Abstract
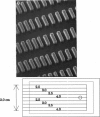
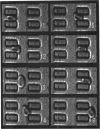
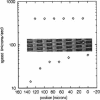
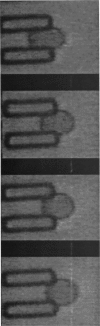
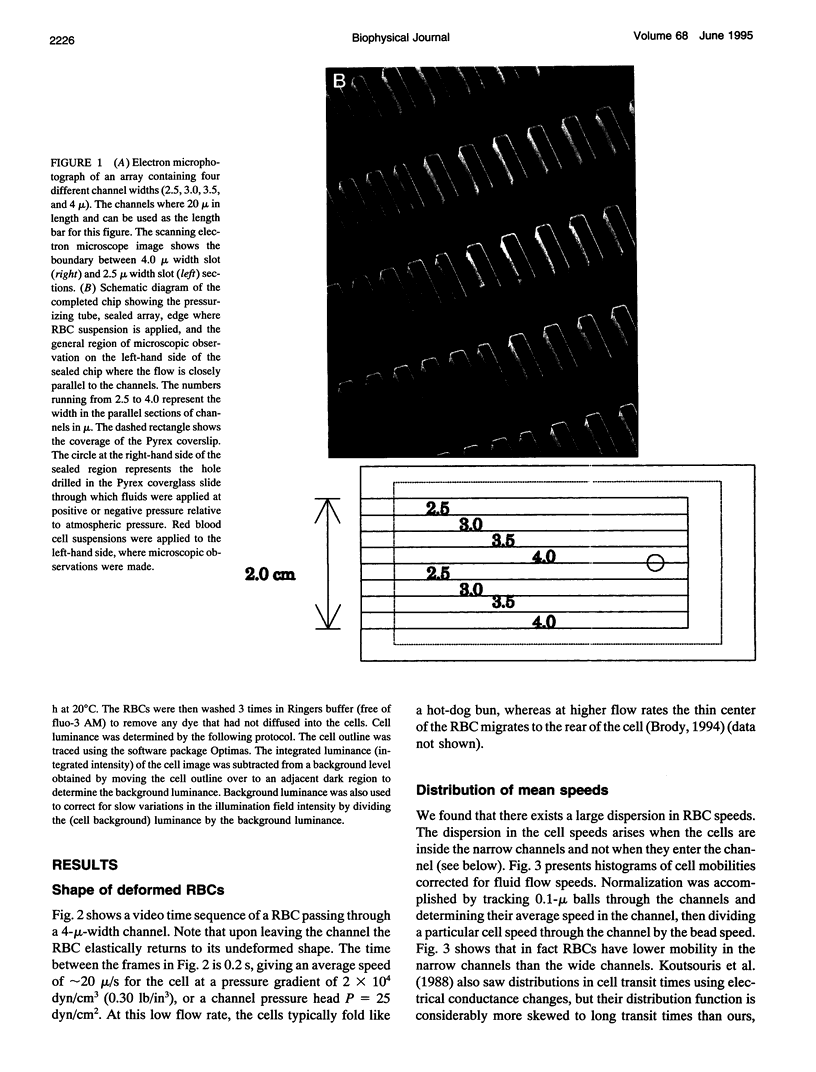
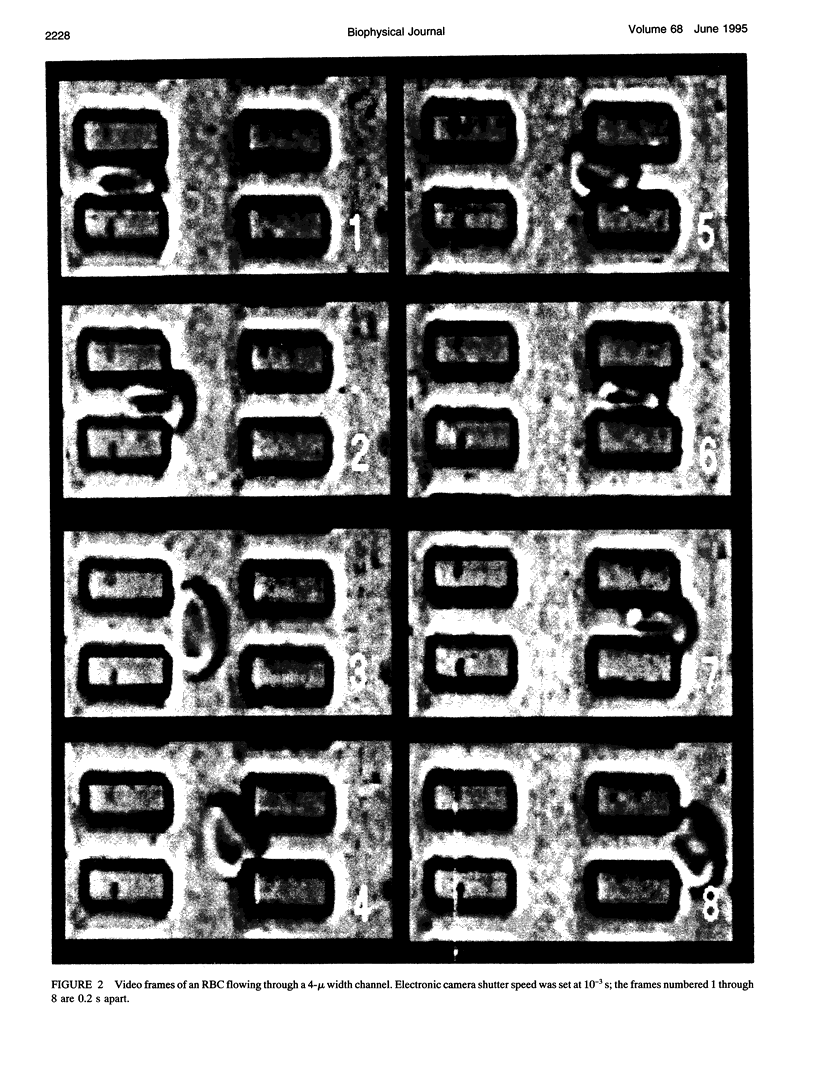
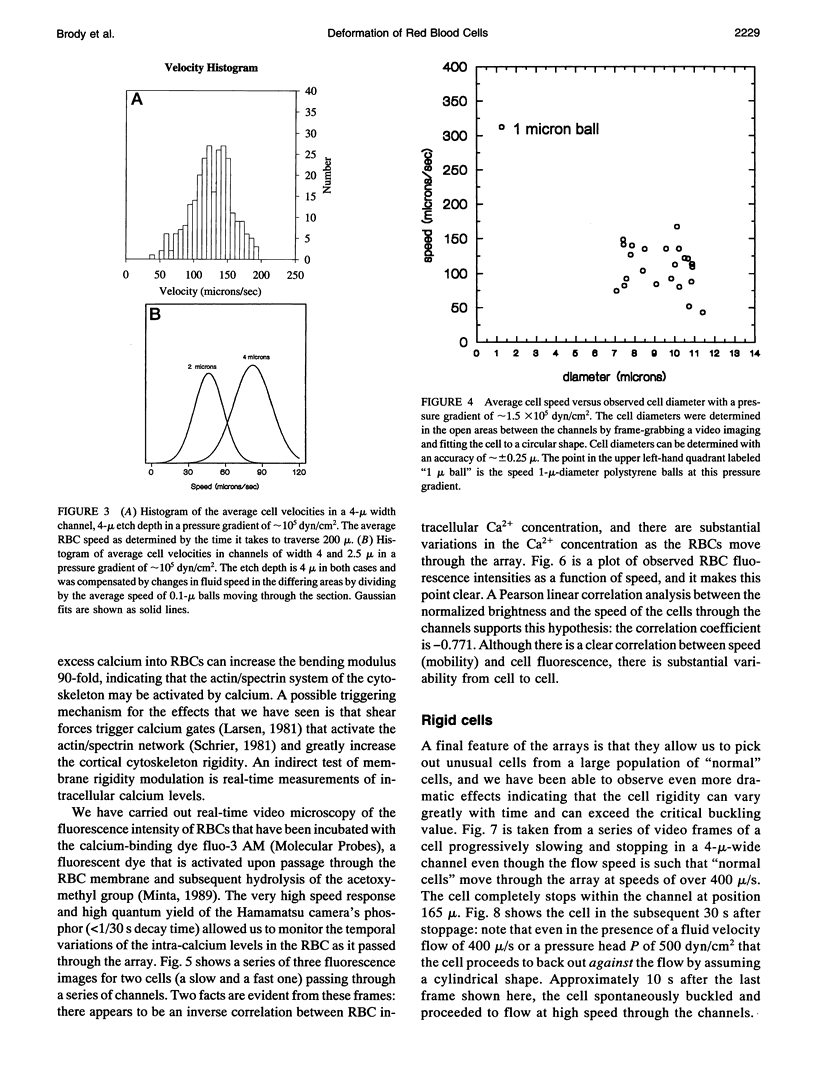
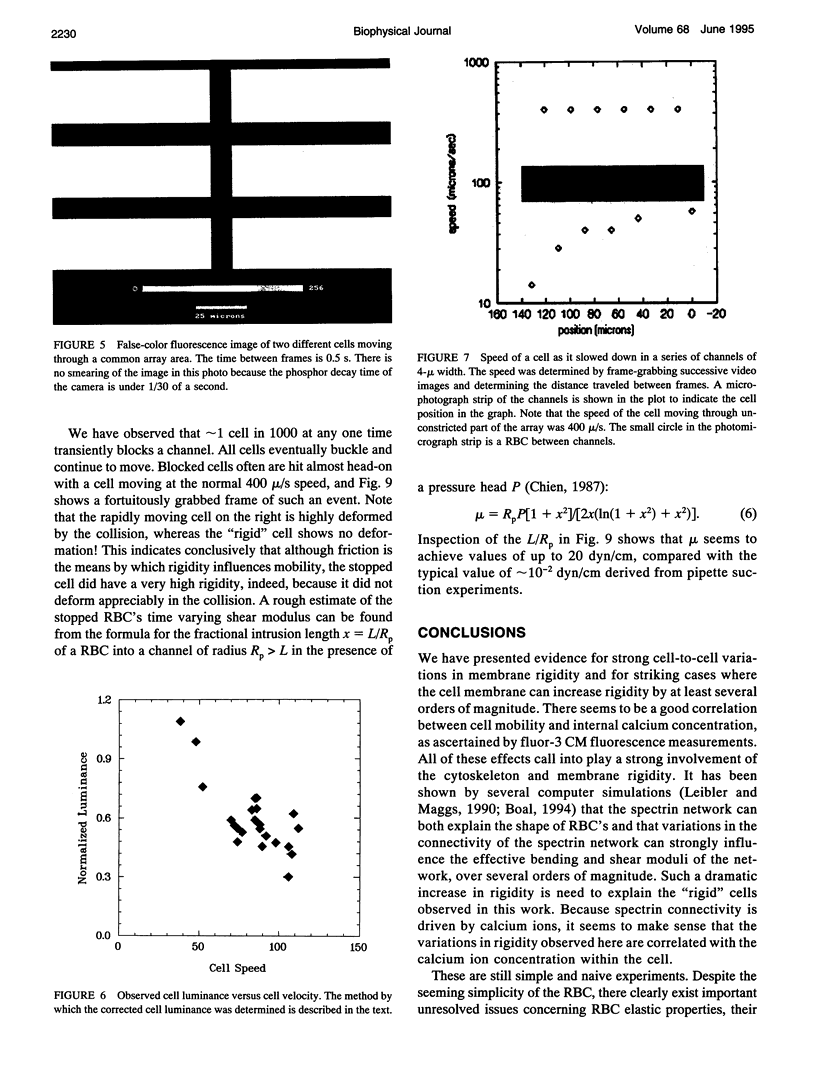
We introduce the use of microfabrication techniques to construct on a silicon wafer a synthetic capillary bed with 2.5- to 4-micron (mu)-wide channels. Establishment of a fluid pressure gradient allowed us to observe simultaneously using optical microscopy hundreds of cells flowing through the bed at physiological speeds. We find a large distribution of mobilities among red cells flowing through the structure; smaller channels provide a greater impedance to flow than larger ones, indicating that kinetic drag variations provide the origin of the distribution. The mobility of a particular cell is not correlated with the cell diameter but appears to be inversely correlated with intracellular calcium concentration of the cell, as determined by fluorescence of the calcium-binding dye fluo-3 AM. Also, we are able to use the parallel processing nature of our arrays to observe isolated events where the rigidity of the red cell seems to change suddenly over several orders of magnitude as it blocks a channel in the array.