Abstract
1. The dark-adaptation of the aspartate-isolated rod receptor potential of the isolated and perfused frog retina has been measured after bleaching about 5-10% of the rhodopsin. The fraction bleached (ΔR) and the decay of rhodopsin photoproducts were determined using alternating measurements with a photometric technique (Donner & Hemilä, 1975).
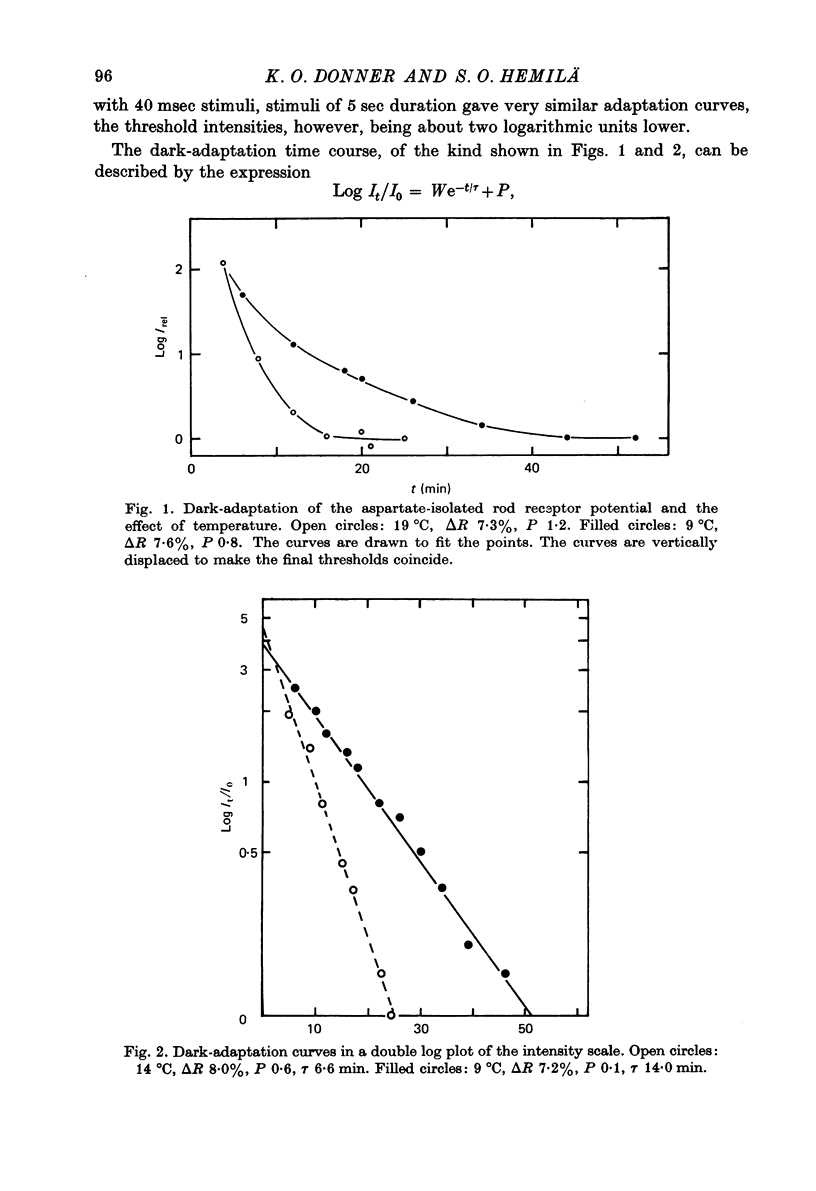
2. The dark-adaptation time course of the log threshold elevation is exponential, log It/I0 = W exp (-t/τ)+P, where W is the extrapolated value for log It/I0-P at t = 0 and P is log It/I0 for t = ∞. When ΔR increases from 2 to 10% W increases from ca. 2·6 to ca. 5. The time constant τ is about 13 min at 9 °C and 7 min at 14 °C (ΔR = 5-10%).
