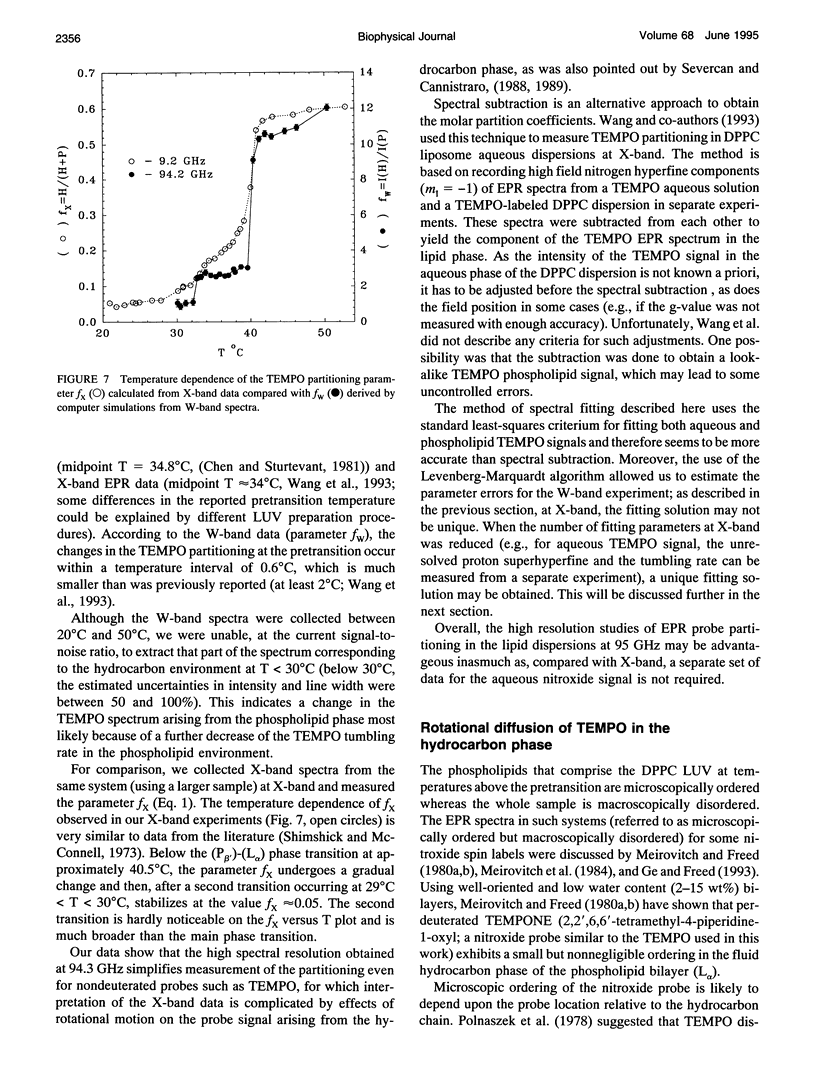
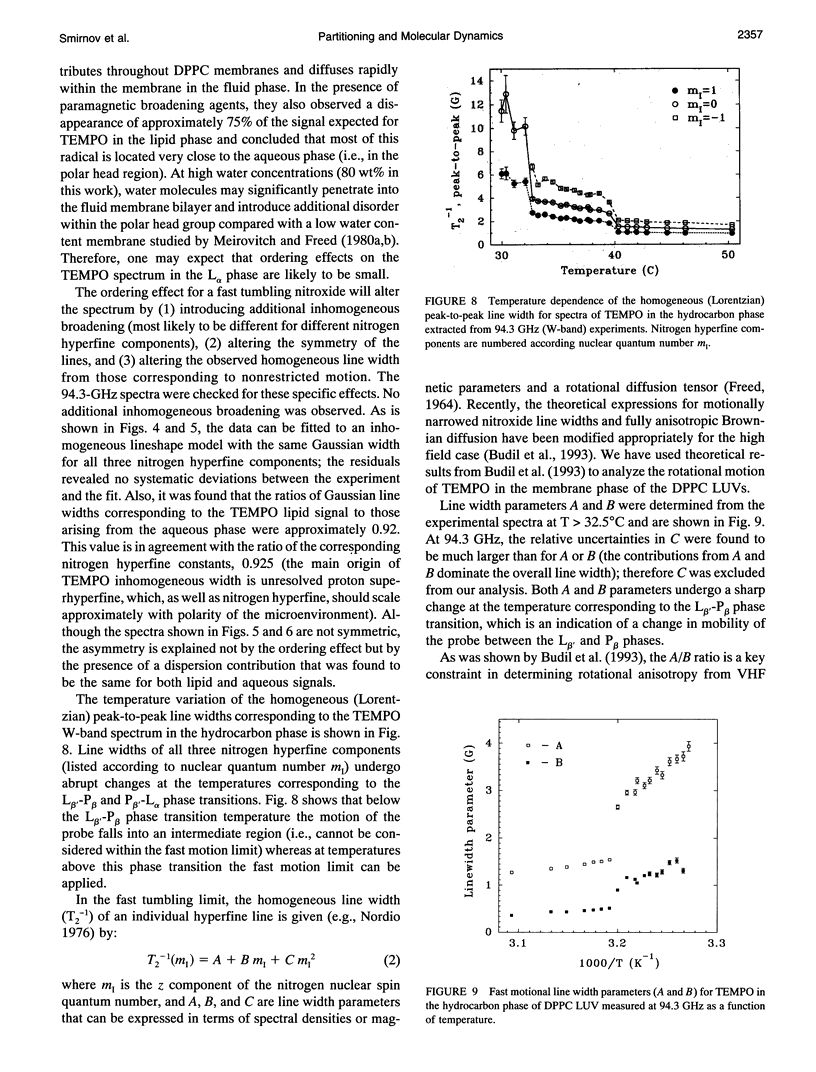
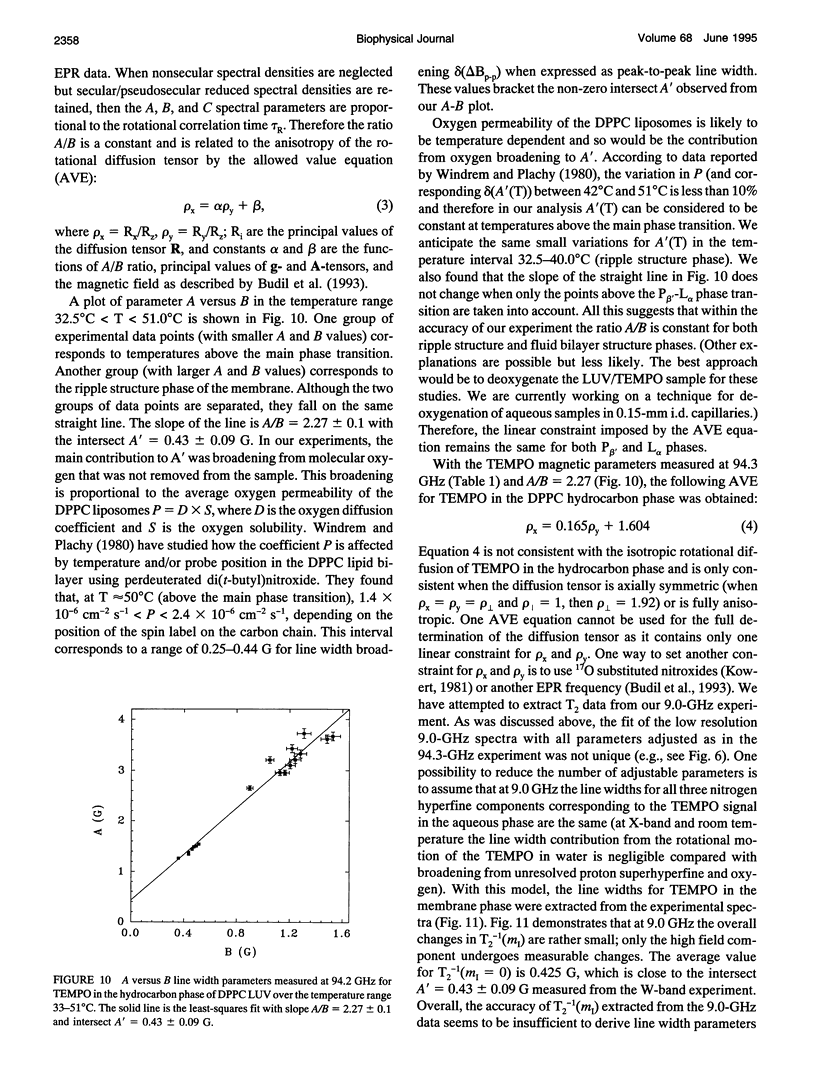
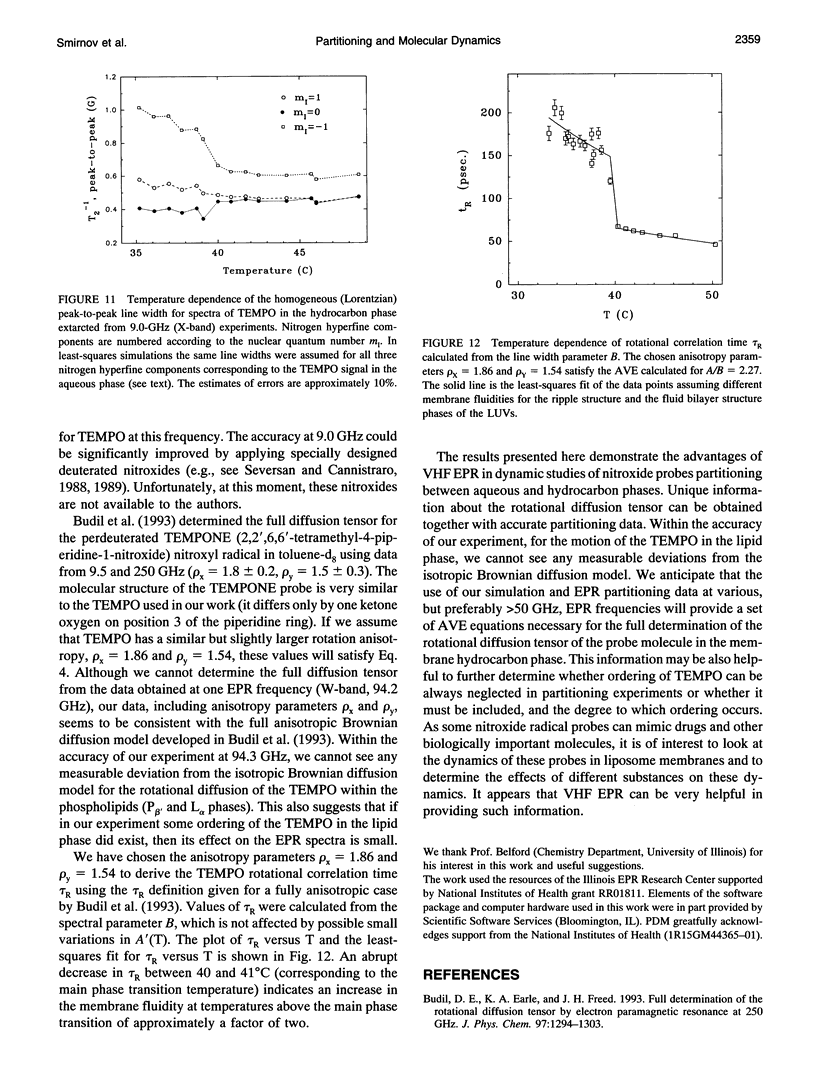
Abstract
Partitioning and molecular dynamics of 2,2,6,6,-tetramethylpiperedine-1-oxyl (TEMPO) nitroxide radicals in large unilamellar liposomes (LUV) composed from 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylcholine were investigated by using very high frequency electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy. Experiments carried out at a microwave frequency of 94.3 GHz completely resolved the TEMPO EPR spectrum in the aqueous and hydrocarbon phases. An accurate computer simulation method combined with Levenberg-Marquardt optimization was used to analyze the TEMPO EPR spectra in both phases. Spectral parameters extracted from the simulations gave the actual partitioning of the TEMPO probe between the LUV hydrocarbon and aqueous phases and allowed analysis of picosecond rotational dynamics of the probe in the LUV hydrocarbon phase. In very high frequency EPR experiments, phase transitions in the LUV-TEMPO system were observed as sharp changes in both partitioning and rotational correlation times of the TEMPO probe. The phase transition temperatures (40.5 +/- 0.2 and 32.7 +/- 0.5 degrees C) are in agreement with previously reported differential scanning microcalorimetry data. Spectral line widths were analyzed by using existing theoretical expressions for motionally narrowed nitroxide spectra. It was found that the motion of the small, nearly spherical, TEMPO probe can be well described by anisotropic Brownian diffusion in isotropic media and is not restricted by the much larger hydrocarbon chains existing in ripple structure (P beta') or fluid bilayer structure (L alpha) phases.