Abstract
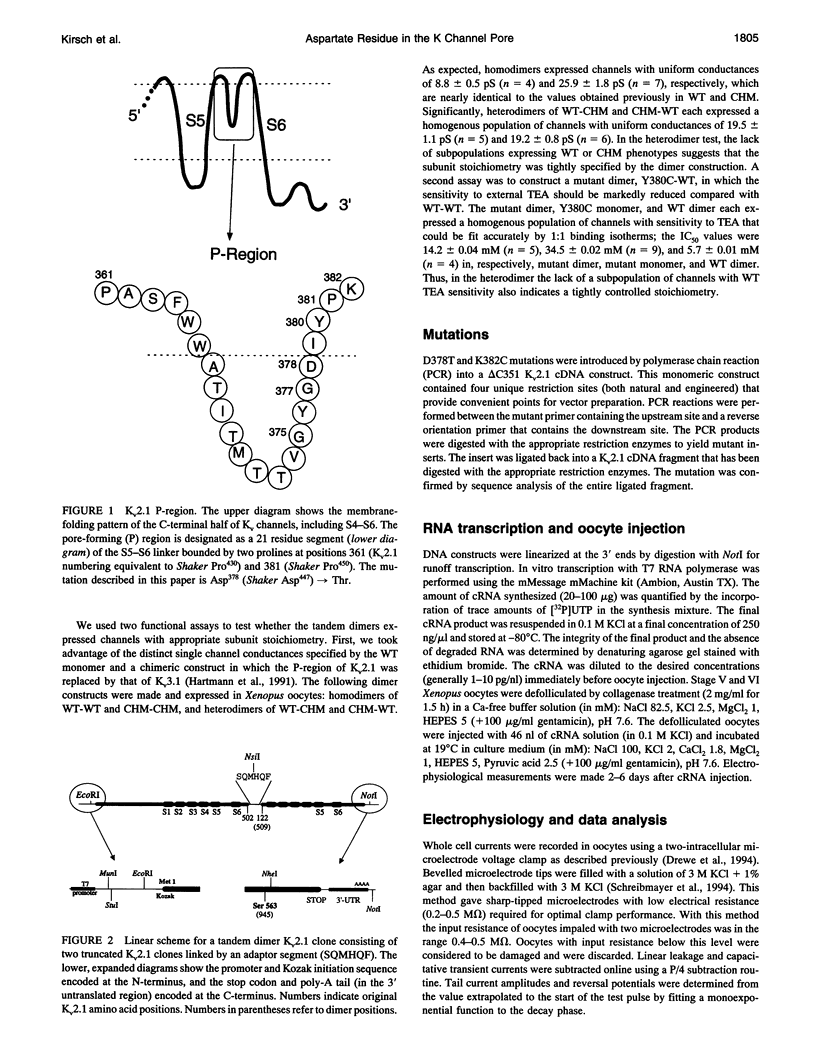
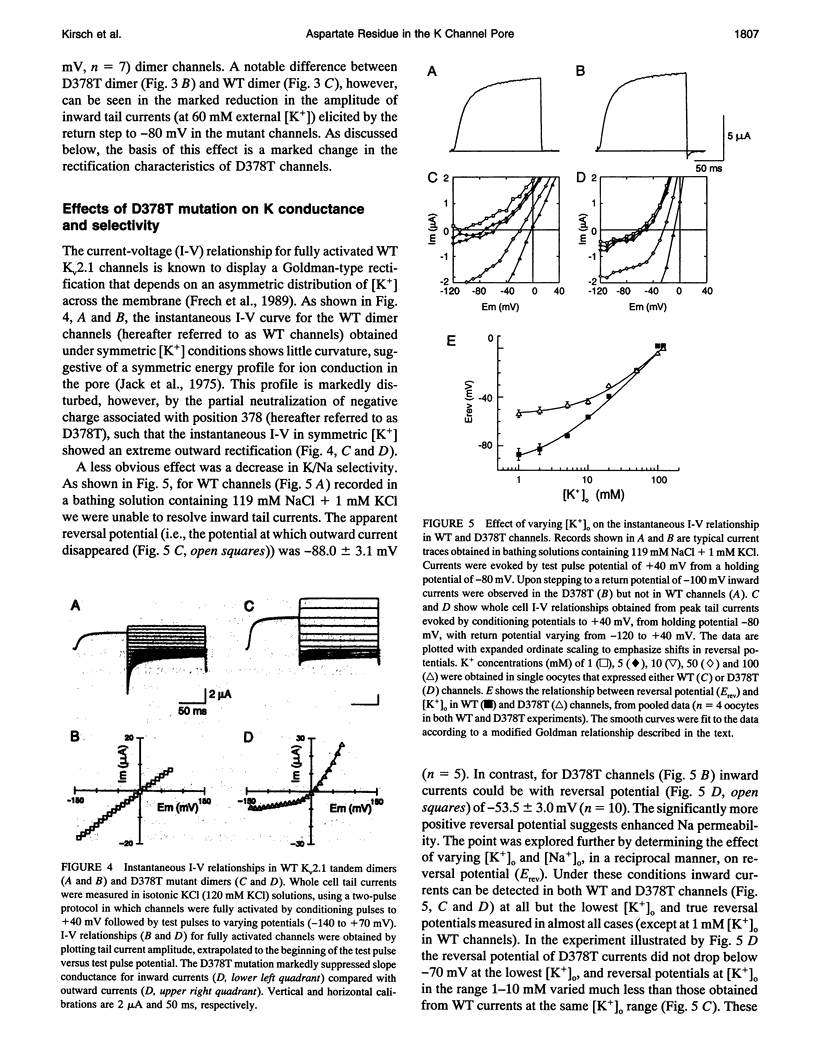
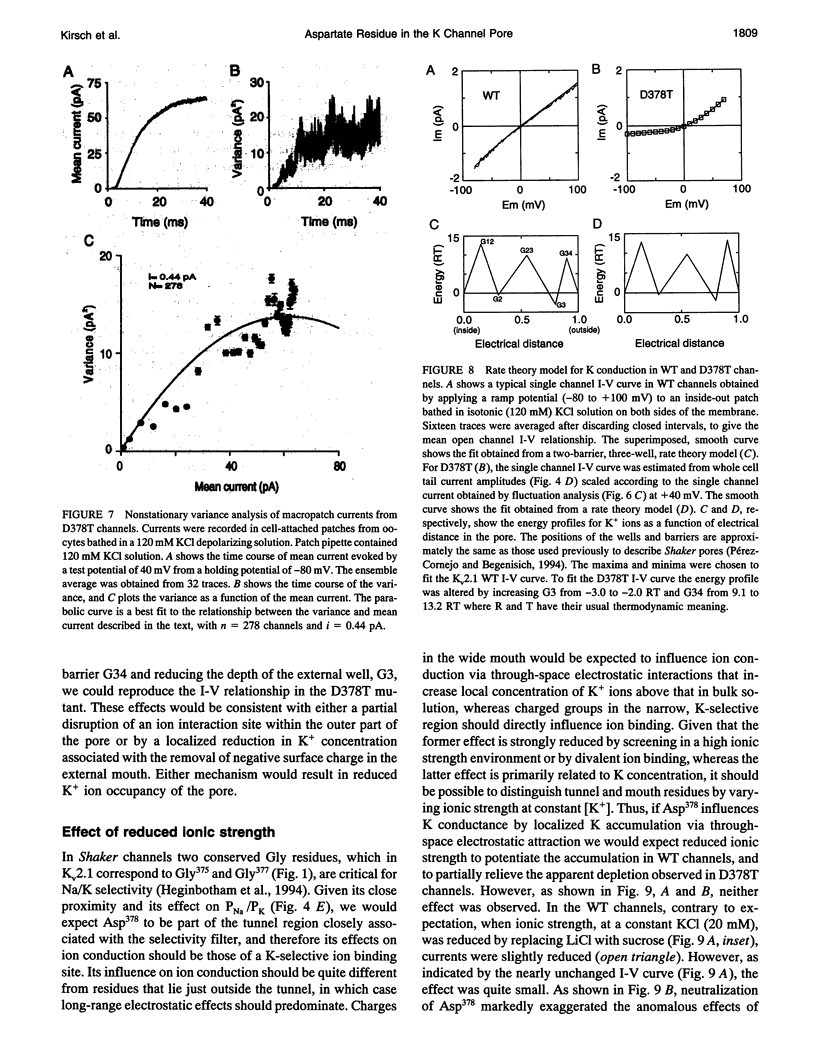
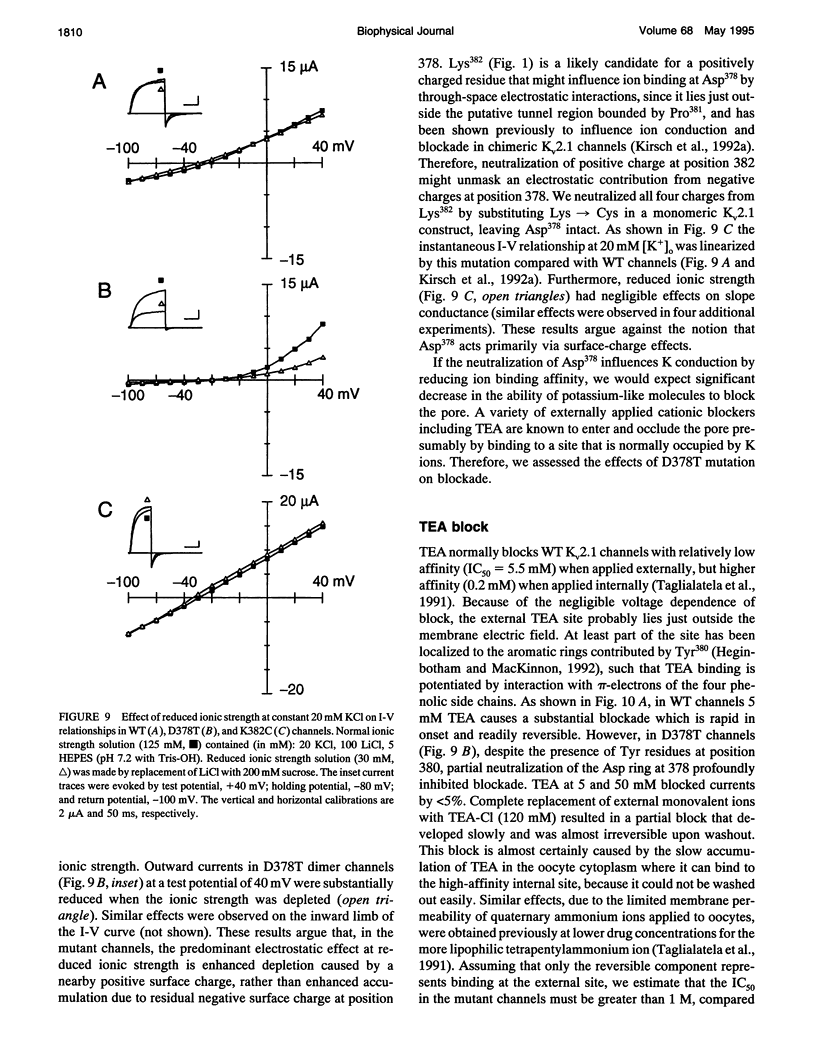
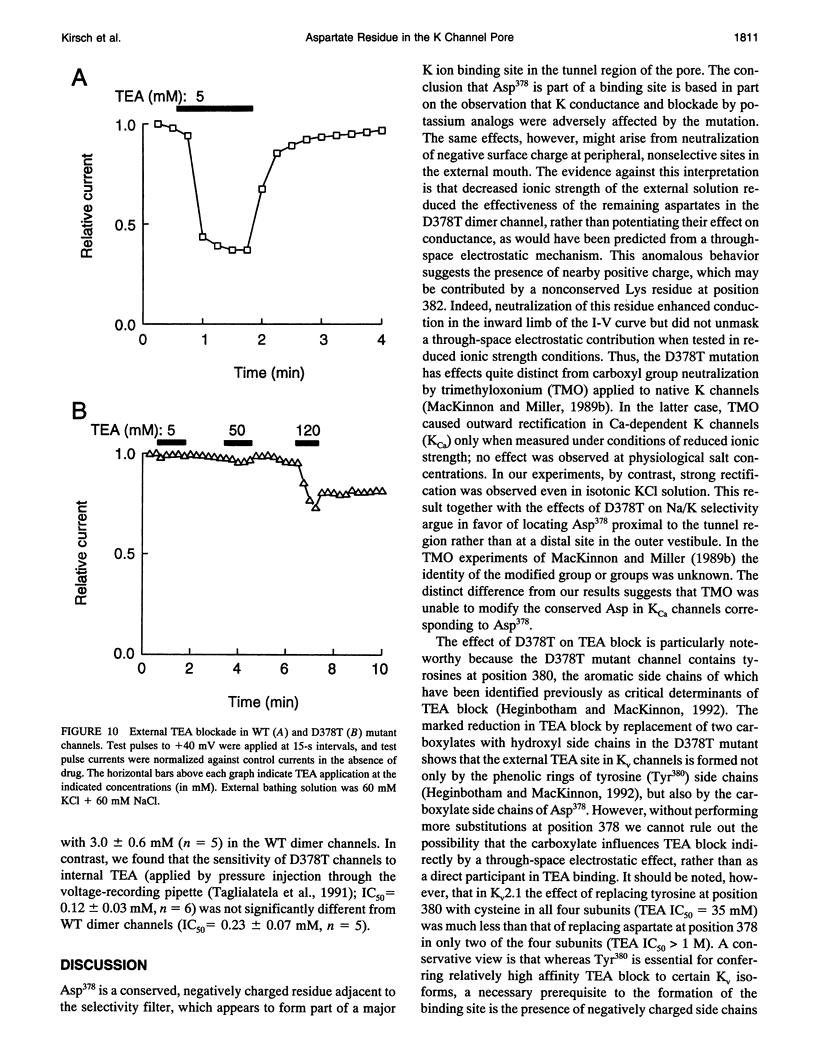
Mutation of the glycines in a conserved Gly-Tyr-Gly-Asp sequence in the P-region of voltage-gated K channels has identified determinants of Na/K selectivity. But the function of the negatively charged Asp is not known because mutations at this position are not tolerated, owing to the fourfold replication of mutations in a tetrameric channel. We have successfully mutated Asp378-->Thr in a tandem dimer Kv2.1 construct to yield a twofold neutralization of charge at this site. When expressed in Xenopus oocytes, the mutated channels showed markedly altered ion conduction and blockade. Potassium conduction in the inward direction was selectively reduced, so that the instantaneous current-voltage relationship obtained in isotonic KCl became strongly outwardly rectifying. The relative permeability to Na+, PNa/PK, increased from 0.02 to 0.10 without changing the ion selectivity sequence K > Rb >> Cs >> Na. The IC50 for block by external tetraethylammonium (TEA) increased more than 100-fold without affecting block by internal TEA. We conclude that Asp378 is an essential part of a potassium ion binding site associated with the Na/K selectivity filter at the external mouth of the pore.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brüggemann A., Pardo L. A., Stühmer W., Pongs O. Ether-à-go-go encodes a voltage-gated channel permeable to K+ and Ca2+ and modulated by cAMP. Nature. 1993 Sep 30;365(6445):445–448. doi: 10.1038/365445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler A., Tsunoda S., McCobb D. P., Wei A., Salkoff L. mSlo, a complex mouse gene encoding "maxi" calcium-activated potassium channels. Science. 