Abstract
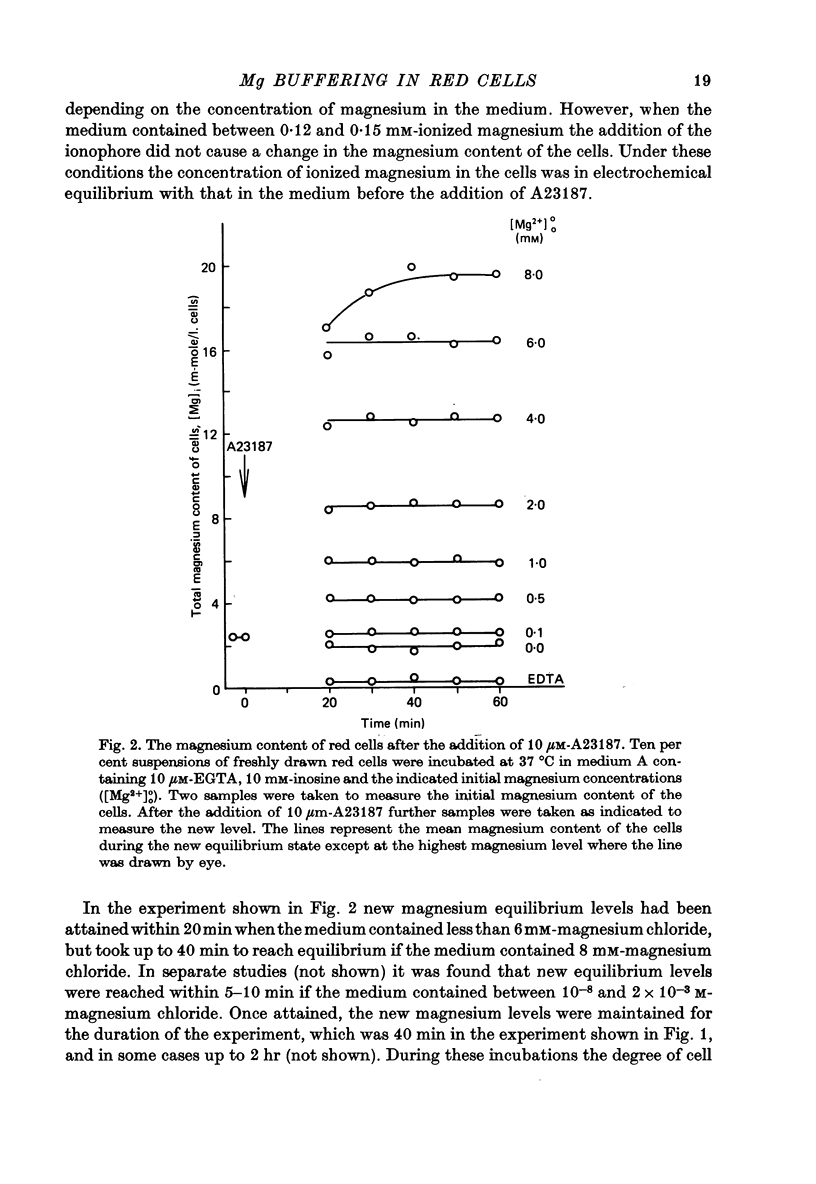
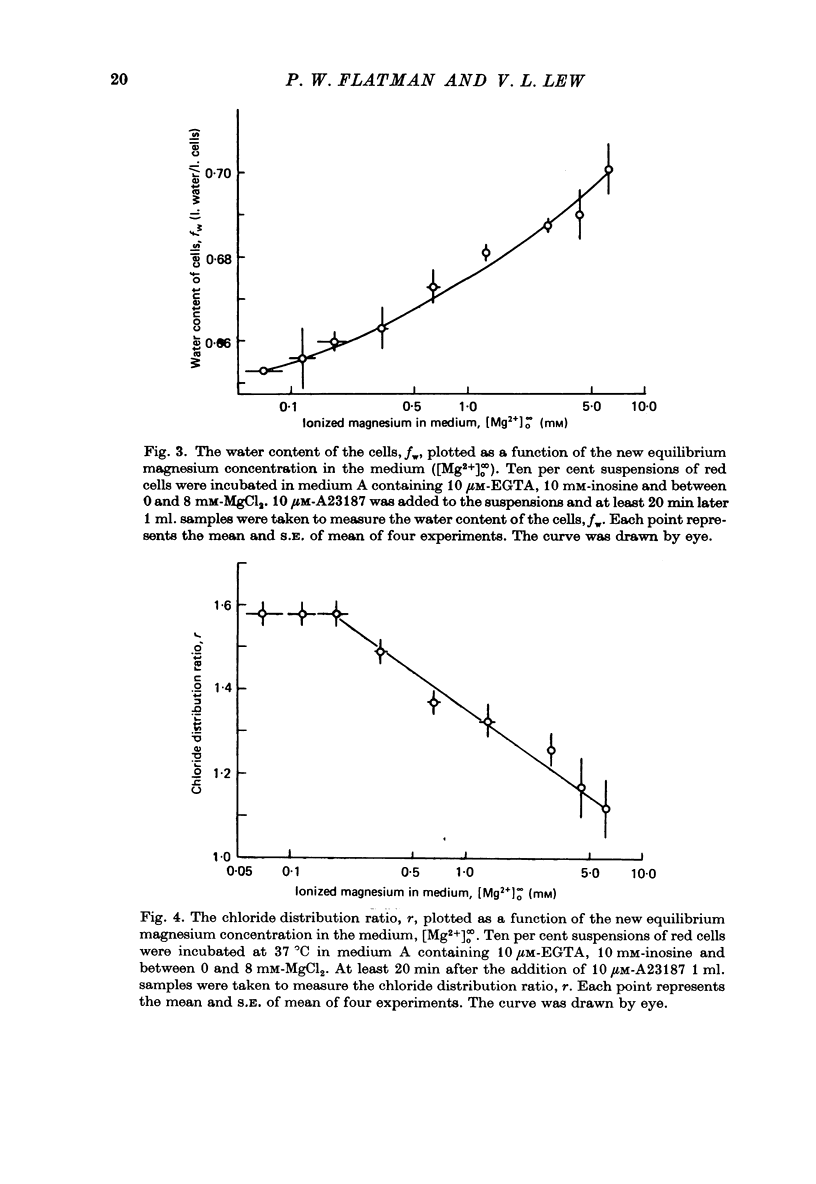
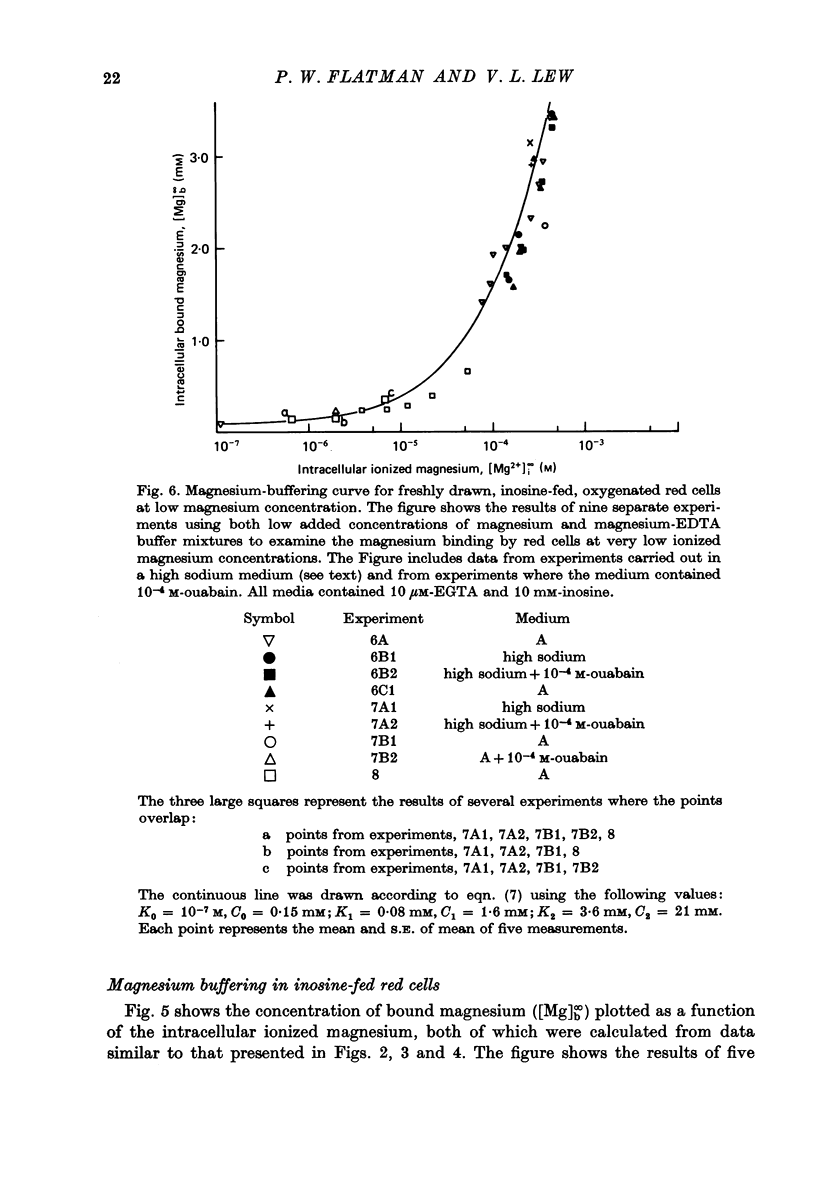
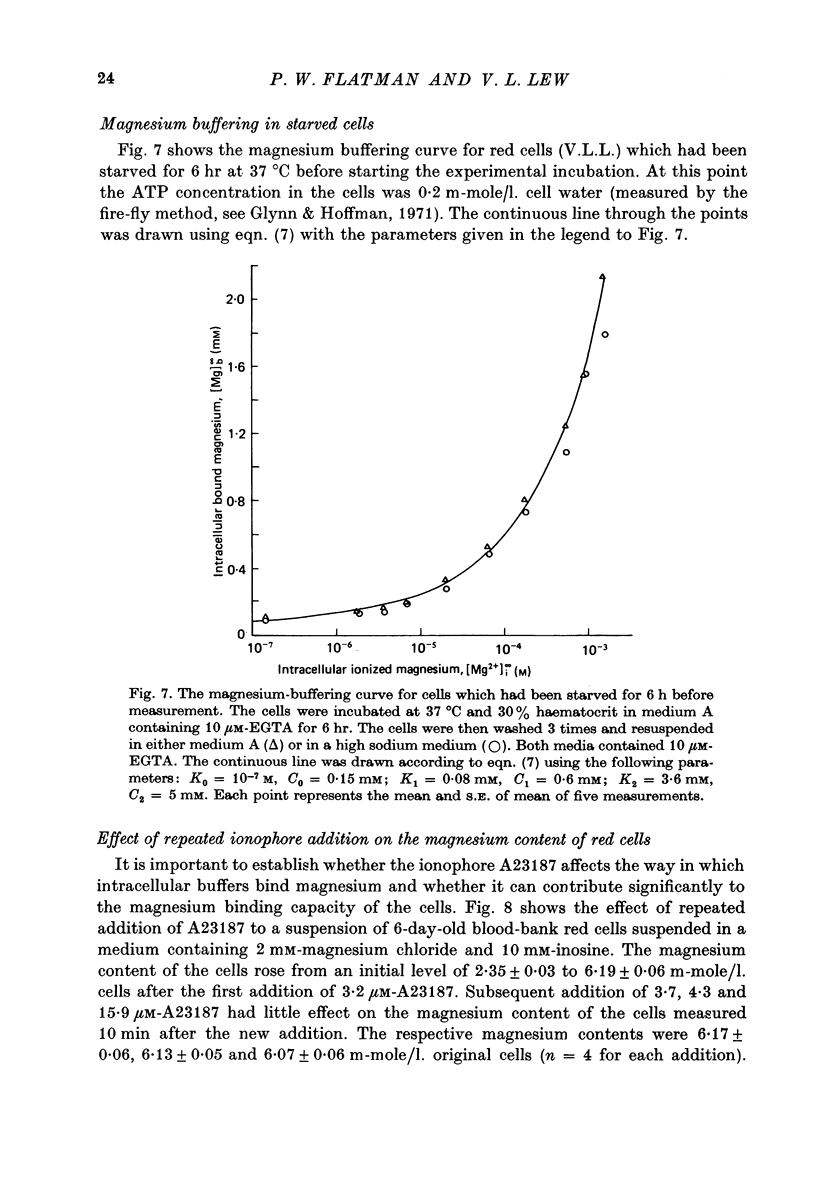
1. A method was developed for measuring the cytoplasmic magnesium buffering of intact red cells using the divalent cation selective ionophore A23187. Addition of A23187 to a suspension of red cells induces rapid equilibration of ionized magnesium across the cell membrane. 2. Entry of magnesium into red cells is associated with cell swelling and depolarization of the membrane potential. 3. At an external ionized magnesium concentration of about 0.15 mM corresponding to an internal ionized concentration of 0.4 mM the addition of A23187 did not produce a change in the magnesium content of the cells. This indicates that the normal ionized magnesium concentration inside the oxygenated red cell is about 0.4 mM. 4. The magnesium buffering curve for oxygenated, inosine-fed human red blood cells is adequately described by the existence of three buffer systems of increasing capacity and decreasing affinity. These are 0.15 mM with a Km < 10(-7) M, probably structural magnesium bound within the cell proteins; 1.6 mM with a Km approximately equal to 0.08 mM, mainly ATP and other nucleotides; and about 21-25 mM with a Km approximately equal to 3.6 mM, a major portion of this being organic phosphates. It is suggested that the contribution of 2,3-DPG to the low affinity site involves each phosphate group acting as an independent binding site for magnesium.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNSTEIN R. E. Alterations in metabolic energetics and cation transport during aging of red cells. J Clin Invest. 