Abstract
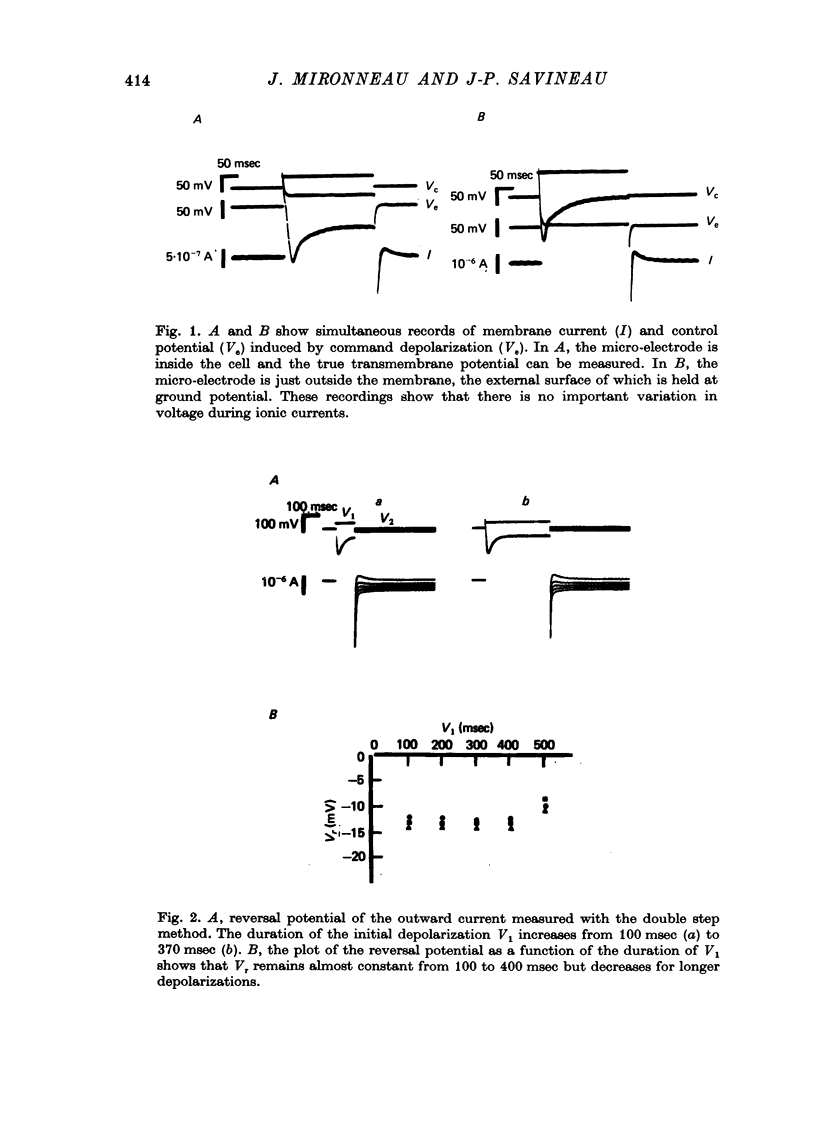
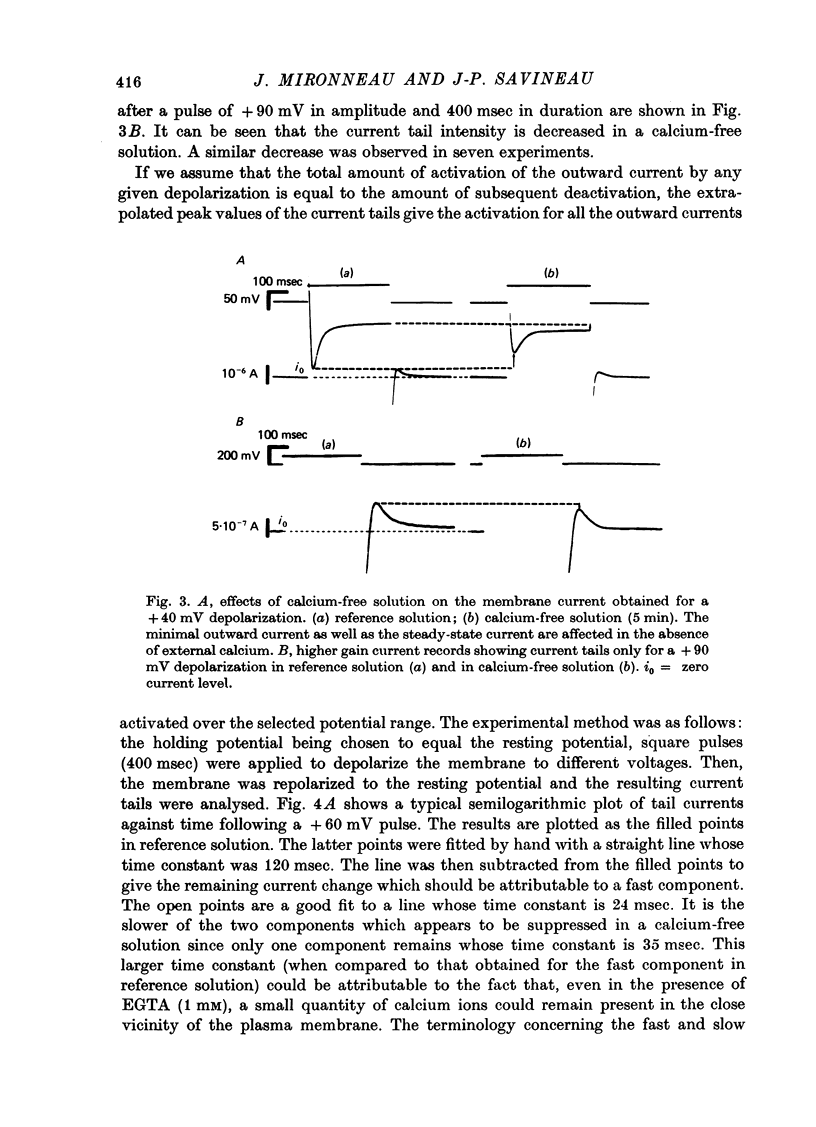
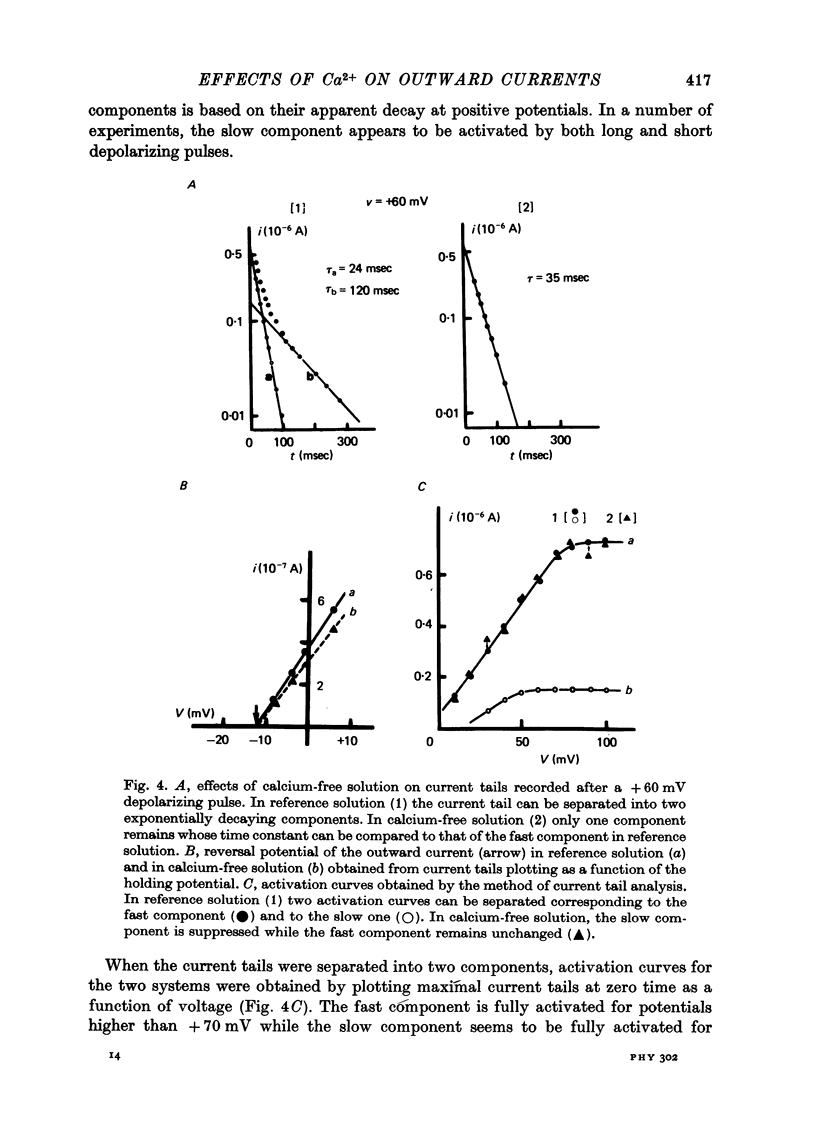
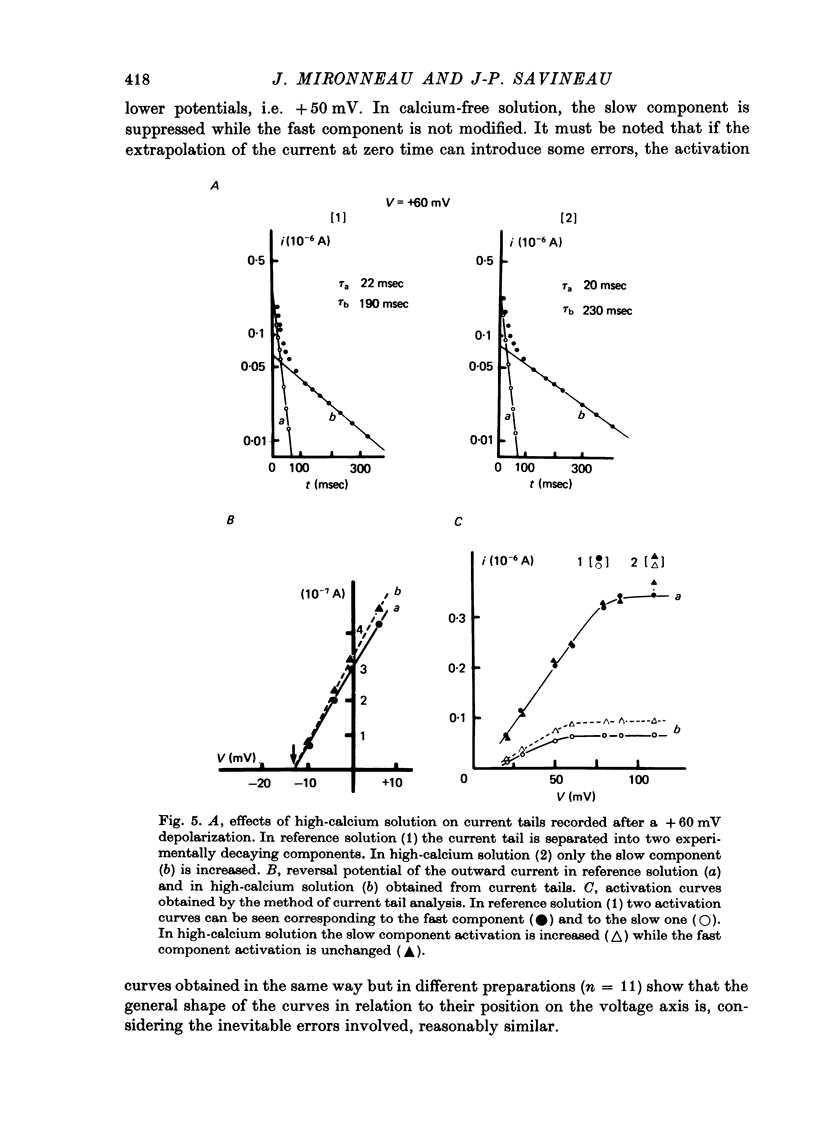
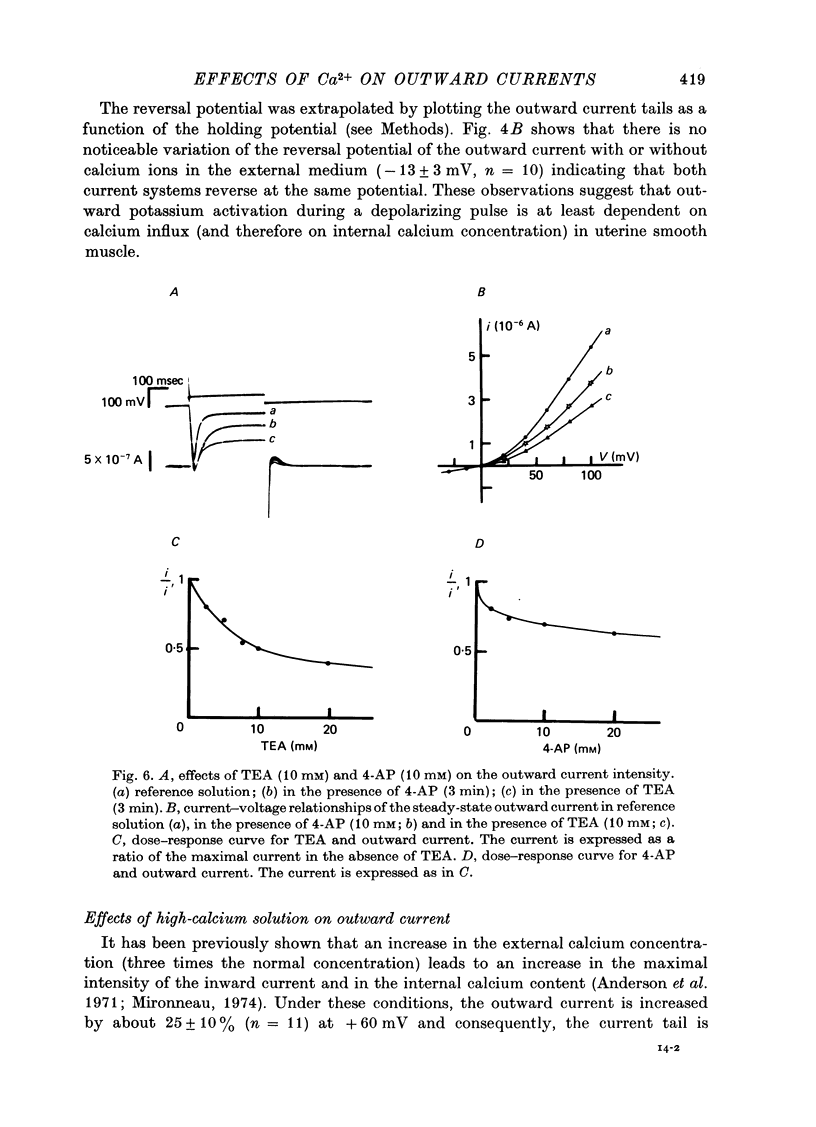
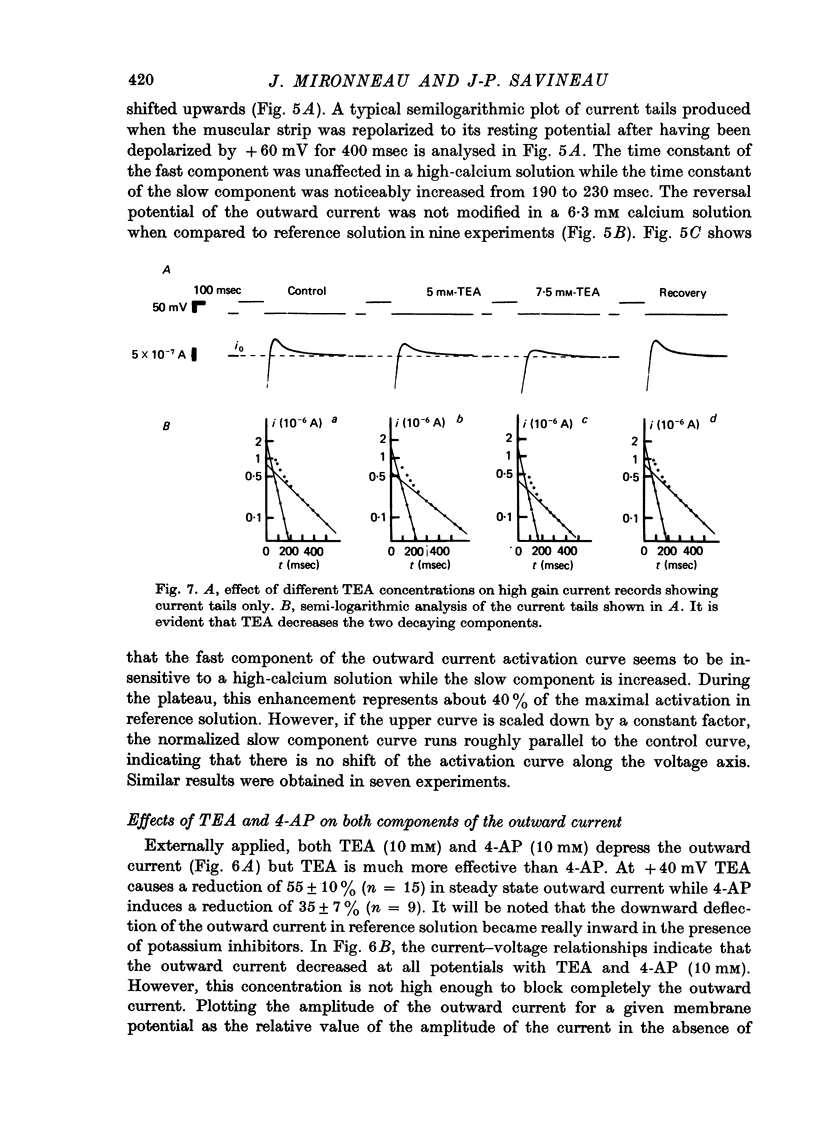
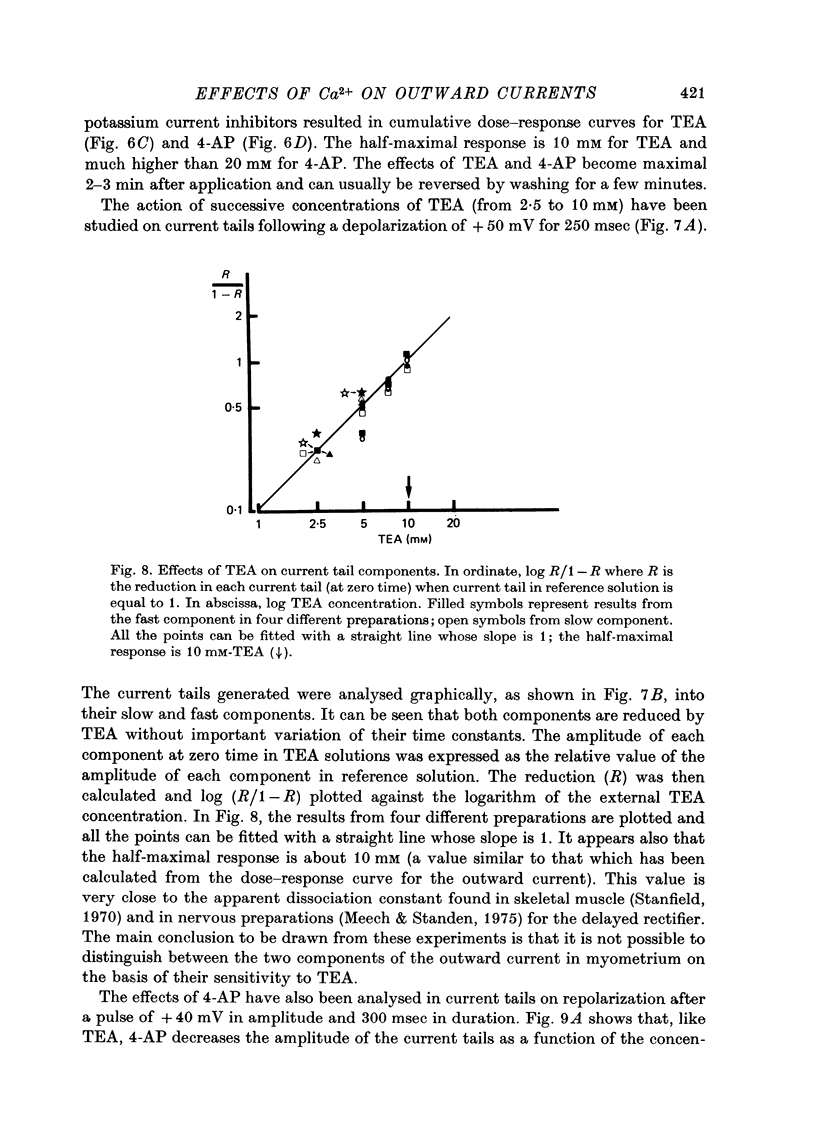
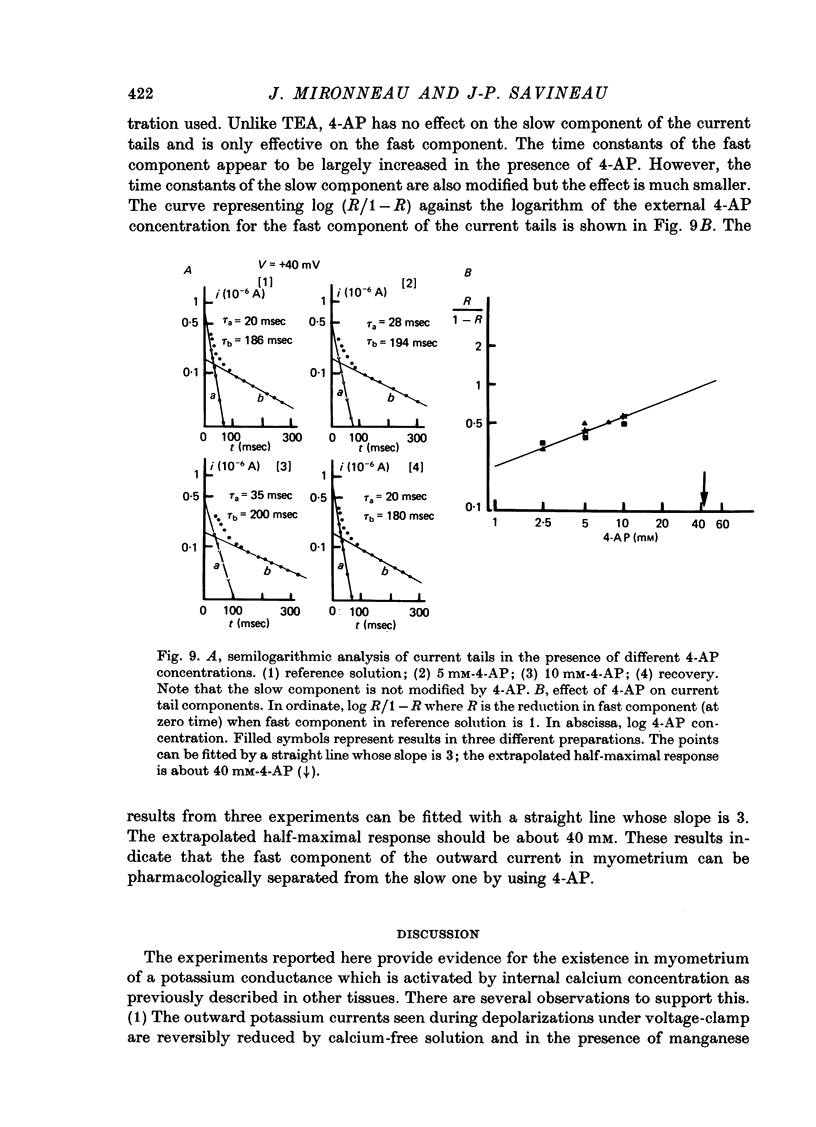
1. The outward membrane current underlying delayed rectification in uterine smooth muscle has been studied by means of a double sucrose gap apparatus with particular reference to the effects of the external calcium. 2. The outward current was reversibly reduced in calcium-free solution and in the presence of manganese (5 mM), or increased in high-calcium solution. 3. In reference solution, when depolarizing steps activated the outward current to its maximal value, the current tails measured at the end of the pulse were made up of two exponentially declining components. The slower of the two components was suppressed in calcium-free solution. The fast component reached full, steady-state activation at about +75 mV and the slow one at less positive potentials, i.e. +50 mV. Altering the external calcium did not shift the activation curves of the outward current along the voltage axis. 4. The reversal potential of the outward current was not affected by alterations of the external calcium concentration. 