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloomfield V. Editorial. Biophys J. 1993 Jul;65(1):1–1. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81020-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. C., Sturtevant J. M. Thermotropic behavior of bilayers formed from mixed-chain phosphatidylcholines. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):713–718. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crepeau R. H., Saxena S., Lee S., Patyal B., Freed J. H. Studies on lipid membranes by two-dimensional Fourier transform ESR: Enhancement of resolution to ordering and dynamics. Biophys J. 1994 May;66(5):1489–1504. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80940-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge M., Freed J. H. An electron spin resonance study of interactions between gramicidin A' and phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biophys J. 1993 Nov;65(5):2106–2123. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81255-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong-wei S., McConnell H. Phase separations in phospholipd membranes. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 25;14(4):847–854. doi: 10.1021/bi00675a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith A. D., Snipes W. Viscosity of cellular protoplasm. Science. 1974 Feb 15;183(4125):666–668. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4125.666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. G., Birdsall N. J., Metcalfe J. C., Toon P. A., Warren G. B. Clusters in lipid bilayers and the interpretation of thermal effects in biological membranes. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 27;13(18):3699–3705. doi: 10.1021/bi00715a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden C. D., Wright K. L., McConnell H. M., Fox C. F. Lateral phase separations in membrane lipids and the mechanism of sugar transport in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2271–2275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L. D., Hope M. J., Cullis P. R. Vesicles of variable sizes produced by a rapid extrusion procedure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 13;858(1):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90302-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto Y., Hosokawa M., Sayo H., Takeuchi Y. ESR study of membrane perturbation and the lysis of liposomes induced by chlorpromazine. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1994 Jan;42(1):123–129. doi: 10.1248/cpb.42.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse P. D., 2nd Use of the spin label tempamine for measuring the internal viscosity of red blood cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 22;77(4):1486–1491. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier S., Polnaszek C. F., Smith I. C. Spin labels in membranes. Problems in practice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 15;515(4):395–436. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severcan F., Cannistraro S. Model membrane partition ESR study in the presence of alpha-tocopherol by a new spin probe. Biosci Rep. 1989 Aug;9(4):489–495. doi: 10.1007/BF01117052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimshick E. J., McConnell H. M. Lateral phase separation in phospholipid membranes. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 5;12(12):2351–2360. doi: 10.1021/bi00736a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smirnov A. I., Norby S. W., Walczak T., Liu K. J., Swartz H. M. Physical and instrumental considerations in the use of lithium phthalocyanine for measurements of the concentration of the oxygen. J Magn Reson B. 1994 Feb;103(2):95–102. doi: 10.1006/jmrb.1994.1016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subczynski W. K., Hyde J. S., Kusumi A. Oxygen permeability of phosphatidylcholine--cholesterol membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4474–4478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D. C., Taraschi T. F., Rubin E., Janes N. Configurational entropy is the driving force of ethanol action on membrane architecture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jan 18;1145(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90391-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windrem D. A., Plachy W. Z. The diffusion-solubility of oxygen in lipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 14;600(3):655–665. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90469-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


