Abstract
The passive permeation of glucose and a small zwitterionic molecule, methyl-phosphoethanolamine, across two-component phospholipid bilayers (dimyristoyl phosphatidylcholine (DMPC)/dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine (DPPC) mixtures) exhibit a maximum when gel domains and fluid domains coexist. The permeability data of the two-phase bilayers cannot be fitted to single-rate kinetics, but are consistent with a Gaussian distribution of rate constants. In pure DMPC and DPPC as well as in their mixtures, at the temperature of the maximum excess heat capacity, the logarithm of the average permeability rate constants are linearly correlated with the mole fraction of DPPC in the total system. In addition, in the 50:50 mixture, the excess heat capacity values as well as the apparent fractions of interfacial lipid correlate with the logarithm of the excess permeabilities in the two-phase region. These results suggest that small polar molecules can cross the membrane at the interface between gel and fluid domains at a much faster rate than through the homogeneous phases; the acyl chains located at the domain interface experience lateral density fluctuations that are inversely proportional to their average length, and large enough to allow rapid transmembrane diffusion of the solute molecules. The distribution of the permeability rate constants may reflect temporal and spatial fluctuations of the lipid composition at the phase boundaries.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benga G., Popescu O., Borza V., Pop V. I., Hodârnău A. Water exchange through erythrocyte membranes: biochemical and nuclear magnetic resonance studies re-evaluating the effects of sulfhydryl reagents and of proteolytic enzymes on human membranes. J Membr Biol. 1989 May;108(2):105–113. doi: 10.1007/BF01871022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blok M. C., van der Neut-Kok E. C., van Deenen L. L., de Gier J. The effect of chain length and lipid phase transitions on the selective permeability properties of liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 6;406(2):187–196. