Abstract
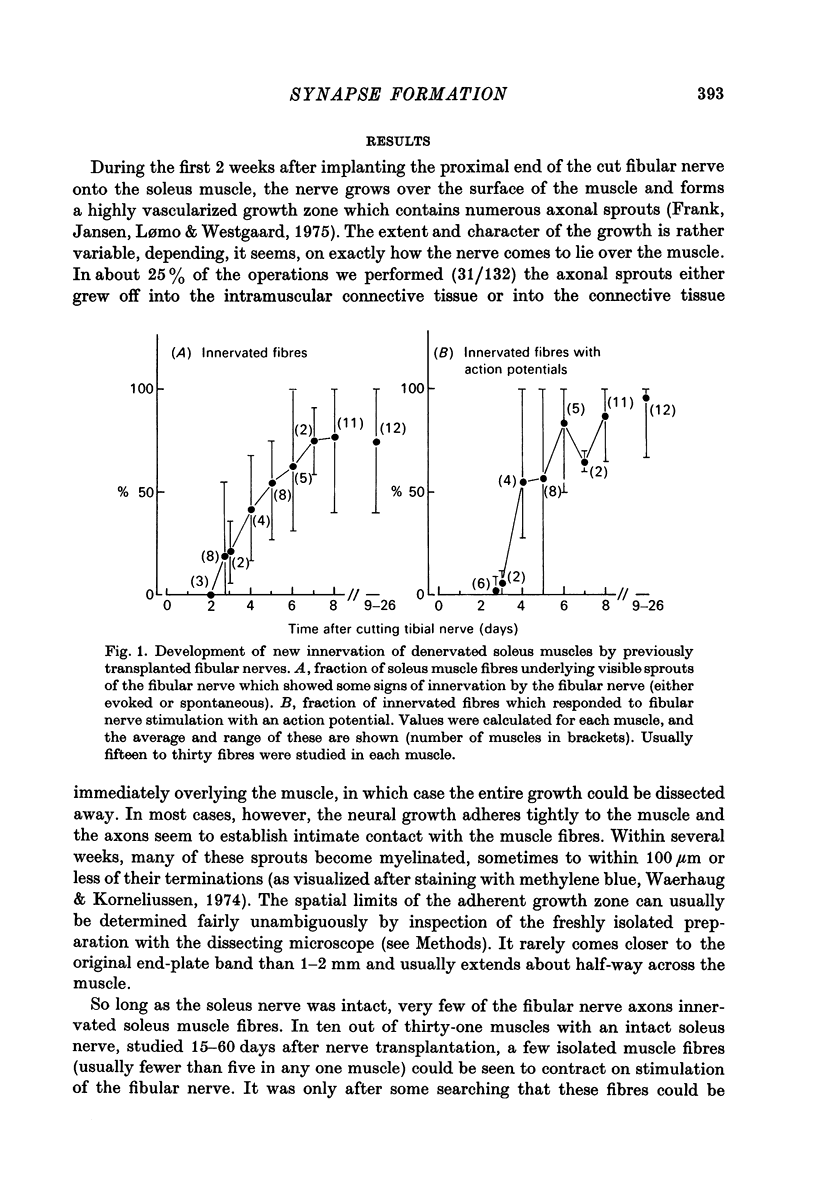
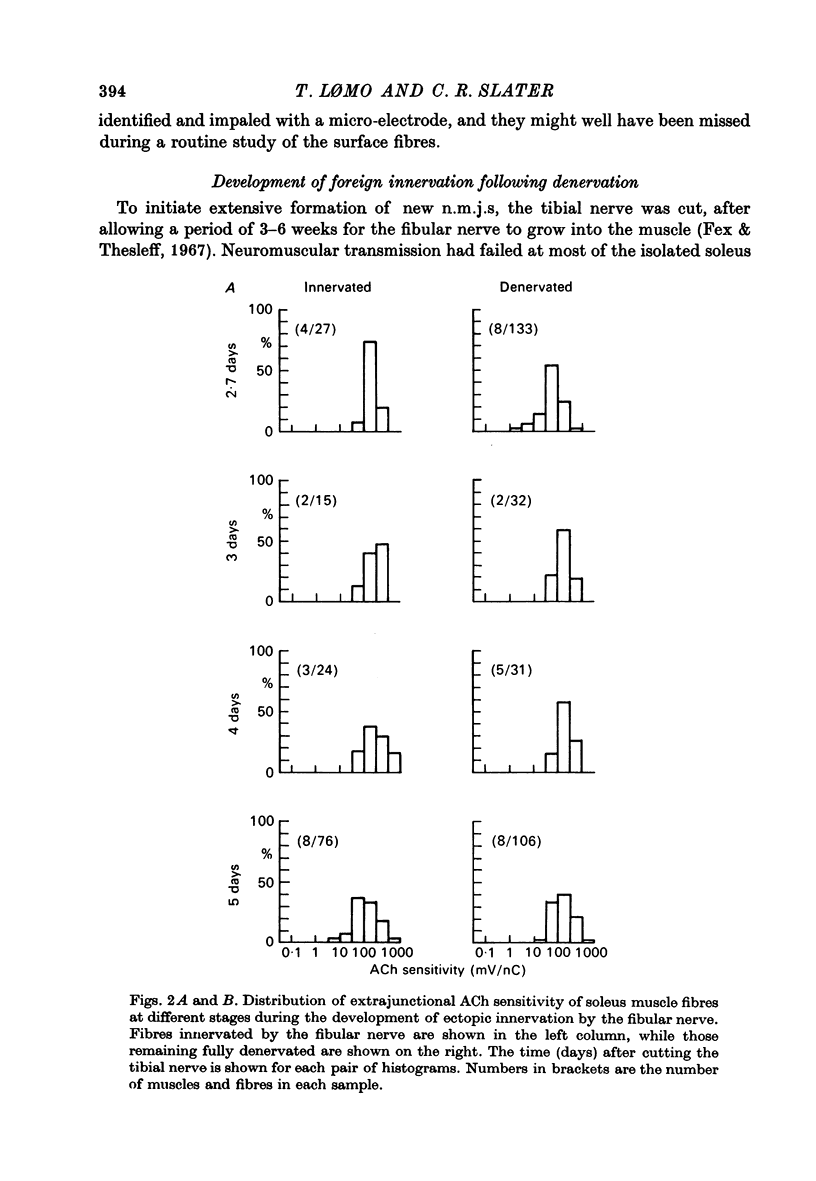
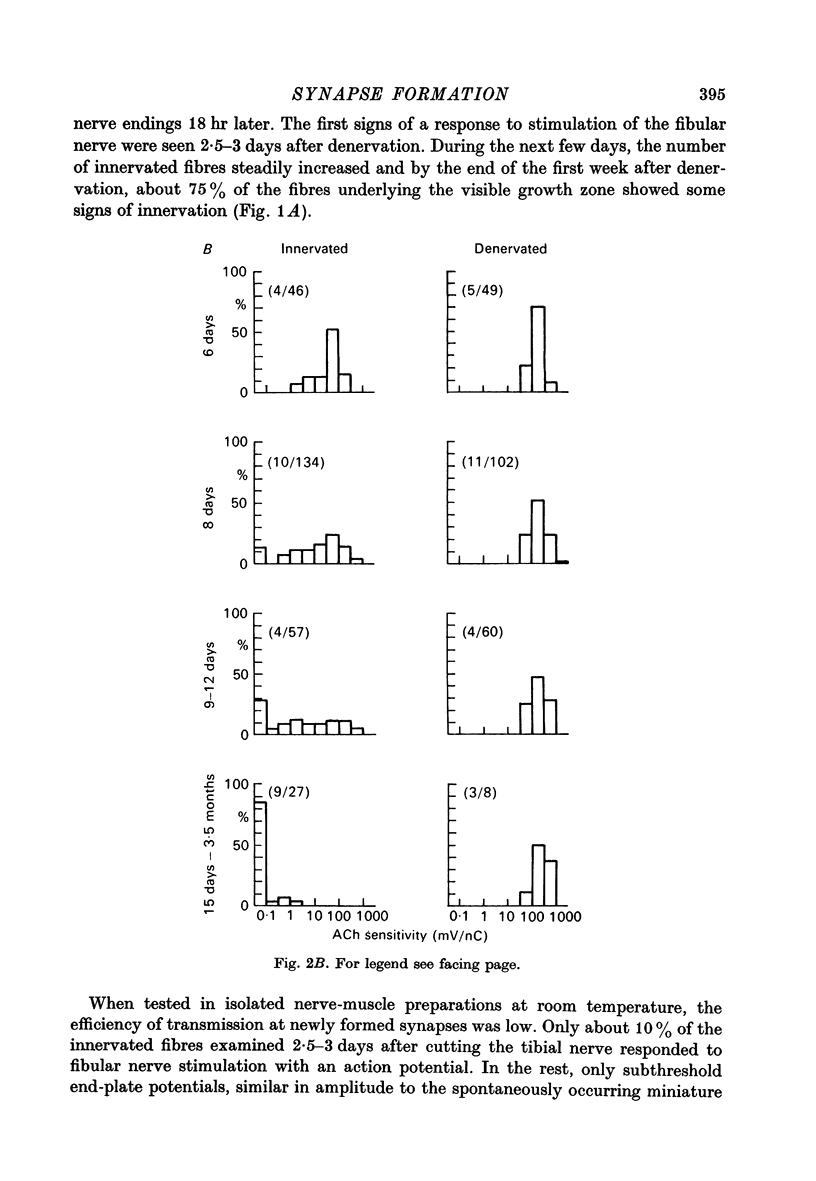
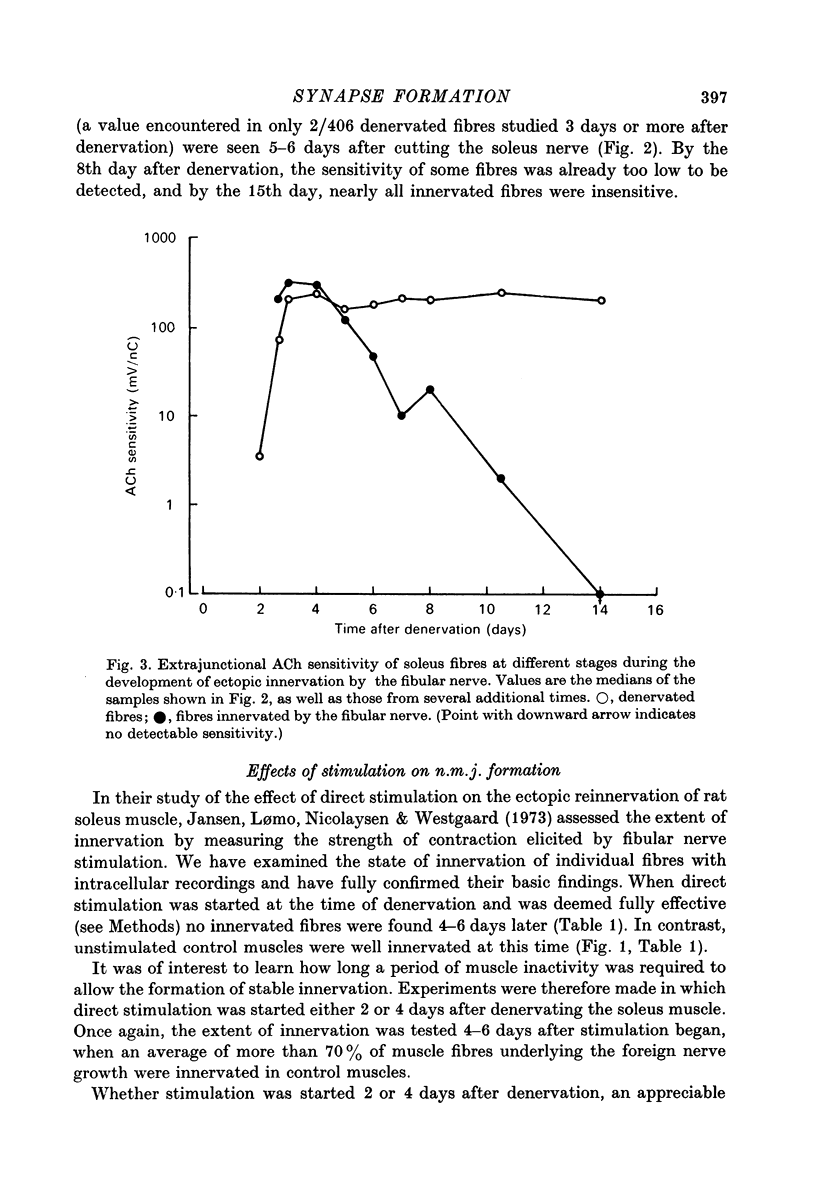
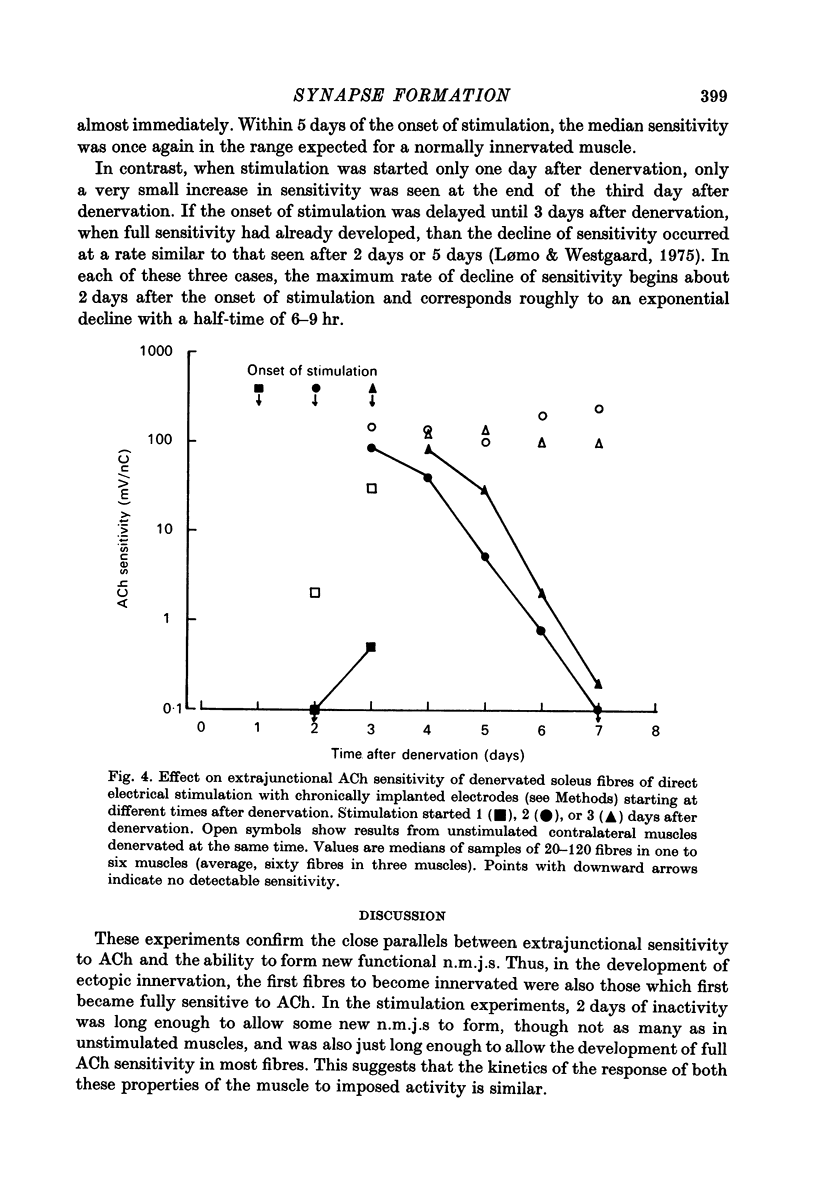
1. The formation of ectopic junctions between the 'foreign' superficial fibular nerve and the soleus muscle of adult rats, and its relation to changes in extrajunctional sensitivity to acetylcholine (ACh), has been studied by denervating the muscle 3-6 weeks after implanting the foreign nerve. 2. The earliest signs of nerve-muscle transmission were seen 2.5-3 days after denervation, in those fibres where the extrajunctional ACh sensitivity first reached its full post-denervation level. The number of innervated fibres continued to increase throughout the first week after denervation until 70-100% of fibres underlying the foreign nerve growth were innervated. 3. Direct stimulation of muscles with chronically implanted electrodes from the time of denervation prevents the formation of functional neuromuscular junctions (n.m.j.s). If stimulation begins 2 or 4 days after denervation, some functional n.m.j.s are formed which can be detected 7-9 days after denervation, though not as many as in the absence of stimulation. 4. Direct stimulation of muscles from the time of denervation prevents the development of detectable extrajunctional ACh sensitivity. If stimulation begins 2 days after denervation nearly maximal sensitivity develops during the third day and then rapidly declines to undetectable levels by the beginning of the eight day after denervation.