Abstract
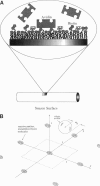
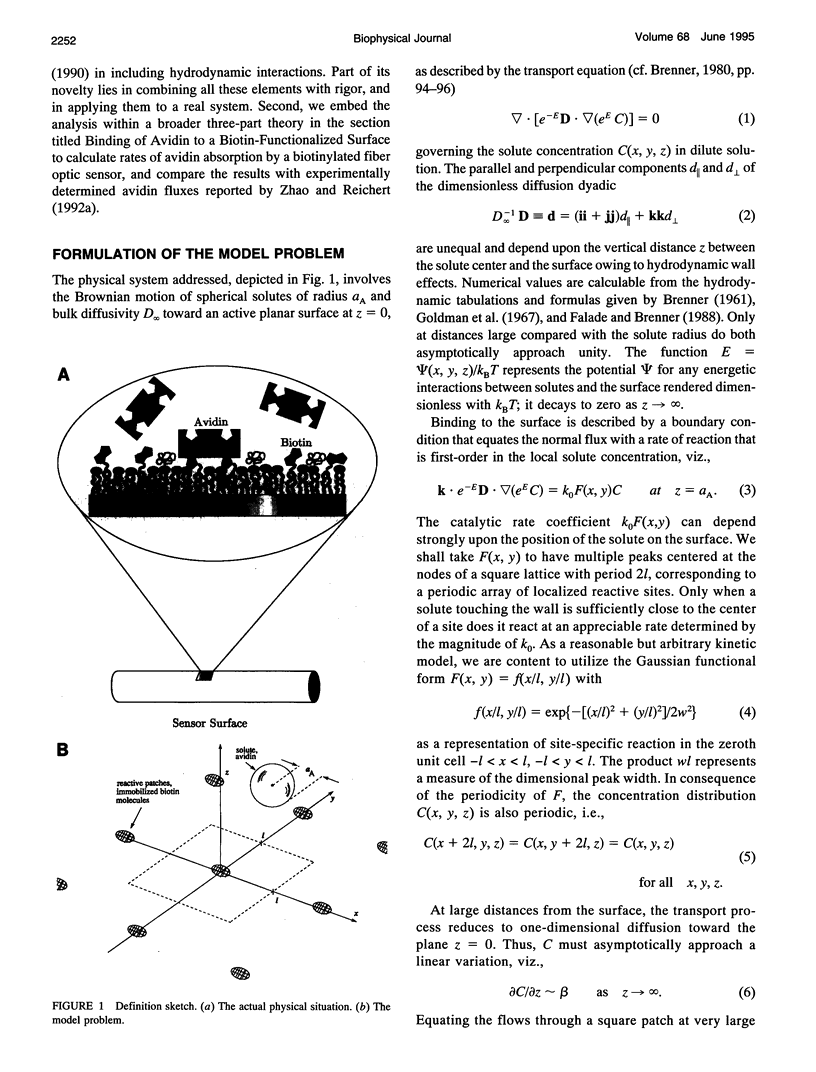
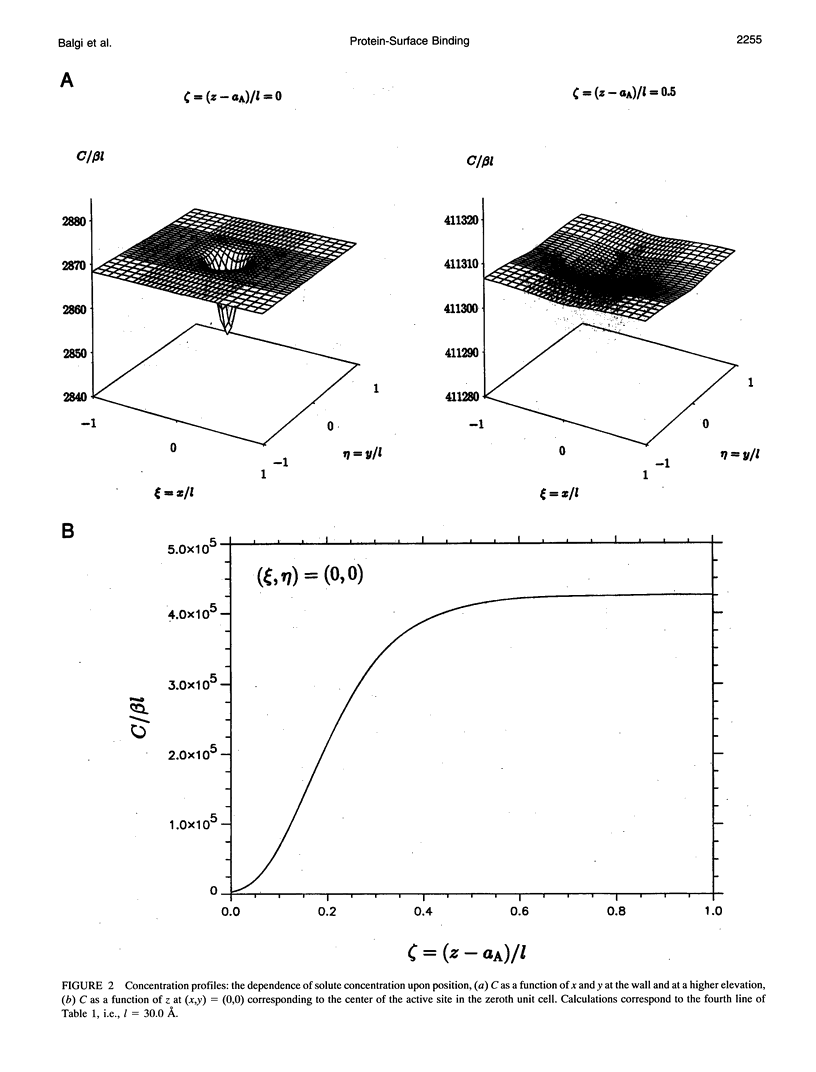
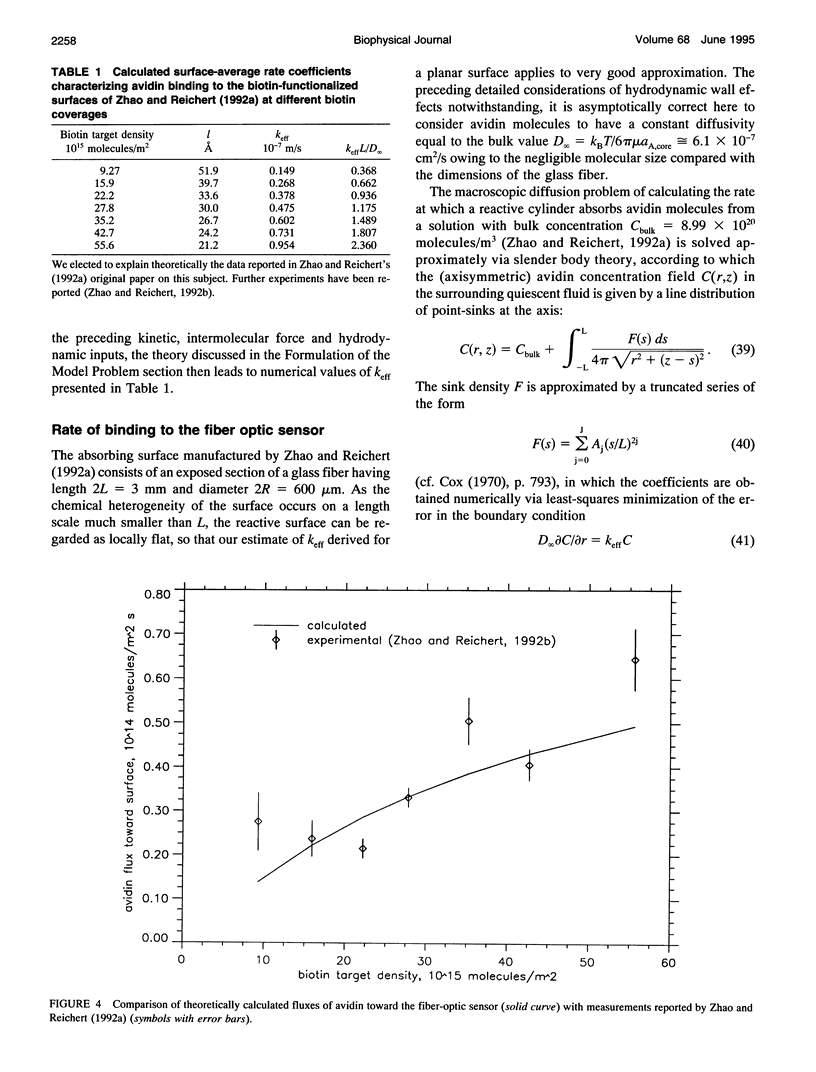
A detailed model is presented for protein binding to active surfaces, with application to the binding of avidin molecules to a biotin-functionalized fiber optic sensor in experiments reported by S. Zhao and W. M. Reichert (American Chemical Society Symposium Series 493, 1992). Kinetic data for binding in solution are used to assign an intrinsic catalytic rate coefficient k to the biotin-avidin pair, deconvoluted from transport and electrostatic factors via application of coagulation theory. This intrinsic chemical constant is built into a reaction-diffusion analysis of surface binding where activity is restricted to localized sites (representing immobilized biotin molecules). The analysis leads to an effective catalytic rate coefficient keff characterizing the active surface. Thereafter, solution of the transport problem describing absorption of avidin molecules by the macroscopic sensor surface leads to predictions of the avidin flux, which are found to be in good agreement with the experimental data. The analysis suggests the following conclusions. 1) Translational diffusion limitations are negligible for avidin-biotin binding in solution owing to the small (kinetically limiting) value k = 0.00045 m/s. 2) The sparse distribution of biotin molecules and the presence of a repulsive hydration force produce an effective surface-average catalytic rate coefficient keff of order 10(-7) m/s, much smaller than k. 3) Avidin binding to the fiber optic sensor occurs in an intermediate regime where the rate is influenced by both kinetics and diffusion.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlers M., Grainger D. W., Herron J. N., Lim K., Ringsdorf H., Salesse C. Quenching of fluorescein-conjugated lipids by antibodies. Quantitative recognition and binding of lipid-bound haptens in biomembrane models, formation of two-dimensional protein domains and molecular dynamics simulations. Biophys J. 1992 Sep;63(3):823–838. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81645-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison S. A., Ganti G., McCammon J. A. Simulation of the diffusion-controlled reaction between superoxide and superoxide dismutase. I. Simple models. Biopolymers. 