Abstract
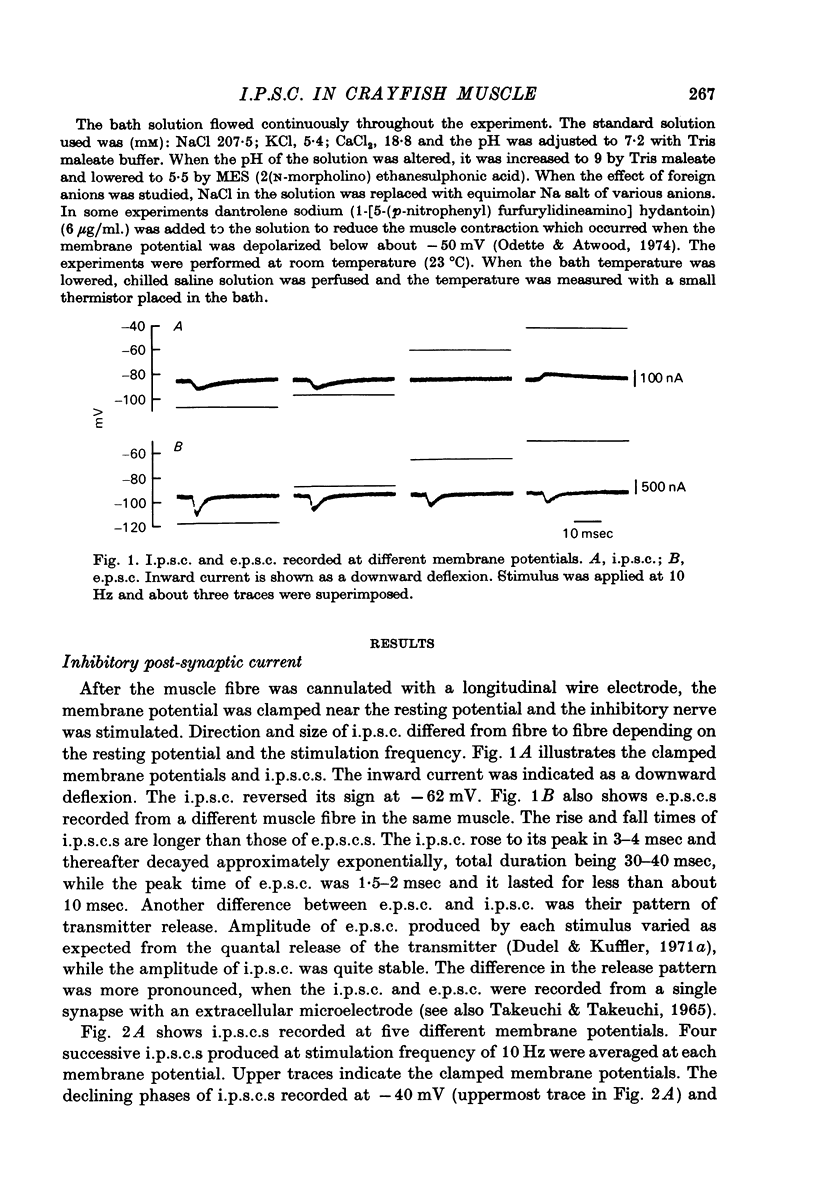
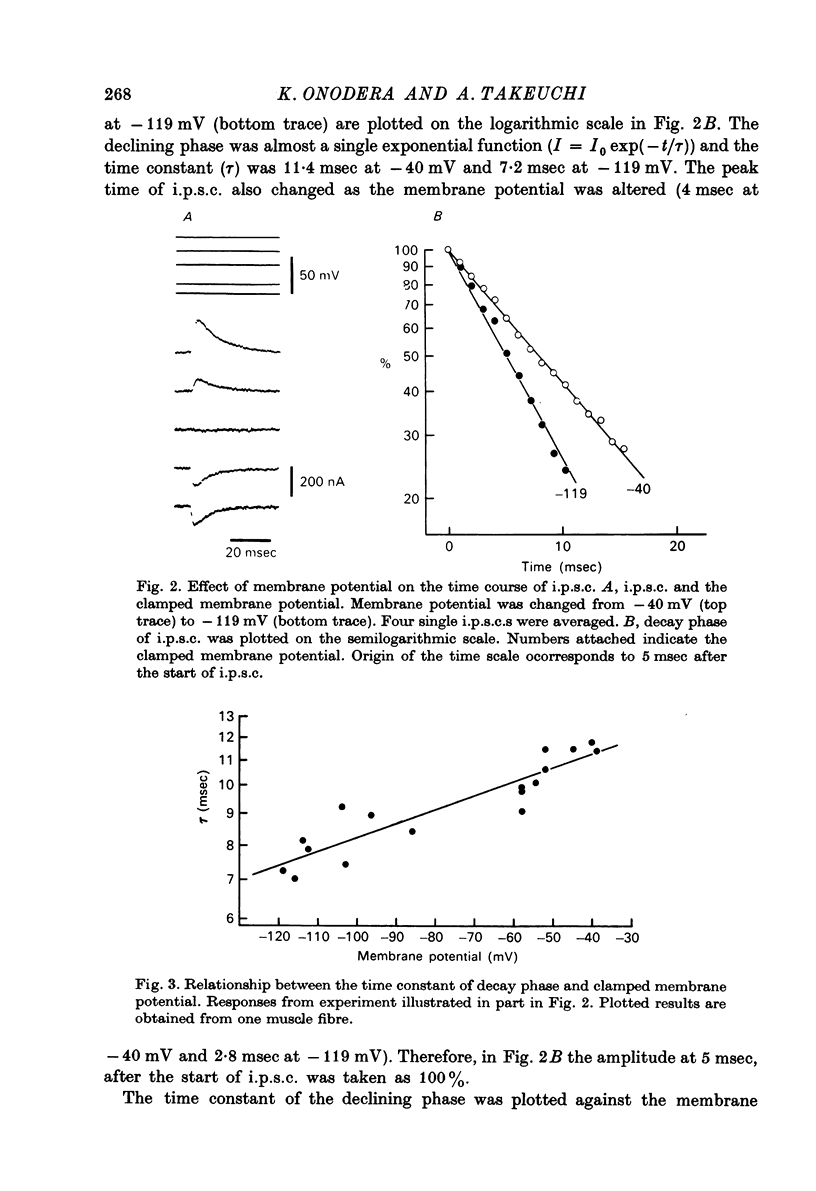
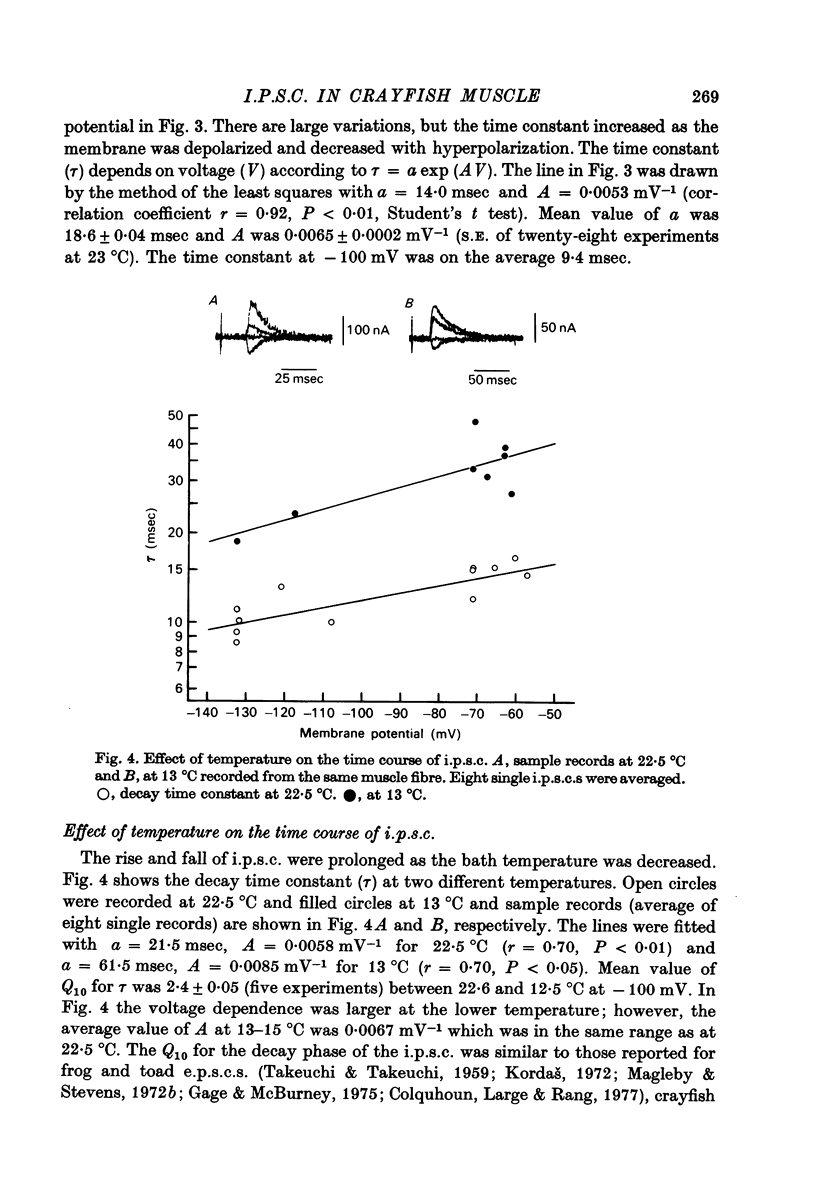
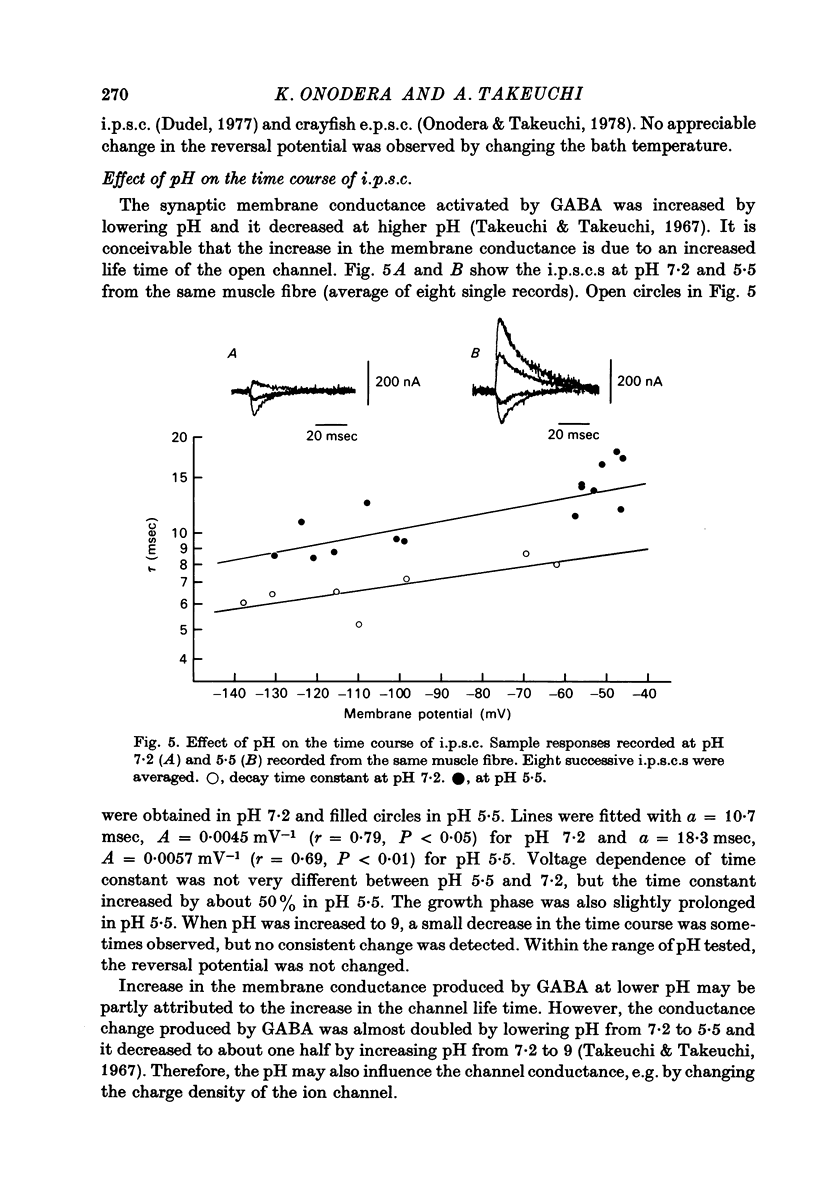
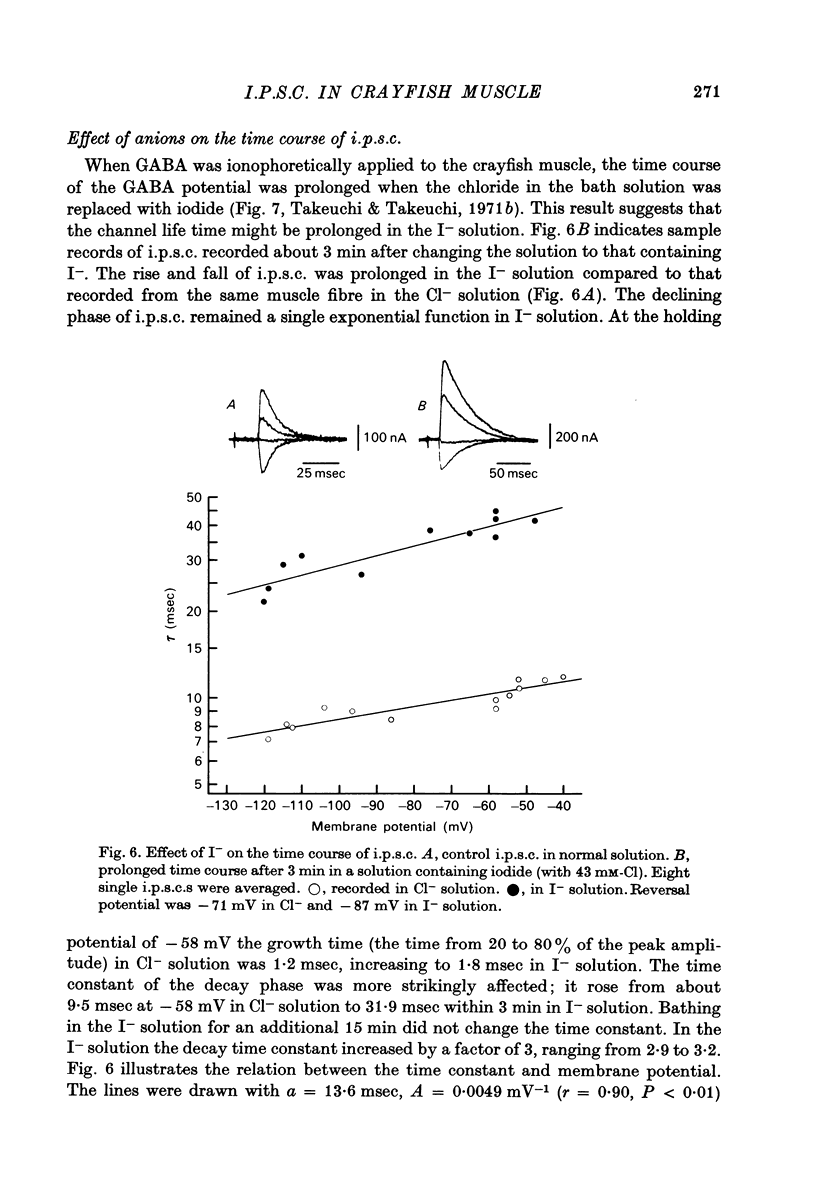
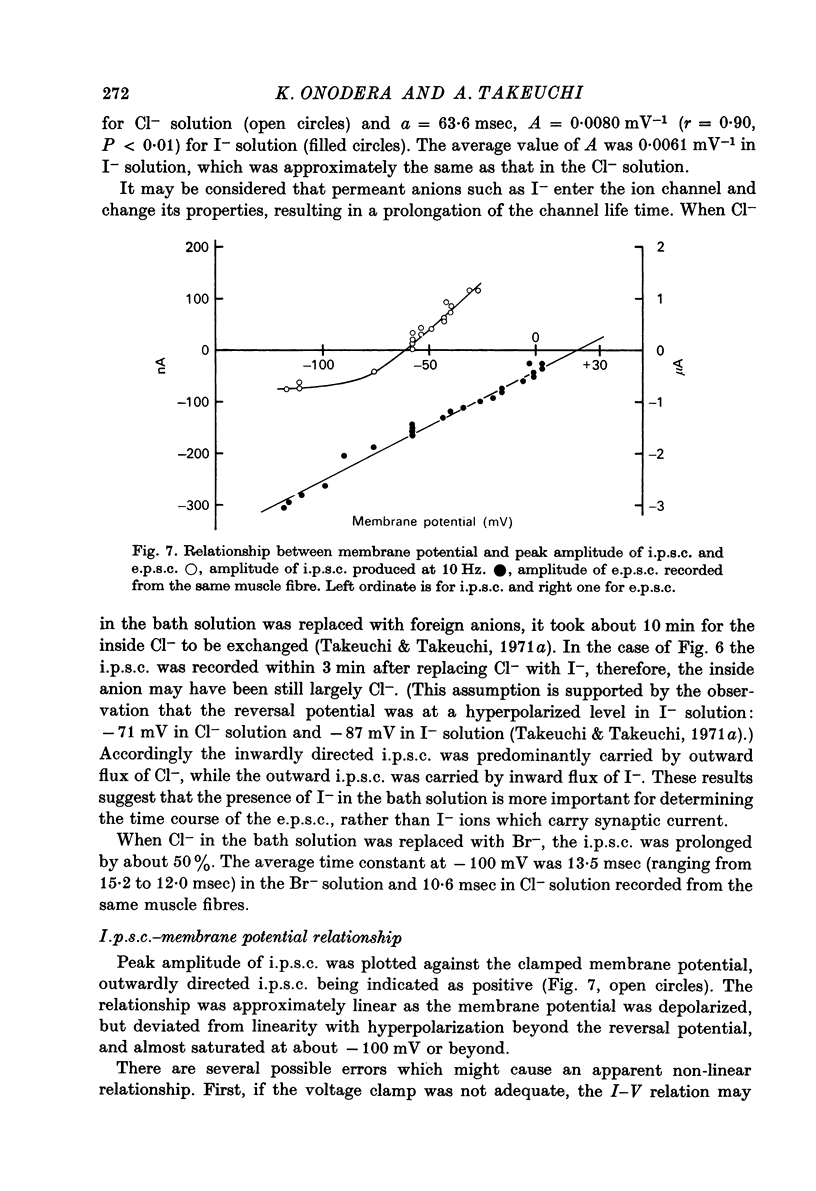
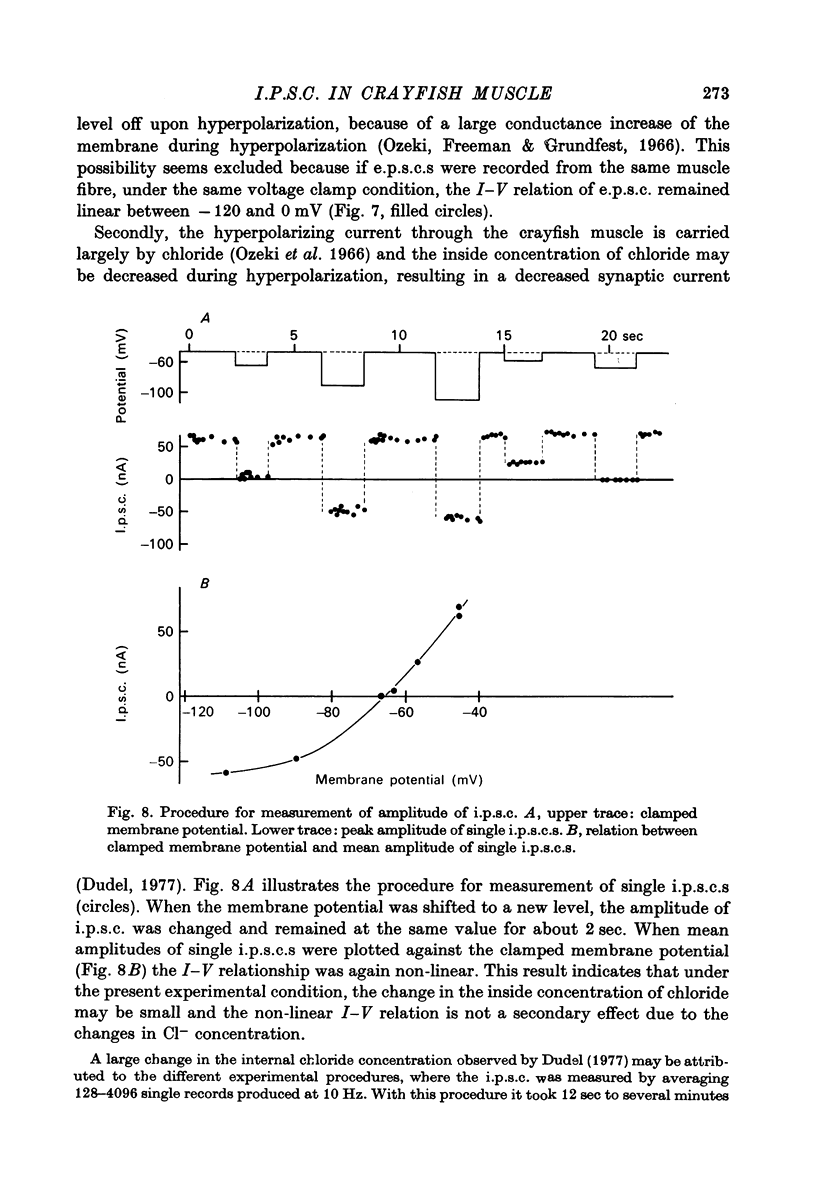
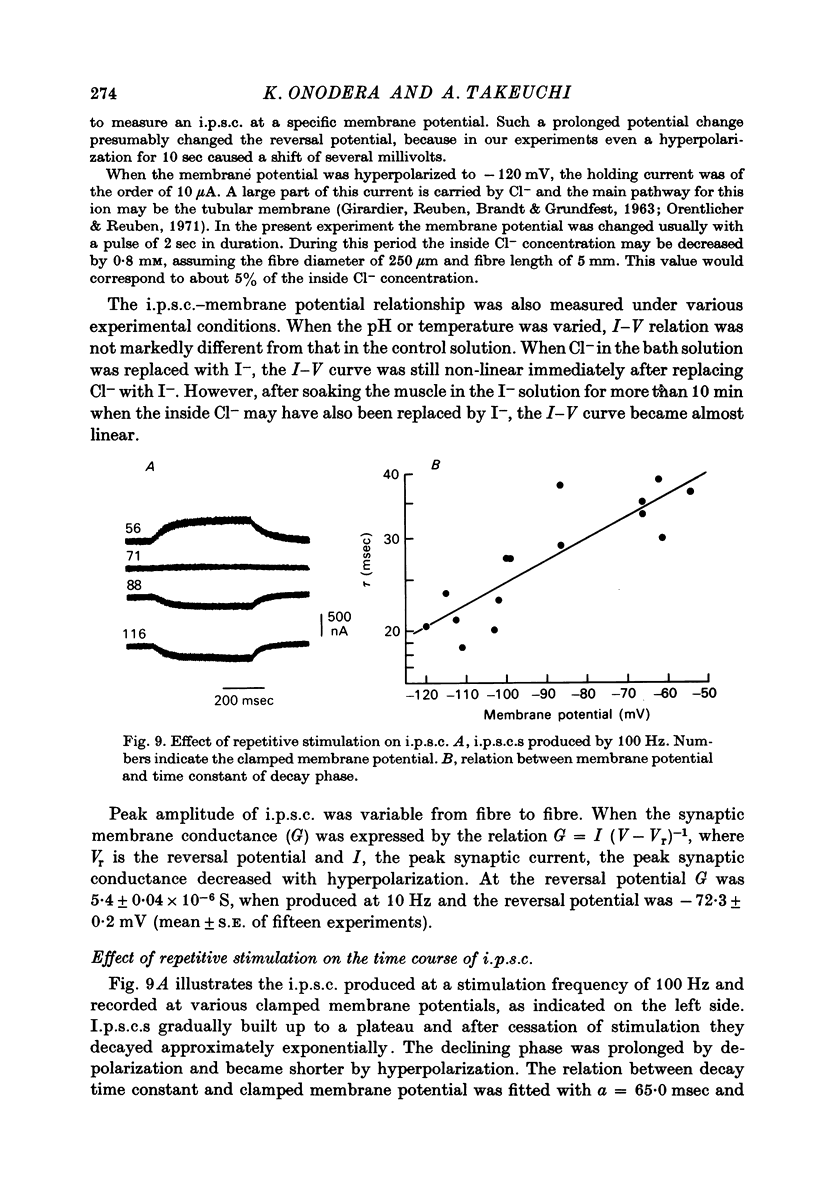
1. Inhibitory post-synaptic currents (i.p.c.s) were recorded from the feed-back current through a wire electrode inserted longitudinally into the opener muscle fibre of the claw in the crayfish (Cambarus clarkii). 2. I.p.s.c. rose to its peak in about 3-4 msec and decayed approximately exponentially. The decay time constant at -100 mV was 9.4 msec. 3. The decay time constant decreased as the membrane was hyperpolarized and increased during depolarization. The time constant (tau) depends on voltage (V) according to the relation tau = a exp (AV), with a = 18.6 msec and A = 0.0065 mV-1. Voltage dependence was opposite in direction to that seen at frog end-plates, but in the same direction as that of e.p.s.c. in crayfish muscle. 4. At lower temperatures, the rise and fall times of i.p.s.c.s were prolonged. Q10 for the decay time constant was 2.4 between 22.6 and 12.5 degrees C. 5. When pH was decreased from 7.2 to 5.5, the decay time constant increased by about 50%, with little change in the voltage dependence of the time course. 