1959 Sep;38:1572–1586. doi: 10.1172/JCI103936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger H., Jänig G. R., Gerber G., Ruckpaul K., Rapoport S. M. Interaction of haemoglobin with ions. Interactions among magnesium, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate, and oxygenated and deoxygenated human haemoglobin under simulated intracellular conditions. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Oct 18;38(3):553–562. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03090.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodemann H. H., Hoffman J. F. Effects of Mg and Ca on the side dependencies of Na and K on ouabain binding to red blood cell ghosts and the control of Na transport by internal Mg. J Gen Physiol. 1976 May;67(5):547–561. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.5.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARR C. W., WOODS K. R. Studies on the binding of small ions in protein solutions with the use of membrane electrodes. V. The binding of magnesium ions in solutions of various proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1955 Mar;55(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(55)90536-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARVALHO A. P., SANUI H., PACE N. CALCIUM AND MAGNESIUM BINDING PROPERTIES OF CELL MEMBRANE MATERIALS. J Cell Physiol. 1963 Dec;62:311–317. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030620311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case G. D., Vanderkooi J. M., Scarpa A. Physical properties of biological membranes determined by the fluorescence of the calcium ionophore A23187. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 May;162(1):174–185. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler D. E., Williams J. A. Intracellular uptake and alpha-amylase and lactate dehydrogenase releasing actions of the divalent cation ionophore A23187 in dissociated pancreatic acinar cells. J Membr Biol. 1977 Apr 22;32(3-4):201–230. doi: 10.1007/BF01905220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier H. B., Lam A. Binding of Ca2+ and Mg2+ by 2,3-diphosphoglycerate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 24;222(2):299–306. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90117-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNHAM E. T., GLYNN I. M. Adenosinetriphosphatase activity and the active movements of alkali metal ions. J Physiol. 1961 Apr;156:274–293. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuticke B., Duhm J., Dierkesmann R. Maximal elevation of 2,3-diphosphoglycerate concentrations in human erythrocytes: influence on glycolytic metabolism and intracellular pH. Pflugers Arch. 1971;326(1):15–34. doi: 10.1007/BF00586792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira H. G., Lew V. L. Use of ionophore A23187 to measure cytoplasmic Ca buffering and activation of the Ca pump by internal Ca. Nature. 1976 Jan 1;259(5538):47–49. doi: 10.1038/259047a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatman P. W. The effect of buffer composition and deoxygenation on the concentration of ionized magnesium inside human red blood cells. J Physiol. 1980 Mar;300:19–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatman P., Lew V. L. Does ionophore A23187 mediate Na transport in the absence of divalent cations? Nature. 1977 Dec 1;270(5636):444–445. doi: 10.1038/270444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatman P., Lew V. L. Use of ionophore A23187 to measure and to control free and bound cytoplasmic Mg in intact red cells. Nature. 1977 May 26;267(5609):360–362. doi: 10.1038/267360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funder J., Wieth J. O. Determination of sodium, potassium, and water in human red blood cells. Elimination of sources of error in the development of a flame photometric method. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1966;18(2):151–166. doi: 10.3109/00365516609051811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Hoffman J. F. Nucleotide requirements for sodium-sodium exchange catalysed by the sodium pump in human red cells. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(1):239–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Lew V. L., Lüthi U. Reversal of the potassium entry mechanism in red cells, with and without reversal of the entire pump cycle. J Physiol. 1970 Apr;207(2):371–391. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt B. J., Manery J. F. Use of ion-exchange resin in preparing erythrocytes for magnesium determinations. Clin Chem. 1970 Apr;16(4):269–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafka M. S., Holz R. W. Ionophores X537A and A23187. Effects on the permeability of lipid bimolecular membranes to dopamine and calcium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 19;426(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90426-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew V. L., Ferreira H. G. Variable Ca sensitivity of a K-selective channel in intact red-cell membranes. Nature. 1976 Sep 23;263(5575):336–338. doi: 10.1038/263336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGERS T. A. The exchange of radioactive magnesium in erythrocytes of several species. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1961 Apr;57:119–121. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030570209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed P. W., Lardy H. A. A23187: a divalent cation ionophore. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6970–6977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose I. A. The state of magnesium in cells as estimated from the adenylate kinase equilibrium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Nov;61(3):1079–1086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.3.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STILES D. E., BATSAKIS J. G., HARDY G. C., BRIERE R. O. INTRACELLULAR (ERYTHROCYTIC) MAGNESIUM: ESTIMATION BY FLUORESCENT ANALYSIS. Am J Clin Pathol. 1965 Jul;44:82–85. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/44.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzmann H. J. Role of magnesium in the (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-stimulated membrane ATPase of human red blood cells. J Membr Biol. 1977 Jun 30;35(2):149–158. doi: 10.1007/BF01869946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALSER M. Ion association. VI. Interactions between calcium, magnesium, inorganic phosphate, citrate and protein in normal human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1961 Apr;40:723–730. doi: 10.1172/JCI104306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELT L. G. EXPERIMENTAL MAGNESIUM DEPLETION. Yale J Biol Med. 1964 Apr;36:325–349. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTAM R. Potassium movements and ATP in human red cells. J Physiol. 1958 Mar 11;140(3):479–497. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wacker W. E. The biochemistry of magnesium. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Aug 15;162(2):717–726. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb13003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam R., Wiley J. S. Some aspects of adenosine triphosphate synthesis from adenine and adenosine in human red blood cells. J Physiol. 1968 Dec;199(2):485–494. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


