Abstract
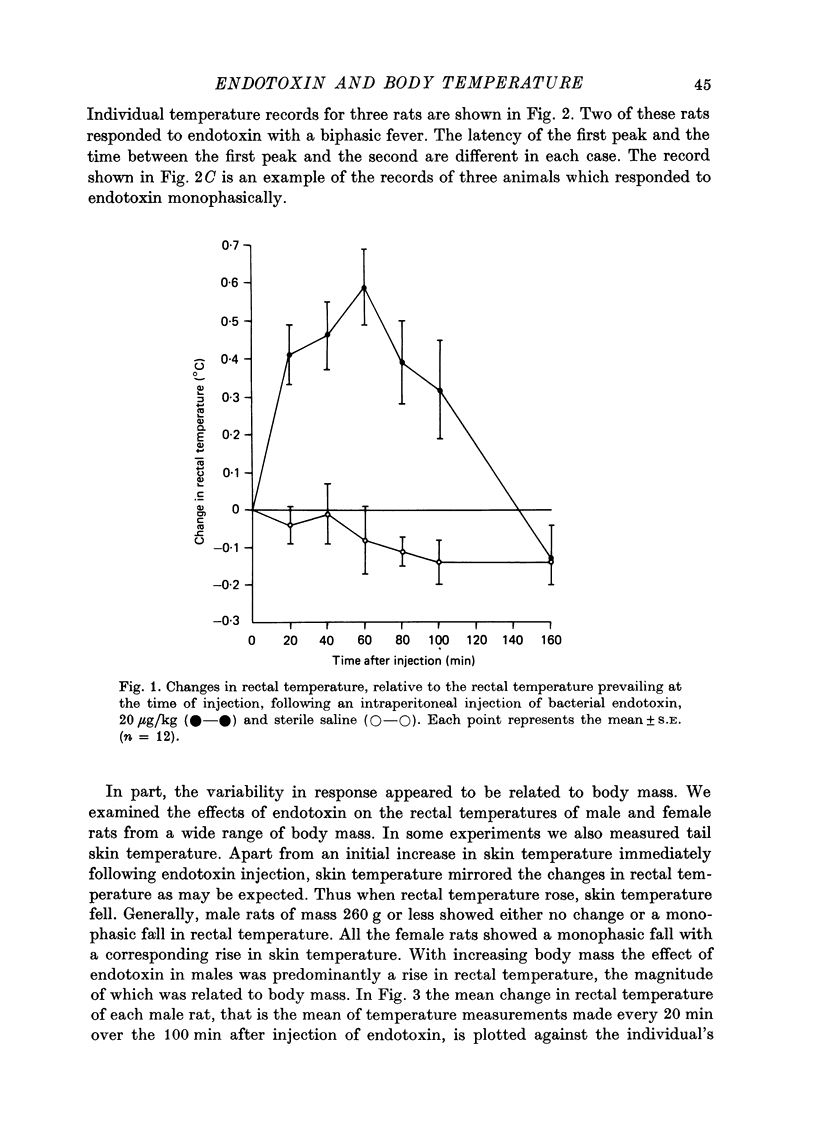
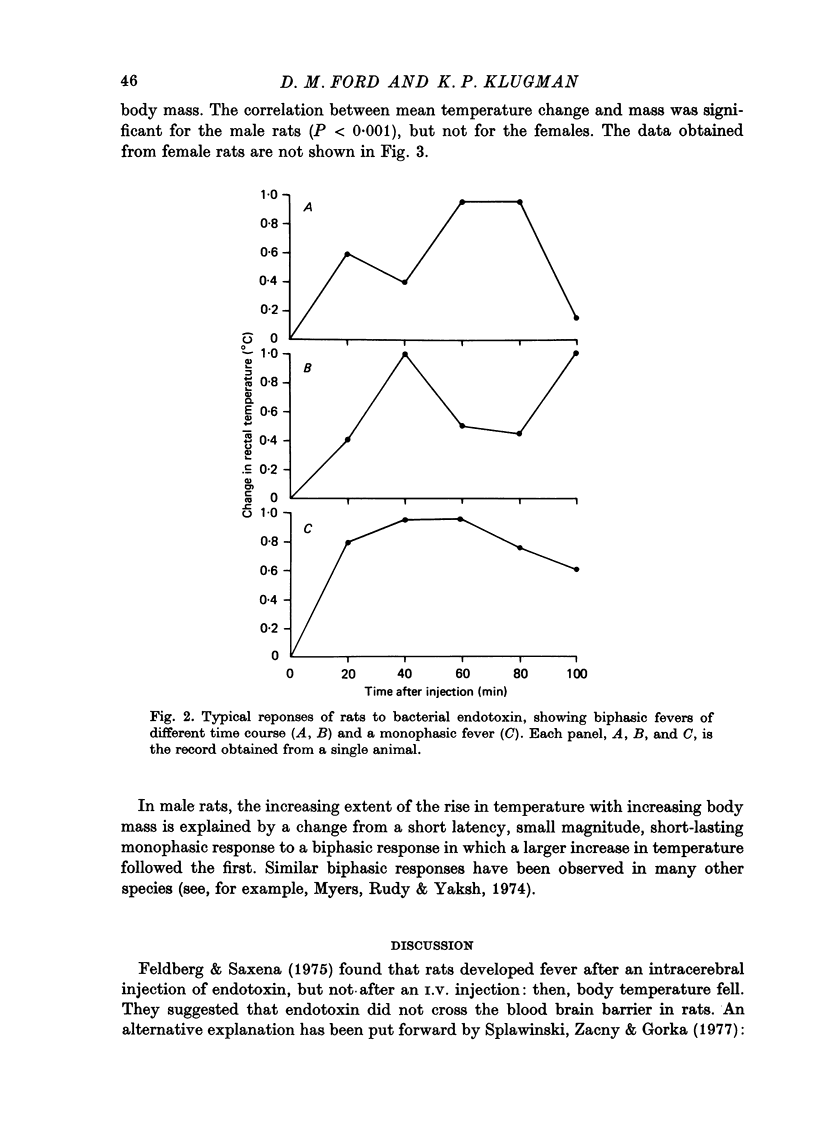
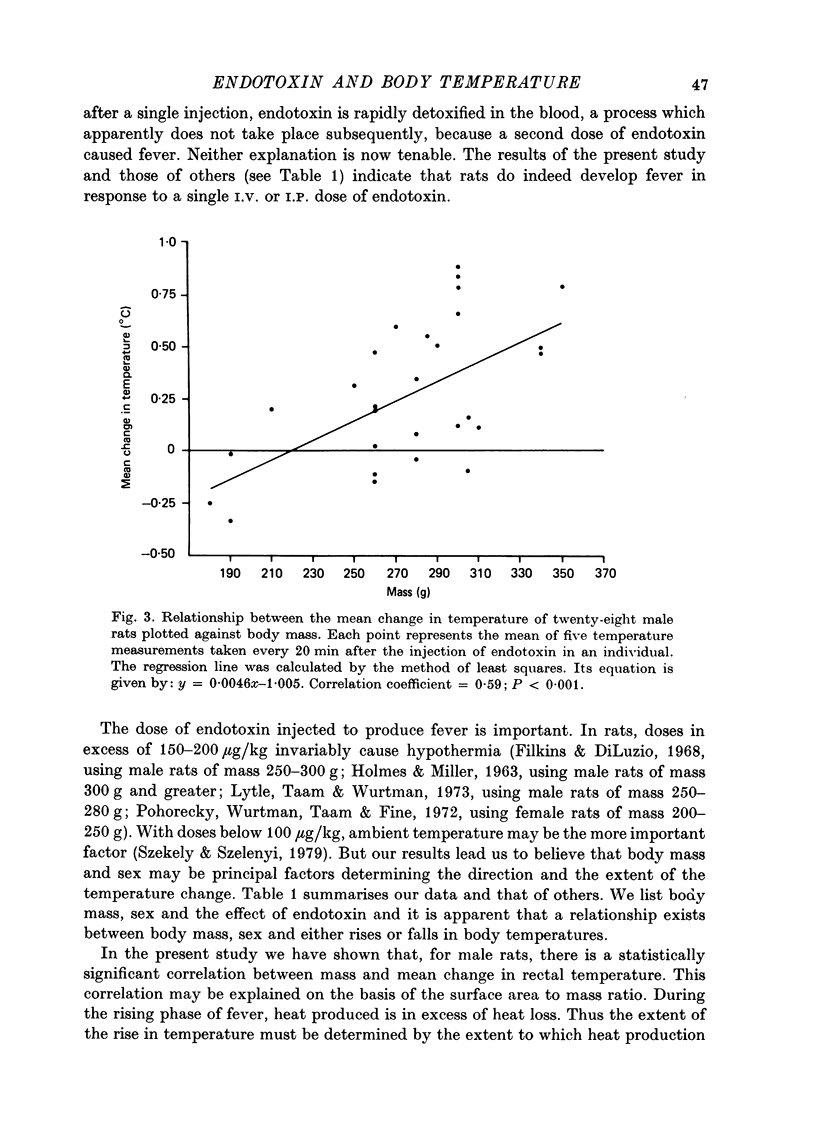
1. We have investigated the effect of a single I.P. injection (20 microgram/kg) of bacterial endotoxin on rectal temperature in rats of both sexes and from a wide range of body mass. 2. In male rats, endotoxin produced a monophasic or a biphasic rise in temperature, or a monophasic fall. 3. The extent of the rise in rectal temperature in male rats is related to body mass. There is a statistically significant correlation between body mass and the mean change in temperature measured over 100 min after injection of endotoxin. 4. In the female rats, endotoxin produced a monophasic fall in rectal temperature. The extent of the fall was not significantly correlated with body mass. 5. We suggest that the effect of endotoxin in male rats is determined by the physical relationship between body mass and surface area, because larger animals developed greater fevers. 6. The difference between the effect of endotoxin in male and female rats may have a physiological explanation and may involve differences in susceptibility to cutaneous vasodilation occurring immediately after injection of endotoxin.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avery D. D., Penn P. E. Blockade of pyrogen induced fever by intrahypothalamic injections of salicylate in the rat. Neuropharmacology. 1974 Dec;13(12):1179–1185. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(74)90068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Saxena P. N. Prostaglandins, endotoxin and lipid A on body temperature in rats. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;249(3):601–615. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filkins J. P., Di Luzio N. R. Endotoxin induced hypothermia and tolerance in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Dec;129(3):724–726. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAAN J., ALBERS C. [On the induction of thermoregulatory reactions in the dog following the action of pyrogens]. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1960;271:537–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMES J. E., MILLER N. E. EFFECTS OF BACTERIAL ENDOTOXIN ON WATER INTAKE, FOOD INTAKE, AND BODY TEMPERATURE IN THE ALBINO RAT. J Exp Med. 1963 Oct 1;118:649–658. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.4.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz B. A., Hanes G. E. Propranolol and pyrogen effects of shivering and nonshivering thermogenesis in rats. Am J Physiol. 1976 Mar;230(3):637–642. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.3.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. D., Rudy T. A., Yaksh T. L. Fever produced by endotoxin injected into the hypothalamus of the monkey and its antagonism by salicylate. J Physiol. 1974 Nov;243(1):167–193. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohorecky L. A., Wurtman R. J., Taam D., Fine J. Effects of endotoxin on monoamine metabolism in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Jul;140(3):739–746. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Splawiński J. A., Zacny E., Górka Z. Fever in rats after intravenous E. coli endotoxin administration. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Mar 11;368(1-2):125–128. doi: 10.1007/BF01063464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Székely M. Endotoxin fever in the new-born guinea-pig and the modulating effects of indomethacin and p-chlorophenylalanine. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:467–476. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Székely M., Szelényi Z., Sümegi I. Brown adipose tissue as a source of heat during pyrogen-induced fever. Acta Physiol Acad Sci Hung. 1973;43(1):85–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG D. R., COOK S. F. Body lipids in small mammals following prolonged exposures to high and low temperatures. Am J Physiol. 1955 Apr;181(1):72–74. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.181.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Miert A. S., Frens J. The reaction of different animal species to bacterial pyrogens. Zentralbl Veterinarmed A. 1968;15(6):532–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0442.1968.tb00456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


