Abstract
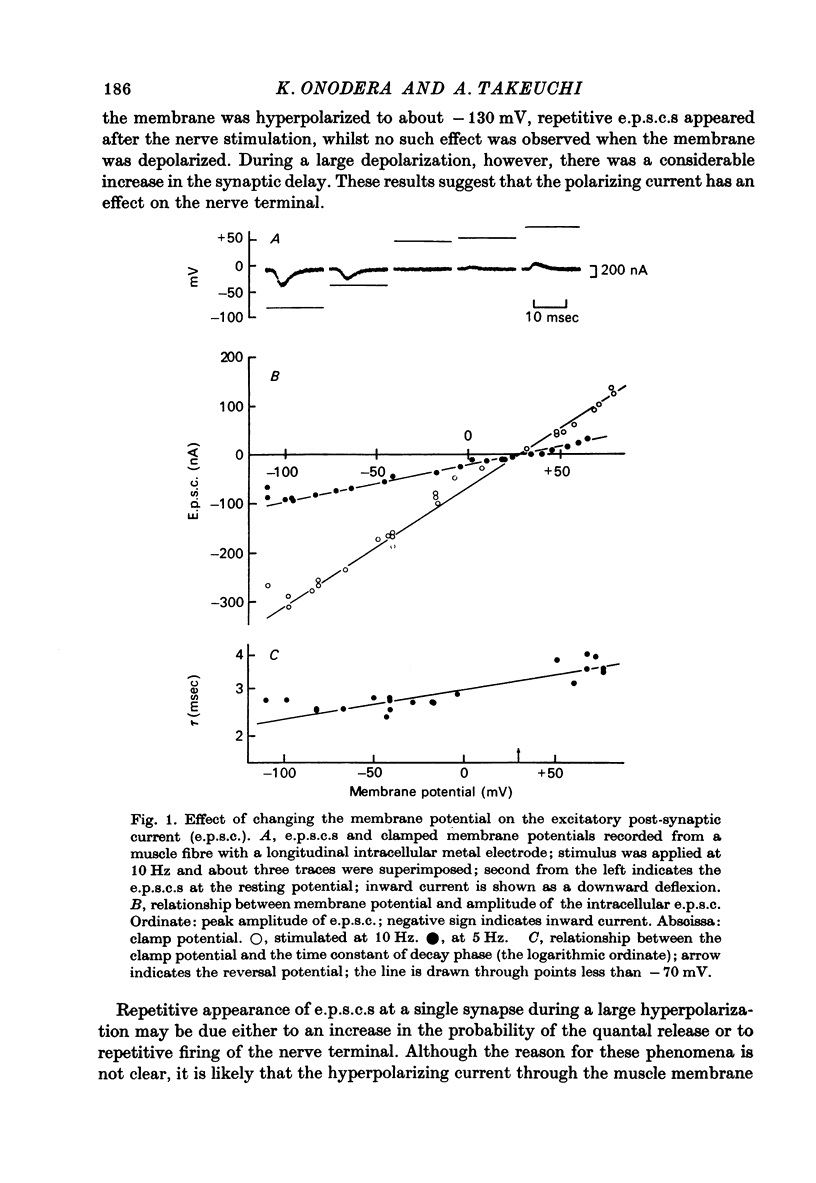
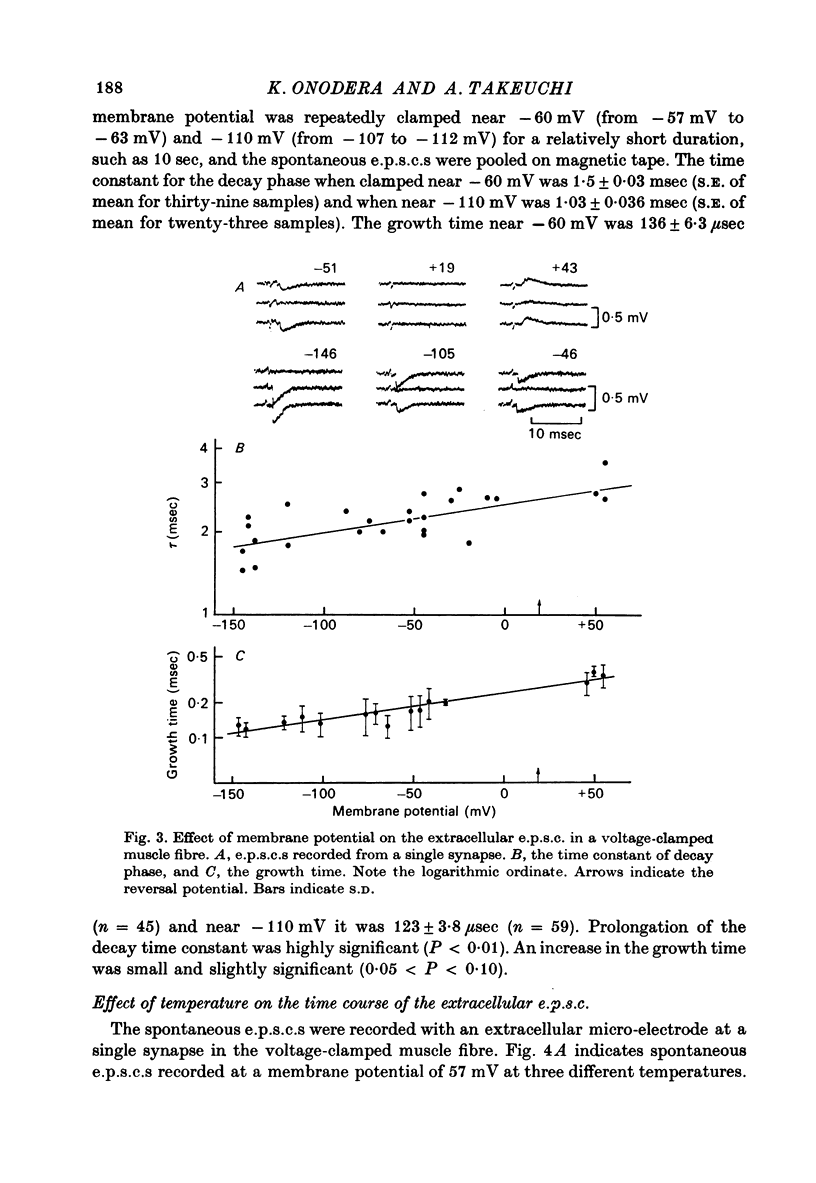
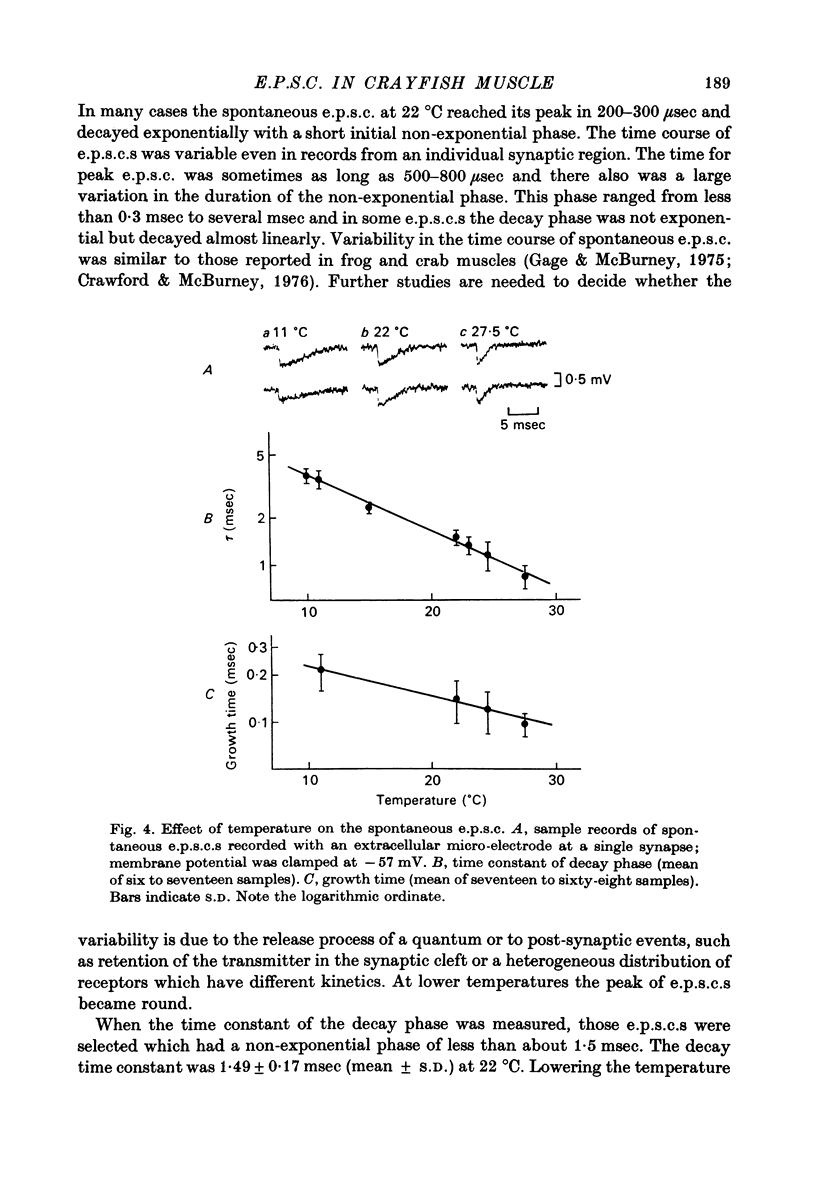
1. Effects of membrane potential and temperature on the excitatory post-synaptic current (e.p.s.c.) were studied in the voltage-clamped crayfish muscle. E.p.c. was recorded either by measuring the feedback current through an intracellular wire electrode or by focal recording with an extracellular micro-electrode. 2. The amplitude of the e.p.s.c. obtained by the voltage clamp method varied almost linearly with membrane potential between -100 mV and +70 mV, whilst the reversal potential was +23.8 +/- 3.9 mV (S.E. of mean). 3. The declining phase of the extracellular e.p.s.c. was slightly prolonged by depolarization and shortened by hyperpolarization. Potential dependence of the decay time constant was expressed by tau = a exp (AV), with a = 2.78 msec and A = 0.0037 mV-1. 4. The decay time constant had a Q10 of 2.3 and the growth time had a Q10 of 1.5. 5. The voltage dependence of the decay phase of the e.p.s. was the reverse of that found in frog end-plate. It is concluded that the voltage dependence of the time course is not related either to the charge of ions which carry the synaptic current or to the charge of the transmitter.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Gage P. W., Hamill O. P. Voltage sensitivity of inhibitory postsynaptic current in Aplysia buccal ganglia. Brain Res. 1976 Oct 22;115(3):506–511. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90368-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Slayman C. L. Membrane potential and conductance during transport of sodium, potassium and rubidium in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1966 Jun;184(4):970–1014. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. R., Cull-Candy S. G., Miledi R. Glutamate and quisqualate noise in voltage-clamped locust muscle fibres. Nature. 1976 May 13;261(5556):151–153. doi: 10.1038/261151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittar E. E., Chen S., Danielson B. G., Hartmann H. A., Tong E. Y. An investigation of sodium transport in barnacle muscle fibres by means of the microsyringe technique. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(2):389–414. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Large W. A., Rang H. P. An analysis of the action of a false transmitter at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1977 Apr;266(2):361–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford A. C., McBurney R. N. On the elementary conductance event produced by L-glutamate and quanta of the natural transmitter at the neuromuscular junctions of Maia squinado. J Physiol. 1976 Jun;258(1):205–225. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUDEL J., KUFFLER S. W. The quantal nature of transmission and spontaneous miniature potentials at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1961 Mar;155:514–529. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne V. E., Stevens C. F. Voltage dependence of agonist effectiveness at the frog neuromuscular junction: resolution of a paradox. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):245–270. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J. Nonlinear voltage dependence of excitatory synaptic current in crayfish muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1974;352(3):227–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00590488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., McBurney R. N. Effects of membrane potential, temperature and neostigmine on the conductance change caused by a quantum or acetylcholine at the toad neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(2):385–407. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The binding of acetylcholine to receptors and its removal from the synaptic cleft. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):549–574. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Joyner R. W., Nicholson C. Equilibrium potential for the postsynaptic response in the squid giant synapse. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Nov;64(5):519–535. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.5.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. A quantitative description of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):173–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. The effect of voltage on the time course of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):151–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B. Voltage-dependence of drug-induced conductance in frog neuromuscular junction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2140–2144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odette L. L., Atwood H. L. Dantrolene sodium: effects on crustacean muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1974 Aug;52(4):887–890. doi: 10.1139/y74-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onodera K., Takeuchi A. Inhibitory postsynaptic current in voltage-clamped crayfish muscle. Nature. 