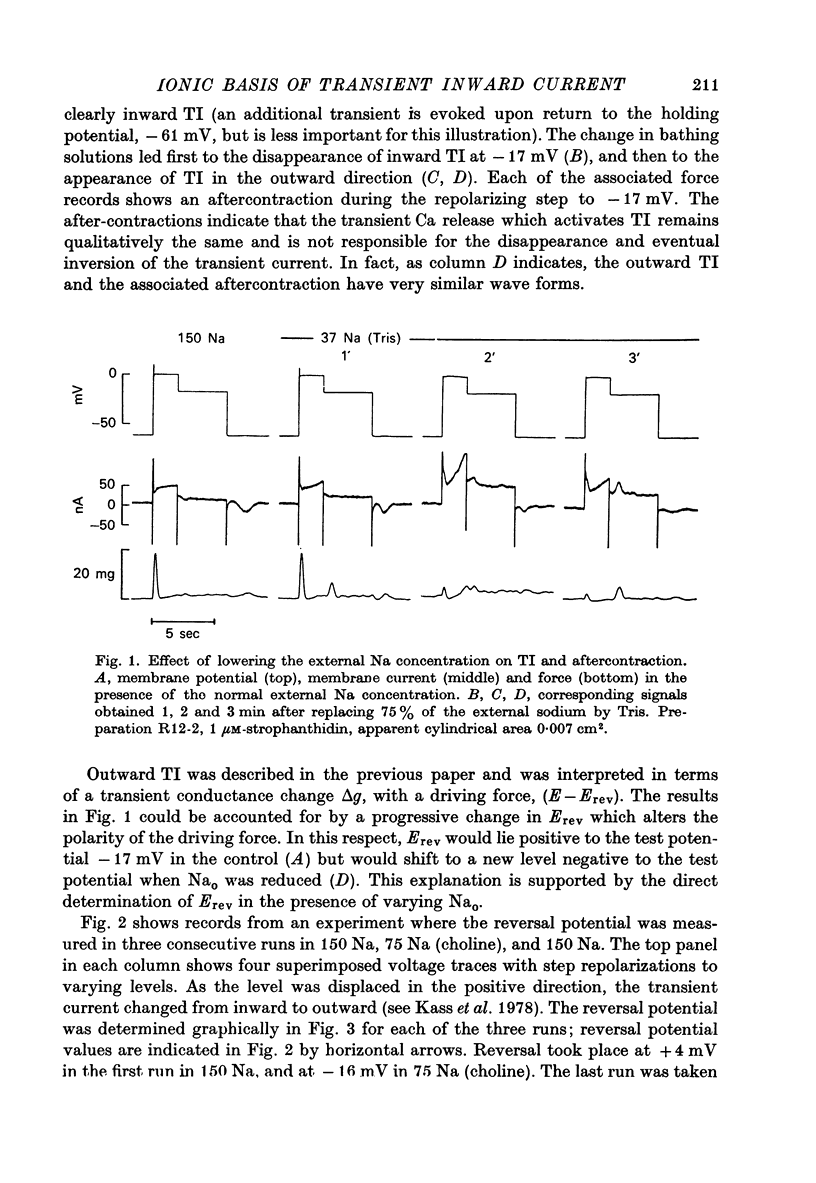
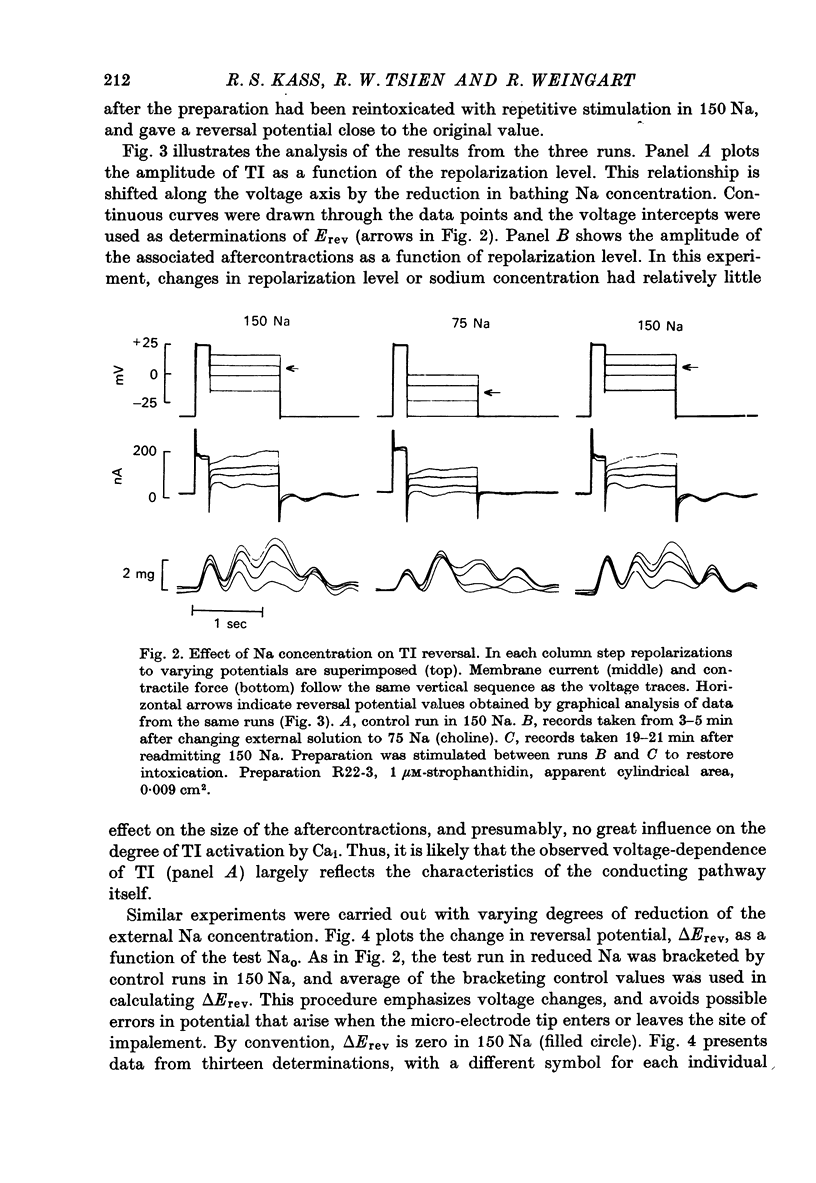
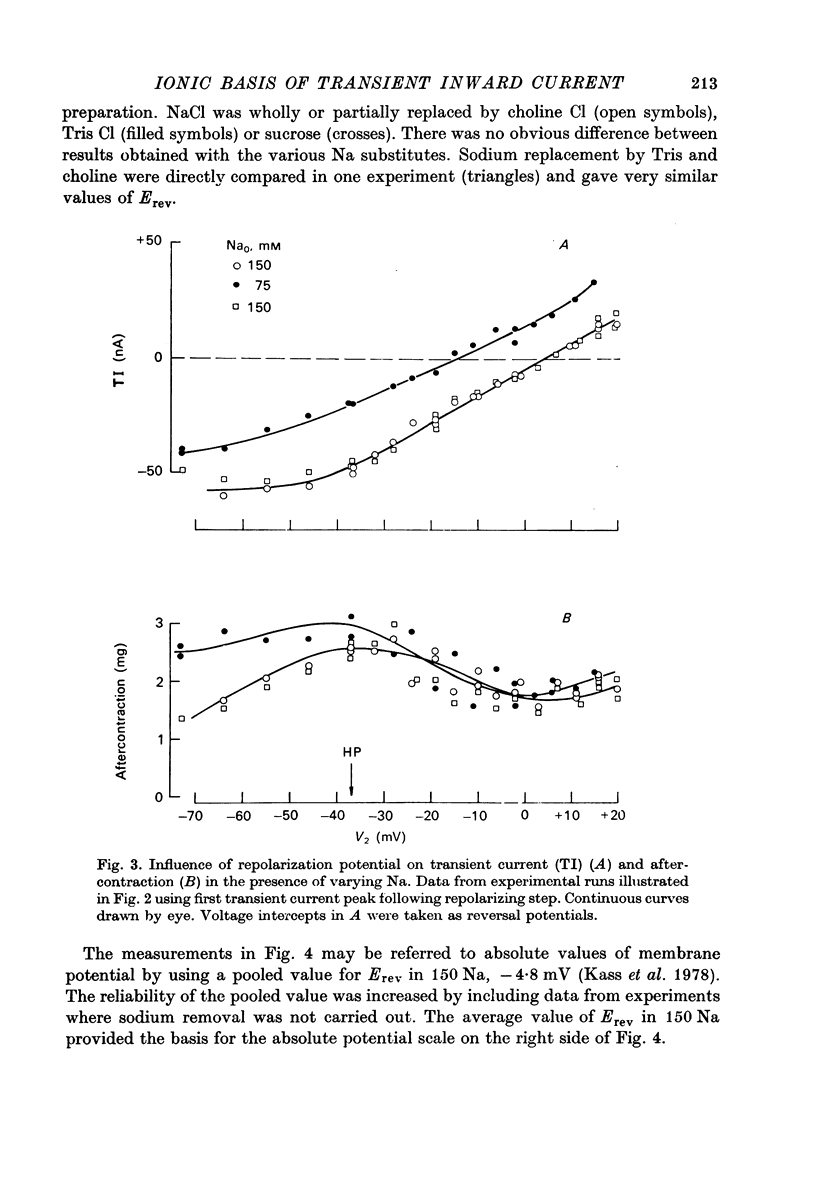
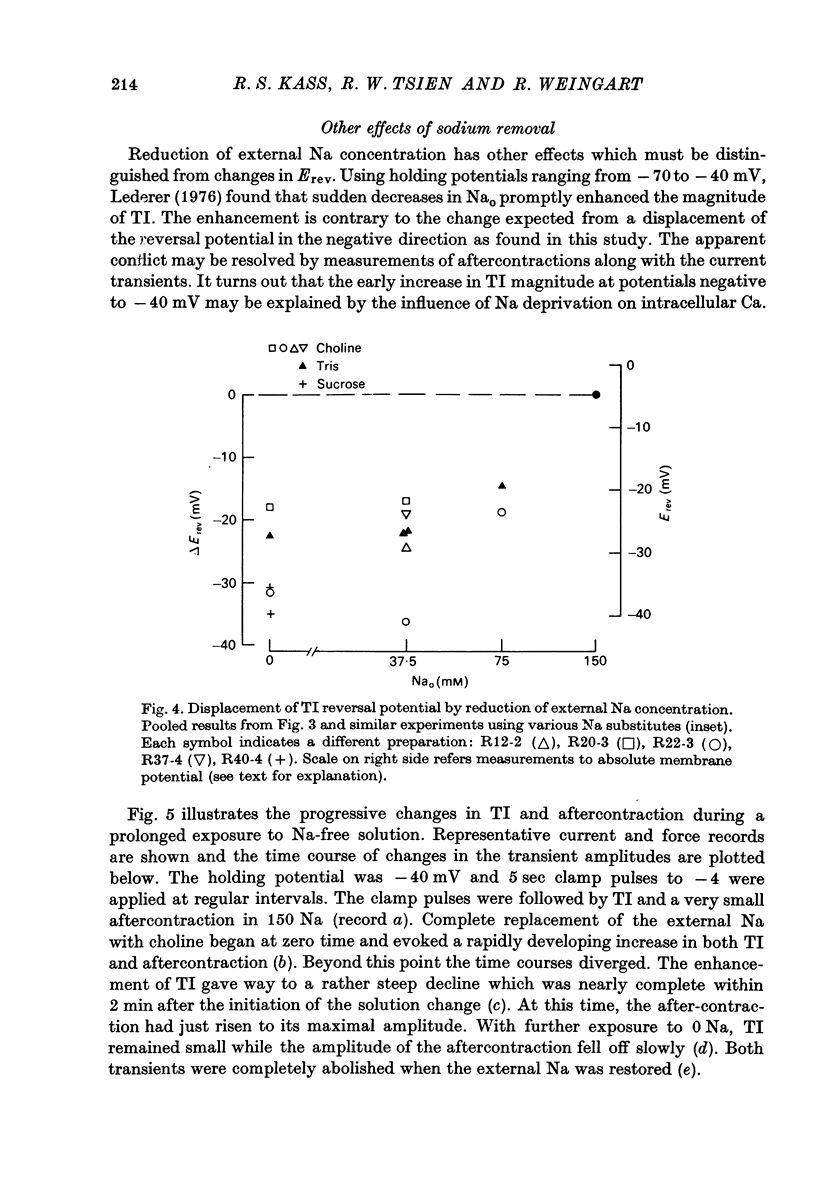
Abstract
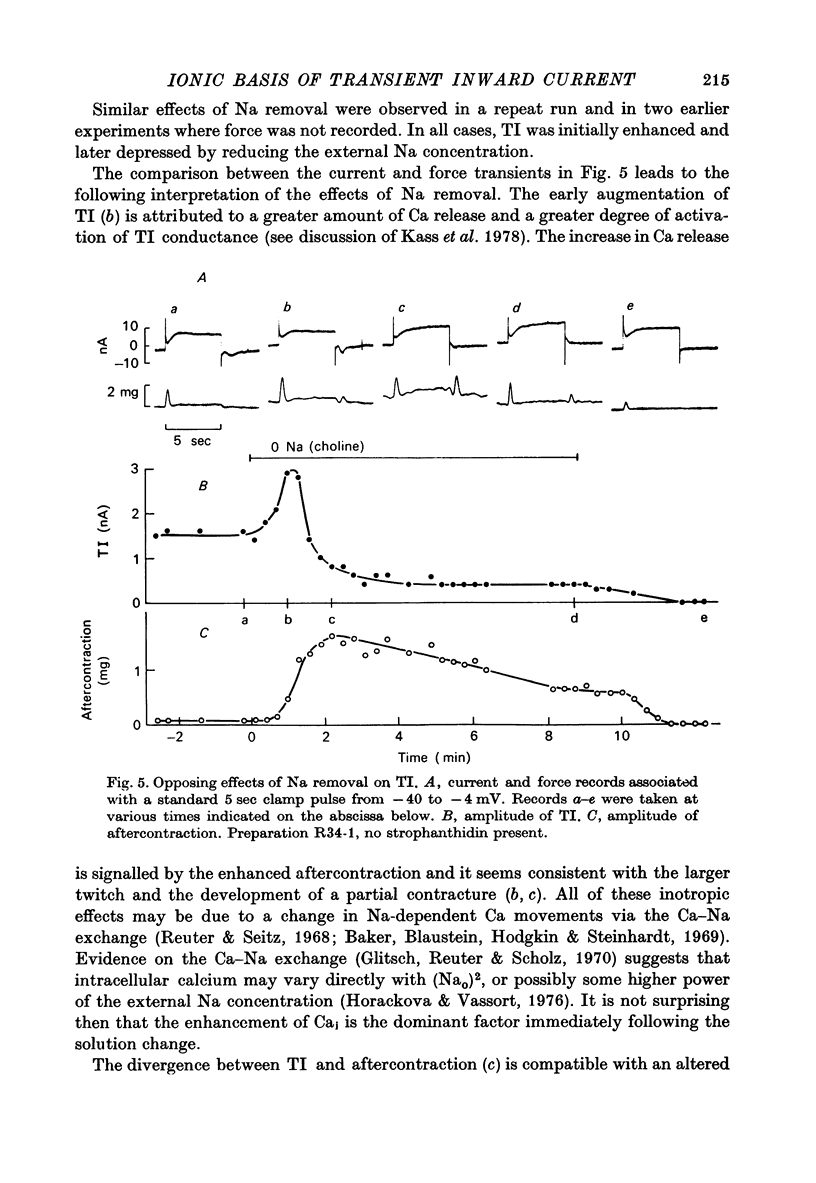
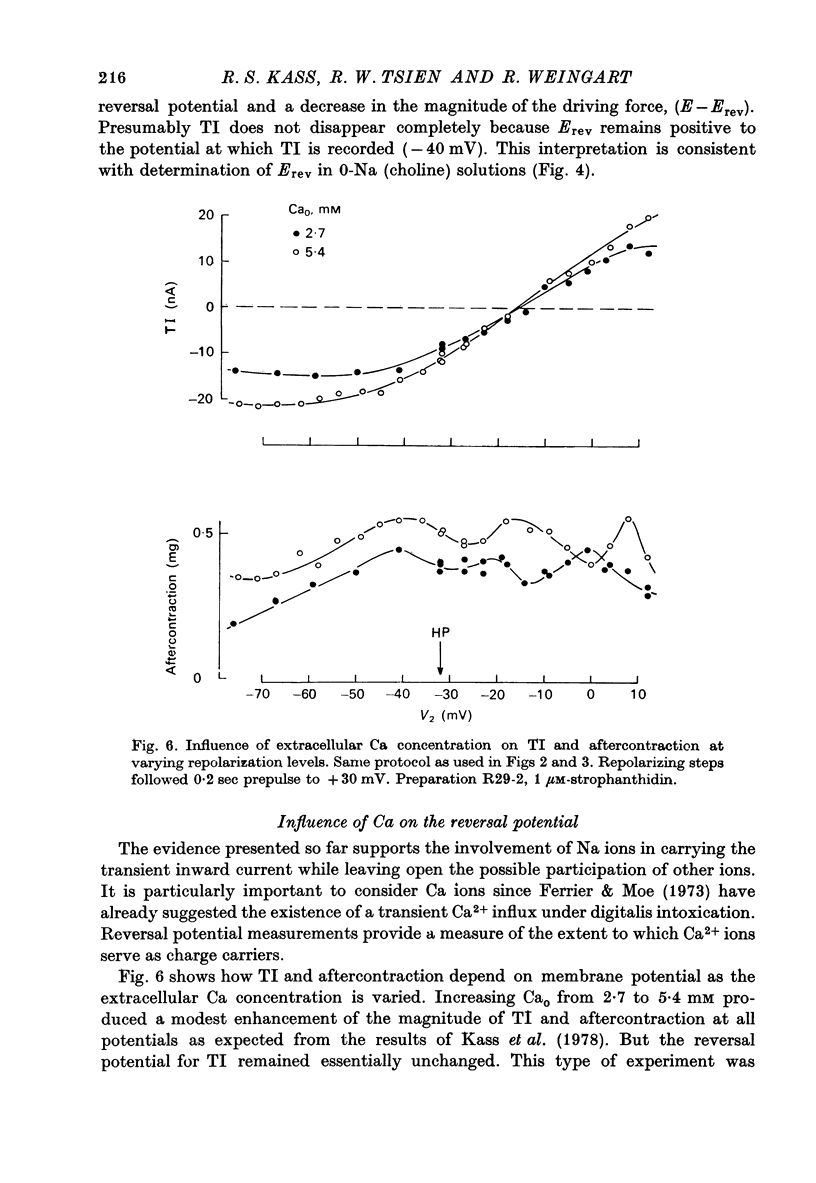
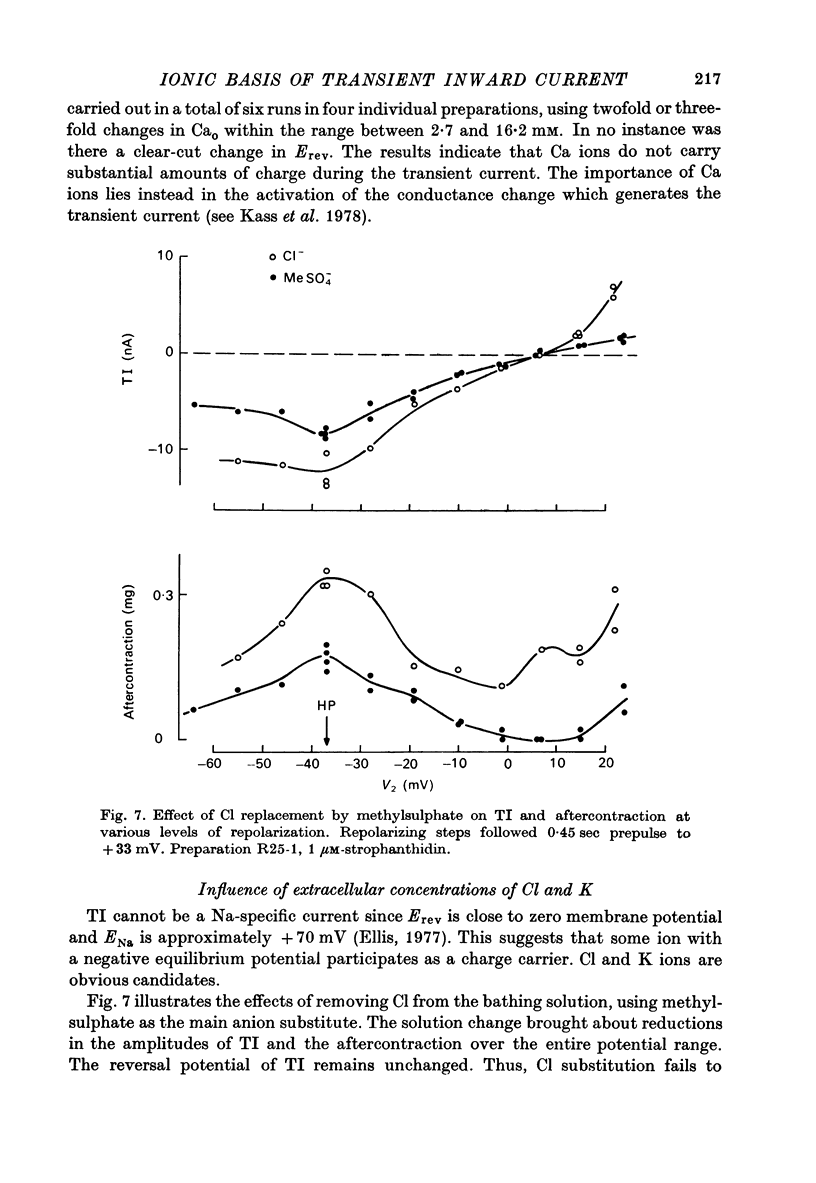
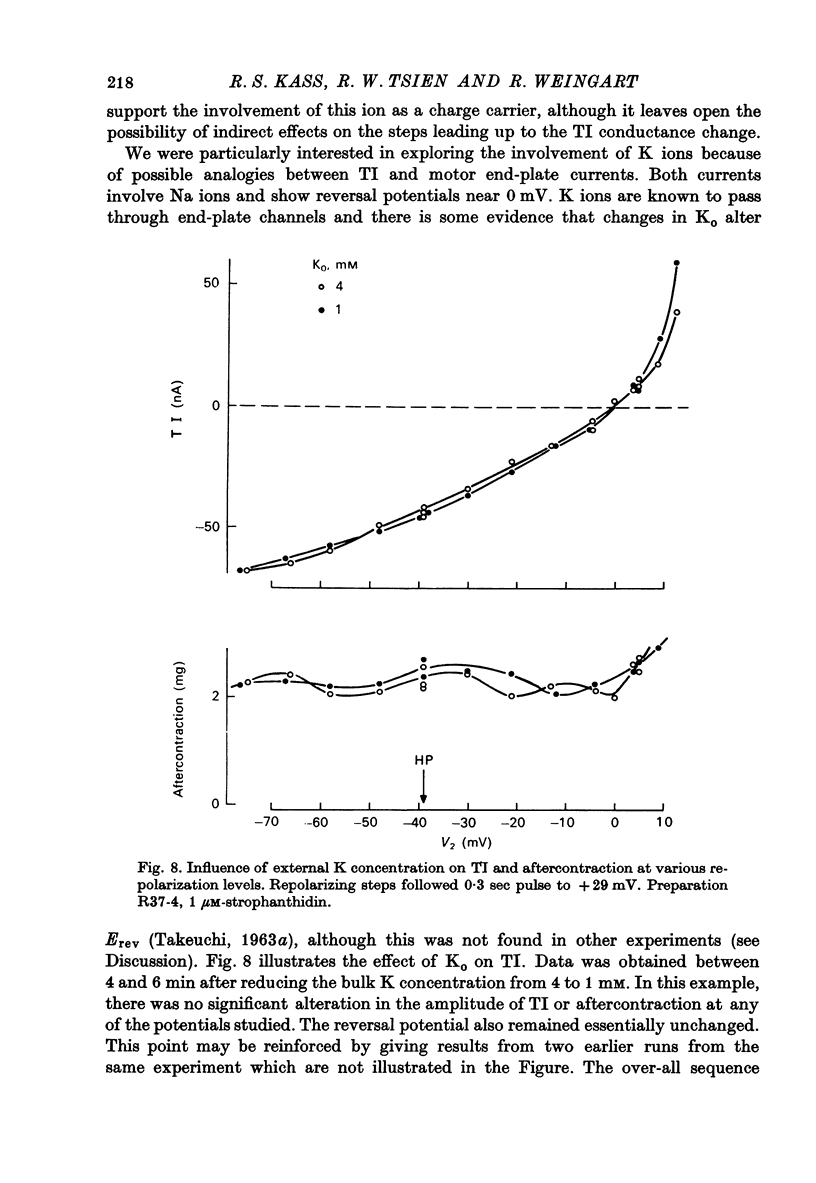
1. Voltage clamp experiements studied the ionic basis of the strophathidin-induced transient inward current (TI) in cardiac Purkinje fibres. 2. The reversal potential of TI (Erev) was determined in the presence of various bathing solutions. Erev averaged --5 m V in the standard modified Tyrode solution (Kass, Lederer, Tsien & Weingart, 1978). Erev was displaced toward more negative potentials when the external Na concentration (NaO) was reduced by replacement of NaCl with Tris Cl, choline Cl or sucrose. 3. A sudden reduction of NaO evoked a temporary increase in TI, followed after a few minutes by a sustained diminution. The initial increase was closely paralleled by an enhanced aftercontraction and could be explained by an indirect effect of NaO on internal Ca. The subsequent fall in TI amplitude could be accounted for by the reduced driving force, E--Erev. 4. Erev was not significantly changed by replacing extracellular Cl with methyl-sulphate, or by limited variations in external Ca (2.7--16.2 mM) or external K (1--8 MM). 5. These results are consistent with an increase in membrane permeability to Na and perhaps K. 6. TI was not directly affected by TTX, which blocks excitatory Na channels, or by Cs, which inhibits inwardly rectifying K channels. TI may be distinguished from the slow inward current by its kinetic, pharmacological and ionic properties. 