Abstract
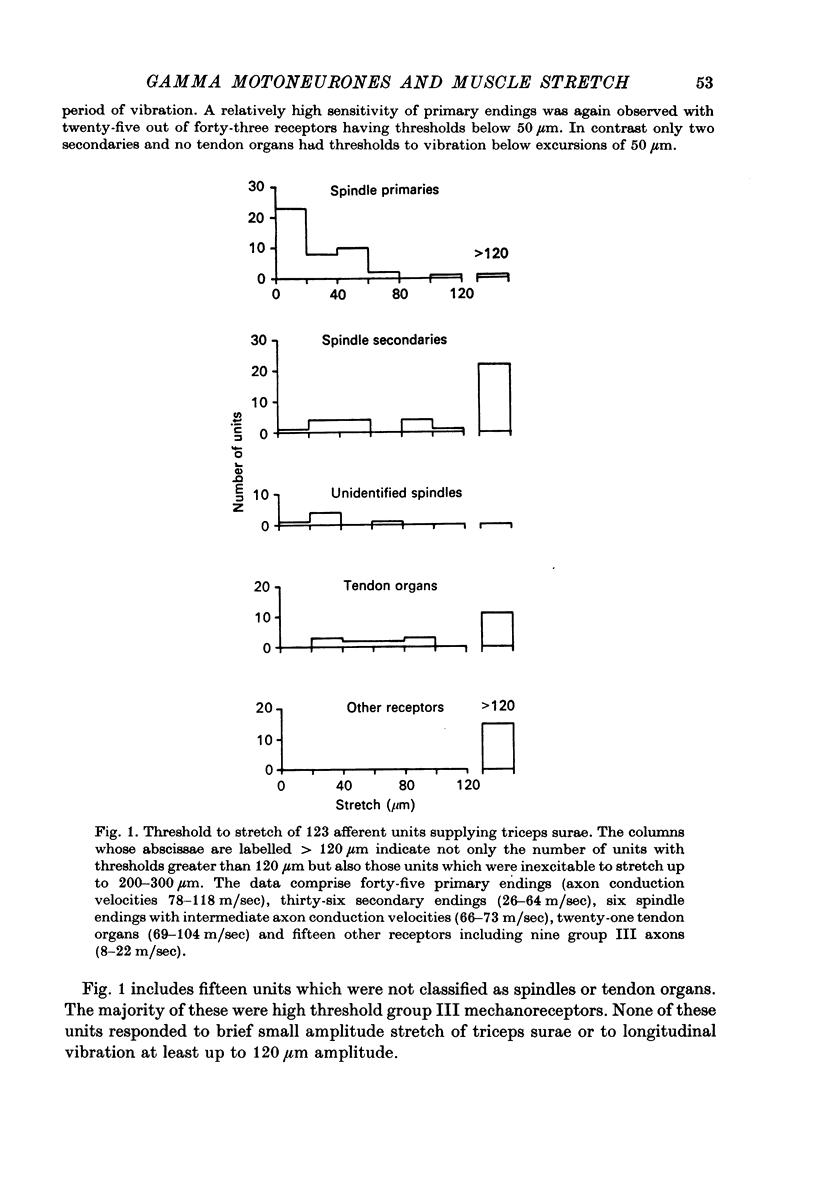
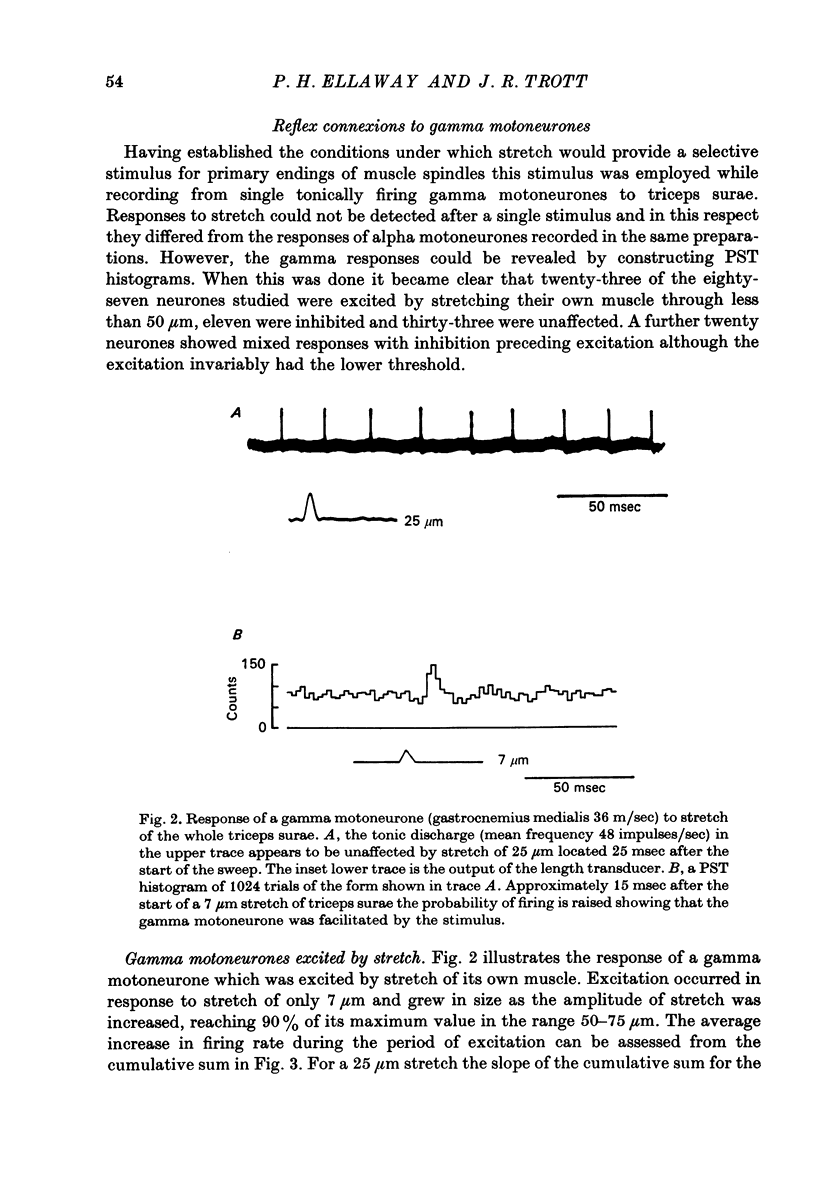
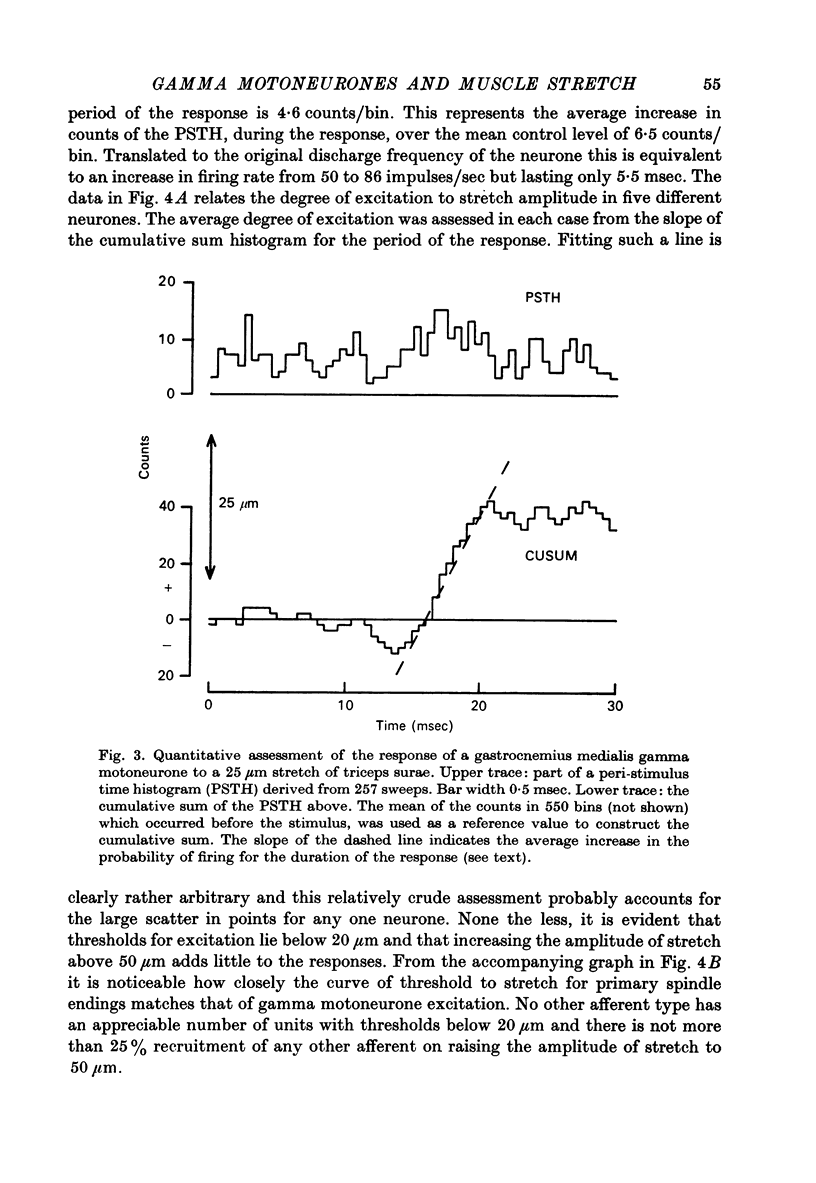
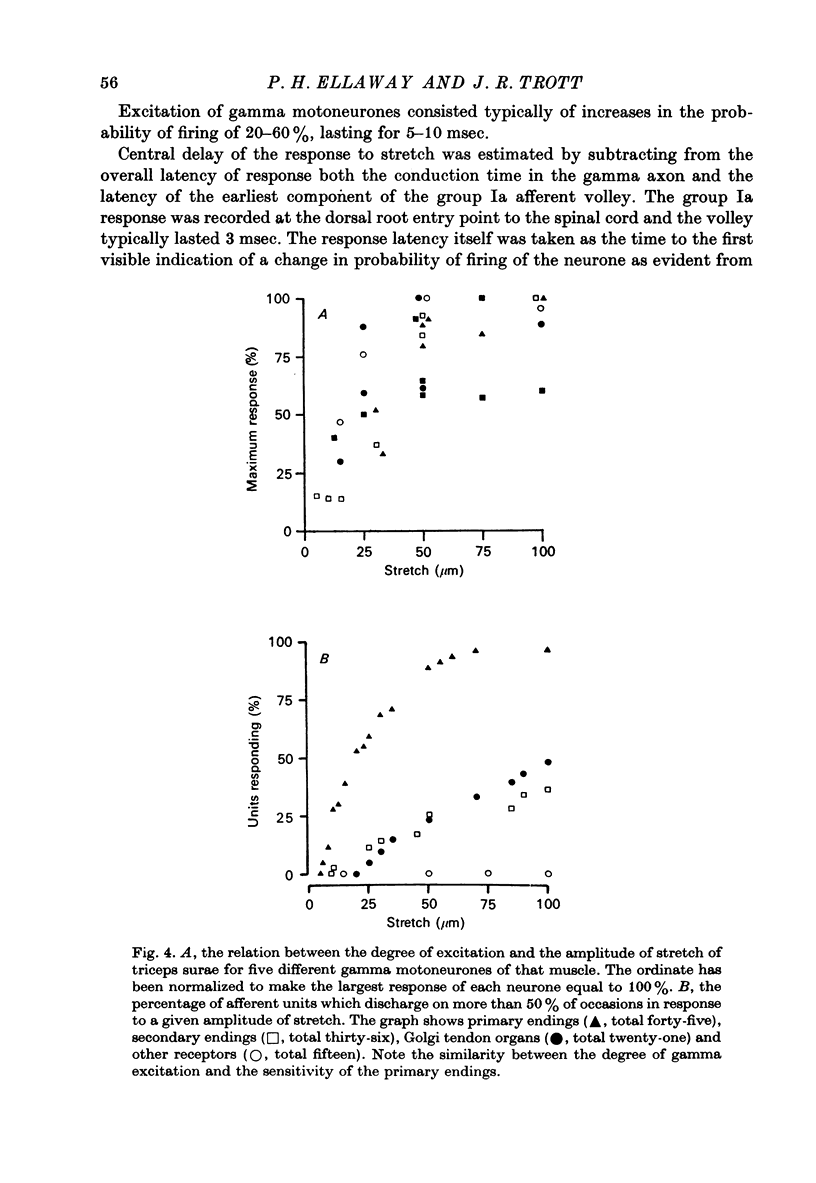
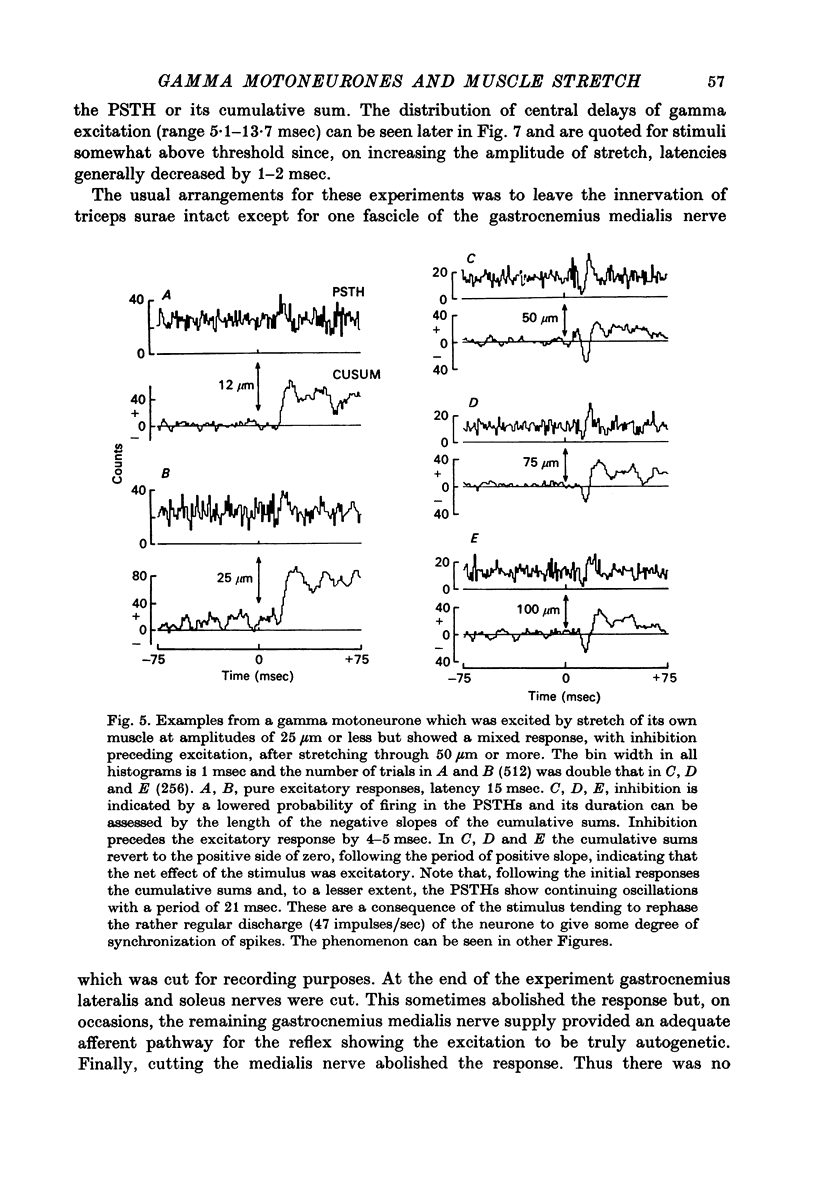
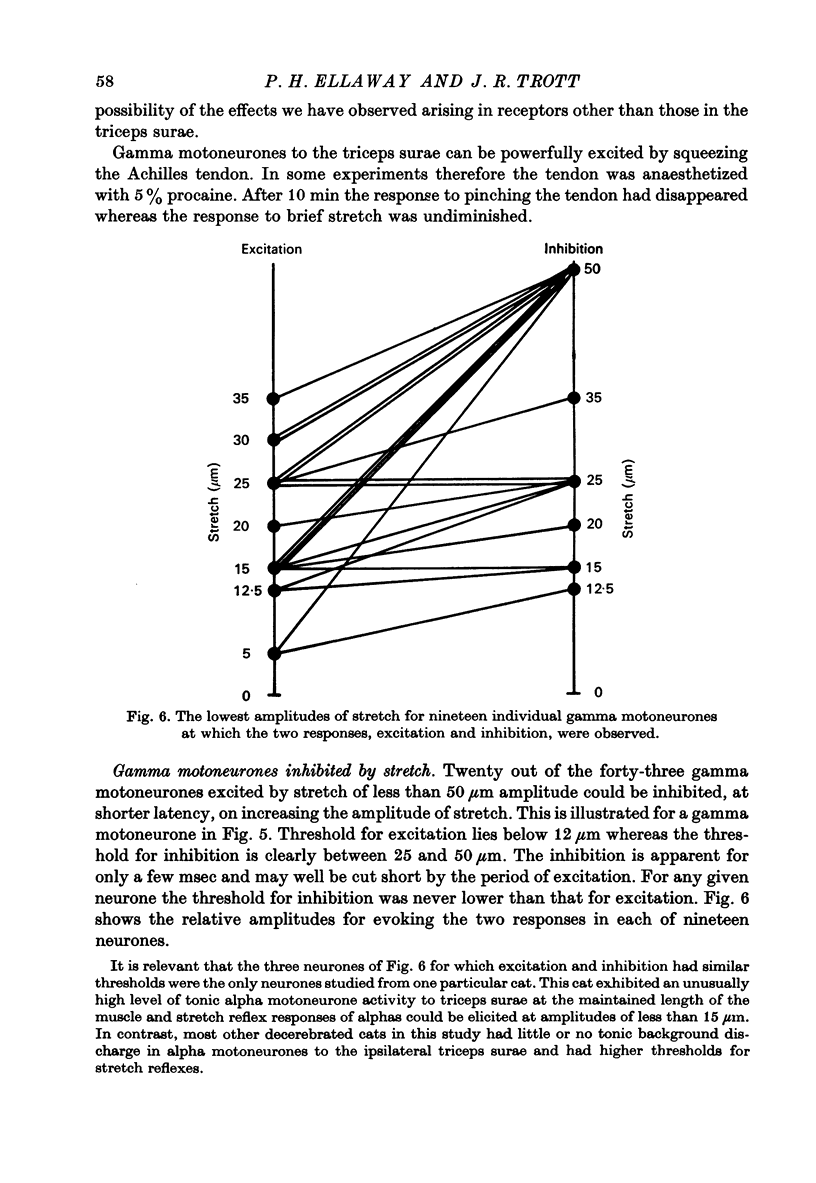
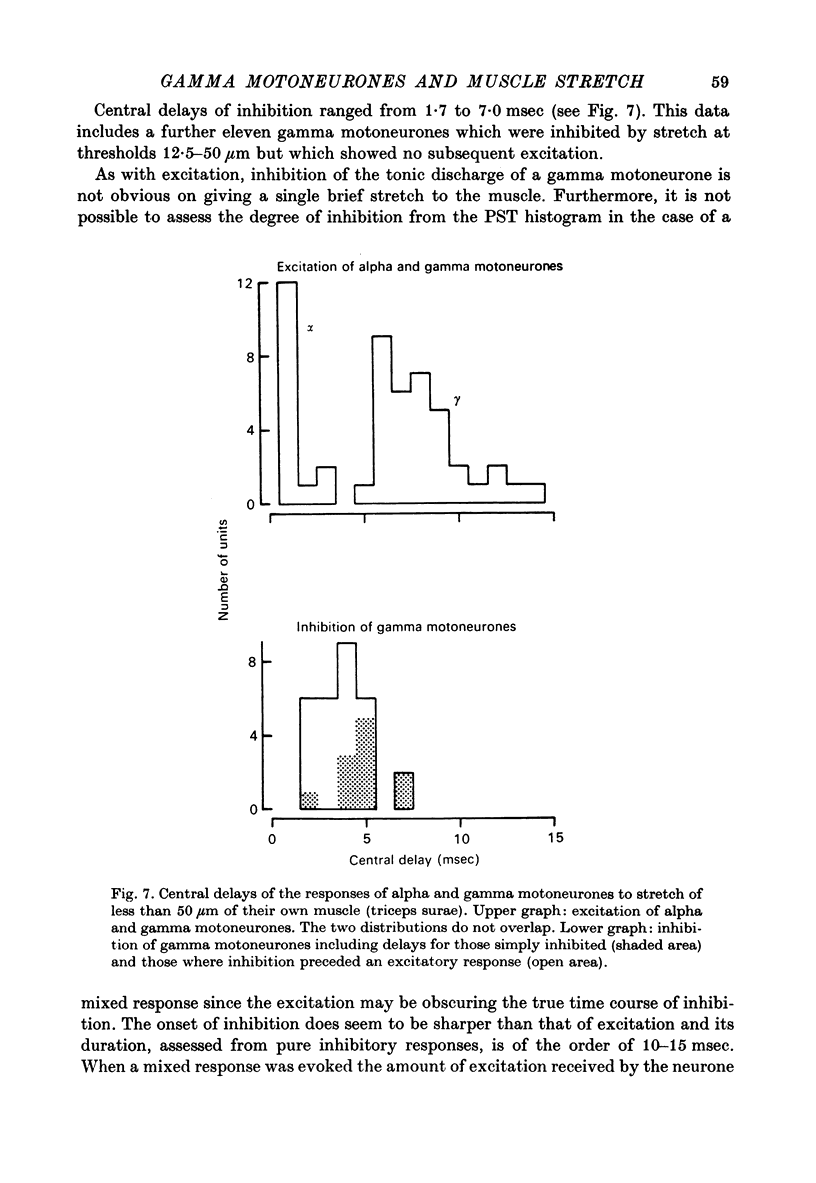
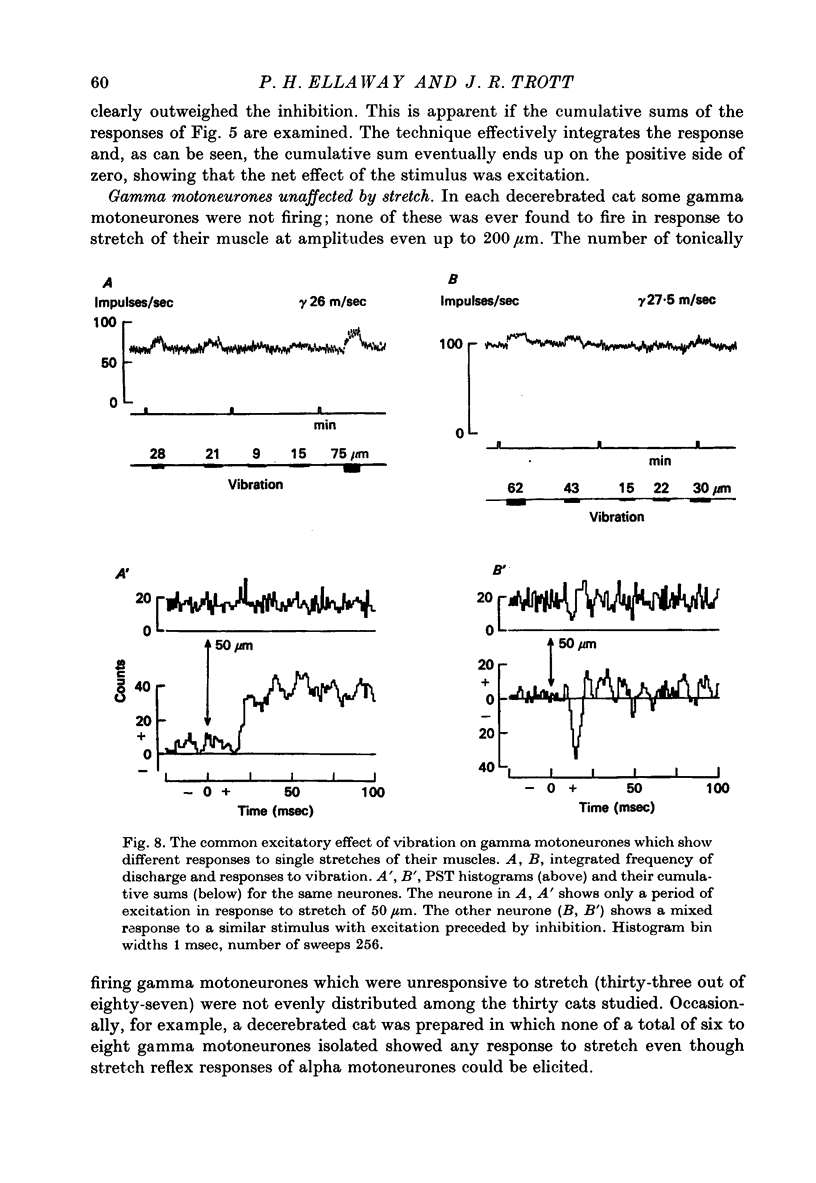
1. Tonically firing gamma motoneurones of known conduction velocity (total eighty-seven, range 15-43 m/sec) have been isolated in peripheral muscular nerves to triceps surae. Their responses to stretch of triceps surae have been studied in decerebrated cats. A small amplitude, quick stretch and release was used to provide a selective stimulus for primary endings of muscle spindles. 2. To check the selectivity, recordings were made from 135 afferents from triceps surae under conditions closely similar to the