Abstract
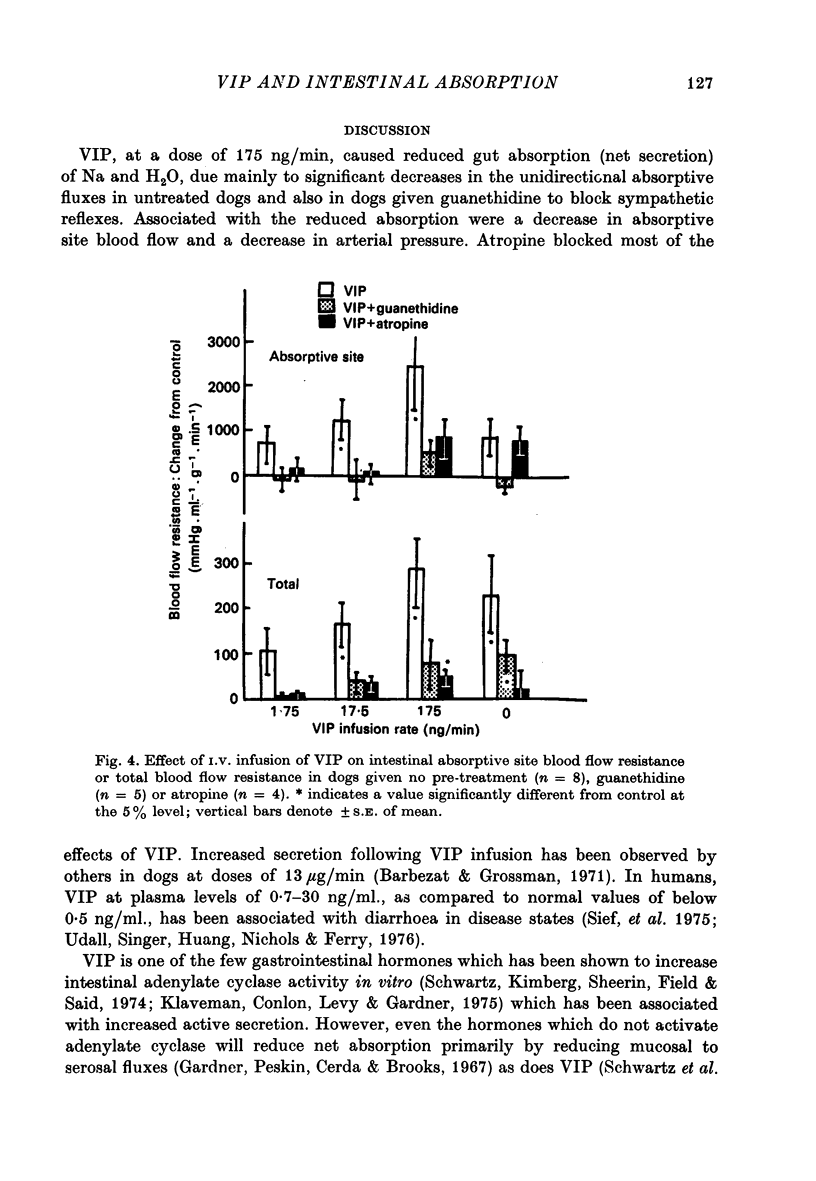
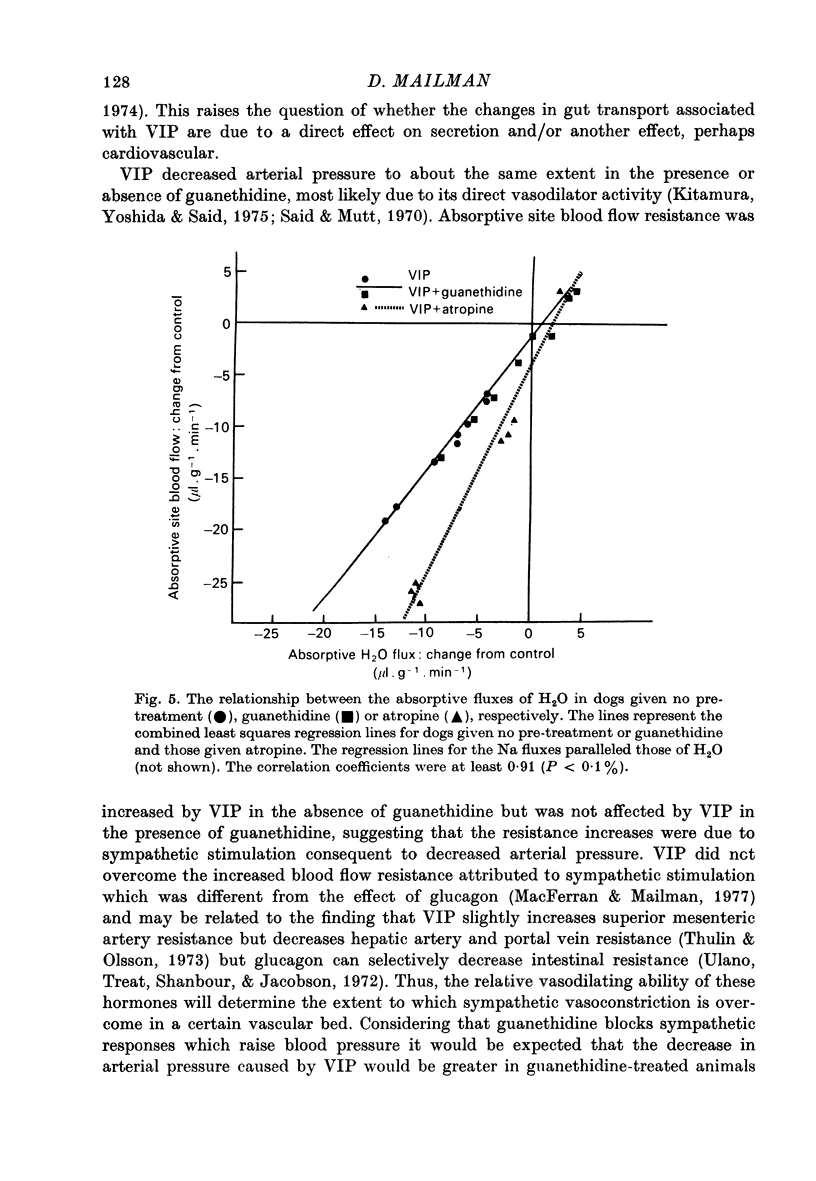
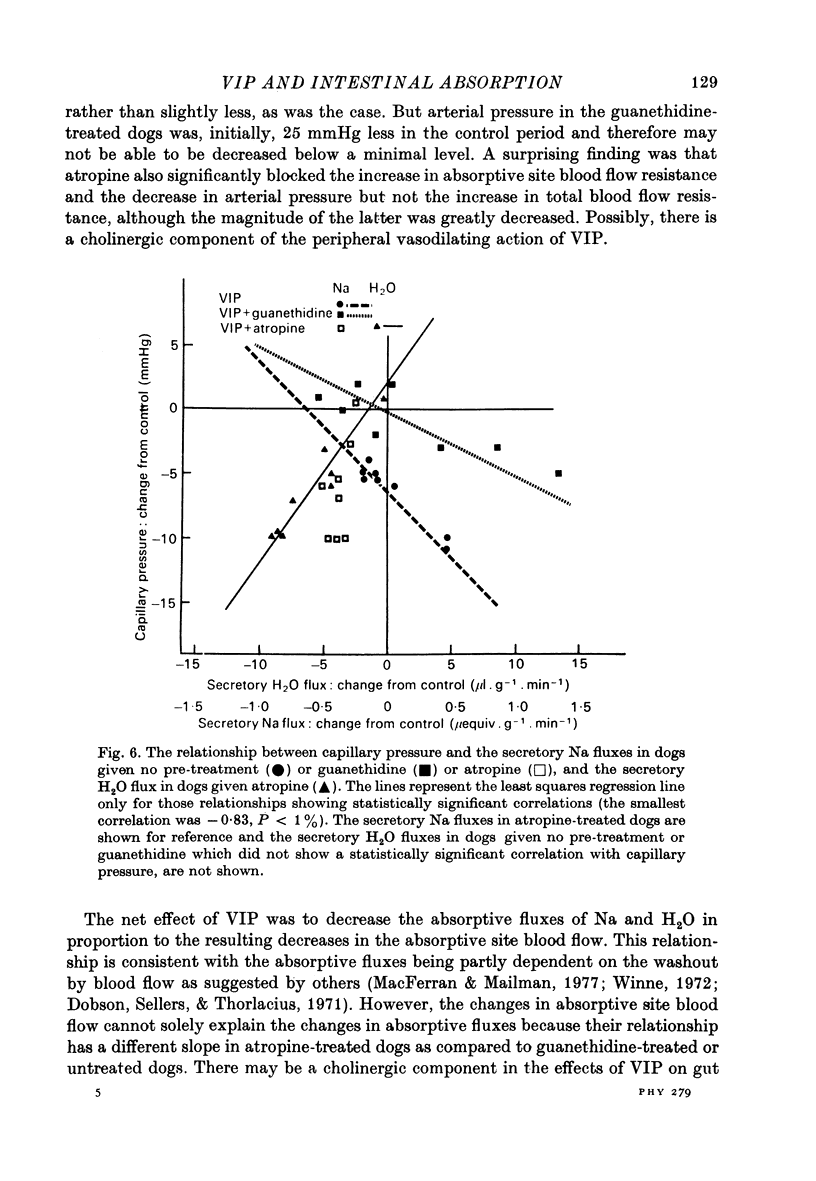
1. Intestinal absorption and blood flow in anaesthetized dogs was determined after I.V. infusion of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) (1.75-175 ng/min) to determine the contribution of the cardiovascular changes to transport. 2. 22Na and 3H2O were utilized to determine the unidirectional fluxes of Na and H2O from saline perfused through the ileal lumen and the clearances of 3H2O were used to determine total and absorptive site blood flow. 3. Net Na and H2O absorption were reversed to secretion by VIP at 175 ng/min due to a significant decrease in unidirectional absorptive fluxes and smaller increases in secretory fluxes. 4. Arterial pressure and absorptive site blood flow were reduced in proportion to the changes in Na and H2O fluxes. 5. Total and absorptive site blood flow decreased and the blood flow resistances increased. 6. Prior treatment with guanethidine to suppress sympathetic effects did not greatly affect the responses to VIP. Prior treatment with atropine to suppress cholinergic effects inhibited most of the effects of VIP. 7. Absorptive site blood flow was linearly related to absorptive fluxes of Na and H2O but with different slopes for results from atropinized dogs as compared to those from dogs given VIP alone or VIP plus guanethidine. 