7. TI might be carried by a pre-existing ionic pathway such as the 'leak' channel which provides inward current underlying normal pace-maker depolarization. Another possibility is that TI reflects Ca extrusion by an electrogenic Ca--Na exchange.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama T., Fozzard H. A. Influence of potassium ions and osmolality on the resting membrane potential of rabbit ventricular papillary muscle with estimation of the activity and the activity coefficient of internal potassium. Circ Res. 1975 Nov;37(5):621–629. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.5.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Blaustein M. P., Hodgkin A. L., Steinhardt R. A. The influence of calcium on sodium efflux in squid axons. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):431–458. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., McNaughton P. A. Kinetics and energetics of calcium efflux from intact squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;259(1):103–144. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F. Transport and metabolism of calcium ions in nerve. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1972;24:177–223. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(72)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassingthwaighte J. B., Fry C. H., McGuigan J. A. Relationship between internal calcium and outward current in mammalian ventricular muscle; a mechanism for the control of the action potential duration? J Physiol. 1976 Oct;262(1):15–37. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Russell J. M., Weer P. Calcium efflux from internally dialyzed squid axons: the influence of external and internal cations. J Supramol Struct. 1974;2(5-6):558–581. doi: 10.1002/jss.400020505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. The interrelationship between sodium and calcium fluxes across cell membranes. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1974;70:33–82. doi: 10.1007/BFb0034293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosteels S., Carmeliet E. Estimation of intracellular Na concentration and transmembrane Na flux in cardiac Purkyne fibres. Pflugers Arch. 1972;336(1):35–47. doi: 10.1007/BF00589140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M. D. Modification of sodium channel gating in frog myelinated nerve fibres by Centruroides sculpturatus scorpion venom. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(2):511–534. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet E., Vereecke J. Adrenaline and the plateau phase of the cardiac action potential. Importance of Ca++, Na+ and K+ conductance. Pflugers Arch. 1969;313(4):300–315. doi: 10.1007/BF00593955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J., Peper K., Rüdel R., Trautwein W. The effect of tetrodotoxin on the membrane current in cardiac muscle (Purkinje fibers). Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1967;295(3):213–226. doi: 10.1007/BF01844101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis D. The effects of external cations and ouabain on the intracellular sodium activity of sheep heart Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(1):211–240. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H. The entry of labelled calcium into the innervated region of the mouse diaphragm muscle. J Physiol. 1974 Aug;240(3):517–533. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrier G. R. Digitalis arrhythmias: role of oscillatory afterpotentials. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1977 May-Jun;19(6):459–474. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(77)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrier G. R., Moe G. K. Effect of calcium on acetylstrophanthidin-induced transient depolarizations in canine Purkinje tissue. Circ Res. 1973 Nov;33(5):508–515. doi: 10.1161/01.res.33.5.508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrier G. R. The effects of tension on acetylstrophanthidin-induced transient depolarizations and aftercontractions in canine myocardial and Purkinje tissues. Circ Res. 1976 Mar;38(3):156–162. doi: 10.1161/01.res.38.3.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glitsch H. G., Reuter H., Scholz H. The effect of the internal sodium concentration on calcium fluxes in isolated guinea-pig auricles. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;209(1):25–43. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D. E. POTENTIAL, IMPEDANCE, AND RECTIFICATION IN MEMBRANES. J Gen Physiol. 1943 Sep 20;27(1):37–60. doi: 10.1085/jgp.27.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horackova M., Vassort G. Proceedings: Regulation of tonic tension in frog atrial muscle by voltage-dependent Na-Ca exchange. J Physiol. 1976 Jun;258(2):77P–78P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg G. Cardiac Purkinje fibers: cesium as a tool to block inward rectifying potassium currents. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Sep 30;365(2-3):99–106. doi: 10.1007/BF01067006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isnberg G. Is potassium conductance of cardiac Purkinje fibres controlled by (Ca2+)? Nature. 1975 Jan 24;253(5489):273–274. doi: 10.1038/253273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki N., Petersen O. H. Acetylcholine-like effects of intracellular calcium application in pancreatic acinar cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):147–149. doi: 10.1038/268147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINSON D. H., NICHOLLS J. G. Contractures and permeability changes produced by acetylcholine in depolarized denervated muscle. J Physiol. 1961 Nov;159:111–127. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. L-glutamate as an excitatory transmitter at the Drosophila larval neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;262(1):215–236. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. A., Lieberman M. Heart: excitation and contraction. Annu Rev Physiol. 1971;33:479–532. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.33.030171.002403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass R. S., Lederer W. J., Tsien R. W., Weingart R. Role of calcium ions in transient inward currents and aftercontractions induced by strophanthidin in cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:187–208. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassignal N. L., Martin A. R. Effect of acetylcholine on postjunctional membrane permeability in eel electroplaque. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Jul;70(1):23–36. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederer W. J., Tsien R. W. Proceedings: Transient inward current underlying strophanthidin's enhancement of pace-maker activity in Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(1):40P–41P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederer W. J., Tsien R. W. Transient inward current underlying arrhythmogenic effects of cardiotonic steroids in Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1976 Dec;263(2):73–100. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. O., Fozzard H. A. Activities of potassium and sodium ions in rabbit heart muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Jun;65(6):695–708. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.6.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R. Permeable junctions. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:49–63. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeno T., Edwards C., Anraku M. Permeability of the endplate membrane activated by acetylcholine to some organic cations. J Neurobiol. 1977 Mar;8(2):173–184. doi: 10.1002/neu.480080208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura D. S., Hoffman B. F., Rosen M. R. The effect of extracellular potassium on the intracellular potassium ion activity and transmembrane potentials of beating canine cardiac Purkinje fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Apr;69(4):463–474. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.4.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins L. J., Brinley F. J., Jr Sensitivity of calcium efflux from squid axons to changes in membrane potential. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Feb;65(2):135–152. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.2.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson O. H., Iwatsuki N. The role of calcium in pancreatic acinar cell stimulus-secretion coupling: an electrophysiological approach. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Apr 28;307:599–617. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb41984.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REITER M. [The origin of "postcontractions" in the myocardium under the influence of calcium and digitalis glycosides in relation to the frequency of stimulation]. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1962;242:497–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P. Acetylcholine receptors. Q Rev Biophys. 1974 Jul;7(3):283–399. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Divalent cations as charge carriers in excitable membranes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1973;26:1–43. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(73)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Exchange of calcium ions in the mammalian myocardium. Mechanisms and physiological significance. Circ Res. 1974 May;34(5):599–605. doi: 10.1161/01.res.34.5.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H., Scholz H. A study of the ion selectivity and the kinetic properties of the calcium dependent slow inward current in mammalian cardiac muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Jan;264(1):17–47. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H., Seitz N. The dependence of calcium efflux from cardiac muscle on temperature and external ion composition. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):451–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie A. K., Fambrough D. M. Ionic properties of the acetylcholine receptor in cultured rat myotubes. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Jun;65(6):751–767. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.6.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbach J. H. Acetylcholine responses on clonal myogenic cells in vitro. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(2):393–405. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. On the permeability of end-plate membrane during the action of transmitter. J Physiol. 1960 Nov;154:52–67. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI N. Effects of calcium on the conductance change of the end-plate membrane during the action of transmitter. J Physiol. 1963 Jun;167:141–155. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI N. Some properties of conductance changes at the end-plate membrane during the action of acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1963 Jun;167:128–140. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASSALLE M., KARIS J., HOFFMAN B. F. Toxic effects of ouabain on Purkinje fibers and ventricular muscle fibers. Am J Physiol. 1962 Sep;203:433–439. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.203.3.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDMANN S. The effect of the cardiac membrane potential on the rapid availability of the sodium-carrying system. J Physiol. 1955 Jan 28;127(1):213–224. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


