Abstract
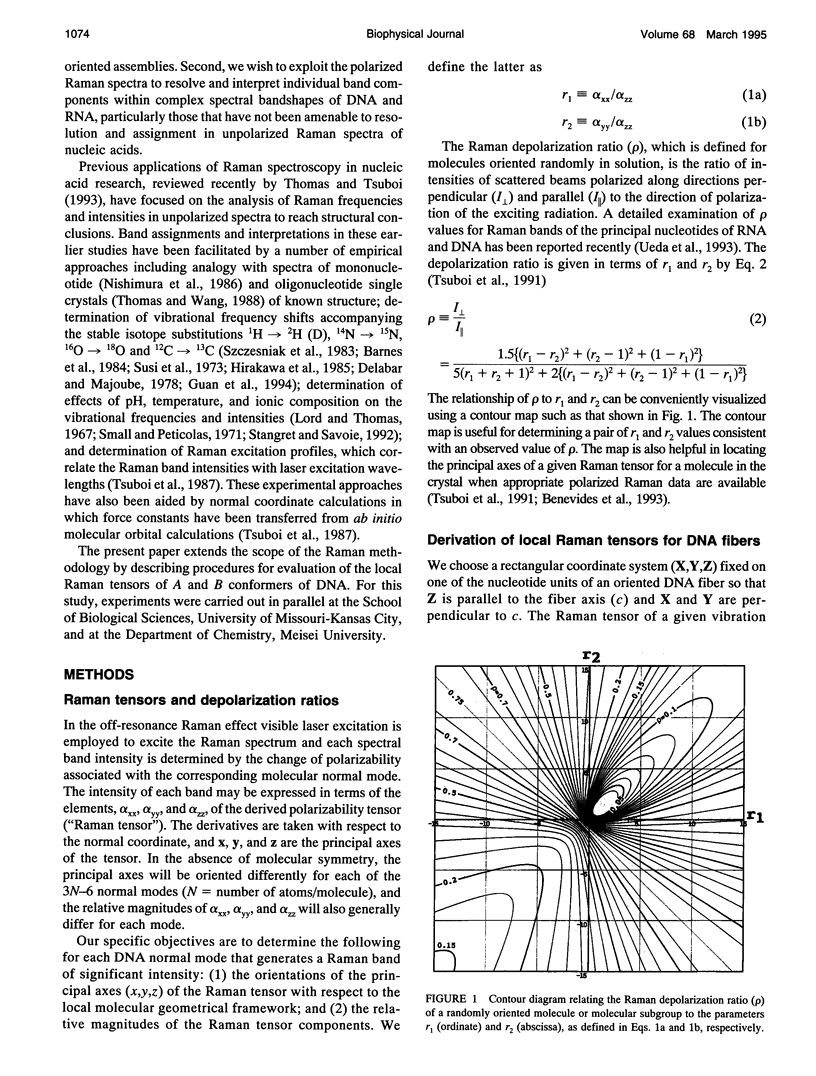
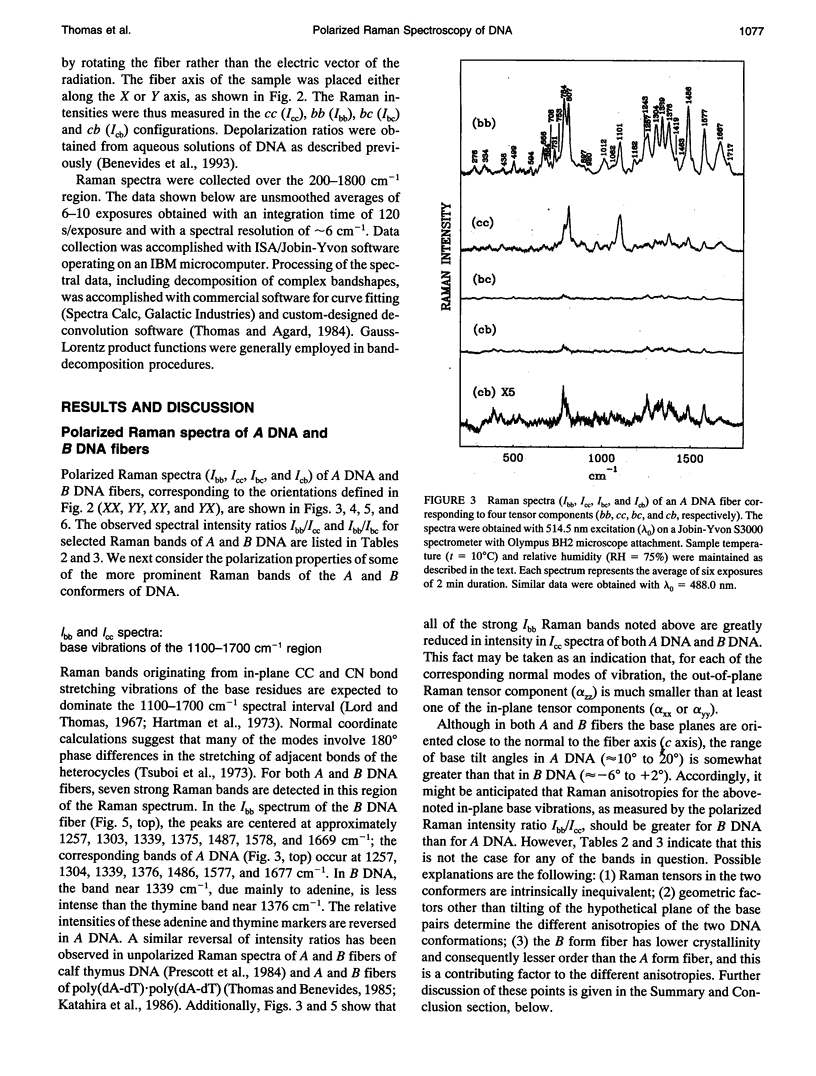
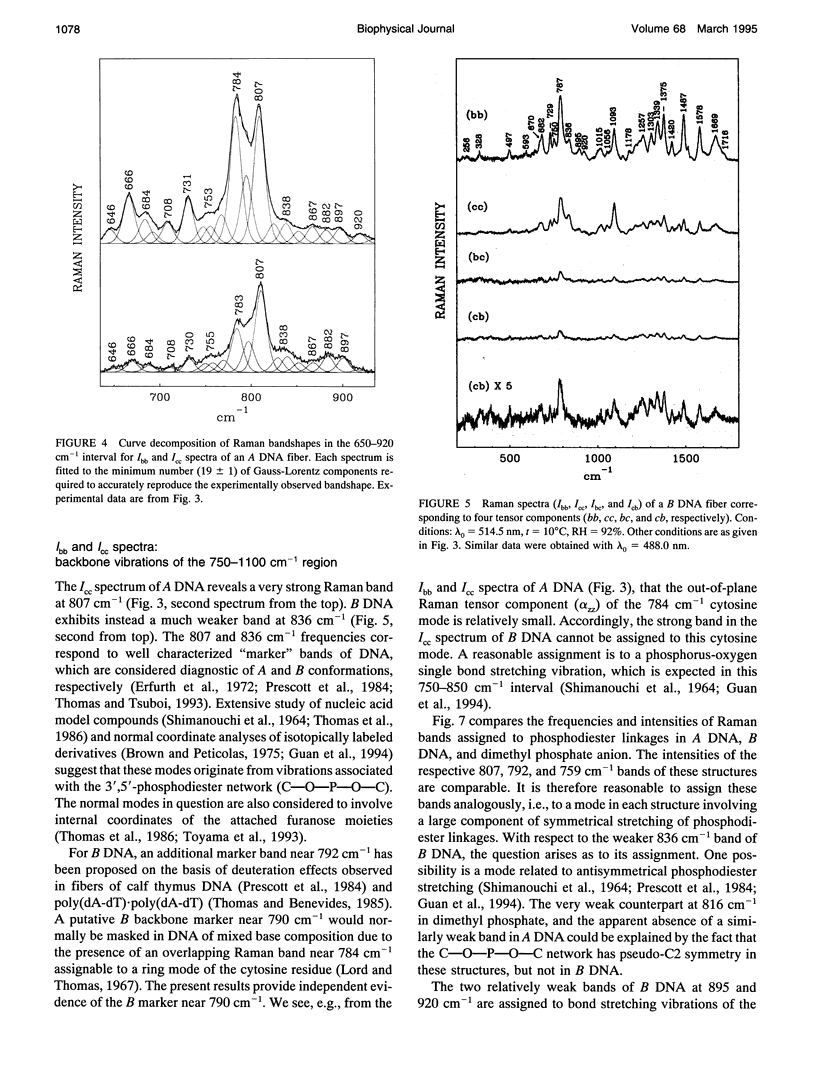
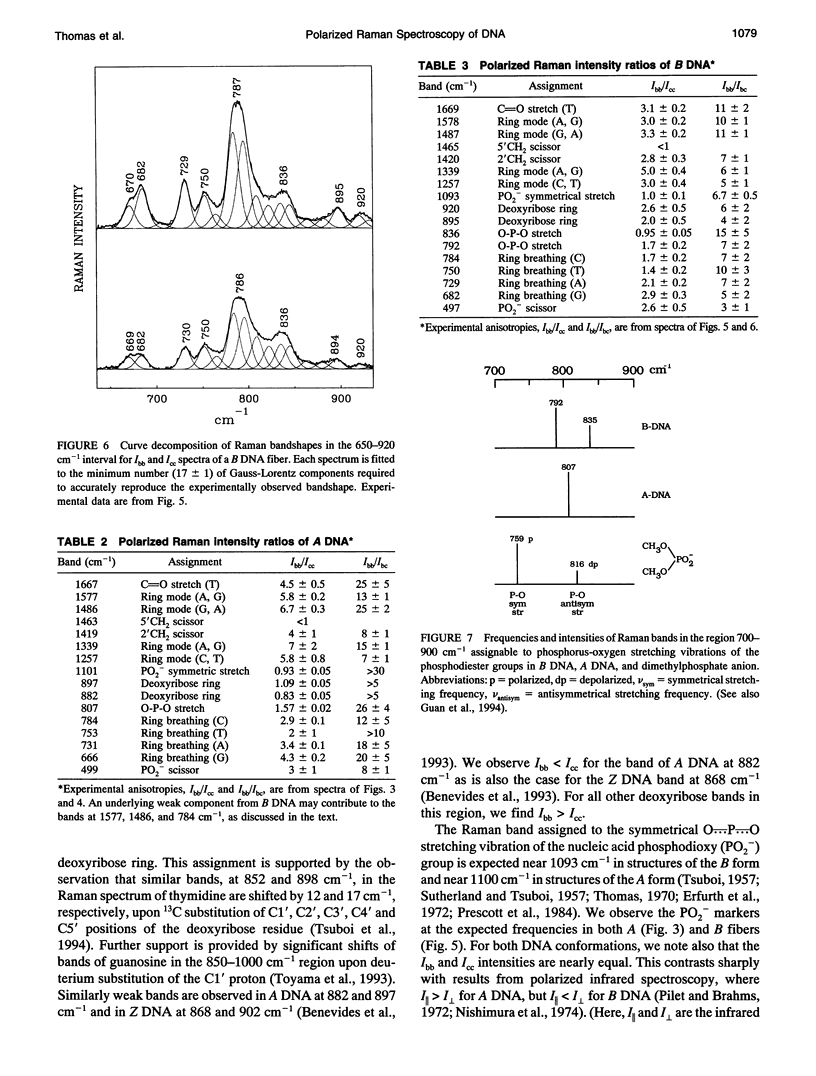
Polarized Raman spectra of oriented fibers of calf thymus DNA in the A and B conformations have been obtained by use of a Raman microscope operating in the 180 degrees back-scattering geometry. The following polarized Raman intensities in the spectral interval 200-1800 cm-1 were measured with both 514.5 and 488.0 nm laser excitations: (1) Icc, in which the incident and scattered light are polarized parallel to the DNA helical axis (c axis); (2) Ibb, in which the incident and scattered light are polarized perpendicular to c; and (3) Ibc and Icb, in which the incident and scattered light are polarized in mutually perpendicular directions. High degrees of structural homogeneity and unidirectional orientation were confirmed for both the A and B form fibers, as judged by comparison of the observed Raman markers and intensity anisotropies with measurements reported previously for oligonucleotide single crystals of known three-dimensional structures. The fiber Raman anisotropies have been combined with solution Raman depolarization ratios to evaluate the local tensors corresponding to key conformation-sensitive Raman bands of the DNA bases and sugar-phosphate backbone. The present study yields novel vibrational assignments for both A DNA and BDNA conformers and also confirms many previously proposed Raman vibrational assignments. Among the significant new findings are the demonstration of complex patterns of A form and B form indicator bands in the spectral intervals 750-900 and 1050-1100 cm-1, the identification of highly anisotropic tensors corresponding to vibrations of base, deoxyribose, and phosphate moieties, and the determination of relatively isotropic Raman tensors for the