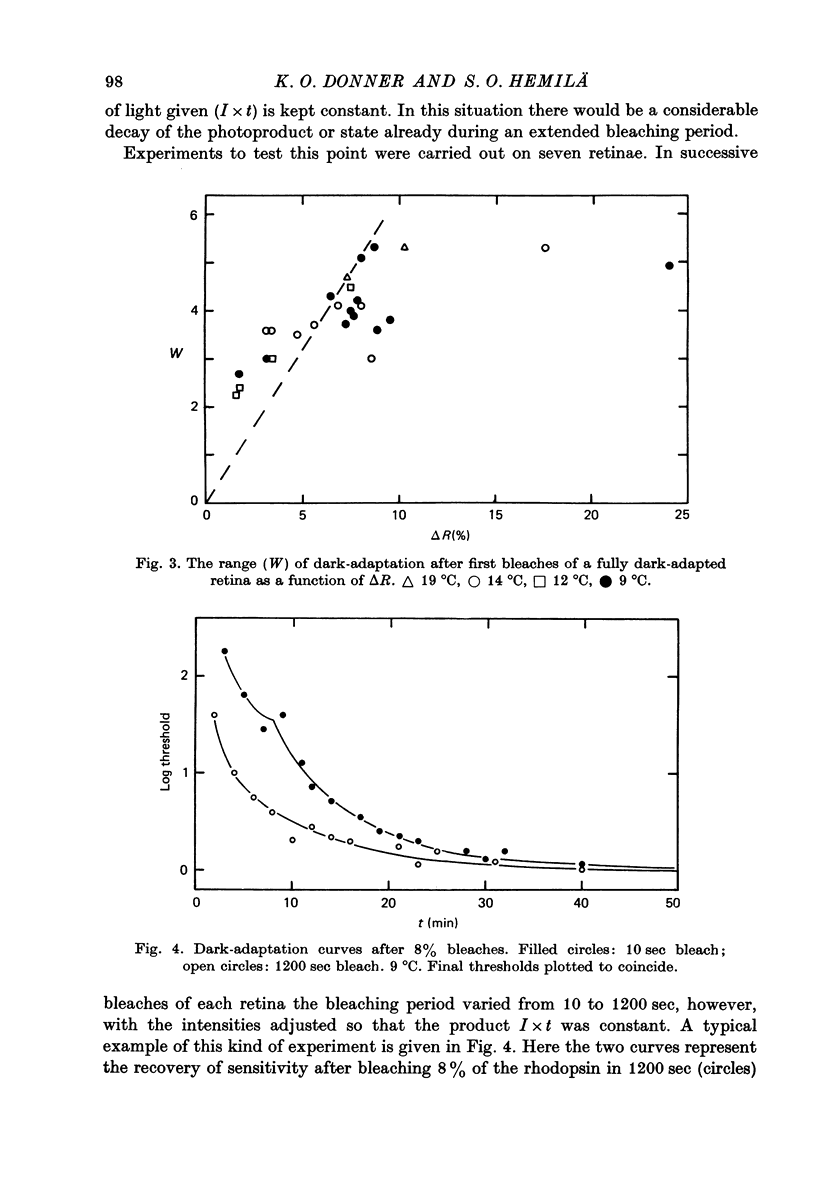
3. When the bleaching period is extended, keeping the amount bleached (I×t) constant, dark-adaptation is completed earlier.
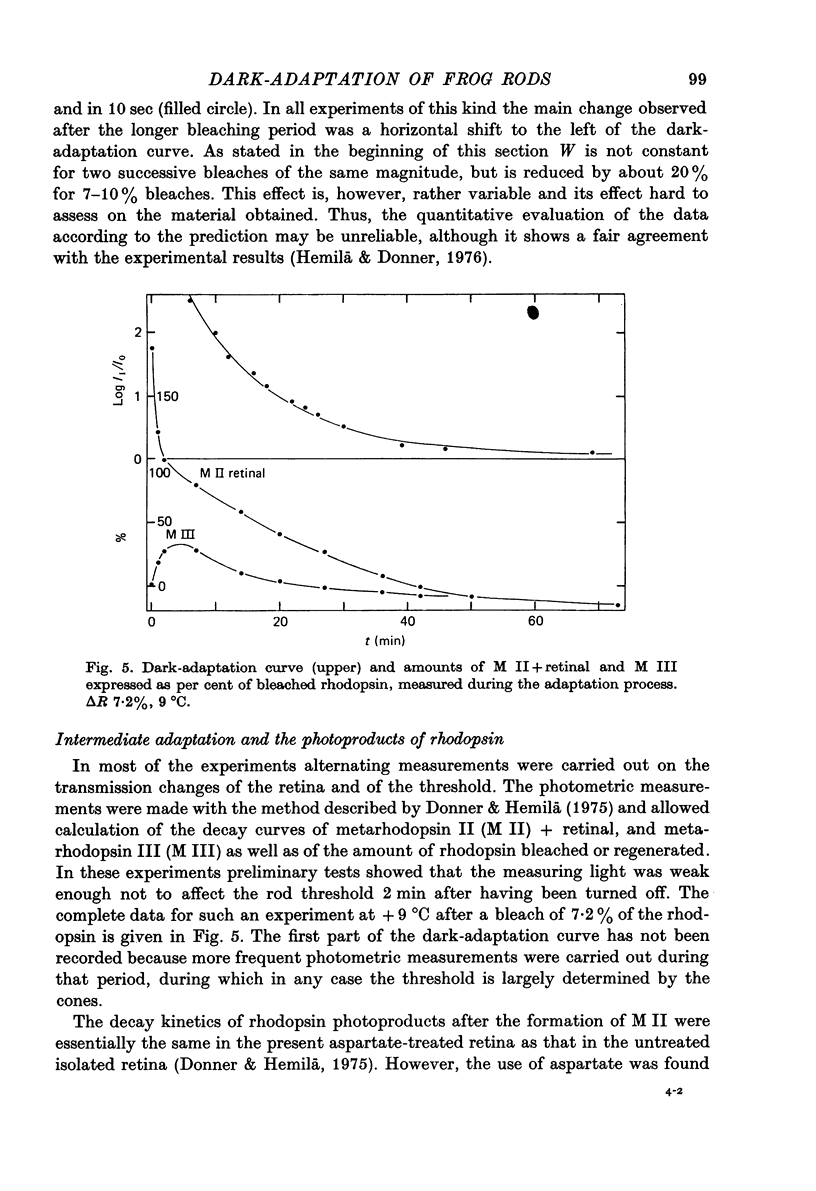
