Abstract
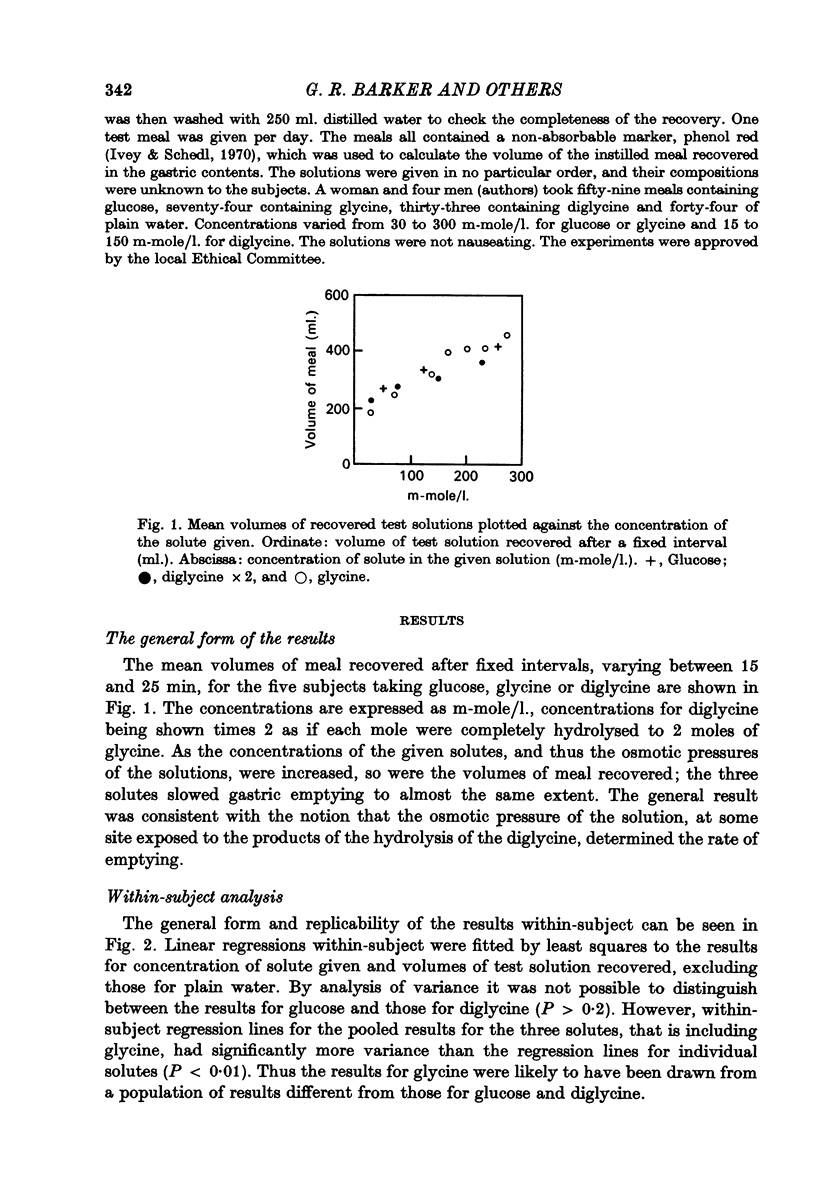
1. Five subjects took 210 test meals of 750 ml. water containing 30--300 m-molal glucose or glycine, or 15--150 m-molal diglycine, or plain water. 2. The greater the concentration of solute, the greater was the volume of original meal recovered from the stomach after a fixed time. 3. On a molal basis glucose was half as effective as diglycine in slowing gastric emptying. This was consistent with the osmoreceptor being exposed to the diglycine after it had been split by the hydrolase of the cytosol of enterocytes (the absorbing cells of the small intestine). 4. The slowing of gastric emptying (ml./mole.1.) was about 10% greater for glycine than it was for glucose. There was apparently a threshold concentration below which glycine did not slow gastric emptying. 5. It was proposed that the response of the doudenal osmoreceptor might depend upon shrinking and swelling of the lateral intercellular space around the enterocytes.
