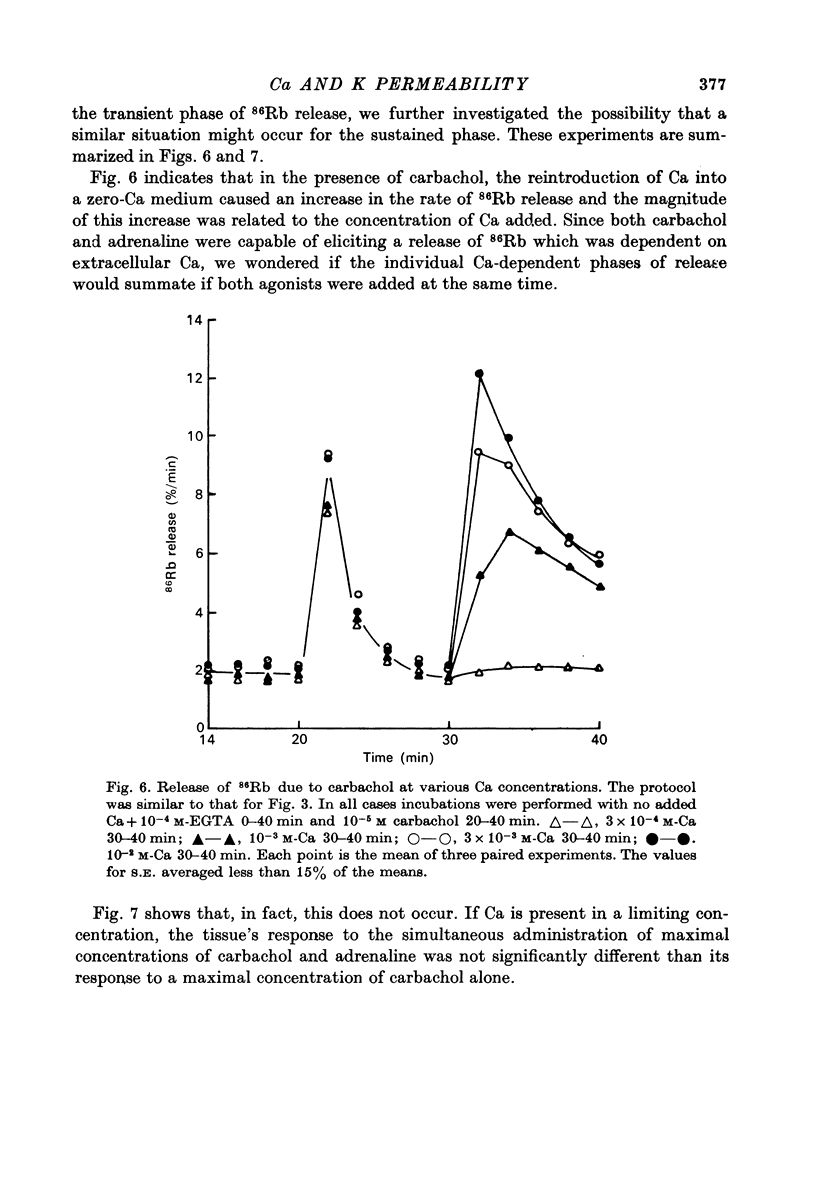
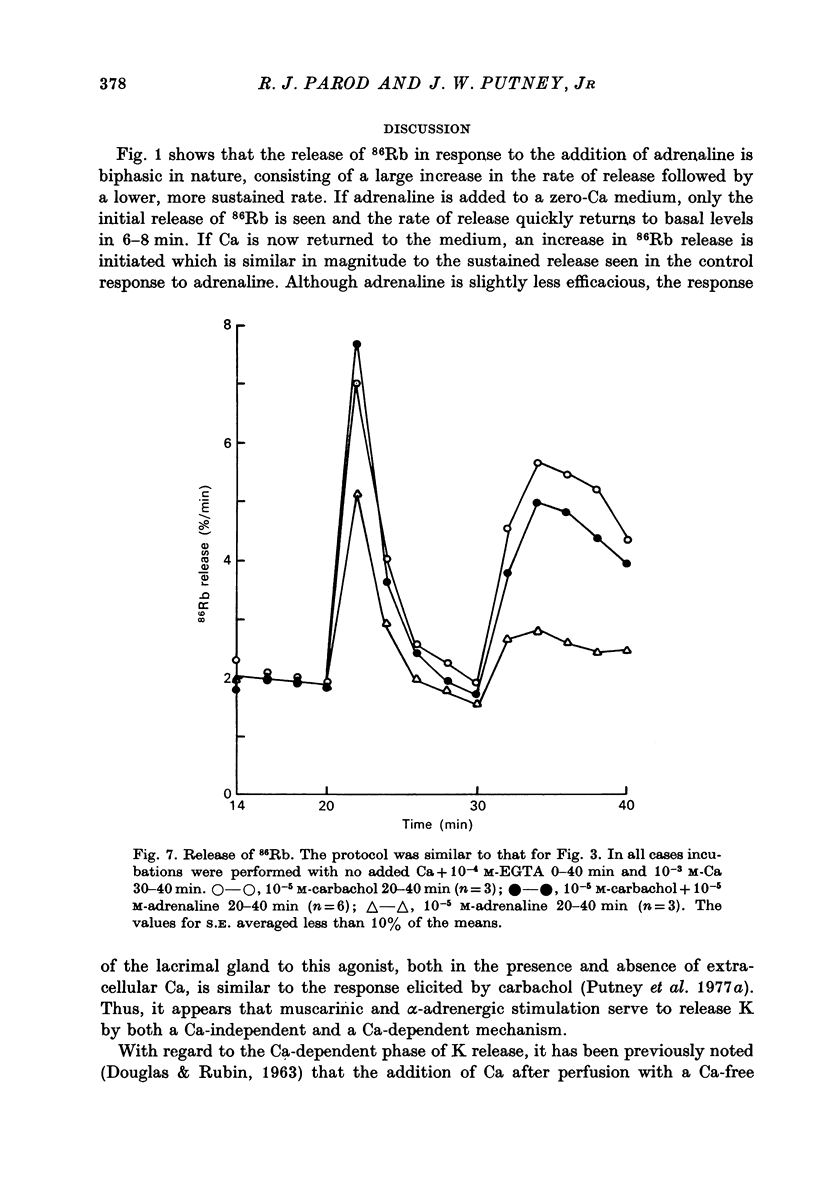
Abstract
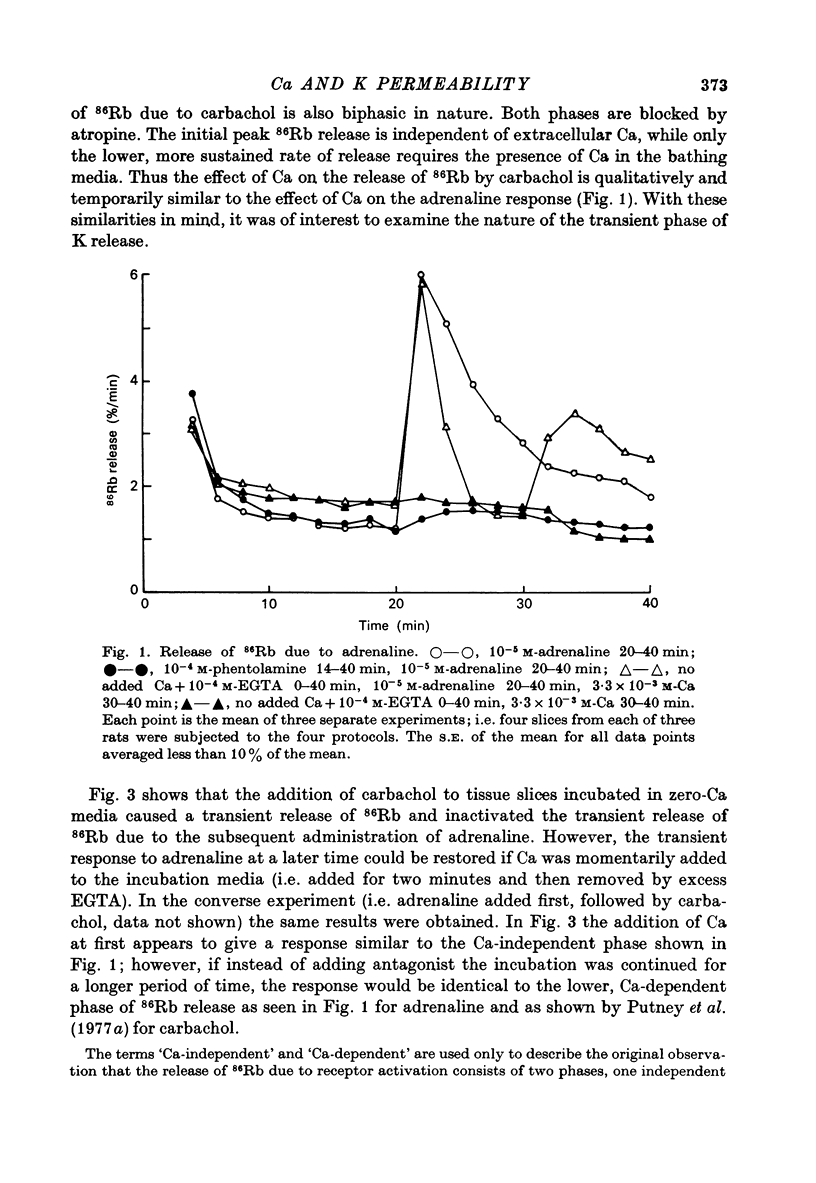
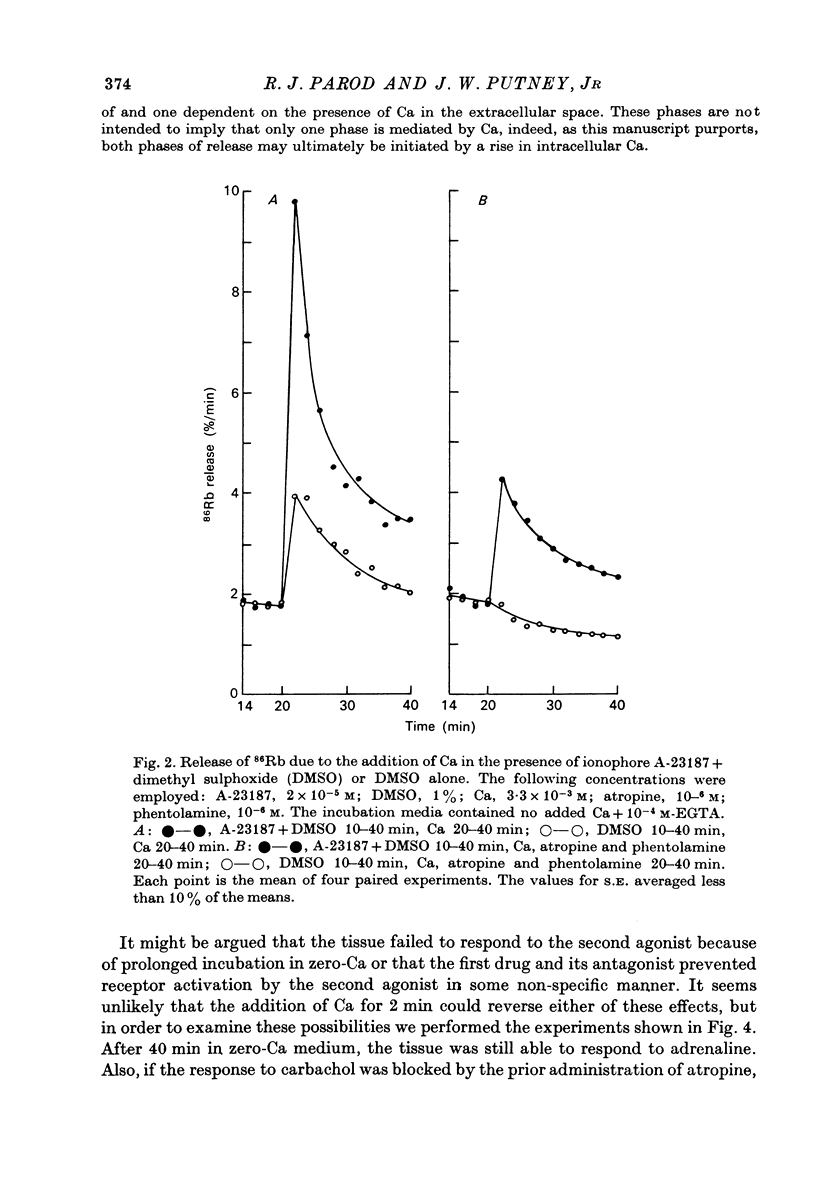
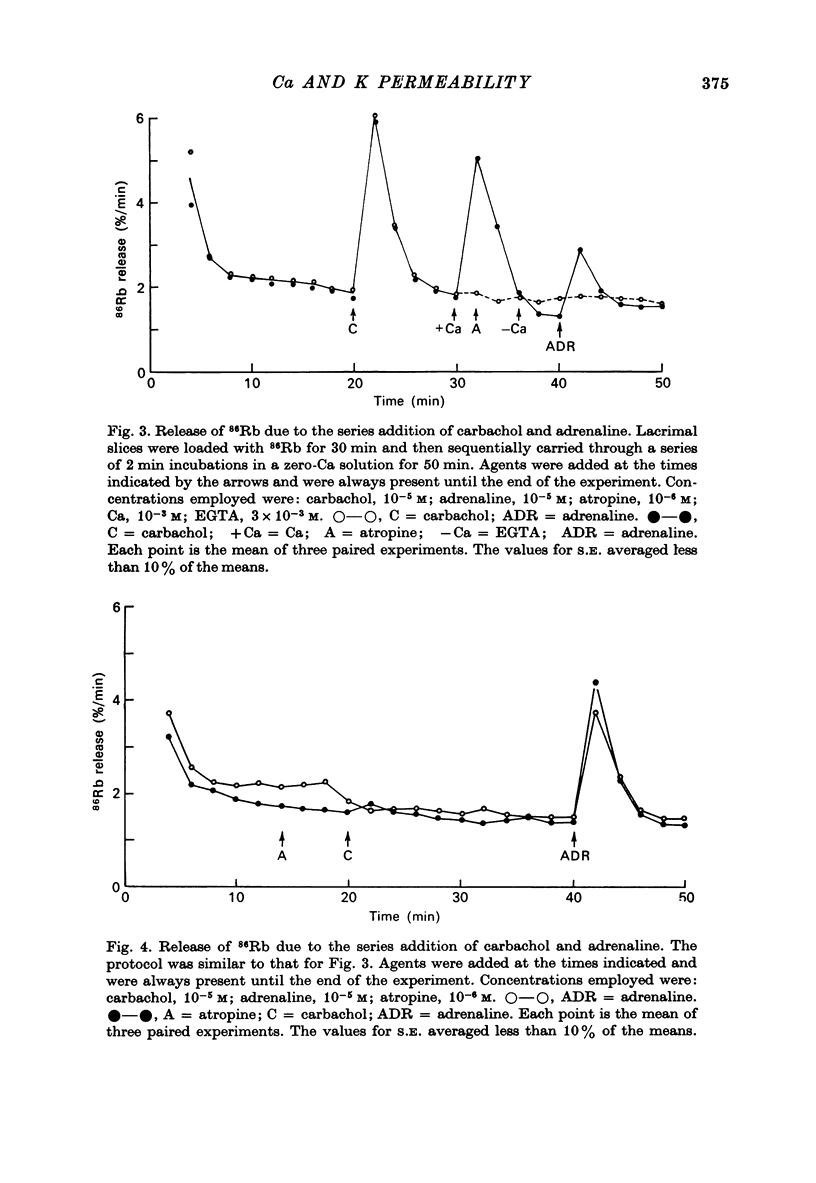
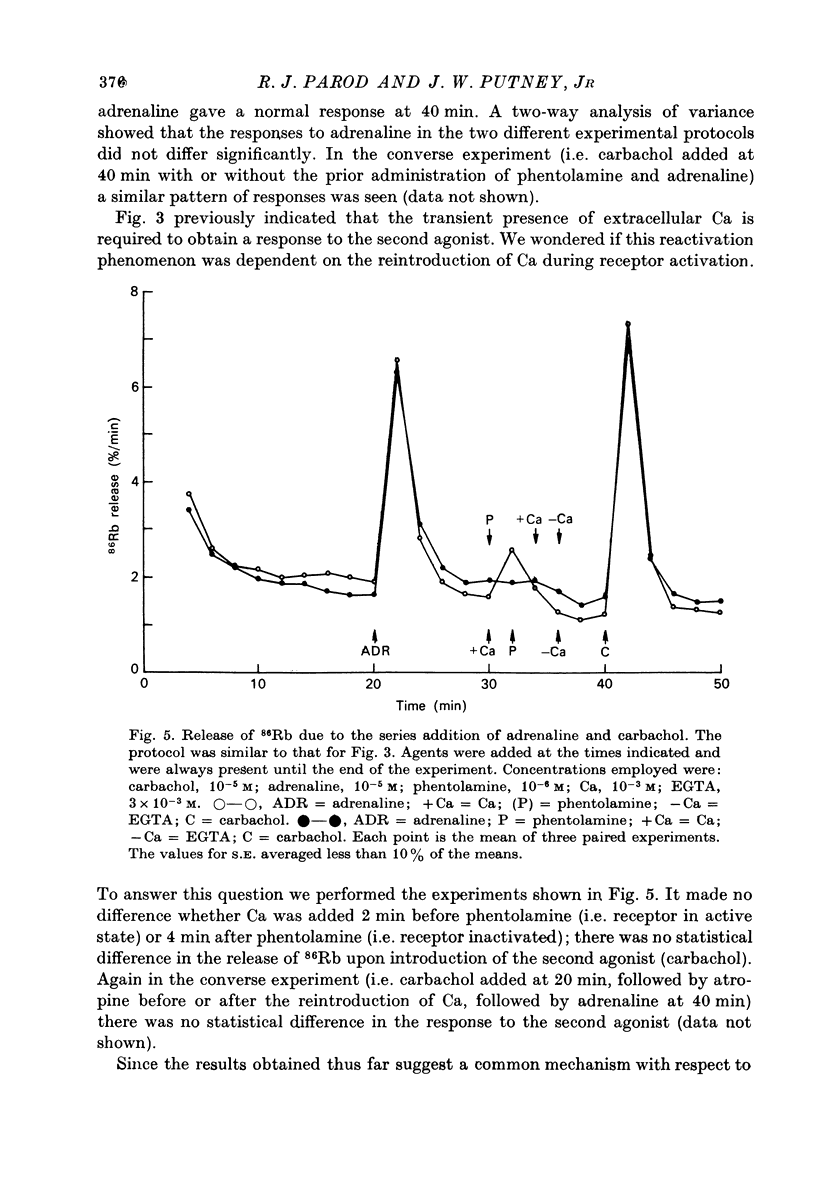
1. In the presence of extracellular Ca, adrenaline stimulated a large increase in the rate of K (86Rb) release from rat lacrimal slices, followed by a lower, more sustained rate. 2. In the absence of extracellular Ca, adrenaline elicited only a transient release of 86Rb. 3. The artificial introduction of Ca into the cytosol by the ionophore A-23187 could also initiate the release of 86Rb. 4. In a zero-Ca medium, if either adrenaline or carbachol produced a transient release of 86Rb, the tissue could not respond to the other agonist with a transient release unless Ca was momentarily reintroduced to the medium. 5. If Ca was present in a limiting concentration, the Ca-dependent rate of 86Rb release elicited from a lacrimal slice exposed simultaneously to carbachol and adrenaline was not significantly different from the release seen with carbachol alone. 