Abstract
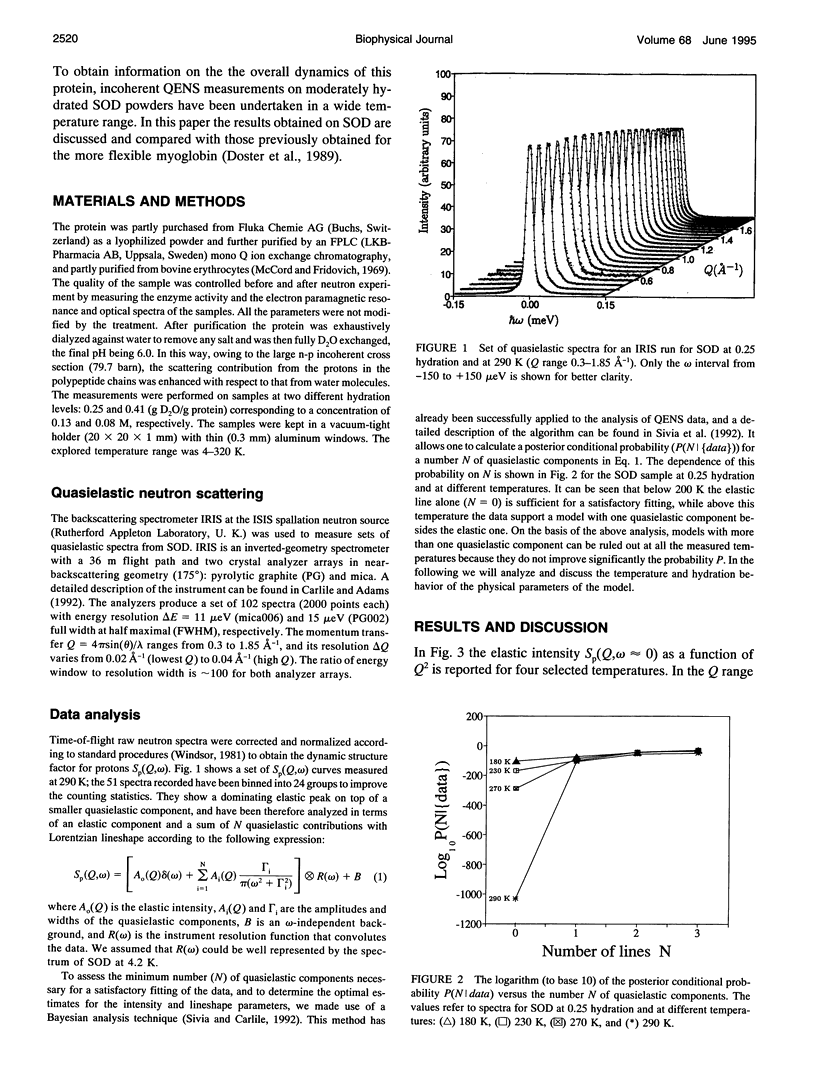
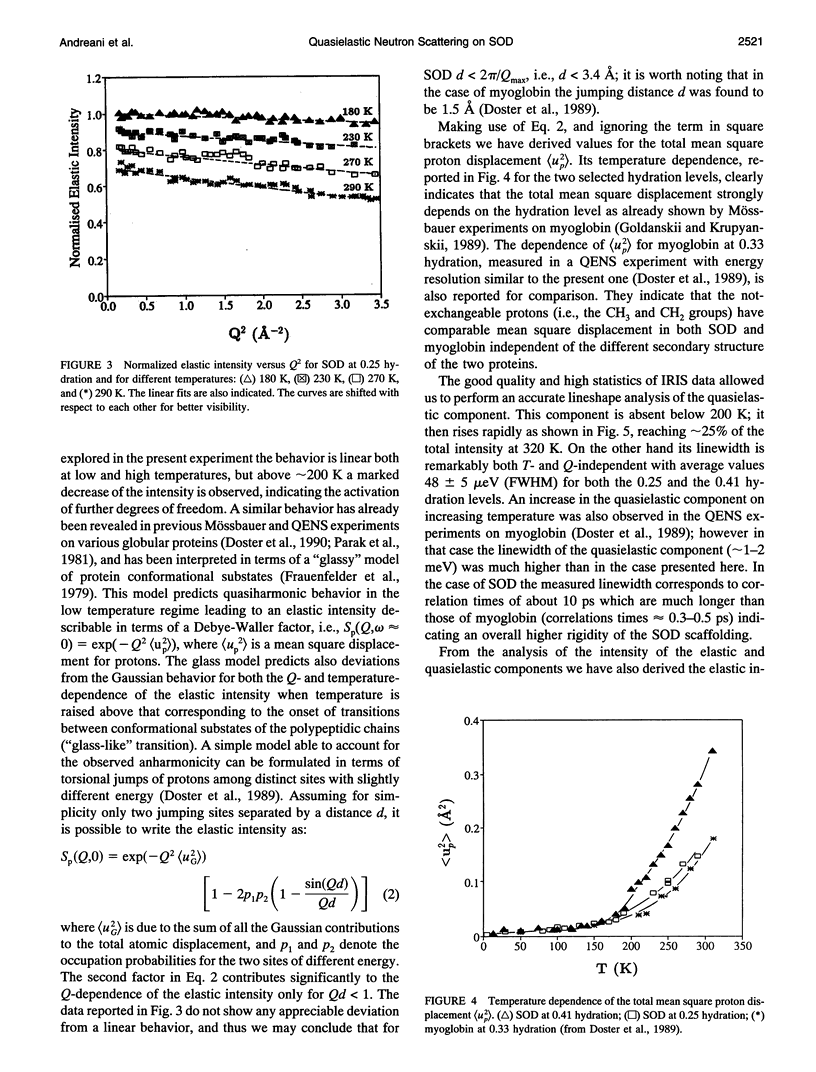
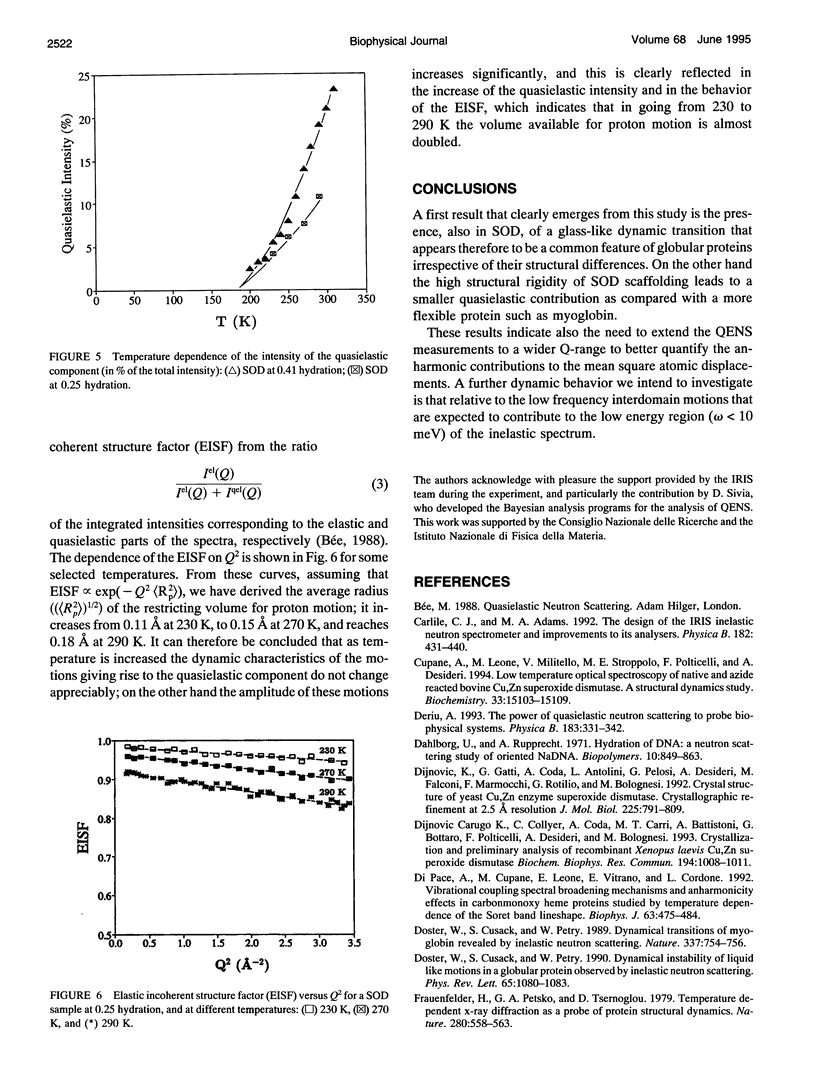
The low energy dynamic of the enzyme Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase have been investigated by means of quasielastic neutron scattering in the temperature range 4-320 K. Below 200 K the scattering is purely elastic, while above this temperature a pronounced decrease in the elastic intensity is observed, together with the onset of a small quasielastic component. This behavior is similar to that previously observed in other more flexible globular proteins, and can be attributed to transitions between slightly different conformational substates of the protein tertiary structure. The presence of only a small quasielastic component, whose intensity is < or = 25% of the total spectrum, is related to the high structural rigidity of this protein.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cupane A., Leone M., Militello V., Stroppolo M. E., Polticelli F., Desideri A. Low-temperature optical spectroscopy of native and azide-reacted bovine Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase. A structural dynamics study. Biochemistry. 1994 Dec 20;33(50):15103–15109. doi: 10.1021/bi00254a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlborg U. Hydration of DNA: a neutron scattering study of oriented NaDNA. Biopolymers. 1971;10(5):849–863. doi: 10.1002/bip.360100509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Pace A., Cupane A., Leone M., Vitrano E., Cordone L. Protein dynamics. Vibrational coupling, spectral broadening mechanisms, and anharmonicity effects in carbonmonoxy heme proteins studied by the temperature dependence of the Soret band lineshape. Biophys J. 1992 Aug;63(2):475–484. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81606-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djinovic Carugo K., Collyer C., Coda A., Carrì M. T., Battistoni A., Bottaro G., Polticelli F., Desideri A., Bolognesi M. Crystallisation and preliminary crystallographic analysis of recombinant Xenopus laevis Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase b. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Aug 16;194(3):1008–1011. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djinovic K., Gatti G., Coda A., Antolini L., Pelosi G., Desideri A., Falconi M., Marmocchi F., Rotilio G., Bolognesi M. Crystal structure of yeast Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase. Crystallographic refinement at 2.5 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jun 5;225(3):791–809. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90401-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doster W., Cusack S., Petry W. Dynamical transition of myoglobin revealed by inelastic neutron scattering. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):754–756. doi: 10.1038/337754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doster W, Cusack S, Petry W. Dynamic instability of liquidlike motions in a globular protein observed by inelastic neutron scattering. Phys Rev Lett. 1990 Aug 20;65(8):1080–1083. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.65.1080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frauenfelder H., Petsko G. A., Tsernoglou D. Temperature-dependent X-ray diffraction as a probe of protein structural dynamics. Nature. 1979 Aug 16;280(5723):558–563. doi: 10.1038/280558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furois-Corbin S., Smith J. C., Kneller G. R. Picosecond timescale rigid-helix and side-chain motions in deoxymyoglobin. Proteins. 