reflex experiments. The threshold of all but a few primary endings of muscle spindles law below 50 micrometer whereas threshold was above 50 micrometer for the majority of secondary endings and tendon organs. A 20 micrometer stretch excited approximately half the primary endings but only one of thirty-six secondaries and no tendon organs responded to such a small stretch. Nine group III afferents were also studied but none responded to stretch. 3. Stretch of up to 50 micrometer excited twenty-three and inhibited eleven gamma motoneurones while thirty-three remained unaffected. A further twenty showed mixed responses, being inhibited initially before being excited at longer latency. Thresholds for reflex responses of gamma motoneurones frequently occurred below 20 mum and responses were close to maximal for stretch of 50 micrometer. 4. Excitation always had a lower threshold to stretch than did inhibition for those gamma motoneurones showing mixed responses and was the more potent of the two effects. 5. Excitation to stretch had central delays, to the incoming group Ia volley, ranging from 5 to 14 msec while similarly calculated delays for excitation of alpha motoneurones ranged from 0.6 to 3.0 msec. Central delays of the gamma inhibitory responses lay in an intermediate range of 1.7-7.0 msec. 6. The long central delays of excitation of gamma motoneurones in response to stretch do not reflect transmission in supraspinal pathways since the reflex persisted following spinal section. 7. Excitation of gamma motoneurones was weak in comparison with that of tonically firing alpha motoneurones recorded in the same preparations and it was always necessary to sum a number of responses in order to reveal an effect...