1985 Jul;24(7):1323–1336. doi: 10.1002/bip.360240717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Purcell E. M. Physics of chemoreception. Biophys J. 1977 Nov;20(2):193–219. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85544-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg O. G., Blomberg C. Association kinetics with coupled diffusion III. Ionic-strength dependence of the lac repressor-operator association. Biophys Chem. 1978 Sep;8(4):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(78)80010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg O. G., Blomberg C. Association kinetics with coupled diffusion. An extension to coiled-chain macromolecules applied to the lac repressor-operator system. Biophys Chem. 1977 Jun;7(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(77)87012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg O. G., Blomberg C. Association kinetics with coupled diffusional flows. Special application to the lac repressor--operator system. Biophys Chem. 1976 Jul;4(4):367–381. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(76)80017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg O. G., von Hippel P. H. Diffusion-controlled macromolecular interactions. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1985;14:131–160. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.14.060185.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisi C., Wiegel F. W. Effect of nonspecific forces and finite receptor number on rate constants of ligand--cell bound-receptor interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5569–5572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebato H., Gentry C. A., Herron J. N., Müller W., Okahata Y., Ringsdorf H., Suci P. A. Investigation of specific binding of antifluorescyl antibody and Fab to fluorescein lipids in Langmuir-Blodgett deposited films using quartz crystal microbalance methodology. Anal Chem. 1994 May 15;66(10):1683–1689. doi: 10.1021/ac00082a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leckband D. E., Schmitt F. J., Israelachvili J. N., Knoll W. Direct force measurements of specific and nonspecific protein interactions. Biochemistry. 