1993 Jun;16(2):141–154. doi: 10.1002/prot.340160203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldanskii V. I., Krupyanskii Y. F. Protein and protein-bound water dynamics studied by Rayleigh scattering of Mössbauer radiation (RSMR). Q Rev Biophys. 1989 Feb;22(1):39–92. doi: 10.1017/s003358350000336x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm H, Stiller H, Majkrzak CF, Rupprecht A, Dahlborg U. Observation of acoustic umklapp-phonons in water-stabilized DNA by neutron scattering. Phys Rev Lett. 1987 Oct 12;59(15):1780–1783. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.59.1780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa Y., Tanaka N., Hata Y., Kusunoki M., Lee G. P., Katsube Y., Asada K., Aibara S., Morita Y. Three-dimensional structure of Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase from spinach at 2.0 A resolution. J Biochem. 1991 Mar;109(3):477–485. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6049–6055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parak F., Frolov E. N., Mössbauer R. L., Goldanskii V. I. Dynamics of metmyoglobin crystals investigated by nuclear gamma resonance absorption. J Mol Biol. 1981 Feb 5;145(4):825–833. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90317-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parge H. E., Hallewell R. A., Tainer J. A. Atomic structures of wild-type and thermostable mutant recombinant human Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6109–6113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tainer J. A., Getzoff E. D., Beem K. M., Richardson J. S., Richardson D. C. Determination and analysis of the 2 A-structure of copper, zinc superoxide dismutase. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 15;160(2):181–217. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90174-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