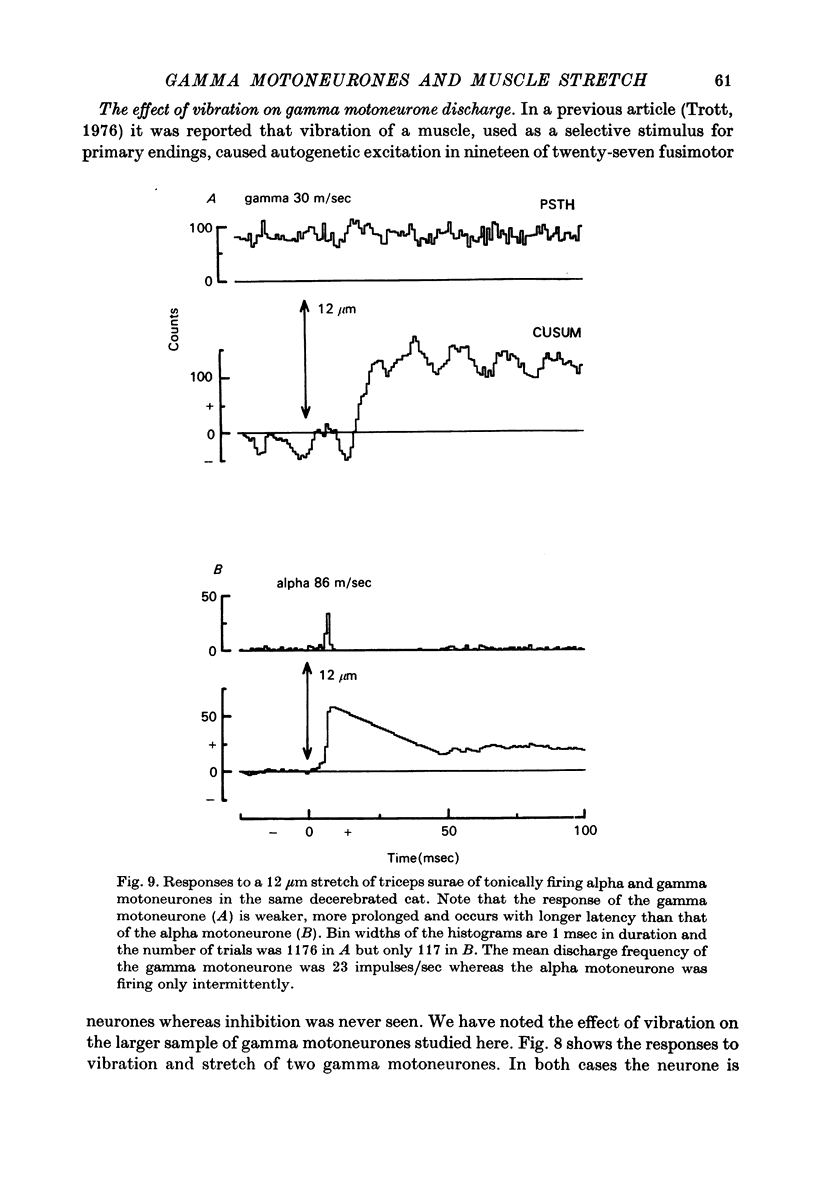
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown M. C., Engberg I., Matthews P. B. The relative sensitivity to vibration of muscle receptors of the cat. J Physiol. 1967 Oct;192(3):773–800. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. C., Lawrence D. G., Matthews P. B. Antidromic inhibition of presumed fusimotor neurones by repetitive stimulation of the ventral root in the decerebrate cat. Experientia. 1968 Dec 15;24(12):1210–1212. doi: 10.1007/BF02146625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellaway P. H. An application of cumulative sum technique (cusums) to neurophysiology [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(1):1P–2P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellaway P. H., Emonet-Denand F., Joffroy M., Laporte