Abstract
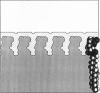
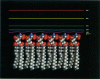
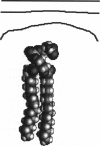
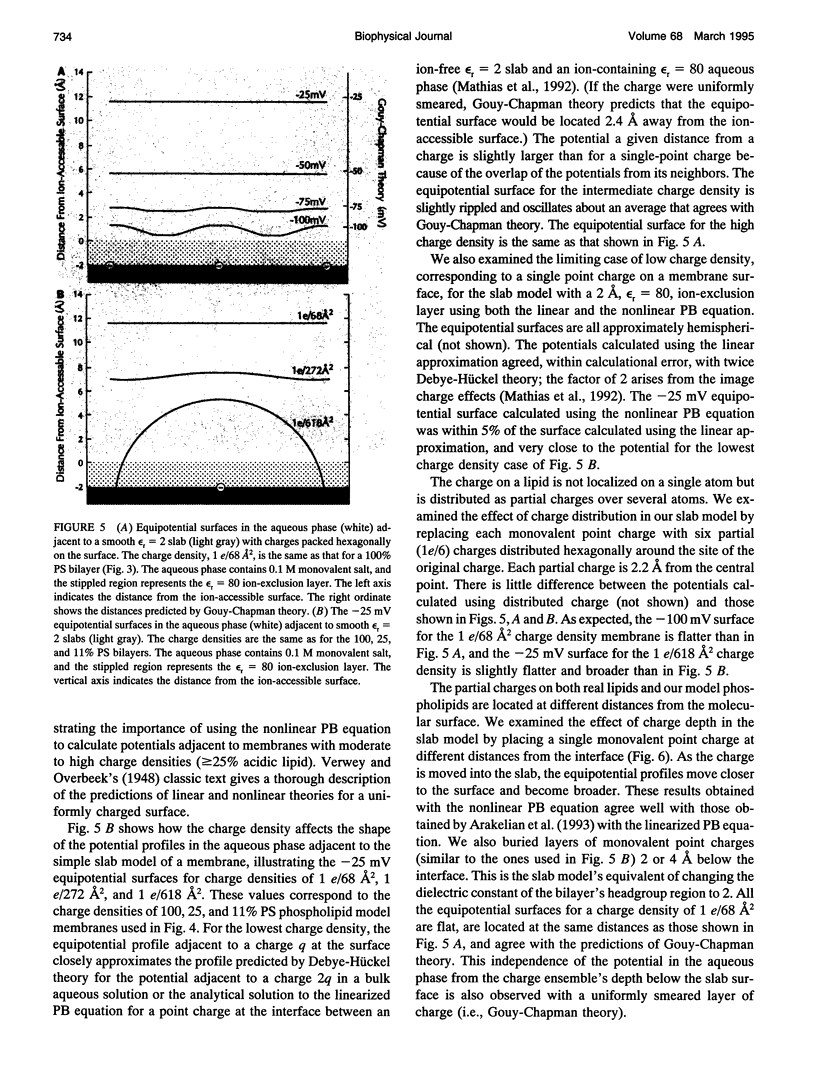
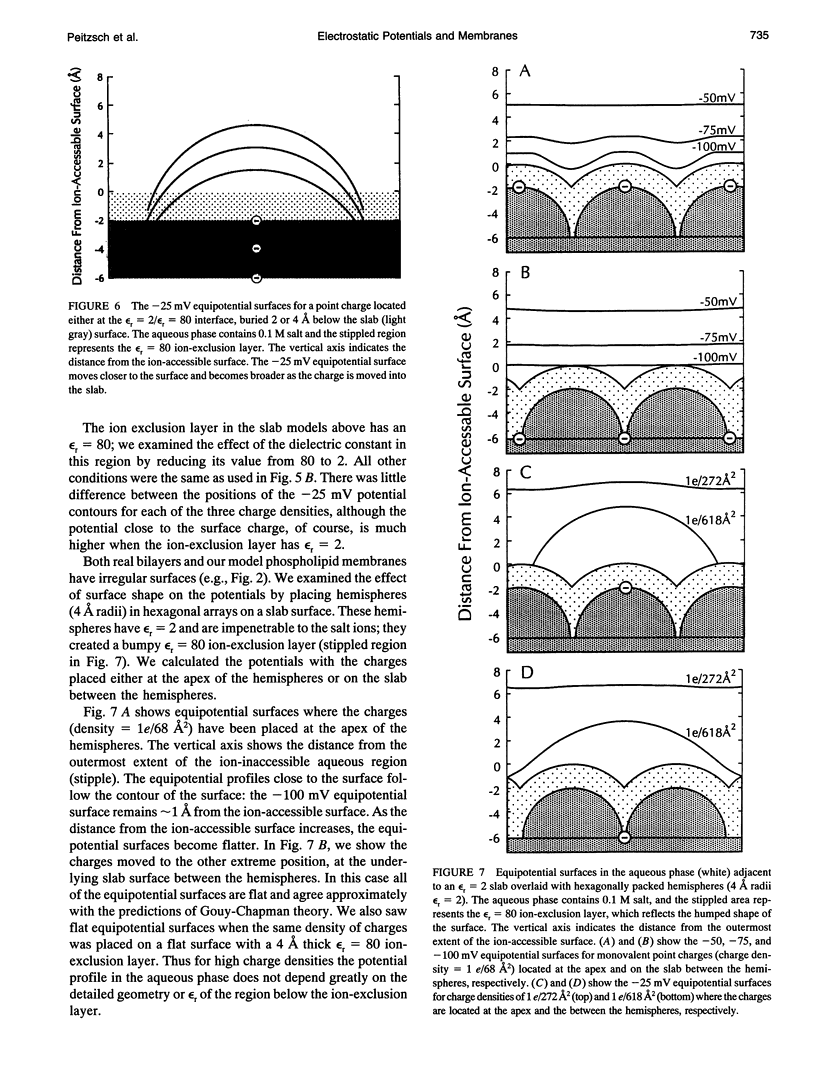
We used the nonlinear Poisson-Boltzmann equation to calculate electrostatic potentials in the aqueous phase adjacent to model phospholipid bilayers containing mixtures of zwitterionic lipids (phosphatidylcholine) and acidic lipids (phosphatidylserine or phosphatidylglycerol). The aqueous phase (relative permittivity, epsilon r = 80) contains 0.1 M monovalent salt. When the bilayers contain < 11% acidic lipid, the -25 mV equipotential surfaces are discrete domes centered over the negatively charged lipids and are approximately twice the value calculated using Debye-Hückel theory. When the bilayers contain > 25% acidic lipid, the -25 mV equipotential profiles are essentially flat and agree well with the values calculated using Gouy-Chapman theory. When the bilayers contain 100% acidic lipid, all of the equipotential surfaces are flat and agree with Gouy-Chapman predictions (including the -100 mV surface, which is located only 1 A from the outermost atoms). Even our model bilayers are not simple systems: the charge on each lipid is distributed over several atoms, these partial charges are non-coplanar, there is a 2 A ion-exclusion region (epsilon r = 80) adjacent to the polar headgroups, and the molecular surface is rough. We investigated the effect of these four factors using smooth (or bumpy) epsilon r = 2 slabs with embedded point charges: these factors had only minor effects on the potential in the aqueous phase.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams R. J., Pollard T. D. Binding of myosin I to membrane lipids. Nature. 1989 Aug 17;340(6234):565–568. doi: 10.1038/340565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akutsu H., Nagamori T. Conformational analysis of the polar head group in phosphatidylcholine bilayers: a structural change induced by cations. Biochemistry. 1991 May 7;30(18):4510–4516. doi: 10.1021/bi00232a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft R. G., Coster H. G., Smith J. R. The molecular organisation of bimolecular lipid membranes. The dielectric structure of the hydrophilic/hydrophobic interface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 22;643(1):191–204. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90232-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buser C. A., Sigal C. T., Resh M. D., McLaughlin S. Membrane binding of myristylated peptides corresponding to the NH2 terminus of Src. Biochemistry. 1994 Nov 8;33(44):13093–13101. doi: 10.1021/bi00248a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büldt G., Gally H. U., Seelig J., Zaccai G. Neutron diffraction studies on phosphatidylcholine model membranes. I. Head group conformation. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 15;134(4):673–691. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90479-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cevc G. Membrane electrostatics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Oct 8;1031(3):311–382. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(90)90015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L., Meves H. The effect of changing the internal solution on sodium inactivation and related phenomena in giant axons. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(4):821–836. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilger J. P., Benz R. Optical and electrical properties of thin monoolein lipid bilayers. J Membr Biol. 1985;85(2):181–189. doi: 10.1007/BF01871270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., Parsegian V. A. Thermal-mechanical fluctuations enhance repulsion between bimolecular layers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7132–7136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawrisch K., Ruston D., Zimmerberg J., Parsegian V. A., Rand R. P., Fuller N. Membrane dipole potentials, hydration forces, and the ordering of water at membrane surfaces. Biophys J. 1992 May;61(5):1213–1223. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81931-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Paterson H., Marshall C. J. A polybasic domain or palmitoylation is required in addition to the CAAX motif to localize p21ras to the plasma membrane. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):133–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90294-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Pascher I., Pearson R. H., Sundell S. Preferred conformation and molecular packing of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 16;650(1):21–51. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(81)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holst M., Kozack R. E., Saied F., Subramaniam S. Protein electrostatics: rapid multigrid-based Newton algorithm for solution of the full nonlinear Poisson-Boltzmann equation. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1994 Jun;11(6):1437–1445. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1994.10508078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig B. H., Hubbell W. L., Flewelling R. F. Electrostatic interactions in membranes and proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:163–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig C. R., Reddy Y. S. Calcium, tropomyosin, and actomyosin as controls of calcium binding by troponin. Recent Adv Stud Cardiac Struct Metab. 1975;8:233–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaram B., Sharp K. A., Honig B. The electrostatic potential of B-DNA. Biopolymers. 1989 May;28(5):975–993. doi: 10.1002/bip.360280506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. C. How pore mouth charge distributions alter the permeability of transmembrane ionic channels. Biophys J. 1987 Feb;51(2):297–311. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83336-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Blackshear P. J., Johnson J. D., McLaughlin S. Phosphorylation reverses the membrane association of peptides that correspond to the basic domains of MARCKS and neuromodulin. Biophys J. 1994 Jul;67(1):227–237. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80473-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Mosior M., Chung L. A., Wu H., McLaughlin S. Binding of peptides with basic residues to membranes containing acidic phospholipids. Biophys J. 1991 Jul;60(1):135–148. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82037-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper I., Hagstrom R., Fine R., Sharp K., Honig B. Focusing of electric fields in the active site of Cu-Zn superoxide dismutase: effects of ionic strength and amino-acid modification. Proteins. 1986 Sep;1(1):47–59. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraayenhof R., Sterk G. J., Sang H. W. Probing biomembrane interfacial potential and pH profiles with a new type of float-like fluorophores positioned at varying distance from the membrane surface. Biochemistry. 1993 Sep 28;32(38):10057–10066. doi: 10.1021/bi00089a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakhdar-Ghazal F., Tichadou J. L., Tocanne J. F. Effect of pH and monovalent cations on the ionization state of phosphatidylglycerol in monolayers. An experimental (surface potential) and theoretical (Gouy-Chapman) approach. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Aug 15;134(3):531–537. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langner M., Cafiso D., Marcelja S., McLaughlin S. Electrostatics of phosphoinositide bilayer membranes. Theoretical and experimental results. Biophys J. 1990 Feb;57(2):335–349. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82535-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li D., Miller M., Chantler P. D. Association of a cellular myosin II with anionic phospholipids and the neuronal plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):853–857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee A. I., Newman C. M., Giannakouros T., Hancock J. F., Fawell E., Armstrong J. Lipid modifications and function of the ras superfamily of proteins. Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 May;20(2):497–499. doi: 10.1042/bst0200497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marra J. Direct measurement of the interaction between phosphatidylglycerol bilayers in aqueous electrolyte solutions. Biophys J. 1986 Nov;50(5):815–825. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83522-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew J. B. Electrostatic effects in proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1985;14:387–417. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.14.060185.002131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J., Magid A. D., Simon S. A. Range of the solvation pressure between lipid membranes: dependence on the packing density of solvent molecules. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7904–7912. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S., Harary H. The hydrophobic adsorption of charged molecules to bilayer membranes: a test of the applicability of the stern equation. Biochemistry. 1976 May 4;15(9):1941–1948. doi: 10.1021/bi00654a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S. The electrostatic properties of membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:113–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S. The mechanism of action of DNP on phospholipid bilayer membranes. J Membr Biol. 1972;9(4):361–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosior M., McLaughlin S. Binding of basic peptides to acidic lipids in membranes: effects of inserting alanine(s) between the basic residues. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 18;31(6):1767–1773. doi: 10.1021/bi00121a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosior M., McLaughlin S. Electrostatics and reduction of dimensionality produce apparent cooperativity when basic peptides bind to acidic lipids in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Mar 23;1105(1):185–187. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(92)90178-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosior M., McLaughlin S. Peptides that mimic the pseudosubstrate region of protein kinase C bind to acidic lipids in membranes. Biophys J. 1991 Jul;60(1):149–159. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82038-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson A. P., Colonomos P., McQuarrie D. A. Electrostatic coupling across a membrane with titratable surface groups. J Theor Biol. 1975 Apr;50(2):317–325. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(75)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson A. P., McQuarrie D. A. The effect of discrete charges on the electrical properties of a membrane. I. J Theor Biol. 1975 Nov;55(1):13–27. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(75)80106-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton A. C. Interaction of proteins with lipid headgroups: lessons from protein kinase C. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1993;22:1–25. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.22.060193.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. H., Pascher I. The molecular structure of lecithin dihydrate. Nature. 