Abstract
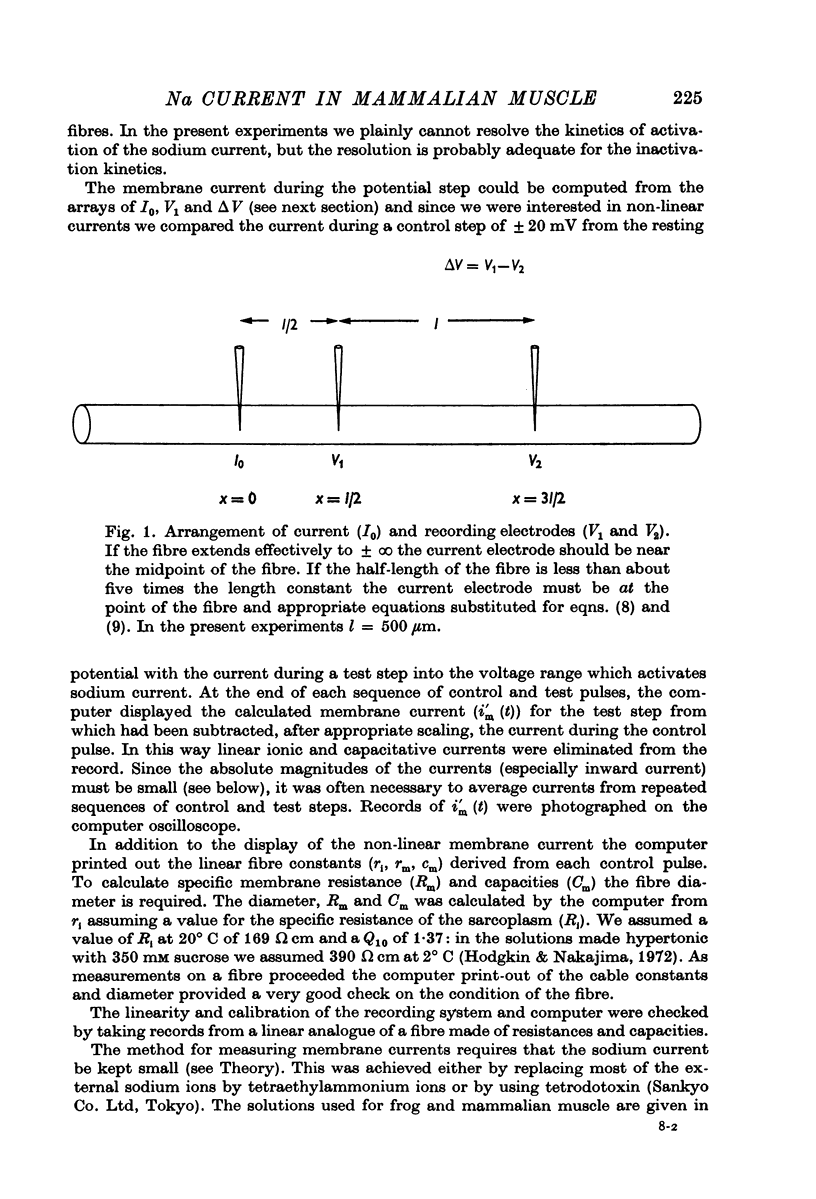
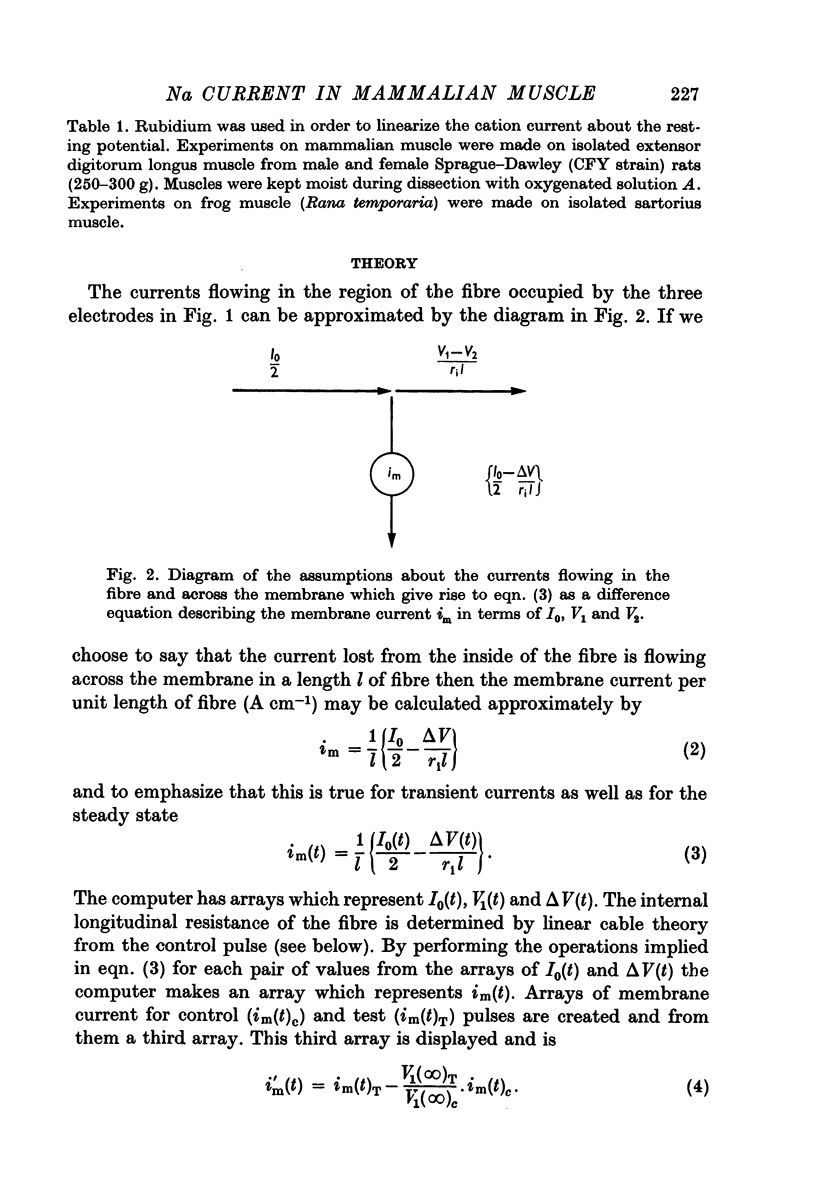
1. A method is described which allows the