6. When chloride in the solution was changed to iodide, the decay time constant was increased by a factor of 3, while voltage dependence of the time course was not changed. In bromide solution the decay time constant increased by about 50%. 7. Peak amplitudes of i.p.s.c.s were approximately linear as the membrane was depolarized, but they levelled off as the membrane was hyperpolarized beyond reversal potential. The non-linear I-V relation did not result from inadequate voltage clamping, nor from a change in the inside concentration of chloride. After equilibration with iodide solution the I-V relation was approximately linear. 8. The decay time constant was increased after repetitive nerve stimulation. This prolongation became more pronounced at lower temperatures. 9. The kinetic process of the transmitter action is discussed. It is suggested that the rate limiting process for i.p.s.c. is binding and unbinding of the transmitter to the receptor.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARAKI T., TERZUOLO C. A. Membrane currents in spinal motoneurons associated with the action potential and synaptic activity. J Neurophysiol. 1962 Nov;25:772–789. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.6.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams D. J., Gage P. W., Hamill O. P. Voltage sensitivity of inhibitory postsynaptic current in Aplysia buccal ganglia. Brain Res. 1976 Oct 22;115(3):506–511. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90368-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R. Relaxation experiments using bath-applied suberyldicholine. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(2):271–289. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. R., Cull-Candy S. G., Miledi R. Glutamate and quisqualate noise in voltage-clamped locust muscle fibres. Nature. 1976 May 13;261(5556):151–153. doi: 10.1038/261151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOISTEL J., FATT P. Membrane permeability change during inhibitory transmitter action in crustacean muscle. J Physiol. 1958 Nov 10;144(1):176–191. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. M., Hagiwara S., Koike H., Meech R. M. Membrane properties of a barnacle photoreceptor examined by the voltage clamp technique. J Physiol. 1970 Jun;208(2):385–413. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. Relaxation and fluctuations of membrane currents that flow through drug-operated channels. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Nov 14;199(1135):231–262. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Large W. A., Rang H. P. An analysis of the action of a false transmitter at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1977 Apr;266(2):361–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUDEL J., KUFFLER S. W. Presynaptic inhibition at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1961 Mar;155:543–562. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUDEL J., KUFFLER S. W. The quantal nature of transmission and spontaneous miniature potentials at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1961 Mar;155:514–529. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne V. E., Ruff R. L. Endplate current fluctuations reveal only one channel type at frog neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1977 Mar 17;266(5599):263–265. doi: 10.1038/266263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne V. E., Stevens C. F. Voltage dependence of agonist effectiveness at the frog neuromuscular junction: resolution of a paradox. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):245–270. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J. Nonlinear voltage dependence of excitatory synaptic current in crayfish muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1974;352(3):227–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00590488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J. Voltage dependence of amplitude and time course of inhibitory synaptic current in crayfish muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Oct 19;371(1-2):167–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00580786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. The effect of inhibitory nerve impulses on a crustacean muscle fibre. J Physiol. 1953 Aug;121(2):374–389. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRARDIER L., REUBEN J. P., BRANDT P. W., GRUNDFEST H. EVIDENCE FOR ANION-PERMSELECTIVE MEMBRANE IN CRAYFISH MUSCLE FIBERS AND ITS POSSIBLE ROLE IN EXCITATION-CONTRACTION COUPLING. J Gen Physiol. 1963 Sep;47:189–214. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W. Generation of end-plate potentials. Physiol Rev. 1976 Jan;56(1):177–247. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.1.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., McBurney R. N. Effects of membrane potential, temperature and neostigmine on the conductance change caused by a quantum or acetylcholine at the toad neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(2):385–407. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsborg B. L., Kado R. T. Voltage-current relationship of a carbachol-induced potassium-ion pathway in Aplysia neurones. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;245(3):713–725. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIWARA S., KUSANO K. Synaptic inhibition in giant nerve cell of Onchidium verruculatum. J Neurophysiol. 1961 Mar;24:167–175. doi: 10.1152/jn.1961.24.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Kuffler S. W., Stickgold R., Yoshikami D. Synaptic excitation and inhibition resulting from direct action of acetylcholine on two types of chemoreceptors on individual amphibian parasympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;271(3):817–846. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Kuffler S. W., Yoshikami D. Post-synaptic potentiation: interaction between quanta of acetylcholine at the skeletal neuromuscular synapse. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):427–463. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L., Kravitz E. A. The metabolism of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the lobster nervous system--uptake of GABA in the nerve-muscle preparations. J Neurochem. 1968 Jul;15(7):609–620. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb08960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The binding of acetylcholine to receptors and its removal from the synaptic cleft. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):549–574. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassignal N. L., Martin A. R. Effect of acetylcholine on postjunctional membrane permeability in eel electroplaque. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Jul;70(1):23–36. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassignal N. L., Martin A. R. Reversal of acetylcholine potentials in eel electroplaque. Science. 1976 Feb 6;191(4226):464–466. doi: 10.1126/science.1246628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. A quantitative description of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):173–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. The effect of voltage on the time course of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):151–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B. Voltage-dependence of drug-induced conductance in frog neuromuscular junction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2140–2144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odette L. L., Atwood H. L. Dantrolene sodium: effects on crustacean muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1974 Aug;52(4):887–890. doi: 10.1139/y74-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onodera K., Takeuchi A. Effects of membrane potential and temperature on the excitatory post-synaptic current in the crayfish muscle. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:183–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onodera K., Takeuchi A. Inhibitory postsynaptic current in voltage-clamped crayfish muscle. Nature. 1976 Sep 9;263(5573):153–154. doi: 10.1038/263153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onodera K., Takeuchi A. Ionic mechanism of the excitatory synaptic membrane of the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;252(1):295–318. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozeki M., Freeman A. R., Grundfest H. The membrane components of crustacean neuromuscular systems. II. Analysis of interactions among the electrogenic components. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Jul;49(6):1335–1349. doi: 10.1085/jgp.0491335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan R. E., Lester H. A. Rates and equilibria at the acetylcholine receptor of Electrophorus electroplaques: a study of neurally evoked postsynaptic currents and of voltage-jump relaxations. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Aug;70(2):187–219. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. LOCALIZED ACTION OF GAMMA-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID ON THE CRAYFISH MUSCLE. J Physiol. 1965 Mar;177:225–238. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Takeuchi N. Anion interaction at the inhibitory post-synaptic membrane of the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(2):337–351. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Takeuchi N. Anion permeability of the inhibitory post-synaptic membrane of the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1967 Aug;191(3):575–590. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Takeuchi N. Variations in the permeability properties of the inhibitory post-synaptic membrane of the crayfish neuromuscular junction when activated by different concentrations of GABA. J Physiol. 1971 Sep;217(2):341–358. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautmann A., Zilber-Gachelin N. F. Further investigations on the effect of denervation and pH on the conductance change at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Jun 29;364(1):53–58. doi: 10.1007/BF01062911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Helden D., Hamill O. P., Gage P. W. Permeant cations alter endplate channel characteristics. Nature. 1977 Oct 20;269(5630):711–713. doi: 10.1038/269711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