6. It is concluded that the agonist-induced release of K from the lacrimal gland consists of both a Ca-independent phase which is initiated by the release of a limited pool of Ca, and a Ca-dependent phase which is mediated by the influx of extracellular Ca. 7. It is also concluded that both alpha-adrenergic and muscarinic receptor occupation activate a common, post-receptor mechanism which may be responsible for both phases of K release.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Deth R., van Breemen C. Agonist induced release of intracellular Ca2+ in the rabbit aorta. J Membr Biol. 1977 Jan 28;30(4):363–380. doi: 10.1007/BF01869677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deth R., van Breemen C. Relative contributions of Ca2+ influx and cellular Ca2+ release during drug induced activation of the rabbit aorta. Pflugers Arch. 1974 Apr 4;348(1):13–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00587735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W., Rubin R. P. The mechanism of catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla and the role of calcium in stimulus-secretion coupling. J Physiol. 1963 Jul;167(2):288–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keryer G., Rossignol B. Effect of carbachol on 45Ca uptake and protein secretion in rat lacrimal gland. Am J Physiol. 1976 Jan;230(1):99–104. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.1.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koelz H. R., Kondo S., Blum A. L., Schulz I. Calcium ion uptake induced by cholinergic and alpha-adrenergic stimulation in isolated cells of rat salivary glands. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Jul 29;370(1):37–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00707943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo S., Schulz I. Calcium ion uptake in isolated pancreas cells induced by secretagogues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 8;419(1):76–92. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90373-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew V. L. On the ATP dependence of the Ca 2+ -induced increase in K + permeability observed in human red cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 1;233(3):827–830. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90185-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marier S. H., Putney J. W., Jr, Van de Walle C. M. Control of calcium channels by membrane receptors in the rat parotid gland. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:141–151. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parod R. J., Putney J. W., Jr An alpha-adrenergic receptor mechanism controlling potassium permeability in the rat lacrimal gland acinar cell. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:359–369. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, Parod R. J., Marier S. H. Control by calcium of protein discharge and membrane permeability to potassium in the rat lacrimal gland. Life Sci. 1977 Jun 1;20(11):1905–1911. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90227-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr Stimulation of 45Ca influx in rat parotid gland by carbachol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Dec;199(3):526–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, Weiss S. J., Leslie B. A., Marier S. H. Is calcium the final mediator of exocytosis in the rat parotid gland? J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Oct;203(1):144–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero P. J., Whittam R. The control by internal calcium of membrane permeability to sodium and potassium. J Physiol. 1971 May;214(3):481–507. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinger Z., Eimerl S., Schramm M. A calcium ionophore simulating the action of epinephrine on the alpha-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):128–131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