approximate computation of membrane current from measurements with three electrodes in the mid-region of a muscle fibre.
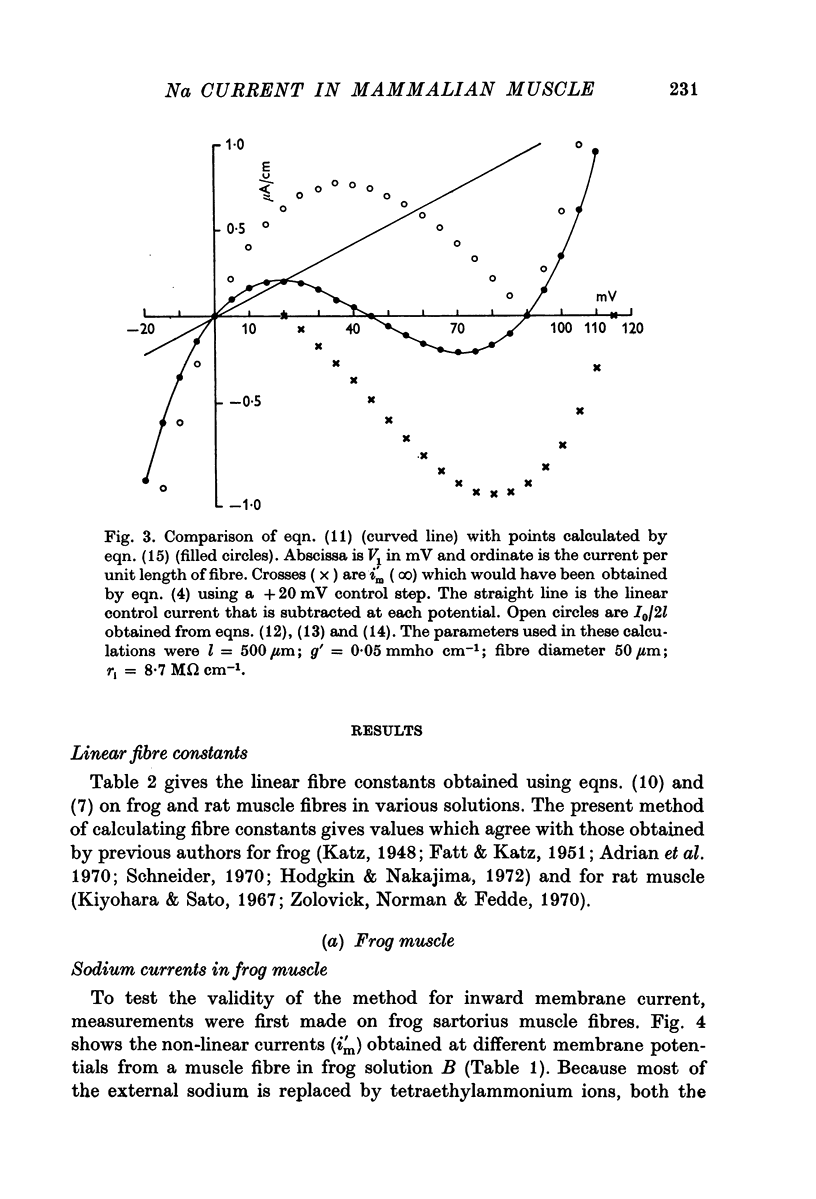
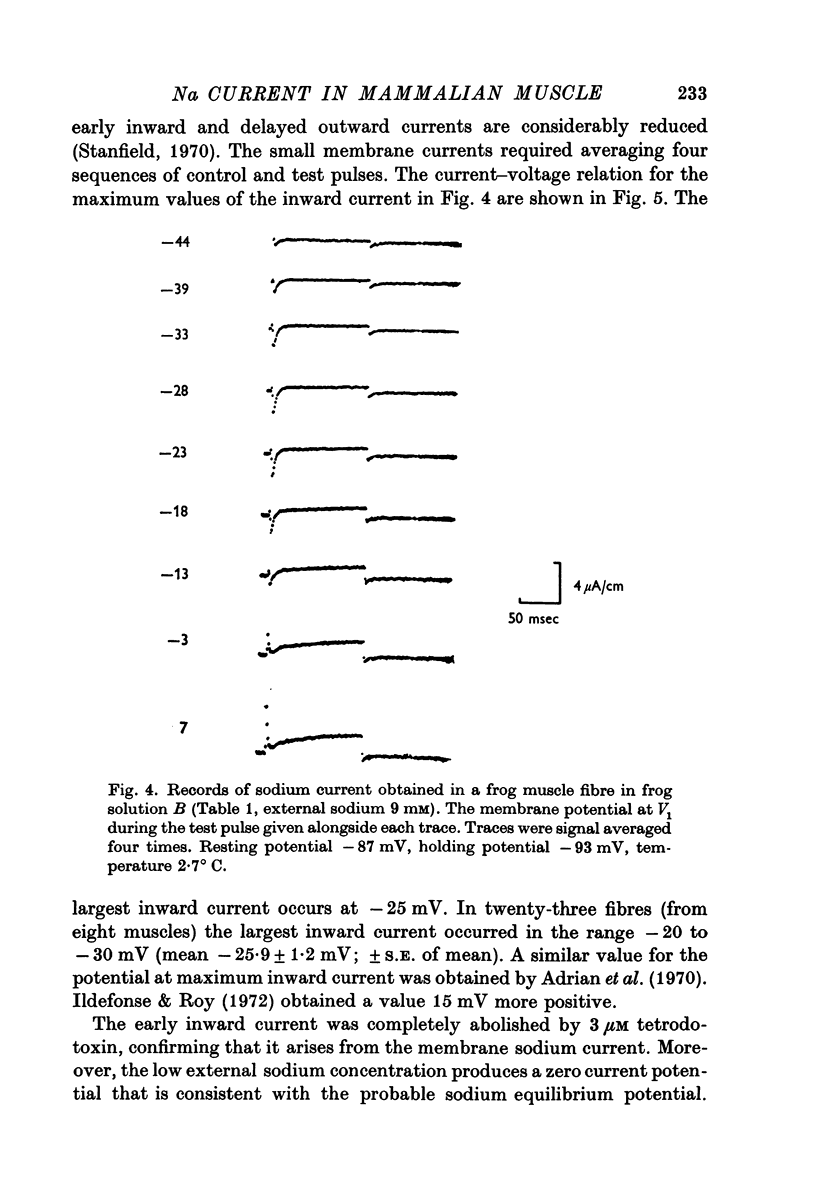
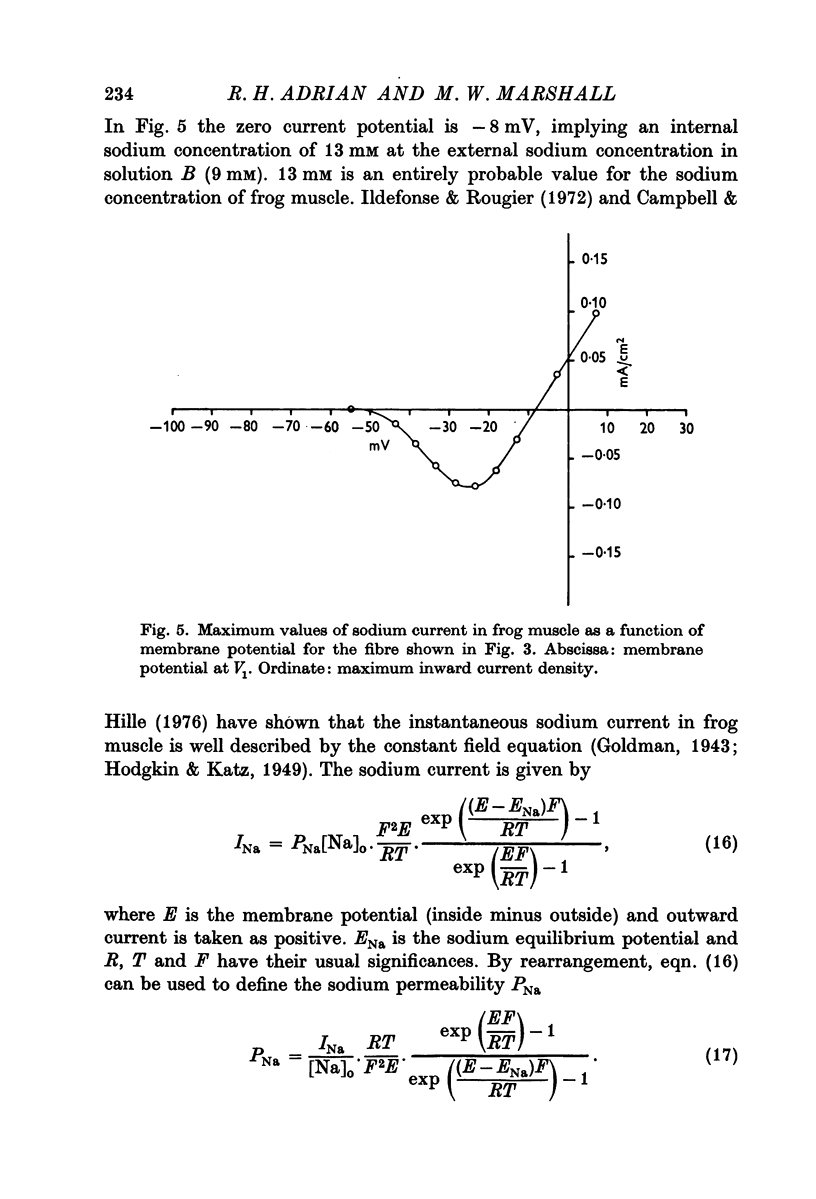
2. Measurements of inward sodium current in frog muscle are compared with the results of previous clamping studies to test the validity of the new method.
