Abstract
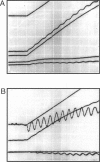
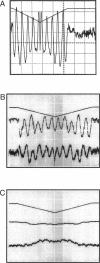
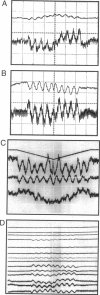
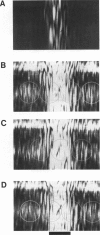
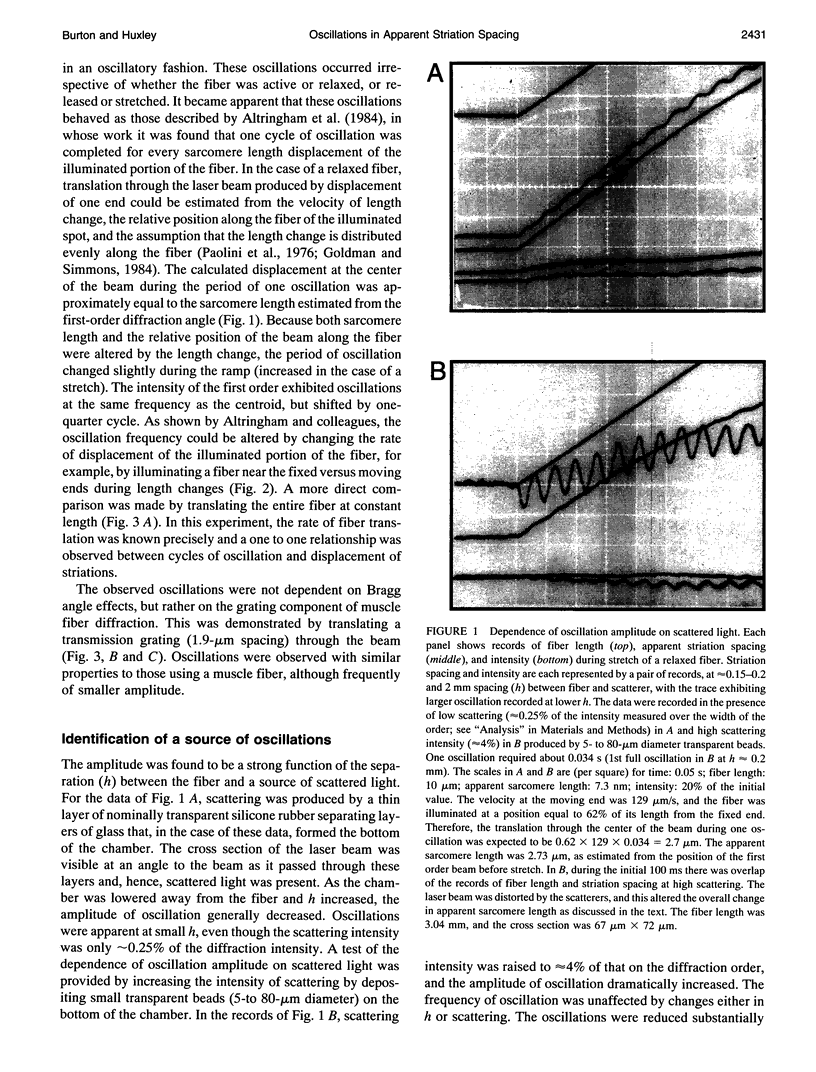
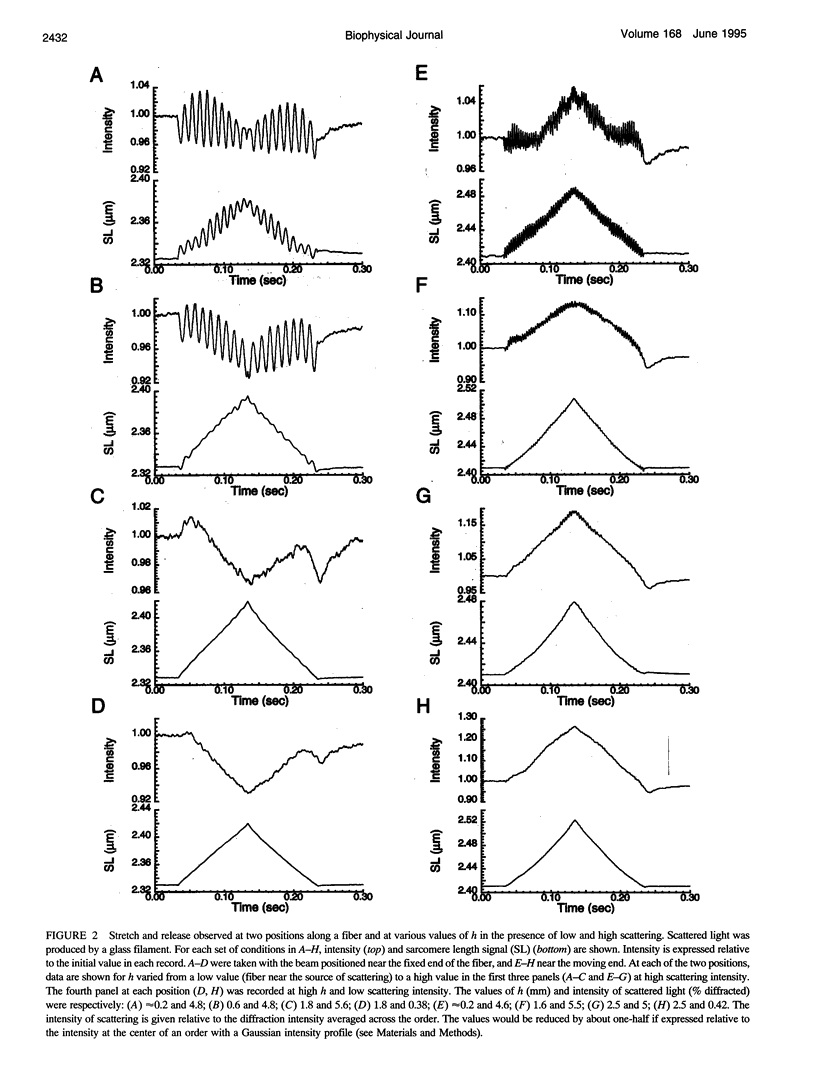
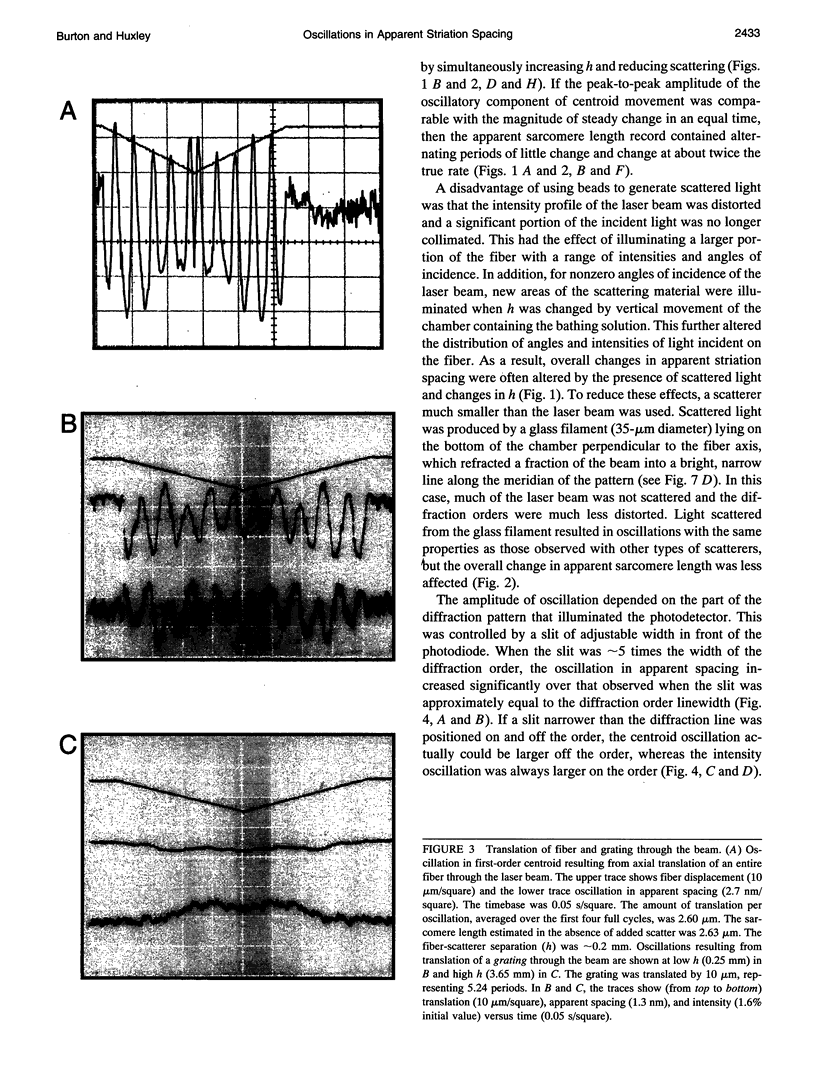
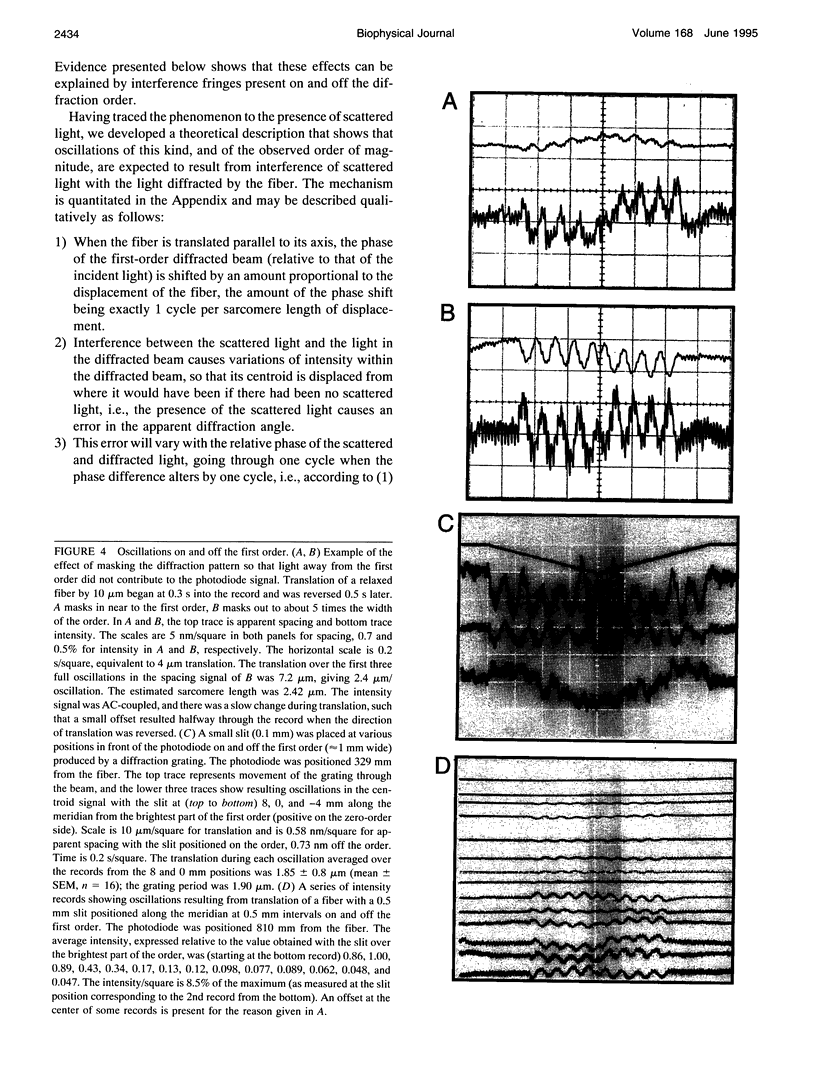
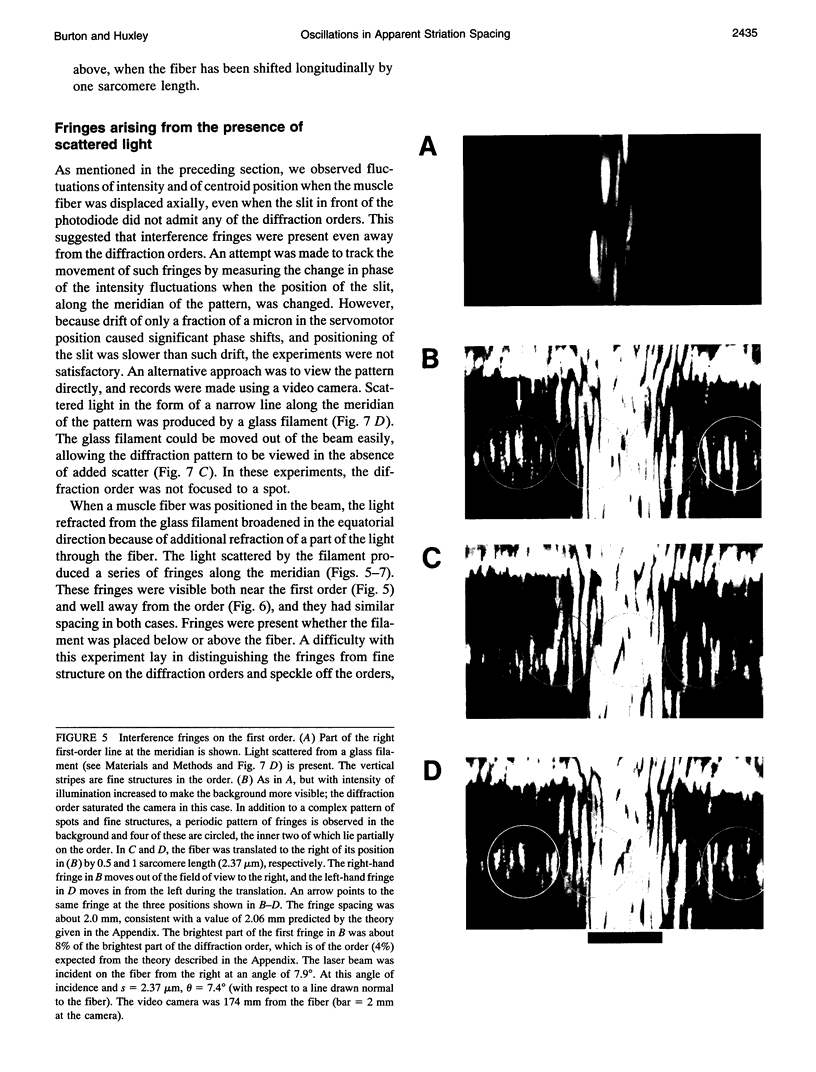
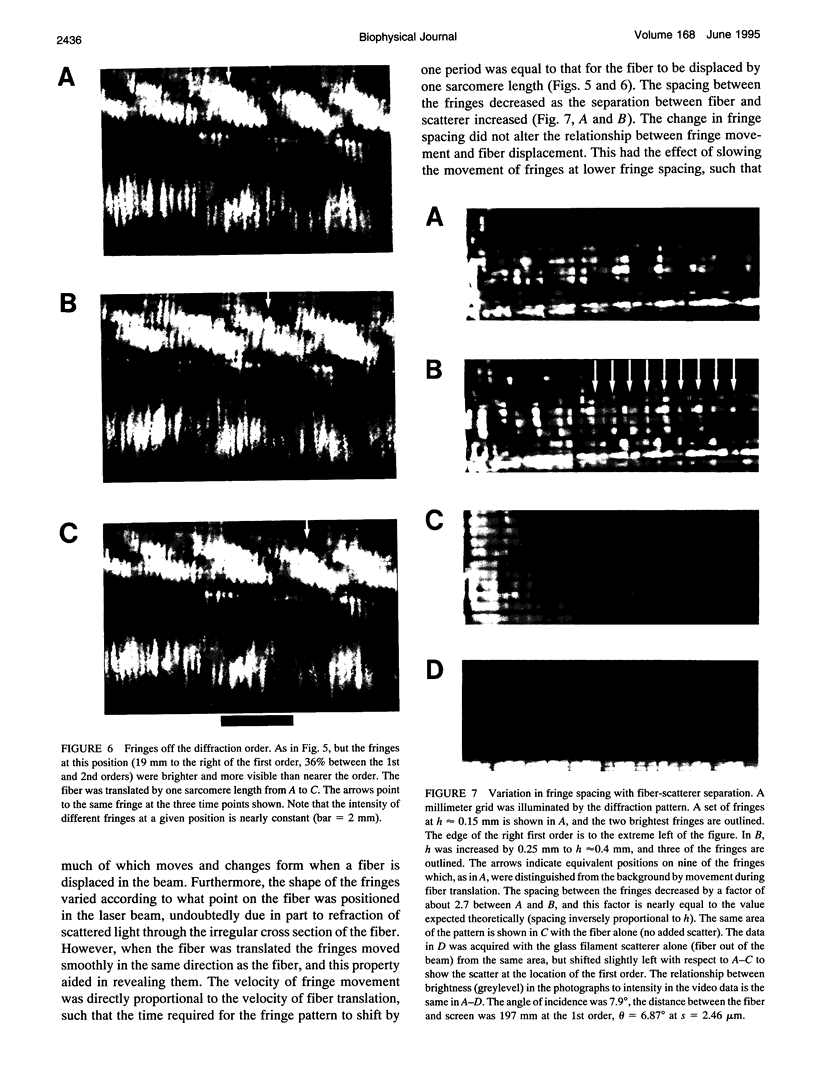
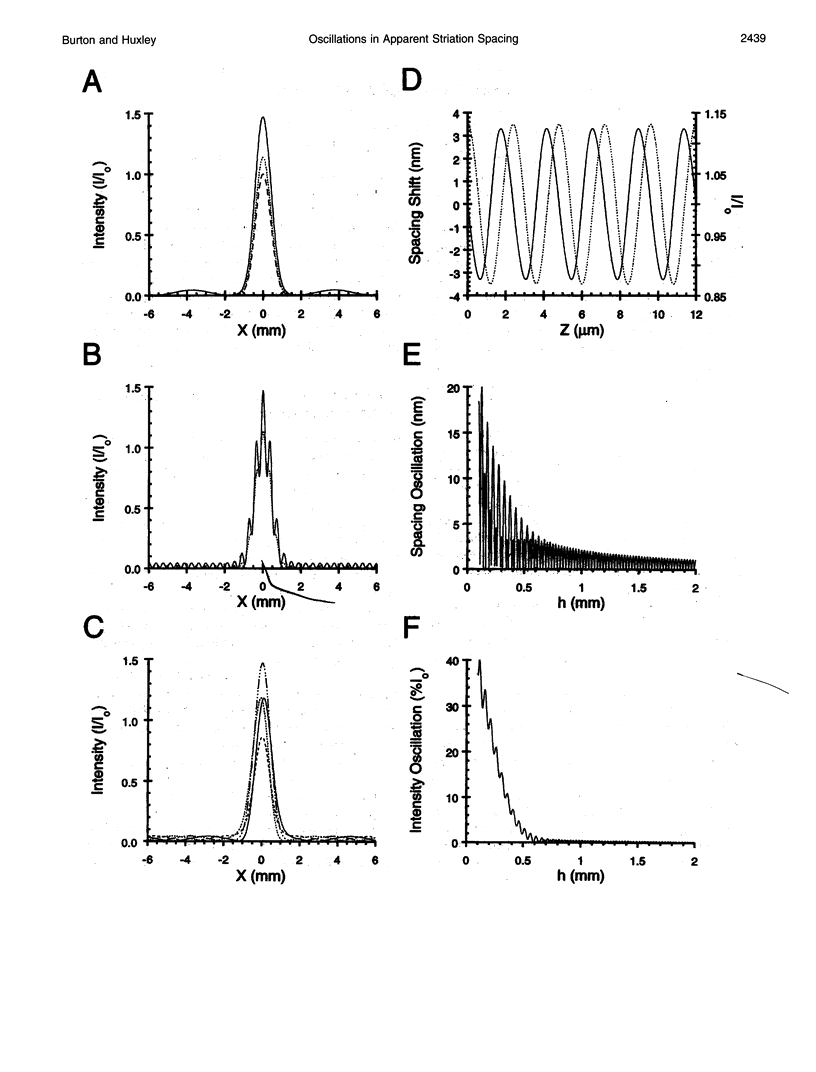
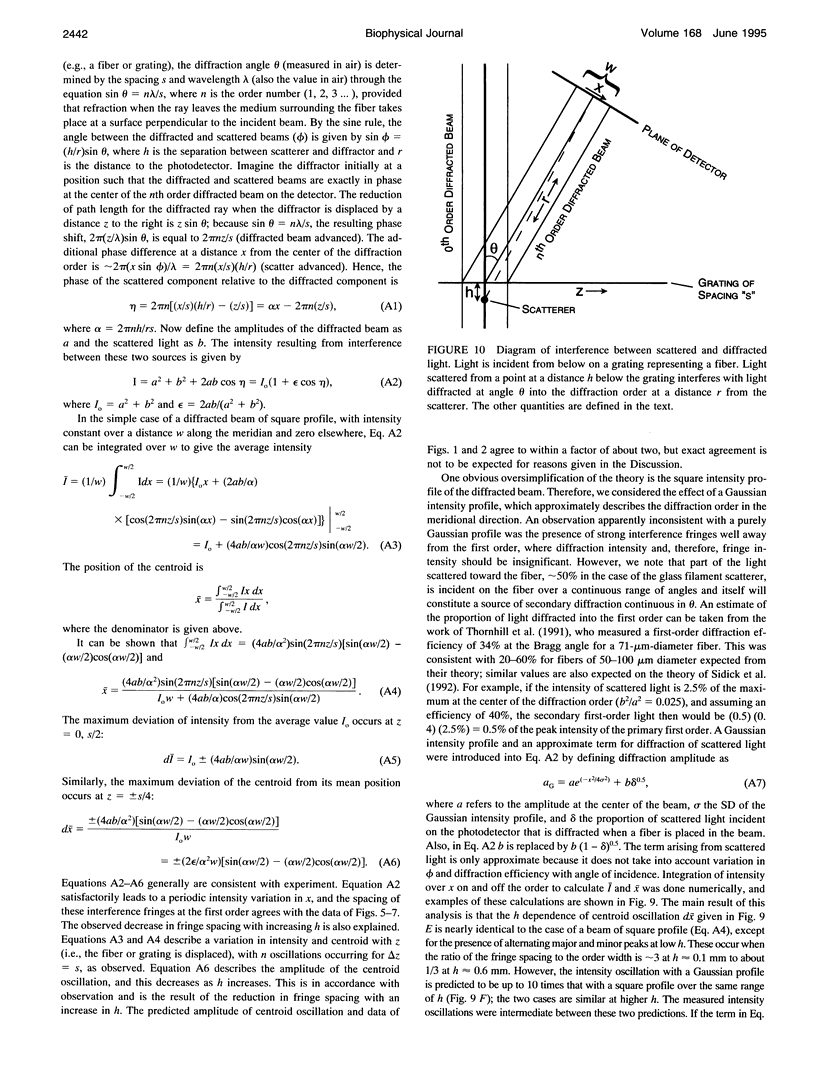
The most widely used technique for dynamic estimates of sarcomere length in muscle is laser light diffraction. We have identified conditions under which artifactual oscillations can arise in apparent sarcomere length measured by this technique and report methods to reduce the effect. Altringham et al. (1984) first reported that the diffraction angle can exhibit one cycle of oscillation for each sarcomere length displacement of the illuminated portion of the fiber. We find that the amplitude of similar oscillations is strongly dependent on the intensity of light scattered from objects near the fiber and on the spacing between fiber and scatterer. The oscillations can be eliminated by minimizing scattered light and positioning the fiber a few millimeters from sources of