Abstract
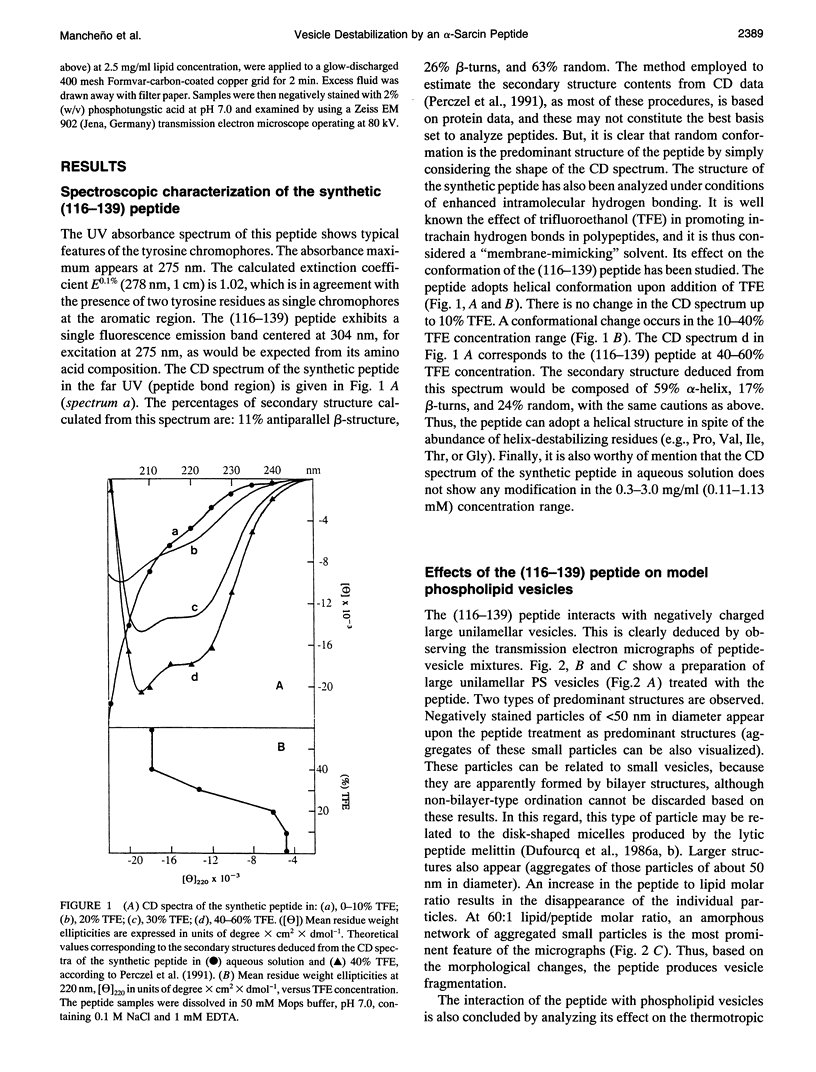
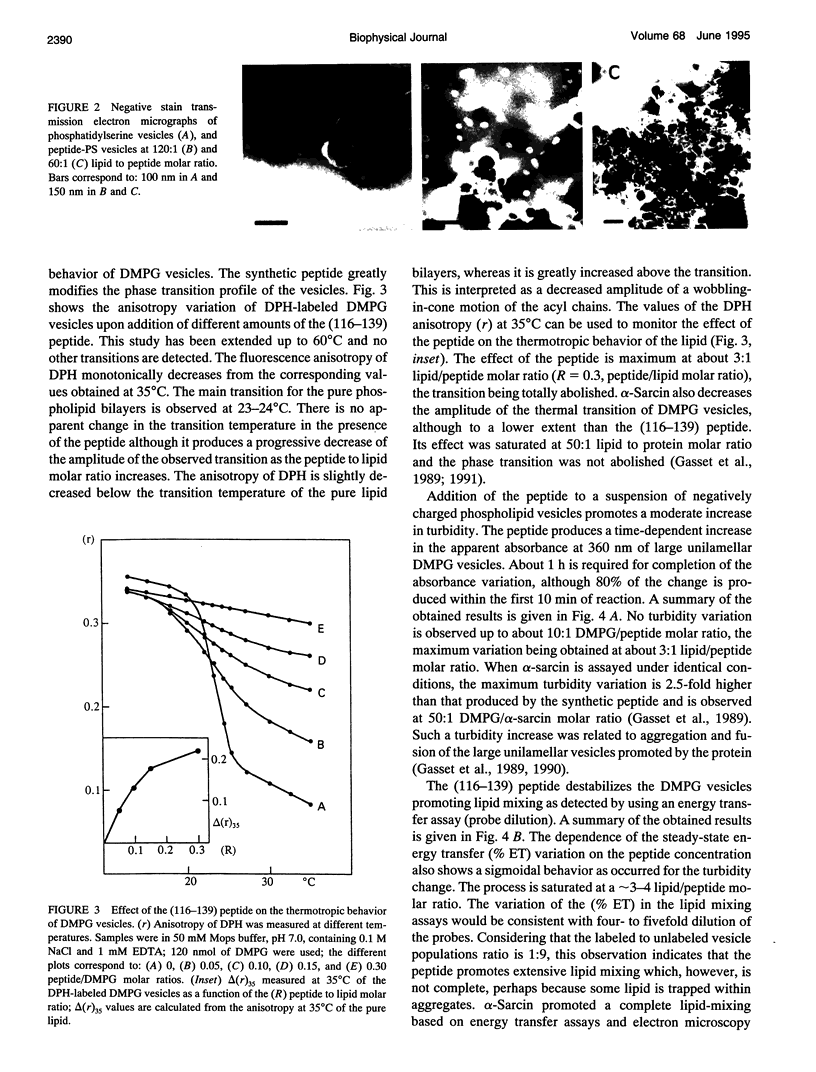
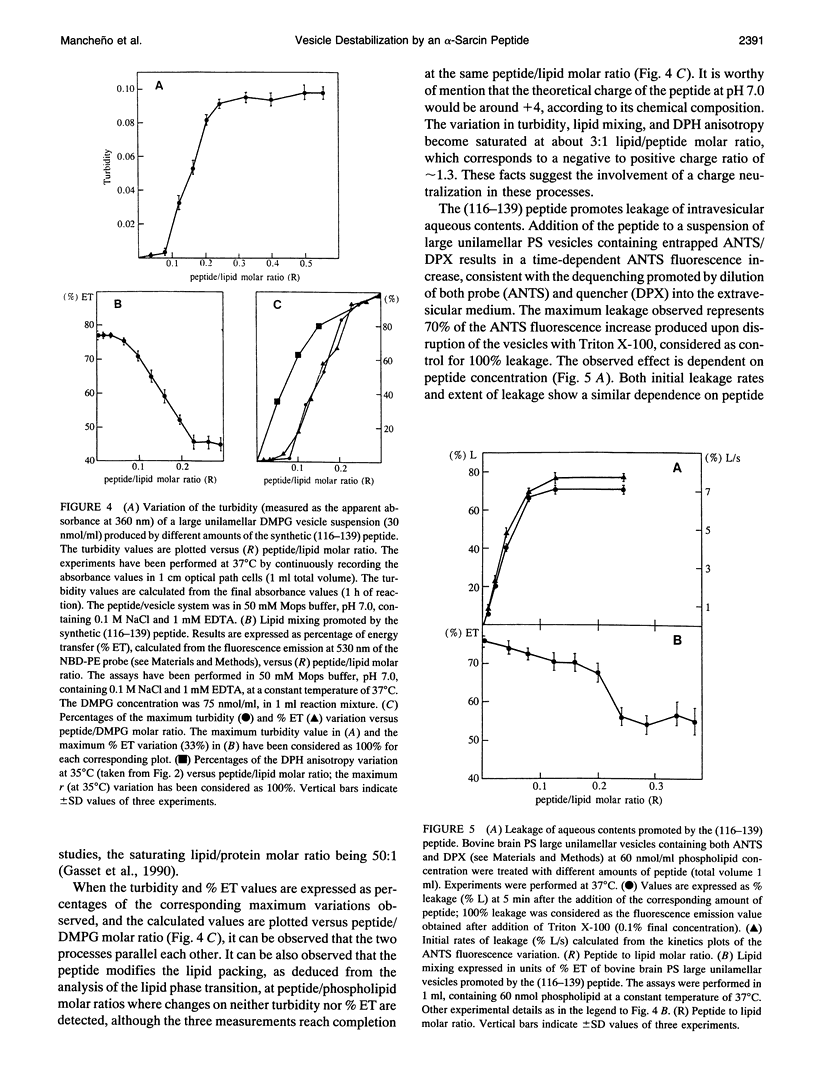
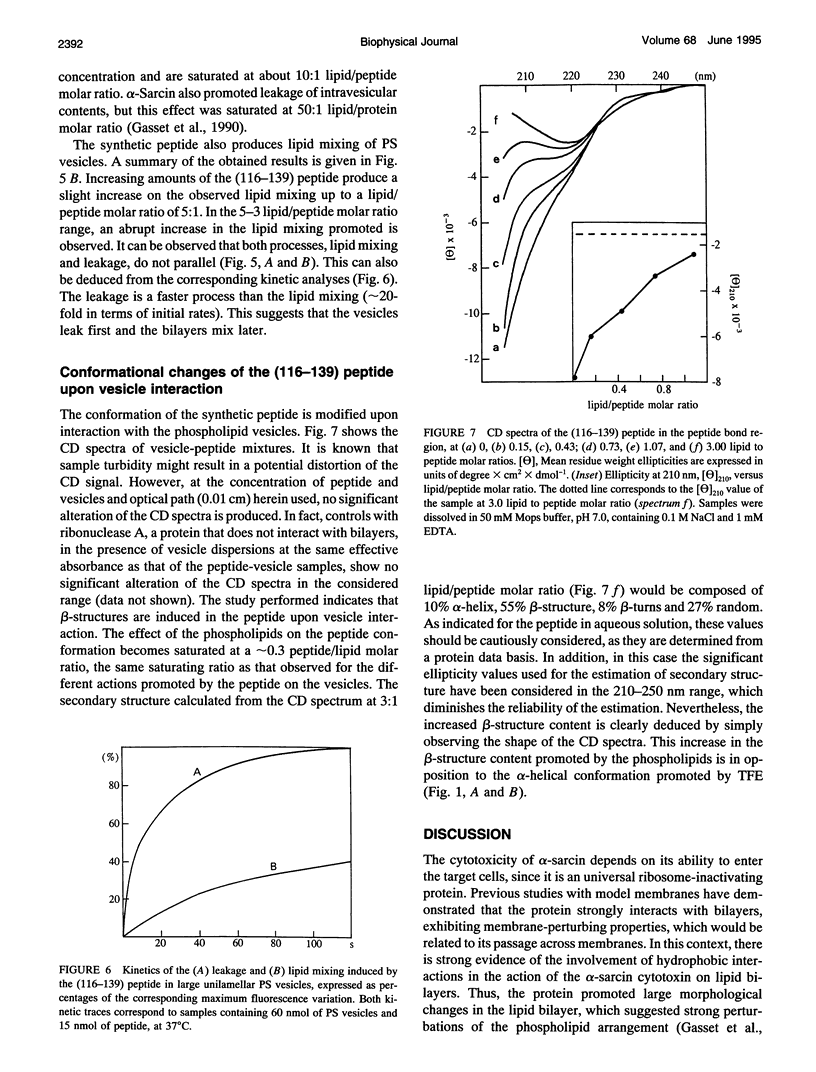
alpha-Sarcin is a cytotoxic protein that strongly interacts with acid phospholipid vesicles. This interaction exhibits a hydrophobic component although alpha-sarcin is a highly polar protein. A peptide comprising the amino acid sequence corresponding to the 116-139th segment of the alpha-sarcin cytotoxin has been synthesized by a standard fluoren-9-yl-methoxycarbonyl-based solid phase method. Its primary structure is: (116)-NPGPARVIYTYPNKVFCGIIAHTK-(139). Two beta-strands have been predicted in this region of alpha-sarcin, where the less polar stretches of the protein are found. The synthetic peptide interacts with negatively charged large unilamellar vesicles of either natural or synthetic phospholipids. An apparent fragmentation of the vesicles is produced by the peptide based on electron microscopy studies. The peptide promotes leakage of the intravesicular aqueous contents and lipid mixing of bilayers. The packing of the phospholipid molecules is greatly perturbed by the peptide, as deduced from the drastic changes induced by the peptide in cooperative properties associated with the phase transition of the bilayers. At saturating peptide/phospholipid ratios, the phase transition of dimyristoylphosphatidylglycerol vesicles is abolished. All of these effects are saturated at about 0.3 peptide/lipid molar ratio. The peptide adopts a mostly random structure in aqueous solution. A conformation composed of a high proportion of antiparallel beta-sheet is induced as a consequence of the interaction with the phospholipid vesicles in opposition to trifluoroethanol that promotes alpha-helical peptide structures, as deduced from circular dichroism measurements. The obtained results are discussed in terms of the potential involvement of the region comprising residues 116-139 of alpha-sarcin in the hydrophobic interactions of this cytotoxic protein with membranes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anantharamaiah G. M., Jones J. L., Brouillette C. G., Schmidt C. F., Chung B. H., Hughes T. A., Bhown A. S., Segrest J. P. Studies of synthetic peptide analogs of the amphipathic helix. Structure of complexes with dimyristoyl phosphatidylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10248–10255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Rudy B. Interactions between membranes and cytolytic peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 12;864(1):123–141. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(86)90018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouillette C. G., Jones J. L., Ng T. C., Kercret H., Chung B. H., Segrest J. P. Structural studies of apolipoprotein A-I/phosphatidylcholine recombinants by high-field proton NMR, nondenaturing gradient gel electrophoresis, and electron microscopy. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 17;23(2):359–367. doi: 10.1021/bi00297a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufourc E. J., Bonmatin J. M., Dufourcq J. Membrane structure and dynamics by 2H- and 31P-NMR. Effects of amphipatic peptidic toxins on phospholipid and biological membranes. Biochimie. 1989 Jan;71(1):117–123. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(89)90141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufourc E. J., Smith I. C., Dufourcq J. Molecular details of melittin-induced lysis of phospholipid membranes as revealed by deuterium and phosphorus NMR. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 21;25(21):6448–6455. doi: 10.1021/bi00369a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufourcq J., Faucon J. F., Fourche G., Dasseux J. L., Le Maire M., Gulik-Krzywicki T. Morphological changes of phosphatidylcholine bilayers induced by melittin: vesicularization, fusion, discoidal particles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jul 10;859(1):33–48. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90315-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellens H., Bentz J., Szoka F. C. H+- and Ca2+-induced fusion and destabilization of liposomes. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 18;24(13):3099–3106. doi: 10.1021/bi00334a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faucon J. F., Dufourcq J., Bernard E., Duchesneau L., Pézolet M. Abolition of the thermotropic transition of charged phospholipids induced by a cardiotoxin from Naja mossambica mossambica as detected by fluorescence polarization, differential scanning calorimetry, and Raman spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 26;22(9):2179–2185. doi: 10.1021/bi00278a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasset M., Martinez del Pozo A., Oñaderra M., Gavilanes J. G. Study of the interaction between the antitumour protein alpha-sarcin and phospholipid vesicles. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 1;258(2):569–575. doi: 10.1042/bj2580569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasset M., Oñaderra M., Martínez del Pozo A., Schiavo G. P., Laynez J., Usobiaga P., Gavilanes J. G. Effect of the antitumour protein alpha-sarcin on the thermotropic behaviour of acid phospholipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Sep 10;1068(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90055-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasset M., Oñaderra M., Thomas P. G., Gavilanes J. G. Fusion of phospholipid vesicles produced by the anti-tumour protein alpha-sarcin. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 1;265(3):815–822. doi: 10.1042/bj2650815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavilanes J. G., Lizarbe M. A., Munico A. M., Oñaderra M. Interaction of dipalmitoyl-phosphatidylcholine with calf thymus histone H1. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1985 Aug;26(2):187–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1985.tb03196.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. J., Epand R. M., Lin K. F., Walton D., Vail W. J. Size and shape of the model lipoprotein complex formed between glucagon and dimyristoylglycerophosphocholine. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2301–2307. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King D. S., Fields C. G., Fields G. B. A cleavage method which minimizes side reactions following Fmoc solid phase peptide synthesis. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1990 Sep;36(3):255–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1990.tb00976.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacadena J., Martínez del Pozo A., Barbero J. L., Mancheño J. M., Gasset M., Oñaderra M., López-Otín C., Ortega S., García J., Gavilanes J. G. Overproduction and purification of biologically active native fungal alpha-sarcin in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1994 May 3;142(1):147–151. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90370-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lins L., Brasseur R., Rosseneu M., Yang C. Y., Sparrow D. A., Sparrow J. T., Gotto A. M., Jr, Ruysschaert J. M. Structure and orientation of apo B-100 peptides into a lipid bilayer. J Protein Chem. 1994 Jan;13(1):77–88. doi: 10.1007/BF01891995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancheño J. M., Gasset M., Lacadena J., Martínez del Pozo A., Oñaderra M., Gavilanes J. G. Predictive study of the conformation of the cytotoxic protein alpha-sarcin: a structural model to explain alpha-sarcin-membrane interaction. J Theor Biol. 1995 Feb 7;172(3):259–267. doi: 10.1006/jtbi.1995.0022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancheño J. M., Gasset M., Lacadena J., Ramón F., Martínez del Pozo A., Oñaderra M., Gavilanes J. G. Kinetic study of the aggregation and lipid mixing produced by alpha-sarcin on phosphatidylglycerol and phosphatidylserine vesicles: stopped-flow light scattering and fluorescence energy transfer measurements. Biophys J. 1994 Sep;67(3):1117–1125. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80578-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin I., Defrise-Quertain F., Decroly E., Vandenbranden M., Brasseur R., Ruysschaert J. M. Orientation and structure of the NH2-terminal HIV-1 gp41 peptide in fused and aggregated liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jan 18;1145(1):124–133. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90389-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez del Pozo A., Gasset M., Oñaderra M., Gavilanes J. G. Conformational study of the antitumor protein alpha-sarcin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Apr 14;953(3):280–288. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(88)90036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merutka G., Stellwagen E. Analysis of peptides for helical prediction. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 10;28(1):352–357. doi: 10.1021/bi00427a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. W., Kallenbach N. R. Persistence of the alpha-helix stop signal in the S-peptide in trifluoroethanol solutions. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 13;28(12):5256–5261. doi: 10.1021/bi00438a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oñaderra M., Mancheño J. M., Gasset M., Lacadena J., Schiavo G., Martínez del Pozo A., Gavilanes J. G. Translocation of alpha-sarcin across the lipid bilayer of asolectin vesicles. Biochem J. 1993 Oct 1;295(Pt 1):221–225. doi: 10.1042/bj2950221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perczel A., Hollósi M., Tusnády G., Fasman G. D. Convex constraint analysis: a natural deconvolution of circular dichroism curves of proteins. Protein Eng. 1991 Aug;4(6):669–679. doi: 10.1093/protein/4.6.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polozov I. V., Polozova A. I., Anantharamaiah G. M., Segrest J. P., Epand R. M. Mixing rates can markedly affect the kinetics of peptide-induced leakage from liposomes. Biochem Mol Biol Int. 1994 Aug;33(6):1073–1079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux M., Nezil F. A., Monck M., Bloom M. Fragmentation of phospholipid bilayers by myelin basic protein. Biochemistry. 1994 Jan 11;33(1):307–311. doi: 10.1021/bi00167a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacco G., Drickamer K., Wool I. G. The primary structure of the cytotoxin alpha-sarcin. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5811–5818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck D. K., Hoekstra D., Pagano R. E. Use of resonance energy transfer to monitor membrane fusion. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4093–4099. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sönnichsen F. D., Van Eyk J. E., Hodges R. S., Sykes B. D. Effect of trifluoroethanol on protein secondary structure: an NMR and CD study using a synthetic actin peptide. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 22;31(37):8790–8798. doi: 10.1021/bi00152a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnay J., Olmo N., Jiménez A., Lizarbe M. A., Gavilanes J. G. Kinetic study of the cytotoxic effect of alpha-sarcin, a ribosome inactivating protein from Aspergillus giganteus, on tumour cell lines: protein biosynthesis inhibition and cell binding. Mol Cell Biochem. 1993 May 12;122(1):39–47. doi: 10.1007/BF00925735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wool I. G., Glück A., Endo Y. Ribotoxin recognition of ribosomal RNA and a proposal for the mechanism of translocation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jul;17(7):266–269. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90407-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