1979 Oct 11;281(5731):499–501. doi: 10.1038/281499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Doberstein S. K., Zot H. G. Myosin-I. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:653–681. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.003253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand R. P. Interacting phospholipid bilayers: measured forces and induced structural changes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1981;10:277–314. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.10.060181.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauvé R., Ohki S. Interactions of divalent cations with negatively charged membrane surfaces. I. Discrete charge potential. J Theor Biol. 1979 Nov 21;81(2):157–179. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(79)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer P. G., Seelig J. Structure and dynamics of the phosphatidylcholine and the phosphatidylethanolamine head group in L-M fibroblasts as studied by deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):2915–2922. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02595.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J., Macdonald P. M., Scherer P. G. Phospholipid head groups as sensors of electric charge in membranes. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7535–7541. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp K. A., Honig B. Electrostatic interactions in macromolecules: theory and applications. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1990;19:301–332. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.19.060190.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. A., McIntosh T. J. Magnitude of the solvation pressure depends on dipole potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9263–9267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi H., Manenti S. Interaction of myristoylated alanine-rich protein kinase C substrate (MARCKS) with membrane phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):9960–9963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener M. C., White S. H. Structure of a fluid dioleoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer determined by joint refinement of x-ray and neutron diffraction data. III. Complete structure. Biophys J. 1992 Feb;61(2):434–447. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81849-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. A., Pohorille A. Molecular dynamics of a water-lipid bilayer interface. J Am Chem Soc. 1994;116(4):1490–1501. doi: 10.1021/ja00083a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winiski A. P., Eisenberg M., Langner M., McLaughlin S. Fluorescent probes of electrostatic potential 1 nm from the membrane surface. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 12;27(1):386–392. doi: 10.1021/bi00401a058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winiski A. P., McLaughlin A. C., McDaniel R. V., Eisenberg M., McLaughlin S. An experimental test of the discreteness-of-charge effect in positive and negative lipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 16;25(25):8206–8214. doi: 10.1021/bi00373a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng C., Vanderkooi G. Molecular origin of the internal dipole potential in lipid bilayers: calculation of the electrostatic potential. Biophys J. 1992 Oct;63(4):935–941. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81673-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kruijff B., Rietveld A., Telders N., Vaandrager B. Molecular aspects of the bilayer stabilization induced by poly(L-lysines) of varying size in cardiolipin liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Nov 7;820(2):295–304. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]