symmetrical stretching mode of phosphodioxy groups in A and B DNA. The present fiber results provide a basis for exploitation of polarized Raman spectroscopy to determine DNA helix orientation as well as to probe specific nucleotide residue orientations in nucleoproteins, viruses, and other complex biological assemblies.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Hukins D. W. Optimised parameters for A-DNA and B-DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 28;47(6):1504–1509. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubrey K. L., Casjens S. R., Thomas G. J., Jr Secondary structure and interactions of the packaged dsDNA genome of bacteriophage P22 investigated by Raman difference spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 1;31(47):11835–11842. doi: 10.1021/bi00162a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandes R., Rupprecht A., Kearns D. R. Interaction of water with oriented DNA in the A- and B-form conformations. Biophys J. 1989 Oct;56(4):683–691. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82715-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. B., Peticolas W. L. Conformational geometry and vibrational frequencies of nucleic acid chains. Biopolymers. 1975 Jun;14(6):1259–1271. doi: 10.1002/bip.1975.360140614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erfurth S. C., Kiser E. J., Peticolas W. L. Determination of the backbone structure of nucleic acids and nucleic acid oligomers by laser Raman scattering. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):938–941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FULLER W., WILKINS M. H., WILSON H. R., HAMILTON L. D. THE MOLECULAR CONFIGURATION OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID. IV. X-RAY DIFFRACTION STUDY OF THE A FORM. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:60–76. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80282-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan Y., Wurrey C. J., Thomas G. J., Jr Vibrational analysis of nucleic acids. I. The phosphodiester group in dimethyl phosphate model compounds: (CH3O)2PO2-, (CD3O)2PO2-, and (13CH3O)2PO2-. Biophys J. 1994 Jan;66(1):225–235. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80767-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katahira M., Nishimura Y., Tsuboi M., Sato T., Mitsui Y., Iitaka Y. Local and overall conformations of DNA double helices with the A - T base pairs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Aug 22;867(4):256–267. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(86)90042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennard O., Hunter W. N. Oligonucleotide structure: a decade of results from single crystal X-ray diffraction studies. Q Rev Biophys. 1989 Aug;22(3):327–379. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li T., Bamford D. H., Bamford J. K., Thomas G. J., Jr Structural studies of the enveloped dsRNA bacteriophage phi 6 of Pseudomonas syringae by Raman spectroscopy. I. The virion and its membrane envelope. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 20;230(2):461–472. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li T., Johnson J. E., Thomas G. J., Jr Raman dynamic probe of hydrogen exchange in bean pod mottle virus: base-specific retardation of exchange in packaged ssRNA. Biophys J. 1993 Nov;65(5):1963–1972. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81272-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Thomas G. J., Jr, Fuller M., King J. Investigations of bacteriophage P22 by laser Raman spectroscopy. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1981;64:271–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilet J., Brahms J. Dependence of B-A conformational change in DNA on base composition. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 29;236(65):99–100. doi: 10.1038/newbio236099a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott B., Steinmetz W., Thomas G. J., Jr Characterization of DNA structures by laser Raman spectroscopy. Biopolymers. 1984 Feb;23(2):235–256. doi: 10.1002/bip.360230206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puppels G. J., Otto C., Greve J., Robert-Nicoud M., Arndt-Jovin D. J., Jovin T. M. Raman microspectroscopic study of low-pH-induced changes in DNA structure of polytene chromosomes. Biochemistry. 1994 Mar 22;33(11):3386–3395. doi: 10.1021/bi00177a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small E. W., Peticolas W. L. Conformational dependence of the Raman scattering intensities from polynucleotides. Biopolymers. 1971;10(1):69–88. doi: 10.1002/bip.360100107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. J., Jr, Agard D. A. Quantitative analysis of nucleic acids, proteins, and viruses by Raman band deconvolution. Biophys J. 1984 Dec;46(6):763–768. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84074-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. J., Jr, Benevides J. M. An A-helix structure for poly(dA-dT) X poly(dA-dT). Biopolymers. 1985 Jun;24(6):1101–1105. doi: 10.1002/bip.360240613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. J., Jr Raman spectral studies of nucleic acids. 3. Laser-excited spectra of ribosomal RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 8;213(2):417–423. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90049-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Ushizawa K., Tsuboi M. Depolarization of Raman scattering from some nucleotides of RNA and DNA. Biopolymers. 1993 Dec;33(12):1791–1802. doi: 10.1002/bip.360331205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