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahm J. Diffusional water permeability of human erythrocytes and their ghosts. J Gen Physiol. 1982 May;79(5):791–819. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.5.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramhall J., Hofmann J., DeGuzman R., Montestruque S., Schell R. Temperature dependence of membrane ion conductance analyzed by using the amphiphilic anion 5/6-carboxyfluorescein. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 6;26(20):6330–6340. doi: 10.1021/bi00394a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruzeiro-Hansson L., Mouritsen O. G. Passive ion permeability of lipid membranes modelled via lipid-domain interfacial area. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Sep 15;944(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90316-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eibl H. Phospholipid synthesis: Oxazaphospholanes and dioxaphospholanes as intermediates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4074–4077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster S., Lloyd J. B. Solute translocation across the mammalian lysosome membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Oct 11;947(3):465–491. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freire E., Biltonen R. Estimation of molecular averages and equilibrium fluctuations in lipid bilayer systems from the excess heat capacity function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 4;514(1):54–68. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimburg T., Marsh D. Investigation of secondary and tertiary structural changes of cytochrome c in complexes with anionic lipids using amide hydrogen exchange measurements: an FTIR study. Biophys J. 1993 Dec;65(6):2408–2417. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81299-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfer U. Kinetic criteria for carrier-mediated transport mechanisms in membrane vesicles. Fed Proc. 1981 Aug;40(10):2480–2485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ipsen J. H., Jørgensen K., Mouritsen O. G. Density fluctuations in saturated phospholipid bilayers increase as the acyl-chain length decreases. Biophys J. 1990 Nov;58(5):1099–1107. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82452-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEDEM O., KATCHALSKY A. Thermodynamic analysis of the permeability of biological membranes to non-electrolytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Feb;27(2):229–246. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90330-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieb W. R., Stein W. D. Biological membranes behave as non-porous polymeric sheets with respect to the diffusion of non-electrolytes. Nature. 1969 Oct 18;224(5216):240–243. doi: 10.1038/224240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden C. D., Wright K. L., McConnell H. M., Fox C. F. Lateral phase separations in membrane lipids and the mechanism of sugar transport in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2271–2275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
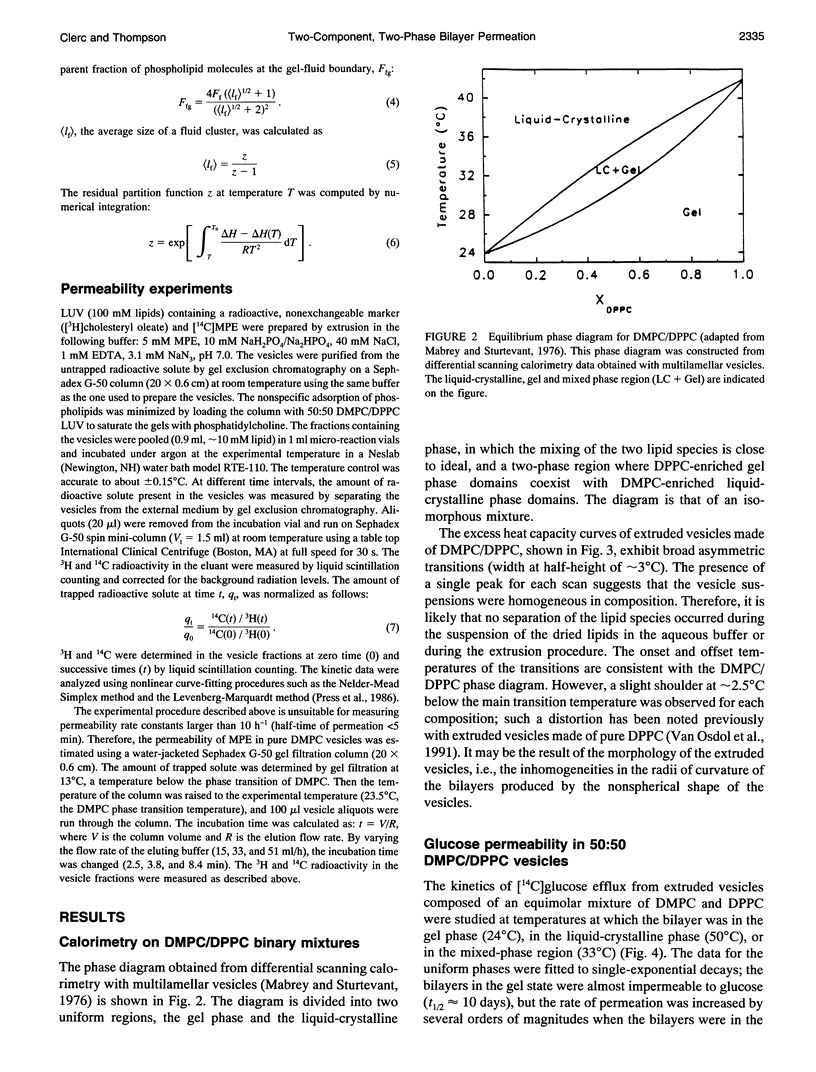
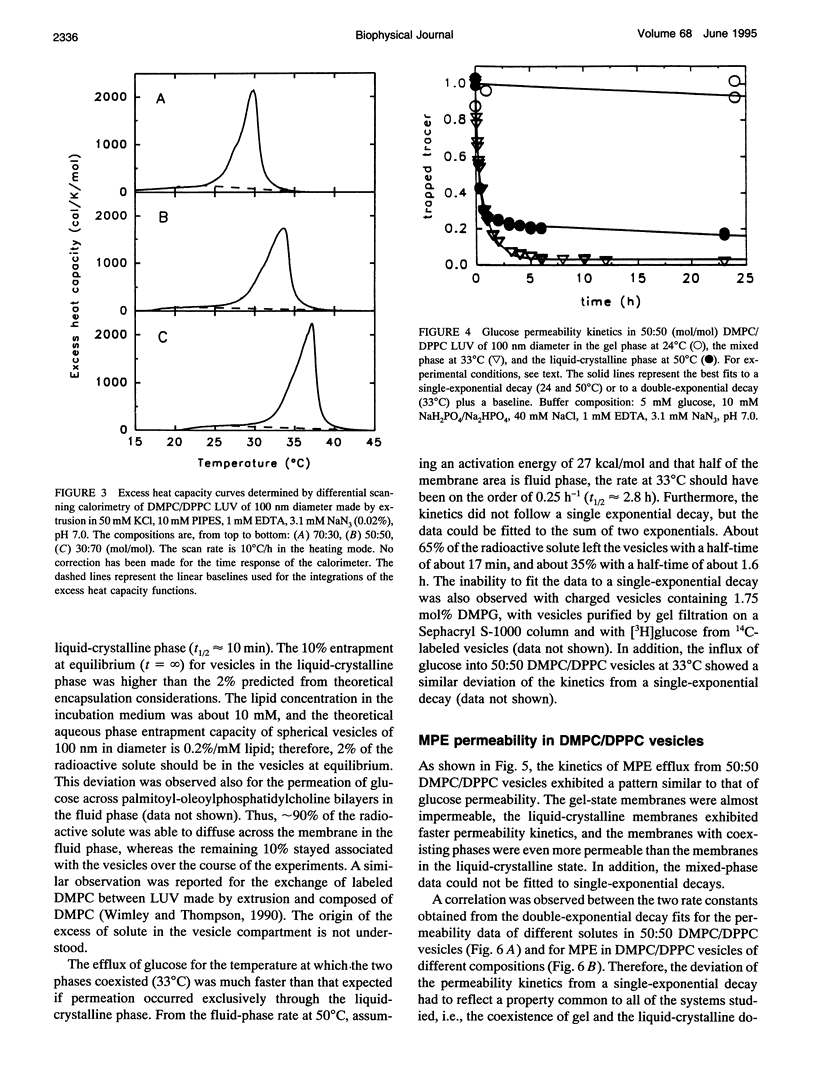
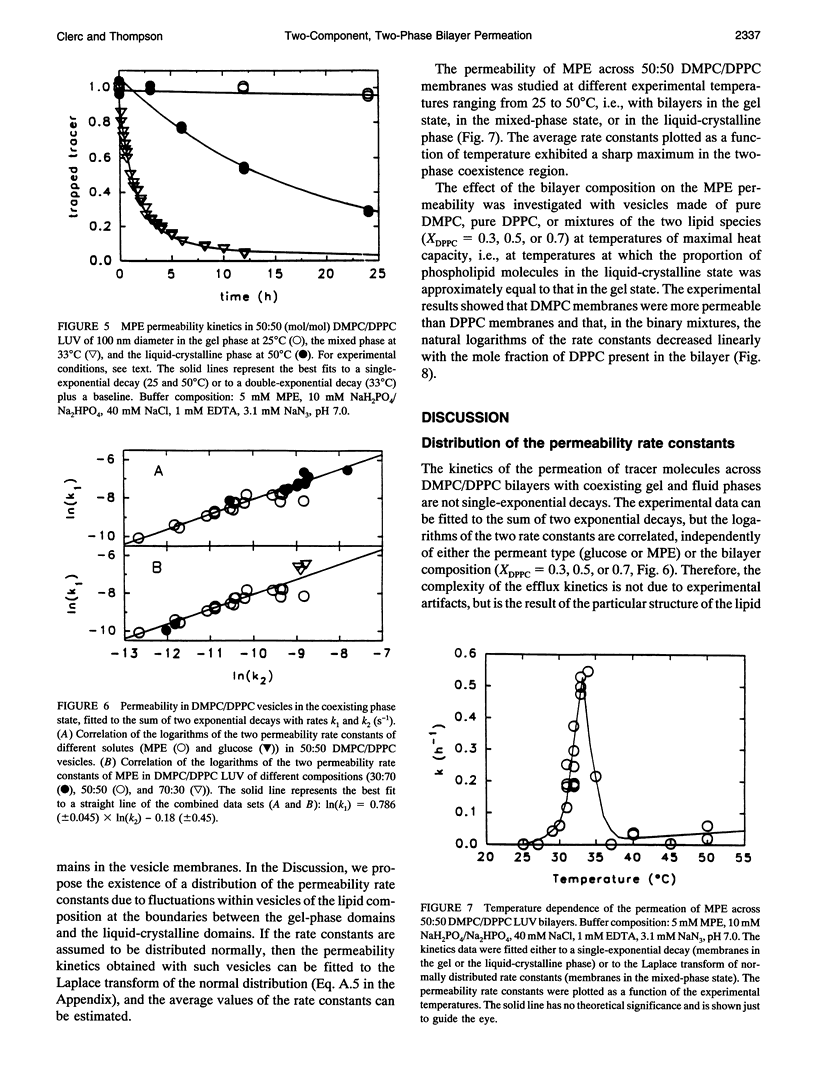
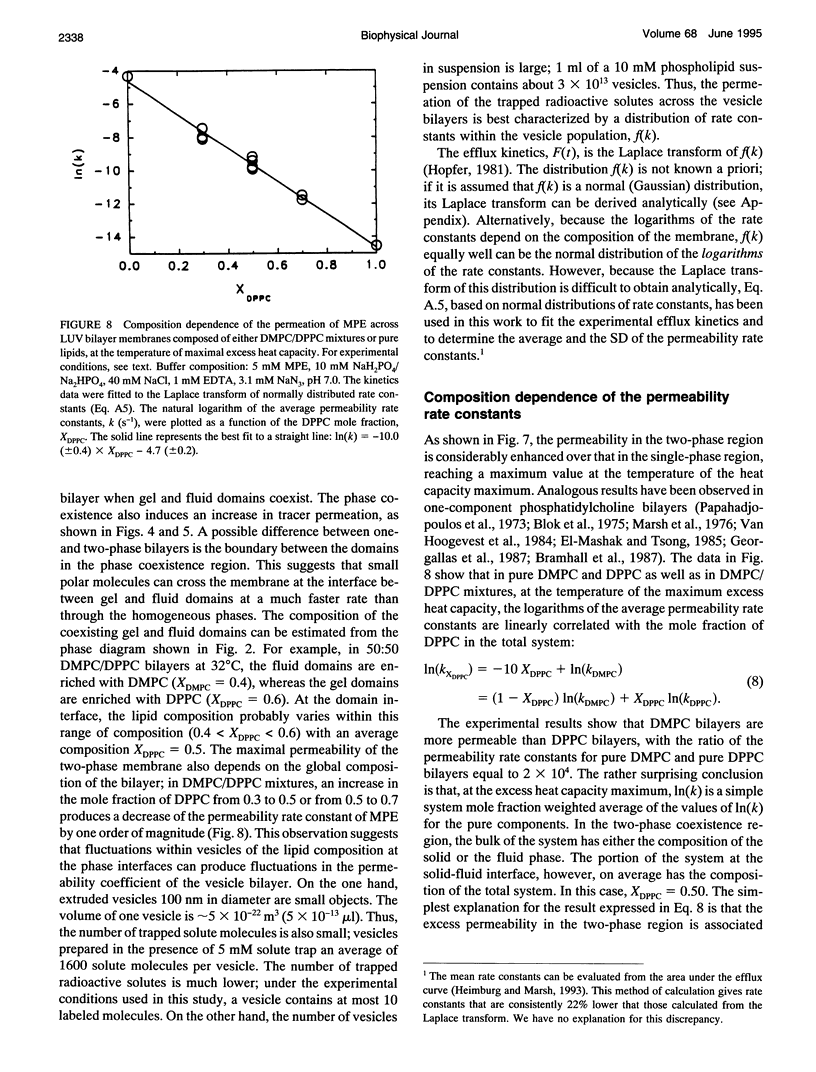
- Mabrey S., Sturtevant J. M. Investigation of phase transitions of lipids and lipid mixtures by sensitivity differential scanning calorimetry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3862–3866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Scott H. L., Jr Lateral compressibility of lipid mono- and bilayers. Theory of membrane permeability. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 2;513(2):236–243. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Jacobson K., Nir S., Isac T. Phase transitions in phospholipid vesicles. Fluorescence polarization and permeability measurements concerning the effect of temperature and cholesterol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 6;311(3):330–348. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90314-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitterich H., Lawaczeck R. On the water and proton permeabilities across membranes from erythrocyte ghosts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 5;821(2):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90092-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. C. Colorimetric determination of phospholipids with ammonium ferrothiocyanate. Anal Biochem. 1980 May 1;104(1):10–14. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90269-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimley W. C., Thompson T. E. Exchange and flip-flop of dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine in liquid-crystalline, gel, and two-component, two-phase large unilamellar vesicles. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 6;29(5):1296–1303. doi: 10.1021/bi00457a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye R. G., Verkman A. S. Simultaneous optical measurement of osmotic and diffusional water permeability in cells and liposomes. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):824–829. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Mashak E. M., Tsong T. Y. Ion selectivity of temperature-induced and electric field induced pores in dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine vesicles. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 4;24(12):2884–2888. doi: 10.1021/bi00333a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Osdol W. W., Johnson M. L., Ye Q., Biltonen R. L. Relaxation dynamics of the gel to liquid-crystalline transition of phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Effects of chainlength and vesicle size. Biophys J. 1991 Apr;59(4):775–785. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82290-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Dreele P. H. Estimation of lateral species separation from phase transitions in nonideal two-dimensional lipid mixtures. Biochemistry. 1978 Sep 19;17(19):3939–3943. doi: 10.1021/bi00612a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