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AXELSSON J., THESLEFF S. A study of supersensitivity in denervated mammalian skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1959 Jun 23;147(1):178–193. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitken J. T. Growth of nerve implants in voluntary muscle. J Anat. 1950 Jan;84(Pt 1):38–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. J., Cohen M. W. Nerve-induced and spontaneous redistribution of acetylcholine receptors on cultured muscle cells. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;268(3):757–773. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. J., Cohen M. W., Zorychta E. Effects of innervation on the distribution of acetylcholine receptors on cultured muscle cells. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;268(3):731–756. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. K., Hall Z. W. Fate of alpha-bungarotoxin bound to acetylcholine receptors of normal and denervated muscle. Science. 1974 Apr 26;184(4135):473–475. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4135.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. K., Hall Z. W. Loss of alpha-bungarotoxin from junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors in rat diaphragm muscle in vivo and in organ culture. J Physiol. 1975 Nov;252(3):771–789. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray J. J., Harris A. J. Dissociation between nerve-muscle transmission and nerve trophic effects on rat diaphragm using type D botulinum toxin. J Physiol. 1975 Dec;253(1):53–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockes J. P., Berg D. K., Hall Z. W. The biochemical properties and regulation of acetylcholine receptors in normal and denervated muscle. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:253–262. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley G. A., Heaton J. A quantitative study of cholinesterase in myoneural junctions from rat and guinea-pig extraocular muscles. J Physiol. 1968 Dec;199(3):743–749. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. C., Huang M. C. Turnover of junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors of the rat diaphragm. Nature. 1975 Feb 20;253(5493):643–644. doi: 10.1038/253643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. W. The development of neuromuscular connexions in the presence of D-tubocurarine. Brain Res. 1972 Jun 22;41(2):457–463. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90515-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M. J., Ort C. A. The distribution of acetylcholine receptors on muscle fibres of regenerating salamander limbs. J Physiol. 1977 Apr;266(3):765–776. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devreotes P. N., Fambrough D. M. Acetylcholine receptor turnover in membranes of developing muscle fibers. J Cell Biol. 1975 May;65(2):335–358. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.2.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsberg C. A. EXPERIMENTS ON MOTOR NERVE REGENERATION AND THE DIRECT NEUROTIZATION OF PARALYZED MUSCLES BY THEIR OWN AND BY FOREIGN NERVES. Science. 1917 Mar 30;45(1161):318–320. doi: 10.1126/science.45.1161.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fex S., Sonesson B., Thesleff S., Zelená J. Nerve implants in botulinum poisoned mammalian muscle. J Physiol. 