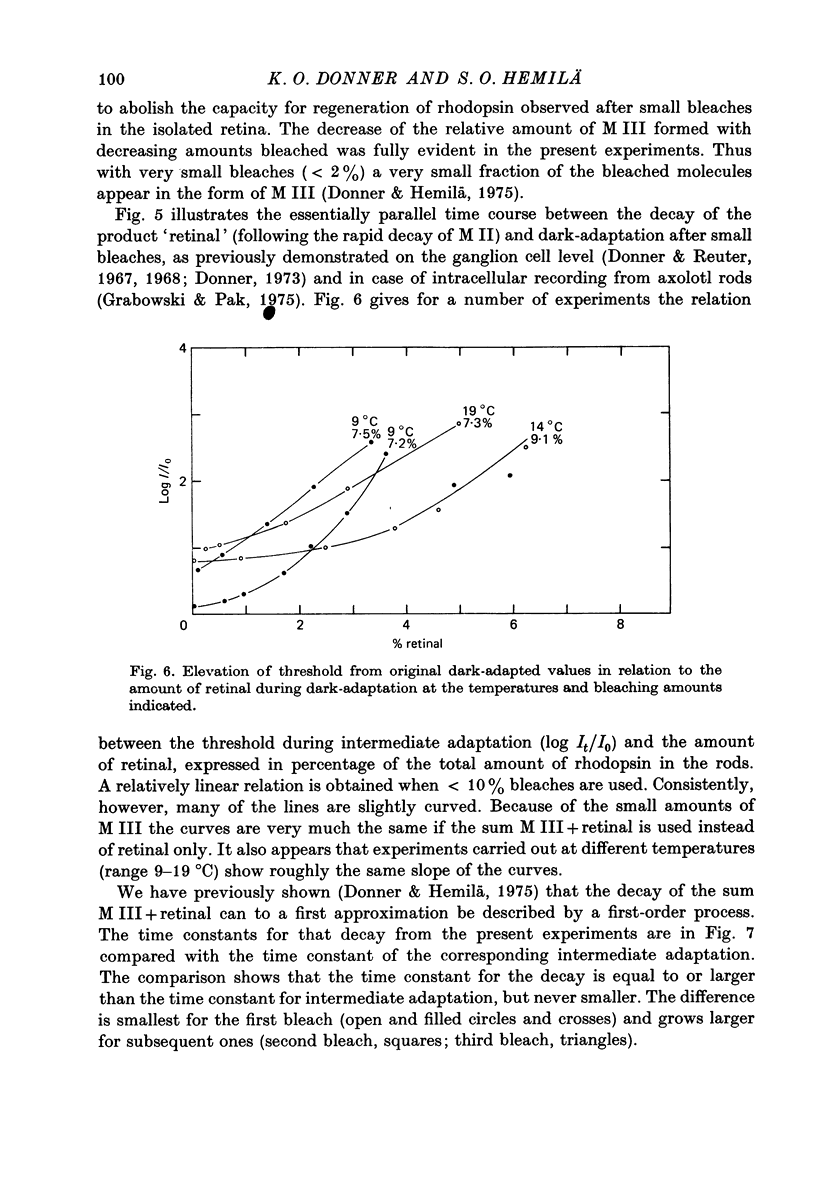
4. The time course of dark-adaptation and the decay of the photoproduct `retinal' are similar, as is also their dependence on temperature (Q10 ≈ 3).