1993 Jul 9;261(5118):221–224. doi: 10.1126/science.7687074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eismann E., Müller F., Heinemann S. H., Kaupp U. B. A single negative charge within the pore region of a cGMP-gated channel controls rectification, Ca2+ blockage, and ionic selectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):1109–1113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frech G. C., VanDongen A. M., Schuster G., Brown A. M., Joho R. H. A novel potassium channel with delayed rectifier properties isolated from rat brain by expression cloning. Nature. 1989 Aug 24;340(6235):642–645. doi: 10.1038/340642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein S. A., Pheasant D. J., Miller C. The charybdotoxin receptor of a Shaker K+ channel: peptide and channel residues mediating molecular recognition. Neuron. 1994 Jun;12(6):1377–1388. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90452-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:127–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann H. A., Kirsch G. E., Drewe J. A., Taglialatela M., Joho R. H., Brown A. M. Exchange of conduction pathways between two related K+ channels. Science. 1991 Feb 22;251(4996):942–944. doi: 10.1126/science.2000495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heginbotham L., Abramson T., MacKinnon R. A functional connection between the pores of distantly related ion channels as revealed by mutant K+ channels. Science. 1992 Nov 13;258(5085):1152–1155. doi: 10.1126/science.1279807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heginbotham L., Lu Z., Abramson T., MacKinnon R. Mutations in the K+ channel signature sequence. Biophys J. 1994 Apr;66(4):1061–1067. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80887-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heginbotham L., MacKinnon R. The aromatic binding site for tetraethylammonium ion on potassium channels. Neuron. 1992 Mar;8(3):483–491. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90276-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann S. H., Conti F., Stühmer W. Recording of gating currents from Xenopus oocytes and gating noise analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1992;207:353–368. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)07024-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The permeability of the sodium channel to organic cations in myelinated nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Dec;58(6):599–619. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.6.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imoto K., Busch C., Sakmann B., Mishina M., Konno T., Nakai J., Bujo H., Mori Y., Fukuda K., Numa S. Rings of negatively charged amino acids determine the acetylcholine receptor channel conductance. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):645–648. doi: 10.1038/335645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch G. E., Drewe J. A., Hartmann H. A., Taglialatela M., de Biasi M., Brown A. M., Joho R. H. Differences between the deep pores of K+ channels determined by an interacting pair of nonpolar amino acids. Neuron. 1992 Mar;8(3):499–505. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90278-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch G. E., Drewe J. A., Taglialatela M., Joho R. H., DeBiasi M., Hartmann H. A., Brown A. M. A single nonpolar residue in the deep pore of related K+ channels acts as a K+:Rb+ conductance switch. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;62(1):136–144. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81800-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo Y., Baldwin T. J., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Primary structure and functional expression of a mouse inward rectifier potassium channel. Nature. 1993 Mar 11;362(6416):127–133. doi: 10.1038/362127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Miller C. Functional modification of a Ca2+-activated K+ channel by trimethyloxonium. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 3;28(20):8087–8092. doi: 10.1021/bi00446a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Miller C. Mutant potassium channels with altered binding of charybdotoxin, a pore-blocking peptide inhibitor. Science. 1989 Sep 22;245(4924):1382–1385. doi: 10.1126/science.2476850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Yellen G. Mutations affecting TEA blockade and ion permeation in voltage-activated K+ channels. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):276–279. doi: 10.1126/science.2218530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Suzuki H., Numa S., Stühmer W. A single point mutation confers tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin insensitivity on the sodium channel II. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81531-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Cornejo P., Begenisich T. The multi-ion nature of the pore in Shaker K+ channels. Biophys J. 1994 Jun;66(6):1929–1938. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80986-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root M. J., MacKinnon R. Identification of an external divalent cation-binding site in the pore of a cGMP-activated channel. Neuron. 1993 Sep;11(3):459–466. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90150-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreibmayer W., Lester H. A., Dascal N. Voltage clamping of Xenopus laevis oocytes utilizing agarose-cushion electrodes. Pflugers Arch. 1994 Mar;426(5):453–458. doi: 10.1007/BF00388310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J. The variance of sodium current fluctuations at the node of Ranvier. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:97–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taglialatela M., Vandongen A. M., Drewe J. A., Joho R. H., Brown A. M., Kirsch G. E. Patterns of internal and external tetraethylammonium block in four homologous K+ channels. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;40(2):299–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang S., Mikala G., Bahinski A., Yatani A., Varadi G., Schwartz A. Molecular localization of ion selectivity sites within the pore of a human L-type cardiac calcium channel. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13026–13029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanDongen A. M., Frech G. C., Drewe J. A., Joho R. H., Brown A. M. Alteration and restoration of K+ channel function by deletions at the N- and C-termini. Neuron. 1990 Oct;5(4):433–443. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90082-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warmke J., Drysdale R., Ganetzky B. A distinct potassium channel polypeptide encoded by the Drosophila eag locus. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1560–1562. doi: 10.1126/science.1840699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Ellinor P. T., Sather W. A., Zhang J. F., Tsien R. W. Molecular determinants of Ca2+ selectivity and ion permeation in L-type Ca2+ channels. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):158–161. doi: 10.1038/366158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