Full text
PDF
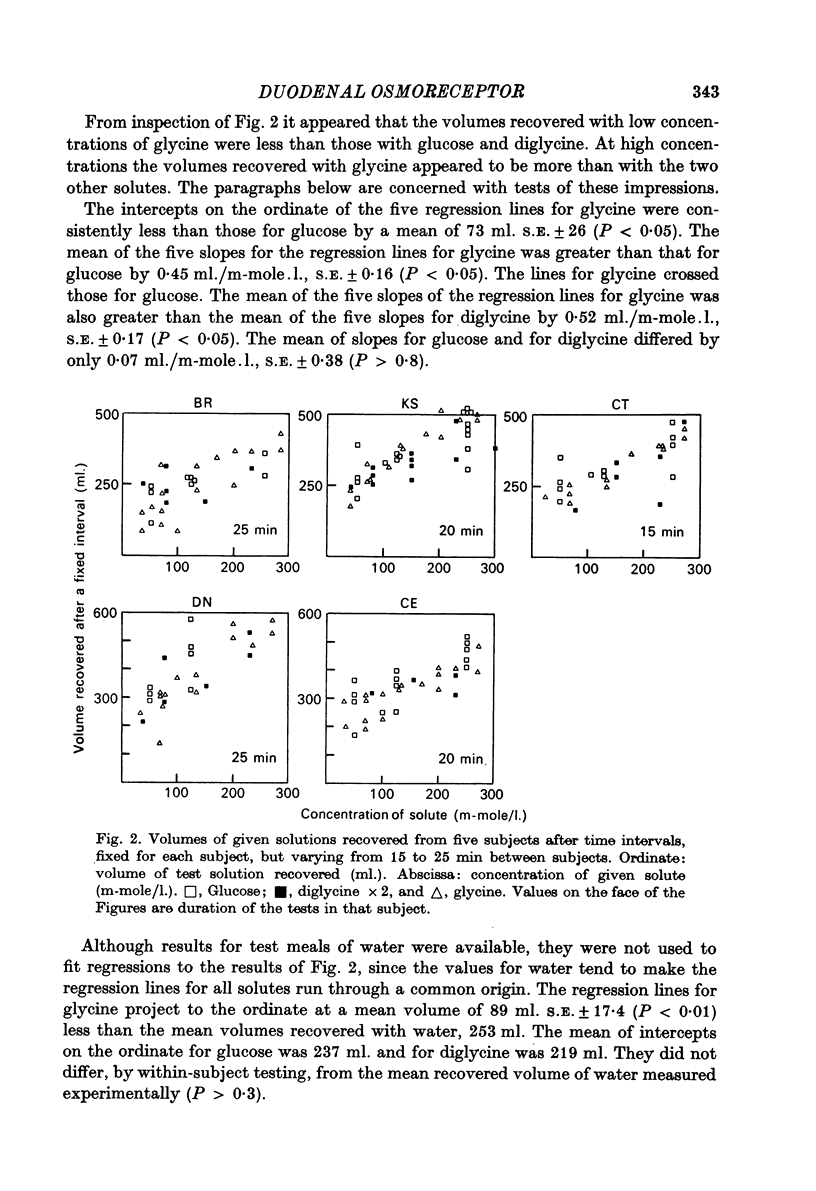



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUCKELL M., WALSH L. EFFECT OF GLYCEROL BY MOUTH ON RAISED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE IN MAN. Lancet. 1964 Nov 28;2(7370):1151–1152. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92671-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker G. R., Cochrane G. M., Corbett G. A., Hunt J. N., Roberts S. K. Actions of glucose and potassium chloride on osmoreceptors slowing gastric emptying. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;237(1):183–186. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell F. R., Mostaghni K. Duodenal control of gastric emptying in the milk-fed calf. J Physiol. 1975 Feb;245(2):387–407. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burn-Murdoch R. A., Fisher M. A., Hunt J. N. The slowing of gastric emptying by proteins in test meals. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:477–485. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito G., Faelli A., Capraro V. Sugar and electrolyte absorption in the rat intestine perfused "in vivo". Pflugers Arch. 1973 Jun 4;340(4):335–348. doi: 10.1007/BF00592311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Rector F. C., Jr, Ewton M. F., Soter N., Kinney J. Permeability characteristics of the human small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1965 Dec;44(12):1935–1944. doi: 10.1172/JCI105299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT J. N., KNOX M. T. The regulation of gastric emptying of meals containing citric acid and salts of citric acid. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;163:34–45. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. N., Knox M. T. A relation between the chain length of fatty acids and the slowing of gastric emptying. J Physiol. 1968 Feb;194(2):327–336. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. N., Knox M. T. The slowing of gastric emptying by four strong acids and three weak acids. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(1):187–208. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. N., Pathak J. D. The osmotic effects of some simple molecules and ions on gastric emptying. J Physiol. 1960 Dec;154(2):254–269. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivey K. J., Schedl H. P. Gastric nonabsorbable indicators for studies in man. Gastroenterology. 1970 Aug;59(2):234–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. S., Birtwhistle W., Kim Y. W. Peptide hydrolases in the bruch border and soluble fractions of small intestinal mucosa of rat and man. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1419–1430. doi: 10.1172/JCI106938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallinson C. N. Effect of pancreatic insufficiency and intestinal lactase deficiency on the gastric emptying of starch and lactose. Gut. 1968 Dec;9(6):737–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meeroff J. C., Go V. L., Phillips S. F. Control of gastric emptying by osmolality of duodenal contents in man. Gastroenterology. 1975 May;68(5 Pt 1):1144–1151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melligott T. F., Beck I. T., Dinda P. K., Thompson S. Correlation of structural changes at different levels of the jejunal villus with positive net water transport in vivo and in vitro. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1975 Jun;53(3):439–450. doi: 10.1139/y75-063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasini J. T., Dobbins W. O. Intestinal mucosal morphology during water and electrolyte absorption. A light and electron microscopic study. Am J Dig Dis. 1970 Mar;15(3):226–238. doi: 10.1007/BF02233453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler P. G., Menzies I. S., Creamer B. Proceedings: Patterns of small intestinal permeability and the effect of hypertonic solutions. Gut. 1976 May;17(5):386–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman G. Site of intestinal dipeptide hydrolysis. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(3):731–743. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