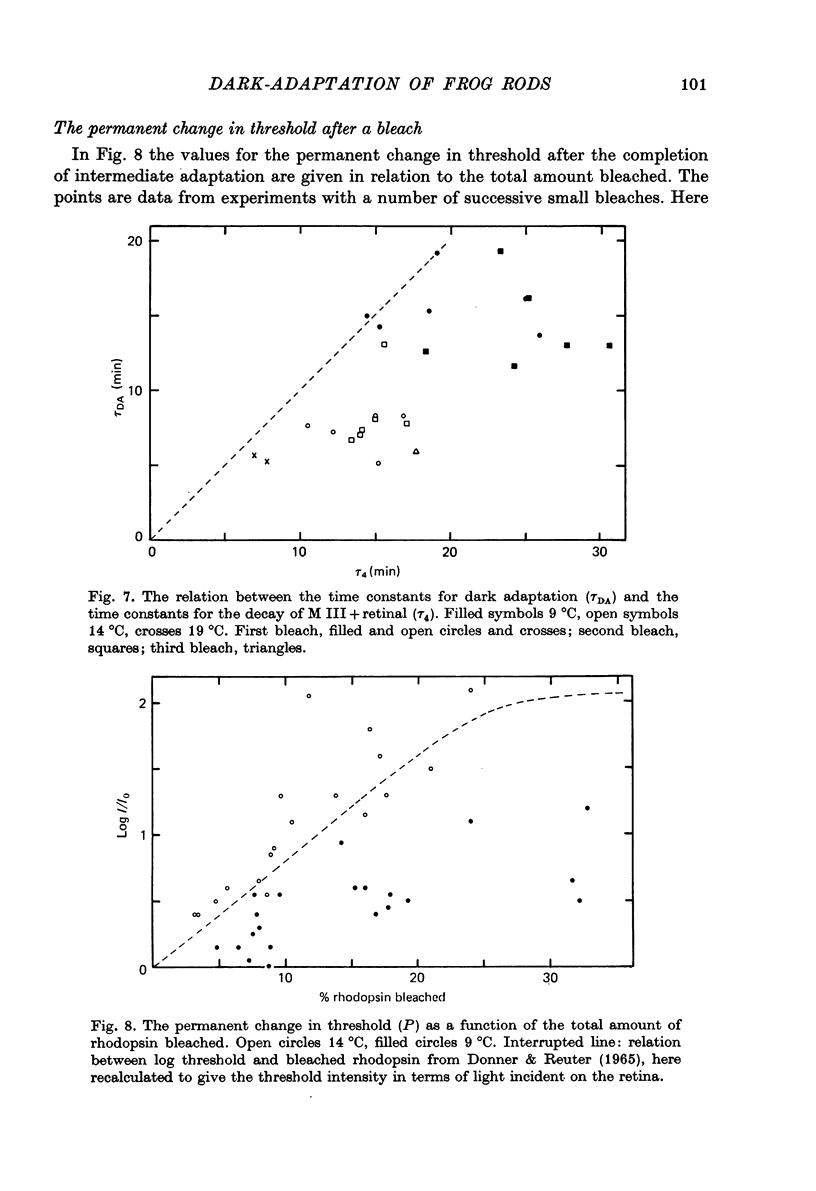
5. The permanent log threshold rise P is approximately proportional to ΔR after small bleaches; when more than about 10% is bleached the slope of the curve P(ΔR) decreases. P is considerably larger (about 2·5-fold) for the same fraction bleached in experiments at 14 °C as compared to experiments at 9 °C.
