Abstract
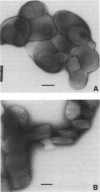
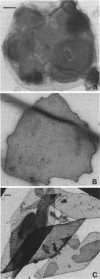
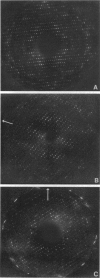
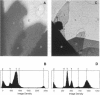
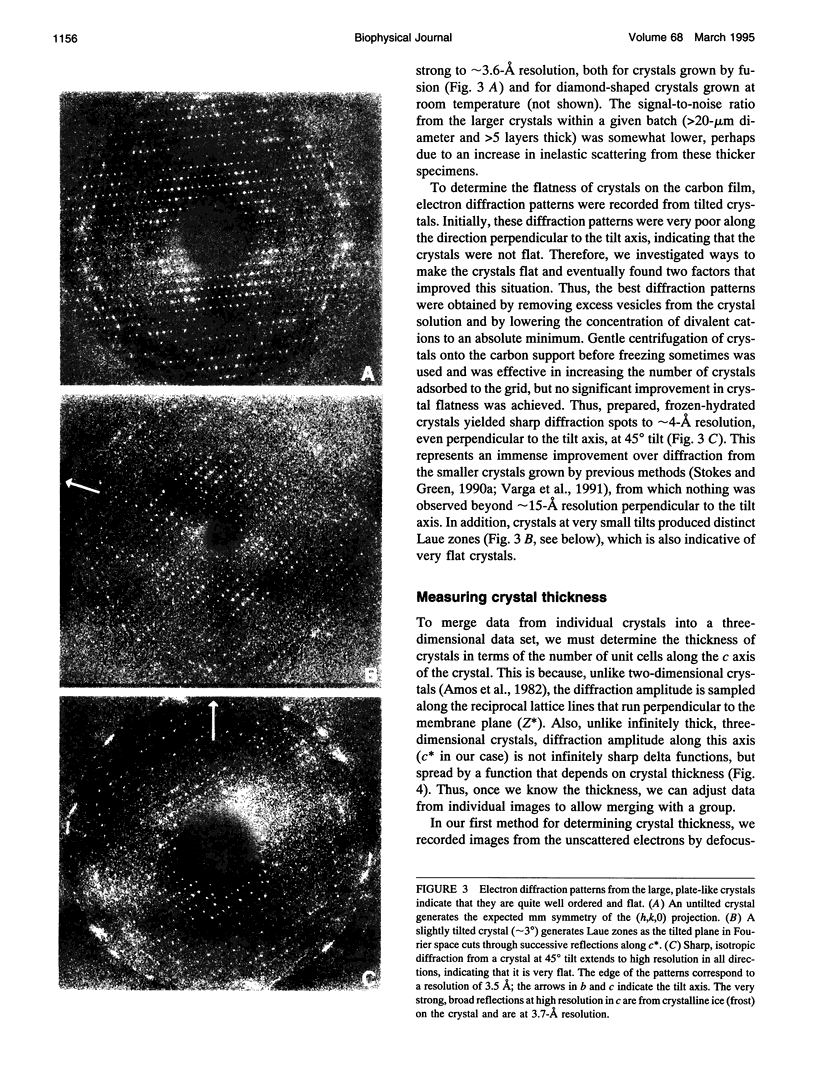
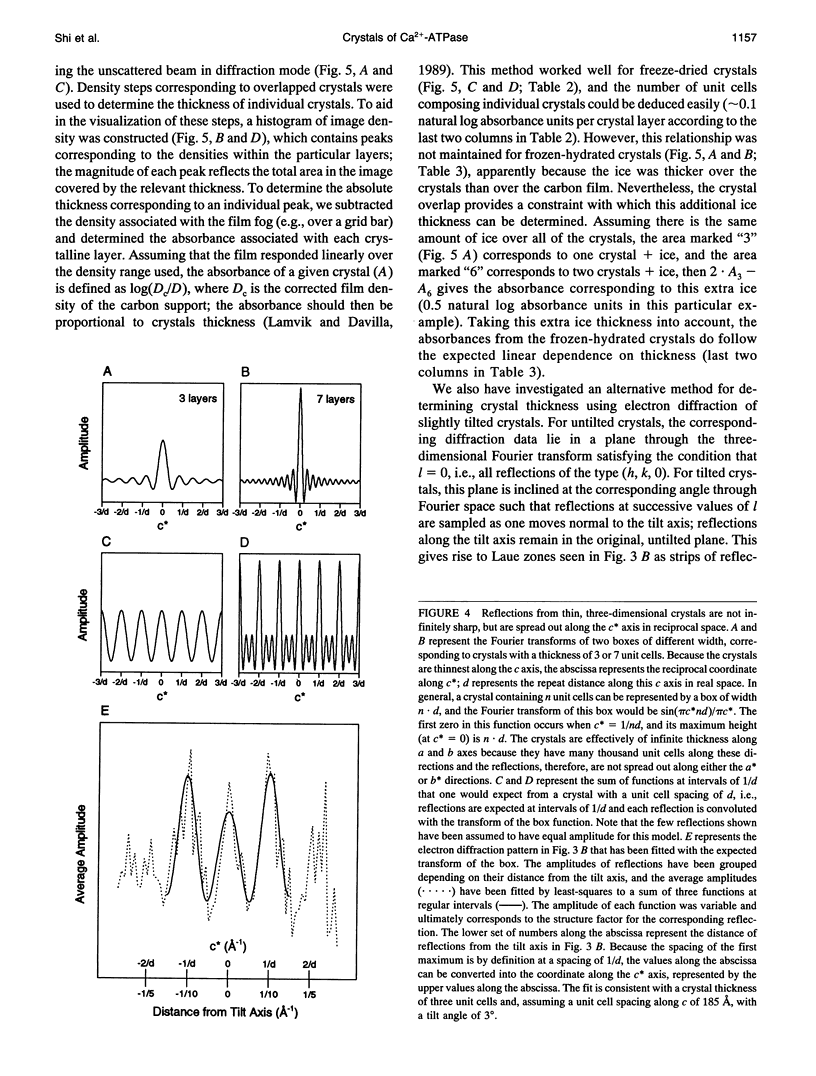
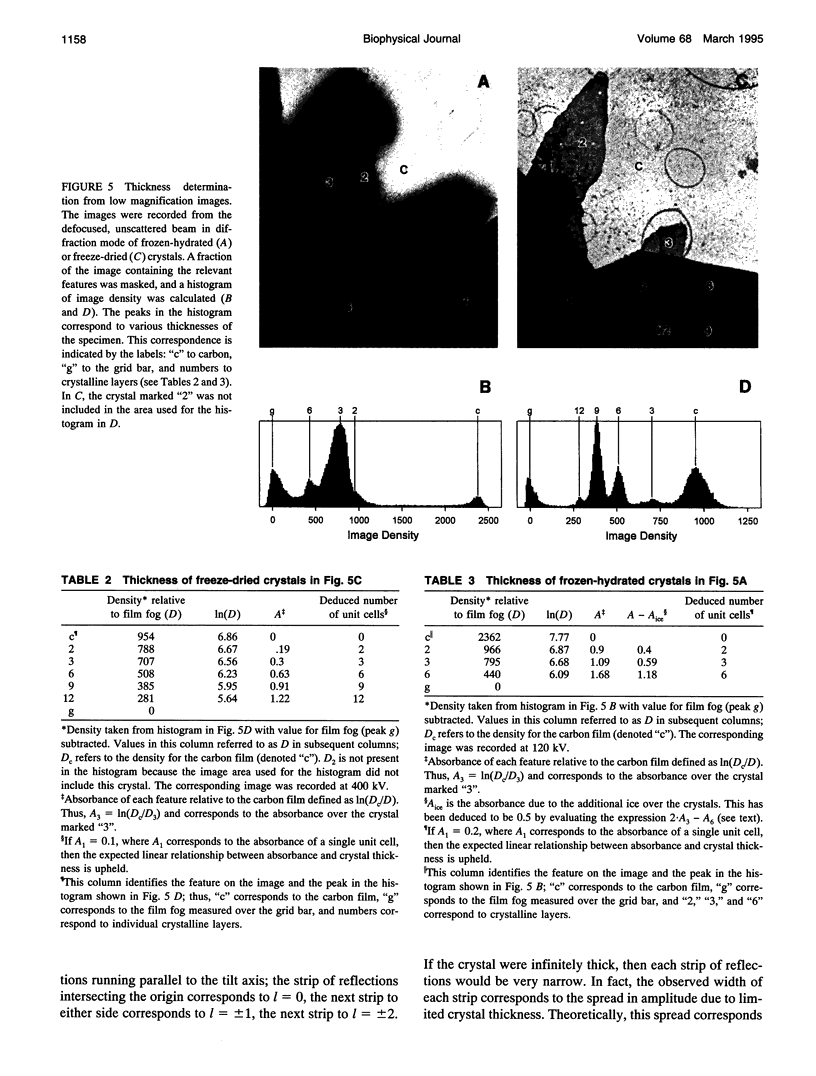
Obtaining large, flat, well ordered crystals represents the key to structure determination by electron crystallography. Multilamellar crystals of Ca(2+)-ATPase are a good candidate for this methodology, and we have optimized methods of crystallization and of preparation for cryoelectron microscopy. In particular, high concentrations of glycerol were found to prevent nucleation and to reduce stacking; thus, by seeding solutions containing 40% glycerol, we obtained thin crystals that were 5-30 microns in diameter and 2-10 unit cells thick. We found that removing vesicles and minimizing concentrations of divalent cations were critical to preparing flat crystals in the frozen-hydrated state. Finally, we developed two methods for determining the number of lamellae composing individual crystals, information that is required for structure determination of this crystal form. The first method, using low magnification images of freeze-dried crystals, is more practical in our case. Nevertheless, the alternative method, involving analysis of Laue zones from electron diffraction patterns of slightly tilted crystals, may be of general use in structure determination from thin, three-dimensional crystals.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amos L. A., Henderson R., Unwin P. N. Three-dimensional structure determination by electron microscopy of two-dimensional crystals. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1982;39(3):183–231. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(83)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asturias F. J., Fischetti R. F., Blasie J. K. Changes in the relative occupancy of metal-binding sites in the profile structure of the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane induced by phosphorylation of the Ca2+ATPase enzyme in the presence of terbium: a time-resolved, resonance x-ray diffraction study. Biophys J. 1994 May;66(5):1665–1677. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80958-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigelow D. J., Inesi G. Contributions of chemical derivatization and spectroscopic studies to the characterization of the Ca2+ transport ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Dec 11;1113(3-4):323–338. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(92)90005-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasie J. K., Herbette L. G., Pascolini D., Skita V., Pierce D. H., Scarpa A. Time-resolved x-ray diffraction studies of the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane during active transport. Biophys J. 1985 Jul;48(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83756-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellani L., Hardwicke P. M., Vibert P. Dimer ribbons in the three-dimensional structure of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Mol Biol. 1985 Oct 5;185(3):579–594. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke D. M., Loo T. W., Inesi G., MacLennan D. H. Location of high affinity Ca2+-binding sites within the predicted transmembrane domain of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):476–478. doi: 10.1038/339476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coll R. J., Murphy A. J. Purification of the CaATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14249–14254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dux L., Martonosi A. Two-dimensional arrays of proteins in sarcoplasmic reticulum and purified Ca2+-ATPase vesicles treated with vanadate. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2599–2603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dux L., Pikula S., Mullner N., Martonosi A. Crystallization of Ca2+-ATPase in detergent-solubilized sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6439–6442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dux L., Taylor K. A., Ting-Beall H. P., Martonosi A. Crystallization of the Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum by calcium and lanthanide ions. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11730–11743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eletr S., Inesi G. Phospholipid orientation in sarcoplasmic membranes: spin-label ESR and proton MNR studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 1;282(1):174–179. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90321-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gekko K., Timasheff S. N. Mechanism of protein stabilization by glycerol: preferential hydration in glycerol-water mixtures. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 4;20(16):4667–4676. doi: 10.1021/bi00519a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gekko K., Timasheff S. N. Thermodynamic and kinetic examination of protein stabilization by glycerol. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 4;20(16):4677–4686. doi: 10.1021/bi00519a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaeser R. M. Specimen flatness of thin crystalline arrays: influence of the substrate. Ultramicroscopy. 1992 Oct;46(1-4):33–43. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(92)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaeser R. M., Zilker A., Radermacher M., Gaub H. E., Hartmann T., Baumeister W. Interfacial energies and surface-tension forces involved in the preparation of thin, flat crystals of biological macromolecules for high-resolution electron microscopy. J Microsc. 1991 Jan;161(Pt 1):21–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1991.tb03071.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M. Evolutionary relationships within the family of P-type cation pumps. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 Nov 30;671:104–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb43788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Baldwin J. M., Ceska T. A., Zemlin F., Beckmann E., Downing K. H. Model for the structure of bacteriorhodopsin based on high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):899–929. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbette L., DeFoor P., Fleischer S., Pascolini D., Scarpa A., Blasie J. K. The separate profile structures of the functional calcium pump protein and the phospholipid bilayer within isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes determined by X-ray and neutron diffraction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jul 11;817(1):103–122. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inesi G. Teaching active transport at the turn of the twenty-first century: recent discoveries and conceptual changes. Biophys J. 1994 Mar;66(3 Pt 1):554–560. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(94)80872-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jap B. K., Walian P. J., Gehring K. Structural architecture of an outer membrane channel as determined by electron crystallography. Nature. 1991 Mar 14;350(6314):167–170. doi: 10.1038/350167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühlbrandt W., Wang D. N., Fujiyoshi Y. Atomic model of plant light-harvesting complex by electron crystallography. Nature. 1994 Feb 17;367(6464):614–621. doi: 10.1038/367614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacapère J. J., Stokes D. L., Chatenay D. Atomic force microscopy of three-dimensional membrane protein crystals. Ca-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biophys J. 1992 Aug;63(2):303–308. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81600-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamvik M. K., Davilla S. Calibration methods for quantitative image processing in electron microscopy. J Electron Microsc Tech. 1989 Feb;11(2):97–101. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1060110202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leapman R. D., Brink J., Chiu W. Low-dose thickness measurement of glucose-embedded protein crystals by electron energy loss spectroscopy and STEM dark-field imaging. Ultramicroscopy. 1993 Nov;52(2):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(93)90186-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra M., Taylor D., Oliver T., Taylor K. Effect of organic anions on the crystallization of the Ca2(+)-ATPase of muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 8;1077(1):107–118. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(91)90532-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikula S., Mullner N., Dux L., Martonosi A. Stabilization and crystallization of Ca2+-ATPase in detergent-solubilized sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5277–5286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes D. L., Green N. M. Structure of CaATPase: electron microscopy of frozen-hydrated crystals at 6 A resolution in projection. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 5;213(3):529–538. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80213-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes D. L., Green N. M. Three-dimensional crystals of CaATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Symmetry and molecular packing. Biophys J. 1990 Jan;57(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82501-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes D. L., Taylor W. R., Green N. M. Structure, transmembrane topology and helix packing of P-type ion pumps. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jun 6;346(1):32–38. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00297-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. A., Dux L., Martonosi A. Three-dimensional reconstruction of negatively stained crystals of the Ca2+-ATPase from muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 5;187(3):417–427. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90442-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. A., Mullner N., Pikula S., Dux L., Peracchia C., Varga S., Martonosi A. Electron microscope observations on Ca2+-ATPase microcrystals in detergent-solubilized sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5287–5294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. A., Varga S. Similarity of three-dimensional microcrystals of detergent-solubilized (Na+,K+)-ATPase from pig kidney and Ca(2+)-ATPase from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):10107–10111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima C., Sasabe H., Stokes D. L. Three-dimensional cryo-electron microscopy of the calcium ion pump in the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. Nature. 1993 Apr 1;362(6419):467–471. doi: 10.1038/362469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valpuesta J. M., Carrascosa J. L., Henderson R. Analysis of electron microscope images and electron diffraction patterns of thin crystals of phi 29 connectors in ice. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jul 22;240(4):281–287. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varga S., Taylor K. A., Martonosi A. Effects of solutes on the formation of crystalline sheets of the Ca(2+)-ATPase in detergent-solubilized sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 9;1070(2):374–386. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90078-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D. N., Kühlbrandt W. High-resolution electron crystallography of light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b-protein complex in three different media. J Mol Biol. 1991 Feb 20;217(4):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90526-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. B., Toon P. A., Birdsall N. J., Lee A. G., Metcalfe J. C. Reconstitution of a calcium pump using defined membrane components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):622–626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]