Abstract
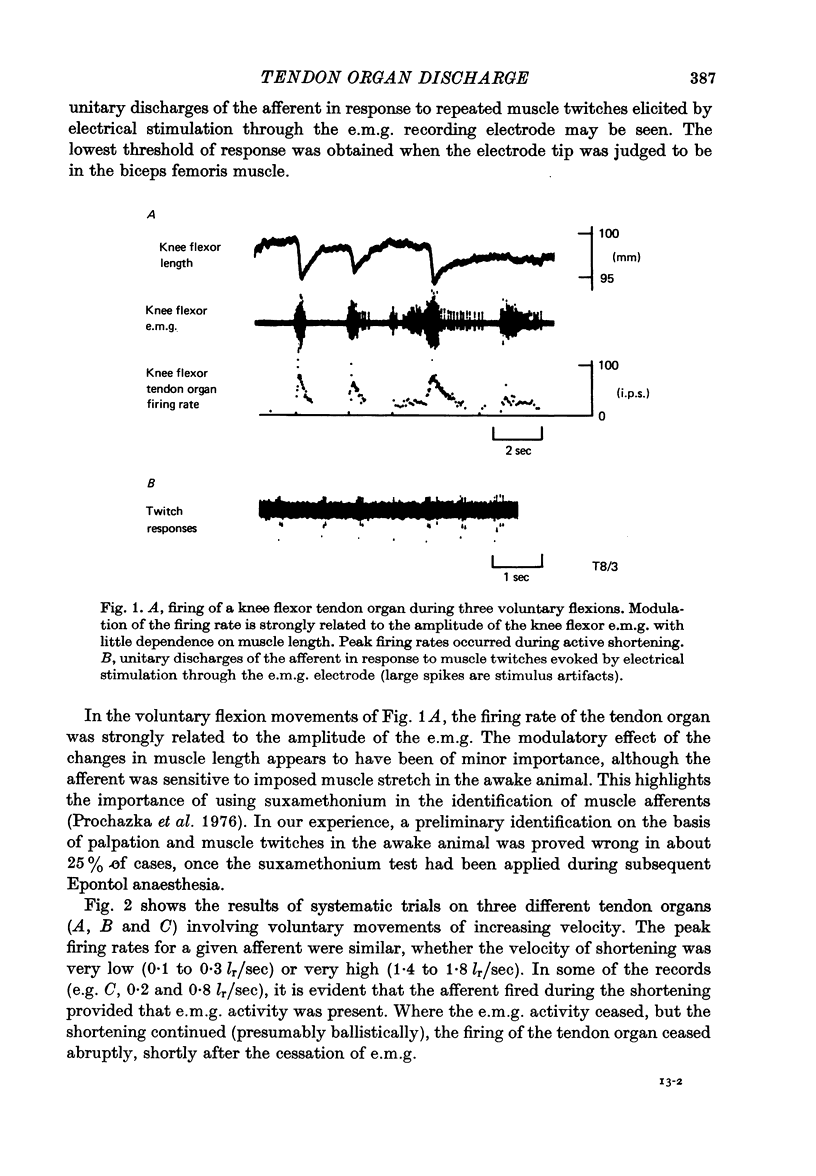
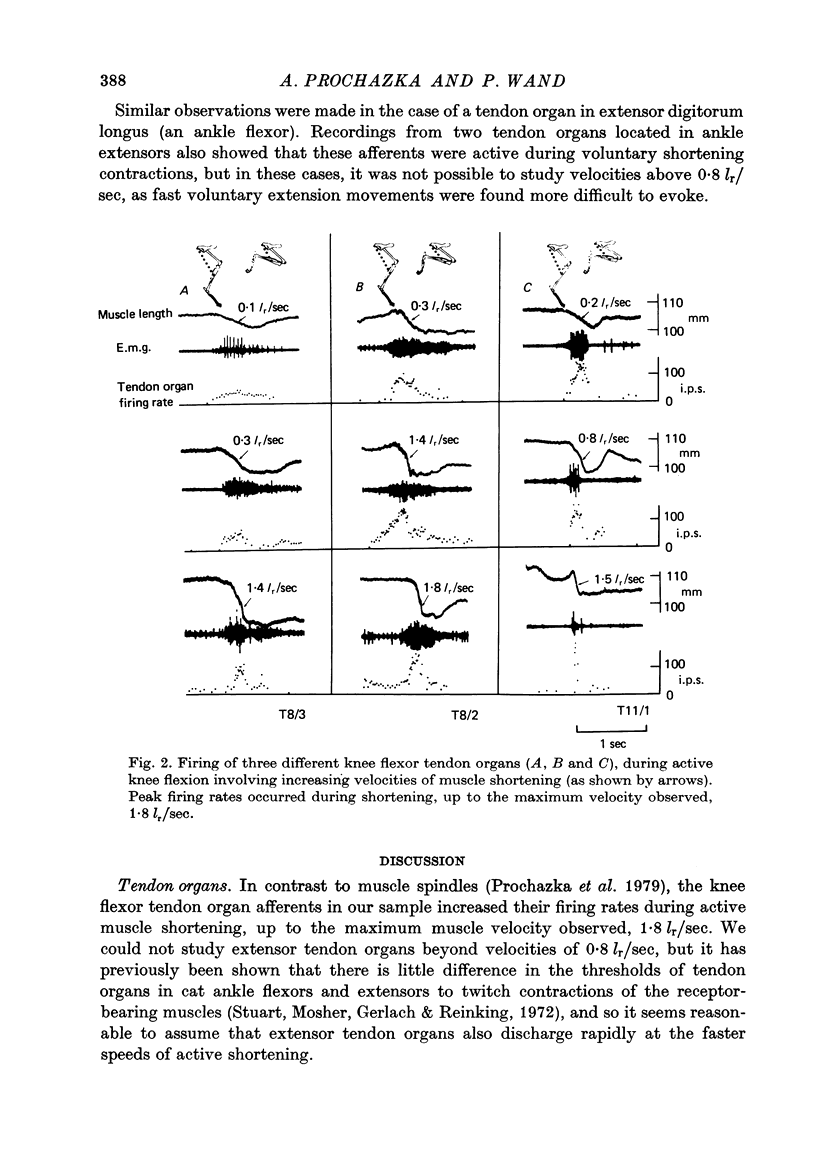
1. The discharge activity of tendon organ afferents was recorded during voluntary movements in cats. 2. The eight tendon organ afferents in our sample all fired during isotonic movements involving active muscle shortening. 3. Firing rates usually exceeded 100 sec-1, even up to the highest muscle shortening velocity observed, 1.8 resting lengths per second (lr/sec). 4. We suggest that during voluntary, isotonic movements involving muscle shortening at velocities exceeding 0.2 lr/sec, the net action of muscle afferents on homonymous motoneurones is often inhibition. 5. These observations on tendon organs, taken together with previous findings on muscle spindles, indicate that in normal fast movements the role of the large muscle afferents is to signal dynamic functions of muscle length and force.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crago P. E., Houk J. C., Hasan Z. Regulatory actions of human stretch reflex. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Sep;39(5):925–935. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.5.925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. N., Sears T. A. The proprioceptive reflex control of the intercostal muscles during their voluntary activation. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(3):711–738. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghez C., Shinoda Y. Spinal mechanisms of the functional stretch reflex. Exp Brain Res. 1978 May 12;32(1):55–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00237390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houk J. C. Regulation of stiffness by skeletomotor reflexes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1979;41:99–114. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.41.030179.000531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houk J., Henneman E. Responses of Golgi tendon organs to active contractions of the soleus muscle of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1967 May;30(3):466–481. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.3.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANSEN J. K., RUDJORD T. ON THE SILENT PERIOD AND GOLGI TENDON ORGANS OF THE SOLEUS MUSCLE OF THE CAT. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 Dec;62:364–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1964.tb10435.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Cutaneous facilitation of transmission in reflex pathways from Ib afferents to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1977 Mar;265(3):763–780. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols T. R., Houk J. C. Improvement in linearity and regulation of stiffness that results from actions of stretch reflex. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Jan;39(1):119–142. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochazka A., Stephens J. A., Wand P. Muscle spindle discharge in normal and obstructed movements. J Physiol. 1979 Feb;287:57–66. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochazka A., Westerman R. A., Ziccone S. P. Discharges of single hindlimb afferents in the freely moving cat. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Sep;39(5):1090–1104. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.5.1090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochazka A., Westerman R. A., Ziccone S. P. Ia afferent activity during a variety of voluntary movements in the cat. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(2):423–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens J. A., Reinking R. M., Stuart D. G. Tendon organs of cat medial gastrocnemius: responses to active and passive forces as a function of muscle length. J Neurophysiol. 1975 Sep;38(5):1217–1231. doi: 10.1152/jn.1975.38.5.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturart D. G., Mosher C. G., Gerlach R. I., Reinking R. M. Mechanical arrangement and transducing properties of Golgi tendon organs. Exp Brain Res. 1972;14(3):274–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00816163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