1966 Jun;184(4):872–882. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fex S., Thesleff S. The time required for innervation of denervated muscles by nerve implants. Life Sci. 1967 Mar 15;6(6):635–639. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank E., Jansen J. K., Lomo T., Westgaard R. H. The interaction between foreign and original motor nerves innervating the soleus muscle of rats. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;247(3):725–743. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan P. G., Marshall J. M., Hall Z. W. Muscle activity decreases rate of degradation of alpha-bungarotoxin bound to extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors. Nature. 1976 May 27;261(5558):328–330. doi: 10.1038/261328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen J. K., Lomo T., Nicolaysen K., Westgaard R. H. Hyperinnervation of skeletal muscle fibers: dependence on muscle activity. Science. 1973 Aug 10;181(4099):559–561. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4099.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen J. K., Van Essen D. C. Re-innervation of rat skeleton muscle in the presence of alpha-bungarotoxin. J Physiol. 1975 Sep;250(3):651–667. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. THE DEVELOPMENT OF ACETYLCHOLINE SENSITIVITY IN NERVE-FREE SEGMENTS OF SKELETAL MUSCLE. J Physiol. 1964 Mar;170:389–396. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korneliussen H., Sommerschild H. Ultrastructure of the new neuromuscular junctions formed during reinnervation of rat soleus muscle by a "foreign" nerve. Cell Tissue Res. 1976 Apr 9;167(4):439–452. doi: 10.1007/BF00215176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomo T., Rosenthal J. Control of ACh sensitivity by muscle activity in the rat. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(2):493–513. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomo T., Westgaard R. H. Control of ACh sensitivity in rat muscle fibers. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:263–274. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomo T., Westgaard R. H. Further studies on the control of ACh sensitivity by muscle activity in the rat. J Physiol. 1975 Nov;252(3):603–626. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILEDI R. Properties of regenerating neuromuscular synapses in the frog. J Physiol. 1960 Nov;154:190–205. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILEDI R. The acetylcholine sensitivity of frog muscle fibres after complete or partial devervation. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:1–23. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonge D. A. Physiological characteristics of re-innervation of skeletal muscle in the mouse. J Physiol. 1974 Aug;241(1):141–153. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waerhaug O., Korneliussen H. Morphological types of motor nerve terminals in rat hindlimb muscles, possibly innervating different muscle fiber types. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch. 1974;144(3):237–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00522809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