5. The outward current components can also be separated on the basis of their sensitivity to 4-aminopyridine (4-AP) and tetracethylammonium (TEA). The fast component was selectively blocked by externally applied 4-AP. TEA blocked both fast and slow components. 6. It is suggested that two sets of potassium channels contribute to the outward current in myometrium and that these channels can be separated pharmacologically.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe Y. Effects of changing the ionic environment on passive and active membrane properties of pregnant rat uterus. J Physiol. 1971 Apr;214(1):173–190. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. C., Ramon F., Snyder A. Studies on calcium and sodium in uterine smooth muscle excitation under current-clamp and voltage-clamp conditions. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Sep;58(3):322–339. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.3.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Interaction of tetraethylammonium ion derivatives with the potassium channels of giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Oct;58(4):413–437. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Dawson C. M., Ribalet B., Rojas E. Potassium permeability activated by intracellular calcium ion concentration in the pancreatic beta-cell. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:575–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassingthwaighte J. B., Fry C. H., McGuigan J. A. Relationship between internal calcium and outward current in mammalian ventricular muscle; a mechanism for the control of the action potential duration? J Physiol. 1976 Oct;262(1):15–37. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeler G. W., McGuigan J. A. Voltage clamping of multicellular myocardial preparations: capabilities and limitations of existing methods. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1978;34(3):219–254. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(79)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B. Effects of stimulating the acetylcholine receptor on the current-voltage relationships of the smooth muscle membrane studied by voltage clamp of potential recorded by micro-electrode. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;250(1):175–202. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brading A. F. Calcium-induced increase in membrane permeability in the guinea-pig taenia coli: evidence for involvement of a sodium-calcium exchange mechanism. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:65–84. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. F., Clark A., Noble S. J. Identification of the pace-maker current in frog atrium. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;258(3):521–545. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleemann L., Morad M. Potassium currents in frog ventricular muscle: evidence from voltage clamp currents and extracellular K accumulation. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:113–143. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clusin W. T., Bennett M. V. Calcium-activated conductance in skate electroreceptors: voltage clamp experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Feb;69(2):145–182. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., McNaughton P. A. The effects of calcium on outward membrane currents in the cardiac Purkinje fibre. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:347–373. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Droogmans G., Raeymaekers L., Casteels R. Electro- and pharmacomechanical coupling in the smooth muscle cells of the rabbit ear artery. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Aug;70(2):129–148. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.2.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Lux H. D. Calcium-dependent depression of a late outward current in snail neurons. Science. 1977 Jul 29;197(4302):472–475. doi: 10.1126/science.17921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosset A., Mironneau J. An analysis of the actions of prostaglandin E1 on membrane currents and contraction in uterine smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):765–784. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Nakajima S. Differences in Na and Ca spikes as examined by application of tetrodotoxin, procaine, and manganese ions. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Mar;49(4):793–806. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.4.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanani M., Shaw C. A potassium contribution to the response of the barnacle photoreceptor. J Physiol. 1977 Aug;270(1):151–163. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The selective inhibition of delayed potassium currents in nerve by tetraethylammonium ion. J Gen Physiol. 1967 May;50(5):1287–1302. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.5.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inomata H., Kao C. Y. Ionic currents in the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1976 Feb;255(2):347–378. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg G. Cardiac Purkinje fibres: [Ca2+]i controls the potassium permeability via the conductance components gK1 and gK2. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Oct 19;371(1-2):77–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00580775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Kuriyama H., Sakamoto Y. Effects of tetraethylammonium chloride on the membrane activity of guinea-pig stomach smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(2):445–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. A., Lieberman M. Heart: excitation and contraction. Annu Rev Physiol. 1971;33:479–532. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.33.030171.002403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Lisiewicz A. Injections of calcium ions into spinal motoneurones. J Physiol. 1972 Sep;225(2):363–390. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama H., Suzuki H. Changes in electrical properties of rat myometrium during gestation and following hormonal treatments. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;260(2):315–333. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. The sensitivity of Helix aspersa neurones to injected calcium ions. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(2):259–277. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekata F. Electrophysiological studies of the smooth muscle cell membrane of the rabbit common carotid artery. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Jun;57(6):738–751. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.6.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meves H., Pichon Y. The effect of internal and external 4-aminopyridine on the potassium currents in intracellularly perfused squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(2):511–532. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mironneau J. Excitation-contraction coupling in voltage clamped uterine smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1973 Aug;233(1):127–141. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mironneau J. Voltage clamp analysis of the ionic currents in uterine smooth muscle using the double sucrose gap method. Pflugers Arch. 1974;352(3):197–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00590485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounier Y., Vassort G. Evidence for a transient potassium membrane current dependent on calcium influx in crab muscle fibre. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(3):609–625. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble D., Tsien R. W. Outward membrane currents activated in the plateau range of potentials in cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1969 Jan;200(1):205–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble S. J. Potassium accumulation and depletion in frog atrial muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;258(3):579–613. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramón F., Anderson N., Joyner R. W., Moore J. W. Axon voltage-clamp simulations. A multicellular preparation. Biophys J. 1975 Jan;15(1):55–69. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85791-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougier O., Vassort G., Stämpfli R. Voltage clamp experiments on frog atrial heart muscle fibres with the sucrose gap technique. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1968;301(2):91–108. doi: 10.1007/BF00362729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelbaum S. A., Tsien R. W., Kass R. S. Role of intracellular calcium in the transient outward current of calf Purkinje fibres. Nature. 1977 Oct 13;269(5629):611–613. doi: 10.1038/269611a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R. The effect of the tetraethylammonium ion on the delayed currents of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;209(1):209–229. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassort G. Voltage-clamp analysis of transmembrane ionic currents in guinea-pig myometrium: evidence for an initial potassium activation triggered by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Nov;252(3):713–734. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


