G. Coupling between rod photoreceptors in a vertebrate retina. Nature. 1976 Mar 4;260(5546):57–59. doi: 10.1038/260057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dartnall H. J. The photosensitivities of visual pigments in the presence of hydroxylamine. Vision Res. 1968 Apr;8(4):339–358. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(68)90104-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detwiler P. B., Hodgkin A. L., McNaughton P. A. A surprising property of electrical spread in the network of rods in the turtle's retina. Nature. 1978 Aug 10;274(5671):562–565. doi: 10.1038/274562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUORTES M. G., YEANDLE S. PROBABILITY OF OCCURRENCE OF DISCRETE POTENTIAL WAVES IN THE EYE OF LIMULUS. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Jan;47:443–463. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.3.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain G. L., Gold G. H., Dowling J. E. Receptor coupling in the toad retina. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:547–561. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain G. L., Gold G. H., Dowling J. E. Receptor coupling in the toad retina. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:547–561. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain G. L., Quandt F. N., Bastian B. L., Gerschenfeld H. M. Contribution of a caesium-sensitive conductance increase to the rod photoresponse. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):466–469. doi: 10.1038/272467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain G. L. Quantum sensitivity of rods in the toad retina. Science. 1975 Mar 7;187(4179):838–841. doi: 10.1126/science.1114328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain G. L. Quantum sensitivity of rods in the toad retina. Science. 1975 Mar 7;187(4179):838–841. doi: 10.1126/science.1114328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagins W. A., Penn R. D., Yoshikami S. Dark current and photocurrent in retinal rods. Biophys J. 1970 May;10(5):380–412. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86308-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagins W. A., Penn R. D., Yoshikami S. Dark current and photocurrent in retinal rods. Biophys J. 1970 May;10(5):380–412. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86308-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hárosi F. I. Absorption spectra and linear dichroism of some amphibian photoreceptors. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Sep;66(3):357–382. doi: 10.1085/jgp.66.3.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The statistical nature of the acetycholine potential and its molecular components. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):665–699. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. H. Theory of flicker and transient responses. I. Uniform fields. J Opt Soc Am. 1971 Apr;61(4):537–546. doi: 10.1364/josa.61.000537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb T. D., Simon E. J. Analysis of electrical noise in turtle cones. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(2):435–468. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb T. D., Simon E. J. Analysis of electrical noise in turtle cones. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(2):435–468. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb T. D., Simon E. J. The relation between intercellular coupling and electrical noise in turtle photoreceptors. J Physiol. 1976 Dec;263(2):257–286. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naka K. I., Rushton W. A. S-potentials from colour units in the retina of fish (Cyprinidae). J Physiol. 1966 Aug;185(3):536–555. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B. Single-channel currents recorded from membrane of denervated frog muscle fibres. Nature. 1976 Apr 29;260(5554):799–802. doi: 10.1038/260799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn R. D., Hagins W. A. Kinetics of the photocurrent of retinal rods. Biophys J. 1972 Aug;12(8):1073–1094. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(72)86145-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E. A. Electrical properties of the rod syncytium in the retina of the turtle. J Physiol. 1976 May;257(2):379–406. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E. A. Electrical properties of the rod syncytium in the retina of the turtle. J Physiol. 1976 May;257(2):379–406. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E. A. Responses of single rods in the retina of the turtle. J Physiol. 1973 Aug;232(3):503–514. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E. A. Rod-rod interaction in the retina of the turtle. J Physiol. 1975 Apr;246(3):617–638. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E. A. Voltage noise observed in rods of the turtle retina. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(2):217–246. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon E. J., Lamb T. D., Hodgkin A. L. Spontaneous voltage fluctuations in retinal cones and bipolar cells. Nature. 1975 Aug 21;256(5519):661–662. doi: 10.1038/256661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita T. Electrical activity of vertebrate photoreceptors. Q Rev Biophys. 1970 May;3(2):179–222. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500004571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W., Lamb T. D., Baylor D. A. Light-induced fluctuations in membrane current of single toad rod outer segments. Nature. 1977 Sep 1;269(5623):78–80. doi: 10.1038/269078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W., Lamb T. D., Baylor D. A. Light-induced fluctuations in membrane current of single toad rod outer segments. Nature. 1977 Sep 1;269(5623):78–80. doi: 10.1038/269078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. W., Droz B. The renewal of protein in retinal rods and cones. J Cell Biol. 1968 Oct;39(1):169–184. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]