1994 Apr 19;33(15):4611–4624. doi: 10.1021/bi00181a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livnah O., Bayer E. A., Wilchek M., Sussman J. L. Three-dimensional structures of avidin and the avidin-biotin complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5076–5080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Ringsdorf H., Rump E., Wildburg G., Zhang X., Angermaier L., Knoll W., Liley M., Spinke J. Attempts to mimic docking processes of the immune system: recognition-induced formation of protein multilayers. Science. 1993 Dec 10;262(5140):1706–1708. doi: 10.1126/science.8259513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter P. H., Eigen M. Diffusion controlled reaction rates in spheroidal geometry. Application to repressor--operator association and membrane bound enzymes. Biophys Chem. 1974 Oct;2(3):255–263. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(74)80050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Spinke J., Bayerl T., Sackmann E., Knoll W. Streptavidin binding to biotinylated lipid layers on solid supports. A neutron reflection and surface plasmon optical study. Biophys J. 1992 Nov;63(5):1385–1392. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81715-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt F. J., Knoll W. Surface-plasmon microscopic observation of site-selective recognition reactions. Biophys J. 1991 Sep;60(3):716–720. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82101-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoup D., Szabo A. Role of diffusion in ligand binding to macromolecules and cell-bound receptors. Biophys J. 1982 Oct;40(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84455-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou H. X. Brownian dynamics study of the influences of electrostatic interaction and diffusion on protein-protein association kinetics. Biophys J. 1993 Jun;64(6):1711–1726. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81543-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwanzig R. Diffusion-controlled ligand binding to spheres partially covered by receptors: an effective medium treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5856–5857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwanzig R., Szabo A. Time dependent rate of diffusion-influenced ligand binding to receptors on cell surfaces. Biophys J. 1991 Sep;60(3):671–678. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82096-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]