Y. Lack of exclusively fusimotor -axons in flexor and extensor leg muscles of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1972 Jan;35(1):149–153. doi: 10.1152/jn.1972.35.1.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellaway P. H., Pascoe J. E., Trott J. R. Proceedings: The effect upon fusimotor neurones of small, brief stretches of their muscles. J Physiol. 1976 Jun;258(2):48P–49P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellaway P. H. Recurrent inhibition of fusimotor neurones exhibiting background discharges in the decerebrate and the spinal cat. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;216(2):419–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellaway P. H., Trott J. R. Reflex connections form muscle stretch receptors to their own fusimotor neurones. Prog Brain Res. 1976;44:113–122. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60727-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm C., Haase J., Noth J. Length-dependent autogenetic inhibition of extensor gamma-motoneurones in the decerebrate cat. Pflugers Arch. 1974;346(3):251–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00595711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm C., Noth J. Reflex responses of gamma motoneurones to vibration of the muscle they innervate. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;256(1):117–136. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm C., Noth J. Vibration-induced autogenetic inhibition of gamma motoneurons. Brain Res. 1975 Jan 17;83(3):495–497. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90842-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., PHILLIPS C. G., SKOGLUND S., STEG G. Differentiation of tonic from phasic alpha ventral horn cells by stretch, pinna and crossed extensor reflexes. J Neurophysiol. 1957 Sep;20(5):470–481. doi: 10.1152/jn.1957.20.5.470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C. The reflex activity of mammalian small-nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1951 Dec 28;115(4):456–469. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBERG A., WINSBURY G. Functional organization of the dorsal spino-cerebellar tract in the cat. VI. Further experiments on excitation from tendon organ and muscle spindle afferents. Acta Physiol Scand. 1960 Jul 15;49:165–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1960.tb01940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pompeiano O., Wand P., Sontag K. H. Excitation of Renshaw cells by orthodromic group Ia volleys following vibration of extensor muscles. Pflugers Arch. 1974 Jan 11;347(2):137–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00592395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart D. G., Mosher C. G., Gerlach R. L., Reinking R. M. Selective activation of Ia afferents by transient muscle stretch. Exp Brain Res. 1970 Jun 25;10(5):477–487. doi: 10.1007/BF00234264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trott J. R. Reflex responses of fusimotor neurones during muscle vibration. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(1):20P–22P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trott J. R. The effect of low amplitude muscle vibration on the discharge of fusimotor neurones in the decerebrate cat. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;255(3):635–649. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