scattering. A theoretical description shows that oscillations of this kind are expected from interference of scattered and diffracted light. Interference fringes were observed along the meridian of the pattern, and these moved during translation of either a fiber or a grating. The movement of fringes across the diffraction order shifts the centroid back and forth and, when associated with steady shortening, can give rise to "steps" and "pauses" in apparent striation spacing.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altringham J. D., Bottinelli R., Lacktis J. W. Is stepwise sarcomere shortening an artefact? Nature. 1984 Feb 16;307(5952):653–655. doi: 10.1038/307653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskin R. J., Lieber R. L., Oba T., Yeh Y. Intensity of light diffraction from striated muscle as a function of incident angle. Biophys J. 1981 Dec;36(3):759–773. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84764-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. Sarcomeric domain organization within single skinned rabbit psoas fibers and its effects on laser light diffraction patterns. Biophys J. 1985 Dec;48(6):967–982. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83860-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton K., Baskin R. J. Light diffraction patterns and sarcomere length variation in striated muscle fibers of Limulus. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Apr;406(4):409–418. doi: 10.1007/BF00590945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton K., Zagotta W. N., Baskin R. J. Sarcomere length behaviour along single frog muscle fibres at different lengths during isometric tetani. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1989 Feb;10(1):67–84. doi: 10.1007/BF01739857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleworth D. R., Edman K. A. Changes in sarcomere length during isometric tension development in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(1):1–17. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delay M. J., Ishide N., Jacobson R. C., Pollack G. H., Tirosh R. Stepwise sarcomere shortening: analysis by high-speed cinemicrography. Science. 1981 Sep 25;213(4515):1523–1525. doi: 10.1126/science.7280674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliar W. G., Bickel W. S., Bailey W. F. Light diffraction studies of single muscle fibers as a function of fiber rotation. Biophys J. 1984 Jun;45(6):1159–1165. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84264-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E. Measurement of sarcomere shortening in skinned fibers from frog muscle by white light diffraction. Biophys J. 1987 Jul;52(1):57–68. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83188-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E., Simmons R. M. Control of sarcomere length in skinned muscle fibres of Rana temporaria during mechanical transients. J Physiol. 1984 May;350:497–518. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldspink G., Larson R. E., Davies R. E. Fluctuations in sarcomere length in the chick anterior and posterior latissimus dorsi muscles during isometric contraction. Experientia. 1970 Jan 15;26(1):16–18. doi: 10.1007/BF01900361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granzier H. L., Pollack G. H. Stepwise shortening in unstimulated frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1985 May;362:173–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hard R., Zeh R., Allen R. D. Phase-randomized laser illumination for microscopy. J Cell Sci. 1977 Feb;23:335–343. doi: 10.1242/jcs.23.1.335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley A. Comments on "Quantal mechanisms in cardiac contraction". Circ Res. 1986 Jul;59(1):9–14. doi: 10.1161/01.res.59.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson R. C., Tirosh R., Delay M. J., Pollack G. H. Quantized nature of sarcomere shortening steps. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1983 Oct;4(5):529–542. doi: 10.1007/BF00712113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Kuntz I. D. Optical diffraction studies of muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1973 Sep;13(9):857–876. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(73)86031-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber R. L., Yeh Y., Baskin R. J. Sarcomere length determination using laser diffraction. Effect of beam and fiber diameter. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):1007–1016. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84246-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolini P. J., Sabbadini R., Roos K. P., Baskin R. J. Sarcomere length dispersion in single skeletal muscle fibers and fiber bundles. Biophys J. 1976 Aug;16(8):919–930. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85742-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack G. H., Granzier H. L., Mattiazzi A., Trombitás C., Periasamy A., Baatsen P. H., Burns D. H. Pauses, steps, and the mechanism of contraction. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1988;226:617–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack G. H., Iwazumi T., ter Keurs H. E., Shibata E. F. Sarcomere shortening in striated muscle occurs in stepwise fashion. Nature. 1977 Aug 25;268(5622):757–759. doi: 10.1038/268757a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack G. H. Quantal mechanisms in cardiac contraction. Circ Res. 1986 Jul;59(1):1–8. doi: 10.1161/01.res.59.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüdel R., Zite-Ferenczy F. Do laser diffraction studies on striated muscle indicate stepwise sarcomere shortening? Nature. 1979 Apr 5;278(5704):573–575. doi: 10.1038/278573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüdel R., Zite-Ferenczy F. Interpretation of light diffraction by cross-striated muscle as Bragg reflexion of light by the lattice of contractile proteins. J Physiol. 1979 May;290(2):317–330. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidick E., Knoesen A., Xian J. K., Yeh Y., Baskin R. J. Rigorous analysis of light diffraction by a striated muscle fibre. Proc Biol Sci. 1992 Sep 22;249(1326):247–257. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1992.0111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundell C. L., Goldman Y. E., Peachey L. D. Fine structure in near-field and far-field laser diffraction patterns from skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1986 Feb;49(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83662-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornhill R. A., Thomas N., Berovic N. Optical diffraction by well-ordered muscle fibres. Eur Biophys J. 1991;20(2):87–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00186257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trovato C., Cerciello A., Carleo R. Effetto della calcitonina sulla funzione gastrica nell'uomo. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1981 Jan 15;57(1):57–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh Y., Baskin R. J., Lieber R. L., Roos K. P. Theory of light diffraction by single skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1980 Mar;29(3):509–522. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85149-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zite-Ferenczy F., Häberle K. D., Rüdel R., Wilke W. Correlation between the light diffraction pattern and the structure of a muscle fibre realized with Ewald's construction. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1986 Jun;7(3):197–214. doi: 10.1007/BF01753553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]