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boal D. H. Computer simulation of a model network for the erythrocyte cytoskeleton. Biophys J. 1994 Aug;67(2):521–529. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80511-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien S. Red cell deformability and its relevance to blood flow. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:177–192. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.001141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A. Bending elastic modulus of red blood cell membrane derived from buckling instability in micropipet aspiration tests. Biophys J. 1983 Jul;43(1):27–30. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84319-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A. New membrane concept applied to the analysis of fluid shear- and micropipette-deformed red blood cells. Biophys J. 1973 Sep;13(9):941–954. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(73)86036-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., Skalak R. Mechanics and thermodynamics of biomembranes: part 1. CRC Crit Rev Bioeng. 1979 Oct;3(3):181–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer T. M. Bending stiffness of lipid bilayers: IV. Interpretation of red cell shape change. Biophys J. 1993 Aug;65(2):687–692. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81107-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles D. W., Chasis J. A., Evans E. A., Mohandas N. Cooperative action between band 3 and glycophorin A in human erythrocytes: immobilization of band 3 induced by antibodies to glycophorin A. Biophys J. 1994 May;66(5):1726–1732. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80965-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koutsouris D., Guillet R., Lelievre J. C., Guillemin M. T., Bertholom P., Beuzard Y., Boynard M. Determination of erythrocyte transit times through micropores. I--Basic operational principles. Biorheology. 1988;25(5):763–772. doi: 10.3233/bir-1988-25504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koutsouris D., Guillet R., Wenby R. B., Meiselman H. J. Determination of erythrocyte transit times through micropores. II-- Influence of experimental and physicochemical factors. Biorheology. 1988;25(5):773–790. doi: 10.3233/bir-1988-25505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowluru R., Bitensky M. W., Kowluru A., Dembo M., Keaton P. A., Buican T. Reversible sodium pump defect and swelling in the diabetic rat erythrocyte: effects on filterability and implications for microangiopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3327–3331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen F. L., Katz S., Roufogalis B. D., Brooks D. E. Physiological shear stresses enhance the Ca2+ permeability of human erythrocytes. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):667–668. doi: 10.1038/294667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibler S., Maggs A. C. Simulation of shape changes and adhesion phenomena in an elastic model of erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6433–6435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minta A., Kao J. P., Tsien R. Y. Fluorescent indicators for cytosolic calcium based on rhodamine and fluorescein chromophores. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8171–8178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier S. L., Hardy B., Junga I., Ma L. Actin-activated ATPase in human red cell membranes. Blood. 1981 Nov;58(5):953–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]