1976 Sep 9;263(5573):153–154. doi: 10.1038/263153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onodera K., Takeuchi A. Ionic mechanism of the excitatory synaptic membrane of the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;252(1):295–318. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozeki M., Freeman A. R., Grundfest H. The membrane components of crustacean neuromuscular systems. II. Analysis of interactions among the electrogenic components. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Jul;49(6):1335–1349. doi: 10.1085/jgp.0491335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Biancri C. P. Site of action of dantrolene in frog sartorius muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1974 Apr;189(1):202–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scuka M. The amplitude and the time course of the end-plate current at various pH levels in the frog sartorius muscle. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):183–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder H. R., Jr, Davis C. S., Bickerton R. K., Halliday R. P. 1-[(5-arylfurfurylidene)amino]hydantoins. A new class of muscle relaxants. J Med Chem. 1967 Sep;10(5):807–810. doi: 10.1021/jm00317a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. Active phase of frog's end-plate potential. J Neurophysiol. 1959 Jul;22(4):395–411. doi: 10.1152/jn.1959.22.4.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takauji M., Takahashi N., Nagai T. Effect of dantrolene sodium on excitation-contraction coupling in frog skeletal muscle. Jpn J Physiol. 1975;25(6):747–758. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.25.747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautmann A., Zilber-Gachelin N. F. Further investigations on the effect of denervation and pH on the conductance change at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Jun 29;364(1):53–58. doi: 10.1007/BF01062911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S. Crayfish neuromuscular facilitation activated by constant presynaptic action potentials and depolarizing pulses. J Physiol. 1974 Aug;241(1):69–89. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