8. It was concluded that VIP reduces gut absorption through a generalized cardiovascular effect and also through a mechanism which depends on the release of ACh by the gut.
Full text
PDF

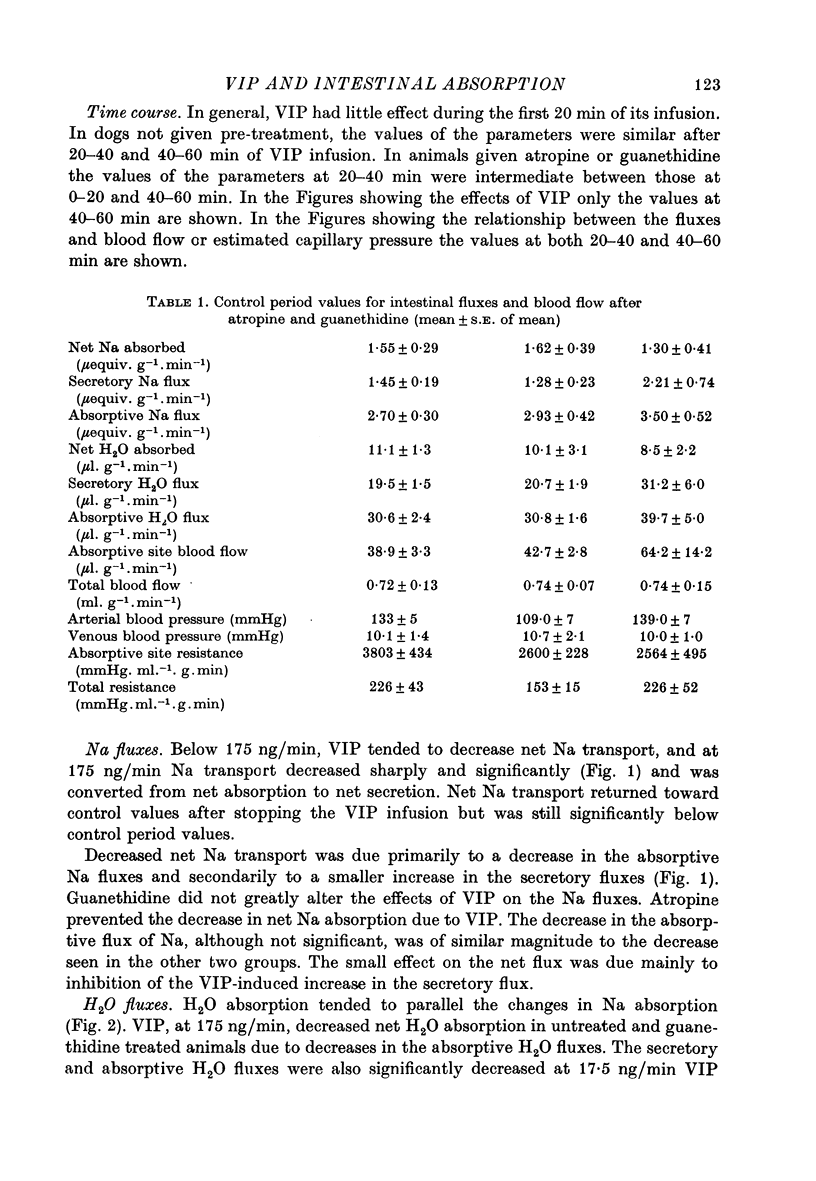
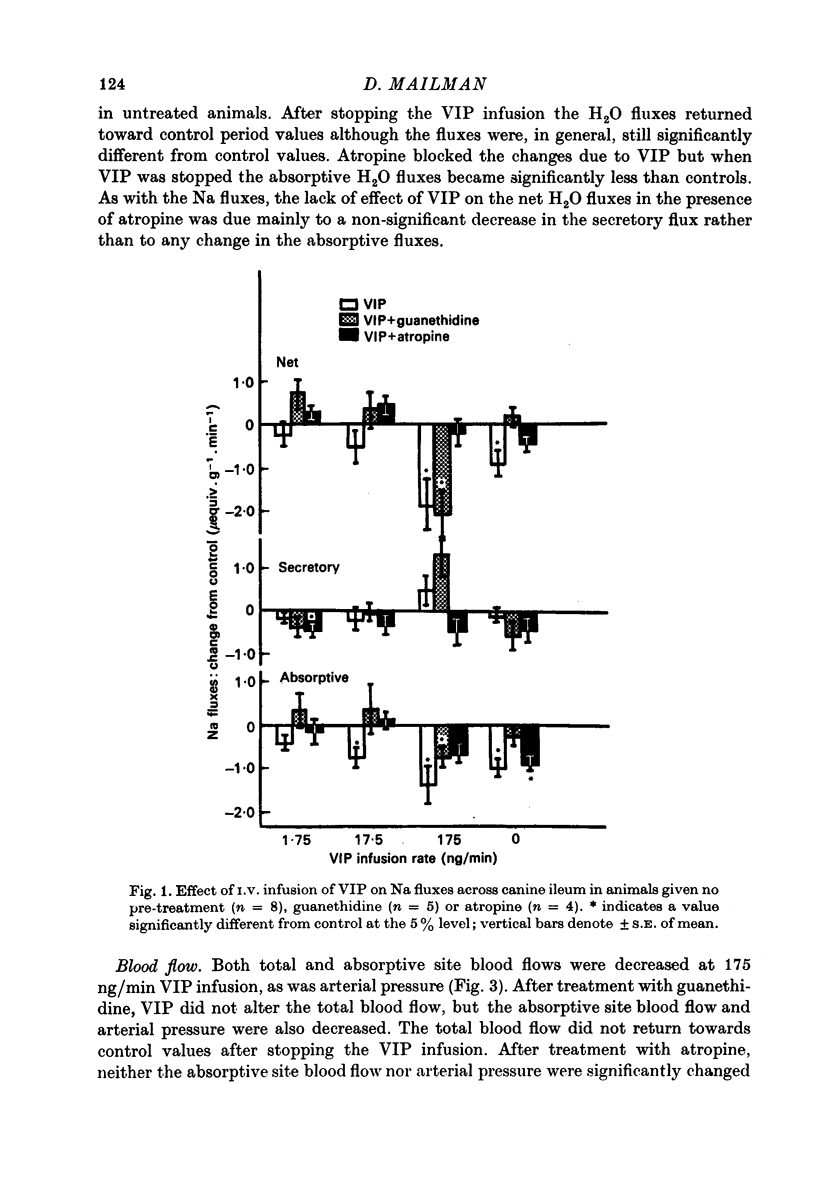
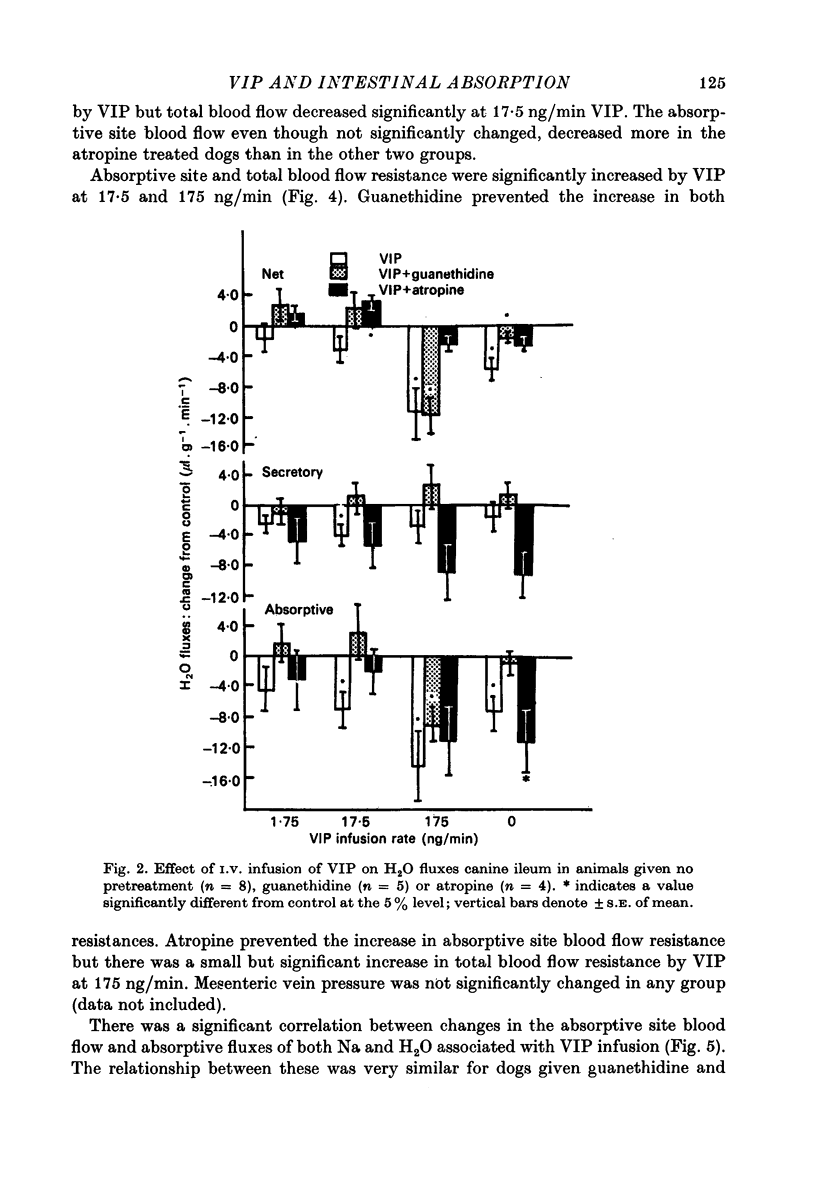
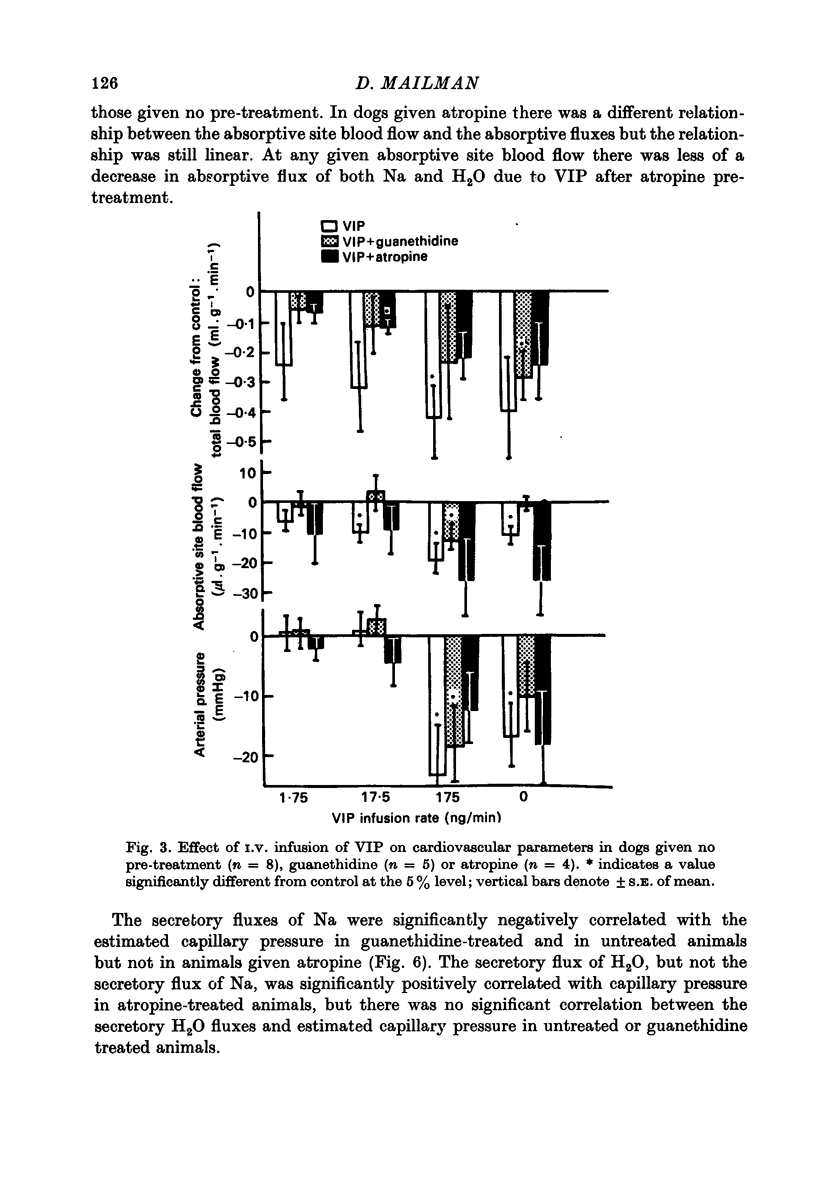



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki N., Von Kaulla K. N. Human serum plasminogen antiactivator: its distinction from antiplasmin. Am J Physiol. 1971 Apr;220(4):1137–1145. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.4.1137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGER E. Y., STEELE J. M. The calculation of transfer rates in two compartment systems not in dynamic equilibrium. J Gen Physiol. 1958 Jul 20;41(6):1135–1152. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.6.1135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbezat G. O., Grossman M. I. Intestinal secretion: stimulation by peptides. Science. 1971 Oct 22;174(4007):422–424. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4007.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V., Hardy R. N., Malinowska K., Silver M. Cardiovascular and endocrine responses to feeding in the young calf. J Physiol. 1975 Dec;253(1):135–155. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Polak J. M., Pearse A. G. Vasoactive intestinal peptide and watery-diarrhoea syndrome. Lancet. 1973 Jul 7;2(7819):14–16. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91947-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen J. C., Pawlik W., Fang W. F., Jacobson E. D. Pharmacologic effects of gastrointestinal hormones on intestinal oxygen consumption and blood flow. Surgery. 1975 Oct;78(4):515–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussjaeger L. J., Johnson L. R. Evidence for hormonal regulation of intestinal absorption by cholecystokinin. Am J Physiol. 1973 Jun;224(6):1276–1279. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.6.1276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bynum T. E., Jacobson E. D., Johnson L. R. Gastrin inhibition of intestinal absorption in dogs. Gastroenterology. 1971 Dec;61(6):858–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkow B. Regional adjustments of intestinal blood flow. Gastroenterology. 1967 Feb;52(2):423–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. D., Peskin G. W., Cerda J. J., Brooks F. P. Alterations of in vitro fluid and electrolyte absorption by gastrointestinal hormones. Am J Surg. 1967 Jan;113(1):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(67)90257-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helman C. A., Barbezat G. O. The effect of gastric inhibitory polypeptide on human jejunal water and electrolyte transport. Gastroenterology. 1977 Feb;72(2):376–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel K. A. Effects of secretin and glucagon on intestinal transport of ions and water in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Feb;139(2):656–658. doi: 10.3181/00379727-139-36208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel K. A. Intestinal ion transport: effect of norepinephrine, pilocarpine, and atropine. Am J Physiol. 1976 Jul;231(1):252–257. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.1.252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura S., Yoshida T., Said S. I. Vasoactive intestinal polypoptide: inactivation in liver and potentiation in lung of anesthetized dogs (384699). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Jan;148(1):25–29. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaeveman H. L., Conlon T. P., Levy A. G., Gardner J. D. Effects of gastrointestinal hormones on adenylate cyclase activity in human jejunal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1975 Apr;68(4 Pt 1):667–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacFerran S. N., Mailman D. Effects of glucagon on canine intestinal sodium and water fluxes and regional blood flow. J Physiol. 1977 Mar;266(1):1–12. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mailman D., Jordan K. The effect of saline and hyperoncotic dextran infusion on canine ileal salt and water absorption and regional blood flow. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;252(1):97–113. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makhlouf G. M. The neuroendocrine design of the gut. The play of chemicals in a chemical playground. Gastroenterology. 1974 Jul;67(1):159–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said S. I., Mutt V. Isolation from porcine-intestinal wall of a vasoactive octacosapeptide related to secretin and to glucagon. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 13;28(2):199–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01903.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said S. I., Mutt V. Potent peripheral and splanchnic vasodilator peptide from normal gut. Nature. 1970 Feb 28;225(5235):863–864. doi: 10.1038/225863a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz C. J., Kimberg D. V., Sheerin H. E., Field M., Said S. I. Vasoactive intestinal peptide stimulation of adenylate cyclase and active electrolyte secretion in intestinal mucosa. J Clin Invest. 1974 Sep;54(3):536–544. doi: 10.1172/JCI107790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seif F. J., Sadowski P., Heni F., Fischer R., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M. Das vasoaktive intestinale Polypeptid beim Verner-Morrison-Syndrom. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1975 Feb 28;100(9):399–405. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1106226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheerin H. E., Field M. Ileal mucosal cyclic AMP and Cl secretion: serosal vs. mucosal addition of cholera toxin. Am J Physiol. 1977 Feb;232(2):E210–E215. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1977.232.2.E210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thulin L., Olsson P. Effects of intestinal peptide mixture G2 and vasoactive intestinal peptide VIP on splanchnic circulation in the dog. Acta Chir Scand. 1973;139(8):691–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udall J. N., Singer D. B., Huang C. T., Nichols B. L., Ferry G. D. Watery diarrhea and hypokalemia associated with increased plasma vasoactive intestinal peptide in a child. J Pediatr. 1976 May;88(5):819–821. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)81121-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulano H. B., Treat E., Shanbour L. L., Jacobson E. D. Selective dilation of the constricted superior mesenteric artery. Gastroenterology. 1972 Jan;62(1):39–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizi S. E., Bertaccini G., Impicciatore M., Knoll J. Evidence that acetylcholine released by gastrin and related polypeptides contributes to their effect on gastrointestinal motility. Gastroenterology. 1973 Feb;64(2):268–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winne D. The influence of blood flow and water net flux on the absorption of tritiated water from the jejunum of the rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1972;272(4):417–436. doi: 10.1007/BF00501248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