6. A comparison with previously obtained corresponding values for dark-adaptation after small bleaches at the ganglion cell level shows a close agreement between the time constants for the dark-adaptation curve, its range and the dependence of threshold on the fraction of rhodopsin bleached.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azuma K., Azuma M., Sickel W. Regeneration of rhodopsin in frog rod outer segments. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;271(3):747–759. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brin K. P., Ripps H. Rhodopsin photoproducts and rod sensitivity in the skate retina. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Jan;69(1):97–120. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONNER K. O. The effect of a coloured adapting field on the spectral sensitivity of frog retinal elements. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:318–326. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWLING J. E. NEURAL AND PHOTOCHEMICAL MECHANISMS OF VISUAL ADAPTATION IN THE RAT. J Gen Physiol. 1963 Jul;46:1287–1301. doi: 10.1085/jgp.46.6.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner K. O., Hemilä S., Hongell K., Reuter T. Long-lived photoproducts of porphyropsin in the retina of the crucian carp (Carassius carassius). Vision Res. 1974 Dec;14(12):1359–1370. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(74)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner K. O., Hemilä S. Kinetics of long-lived rhodopsin photoproducts in the frog retina as a function of the amount bleached. Vision Res. 1975 Aug-Sep;15:985–995. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(75)90241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner K. O., Reuter T. Dark-adaptation processes in the rhodopsin rods of the frog's retina. Vision Res. 1967 Jan;7(1):17–41. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(67)90023-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner K. O., Reuter T. The dark-adaptation of single units in the frog's retina and its relation to the regeneration of rhodopsin. Vision Res. 1965 Dec;5(11):615–632. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(65)90035-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner K. O., Reuter T. The photoproducts of rhodopsin in the isolated retina of the frog. Vision Res. 1969 Jul;9(7):815–847. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(69)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner K. O., Reuter T. Visual adaptation of the rhodopsin rods in the frogs retina. J Physiol. 1968 Nov;199(1):59–87. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling J. E., Ripps H. Adaptation in skate photoreceptors. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Dec;60(6):698–719. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.6.698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst W., Kemp C. M. The effects of rhodopsin decomposition on P3 responses of isolated rat retinae. Vision Res. 1972 Dec;12(12):1937–1946. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(72)90050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank R. N. Properties of "neural" adaptation in components of the frog electroretinogram. Vision Res. 1971 Oct;11(10):1113–1123. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(71)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski S. R., Pak W. L. Intracellular recordings of rod responses during dark-adaptation. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(2):363–391. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski S. R., Pinto L. H., Pak W. L. Adaptation in retinal rods of axolotl: intracellular recordings. Science. 1972 Jun 16;176(4040):1240–1243. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4040.1240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllenberg G., Reuter T., Sippel H. Long-lived photoproducts of rhodopsin in the retina of the frog. Vision Res. 1974 Dec;14(12):1349–1357. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(74)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemilä S. Background adaptation in the rods of the frog's retina. J Physiol. 1977 Mar;265(3):721–741. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood D. C., Hock P. A., Grover B. G. Dark adaptation of the frog's rods. Vision Res. 1973 Oct;13(10):1953–1963. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(73)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood D. C., Mansfield A. F. The isolated receptor potential of the frog isolated retina: action spectra before and after extensive bleaching. Vision Res. 1972 Dec;12(12):2109–2119. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(72)90060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood D., Hock P. A. Light adaptation of the receptors: increment threshold functions for the frog's rods and cones. Vision Res. 1975 May;15(5):545–553. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(75)90301-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt J., Dowling J. E. Intracellular recordings from gecko photoreceptors during light and dark adaptation. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Nov;66(5):617–648. doi: 10.1085/jgp.66.5.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSHTON W. A. Rhodopsin measurement and dark-adaptation in a subject deficient in cone vision. J Physiol. 1961 Apr;156:193–205. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter T. Photoregeneration of rhodopsin and isorhodopsin from metarhodopsin III in the frog retina. Vision Res. 1976;16(9):909–917. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(76)90220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushton W. A., Powell D. S. The early phase of dark adaptation. Vision Res. 1972 Jun;12(6):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(72)90099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillman A. J., Owen W. G., Fernandez H. R. Rapid dark adaptation in the frog rod. Vision Res. 1973 Feb;13(2):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(73)90116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkovsky P., Gallin E., Hollyfield J. G., Ripps H., Bridges C. D. Photoreceptor thresholds and visual pigment levels in normal and vitamin A-deprived Xenopus tadpoles. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Nov;39(6):1272–1287. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.6.1272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkovsky P., Nelson J., Ripps H. Action spectra and adaptation properties of carp photoreceptors. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Apr;61(4):401–423. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.4.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