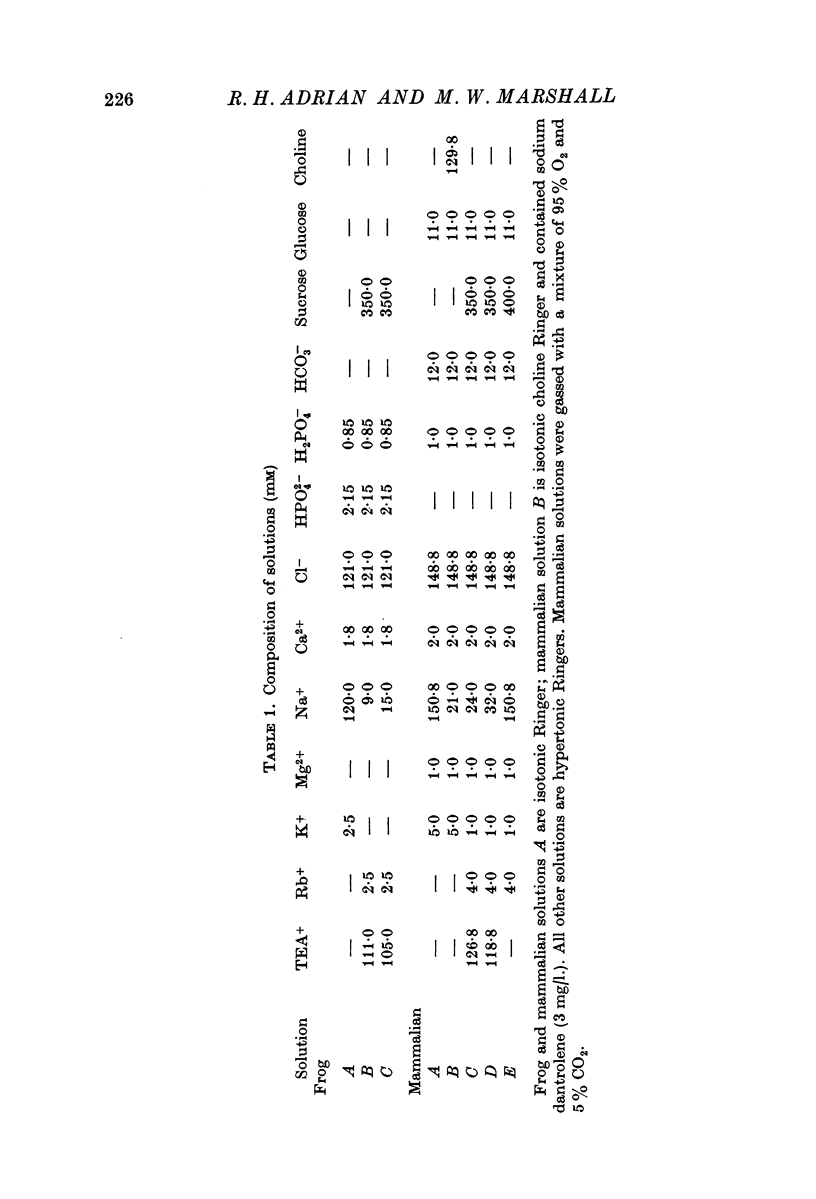
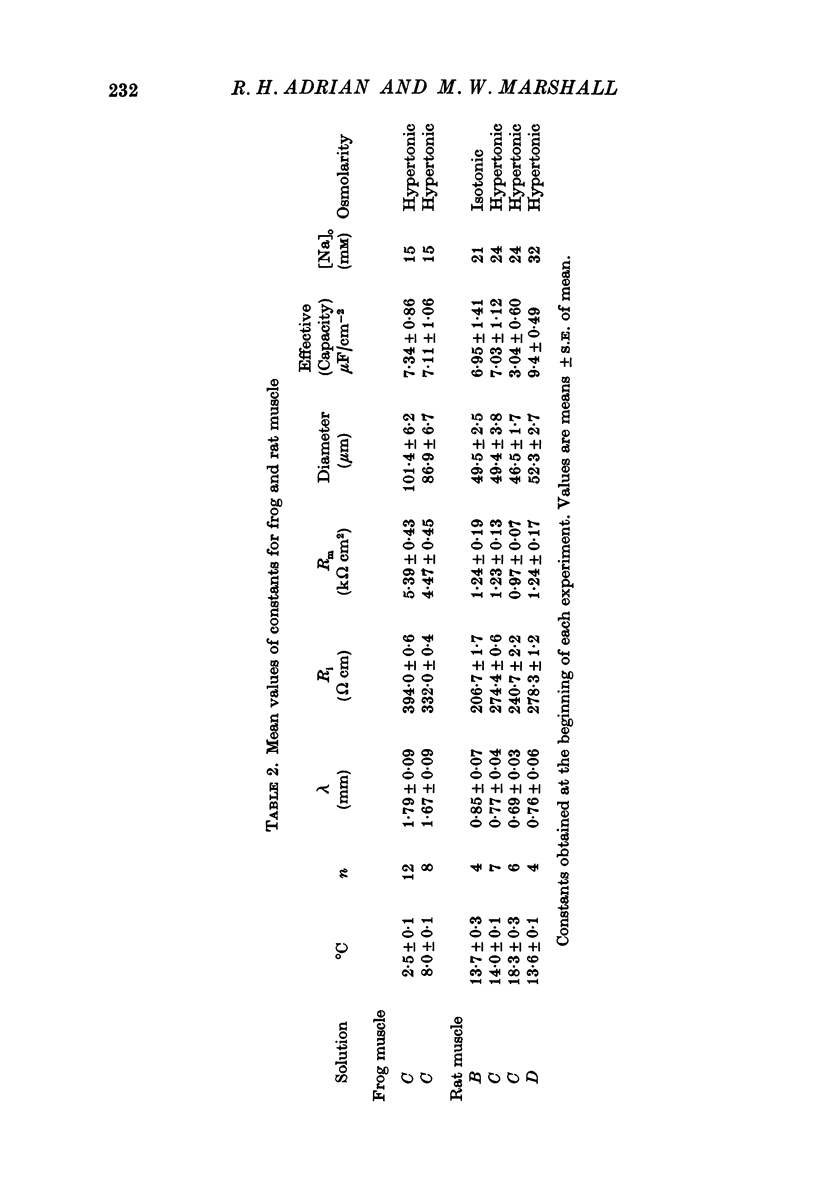
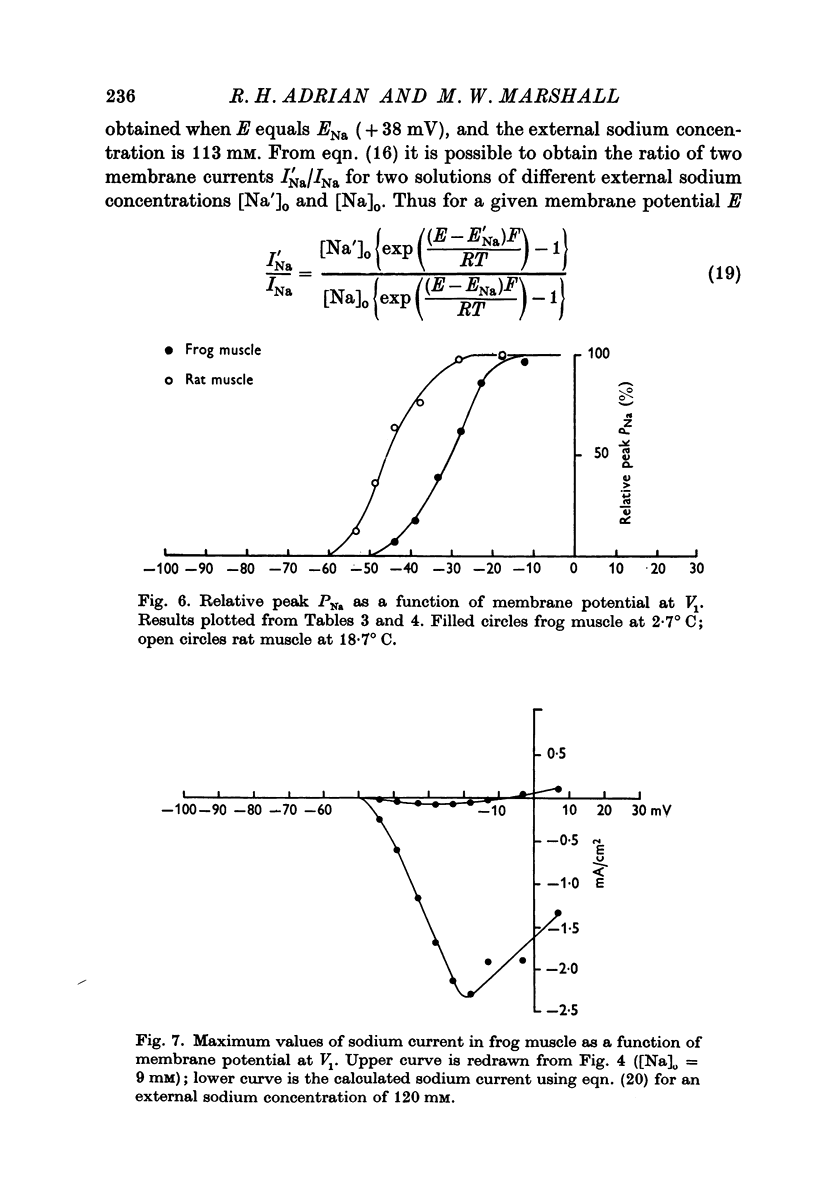
3. Sodium current in rat muscle (extensor digitorum longus) is in general similar to sodium current in frog muscle. Two differences in detail have been found between sodium current in rat and frog muscle: (a) at the same temperature (in the range 0-20° C) inactivation is slower in the rat than in the frog; (b) in rat the steady-state activation is shifted negatively on the voltage axis by some 10-15 mV.
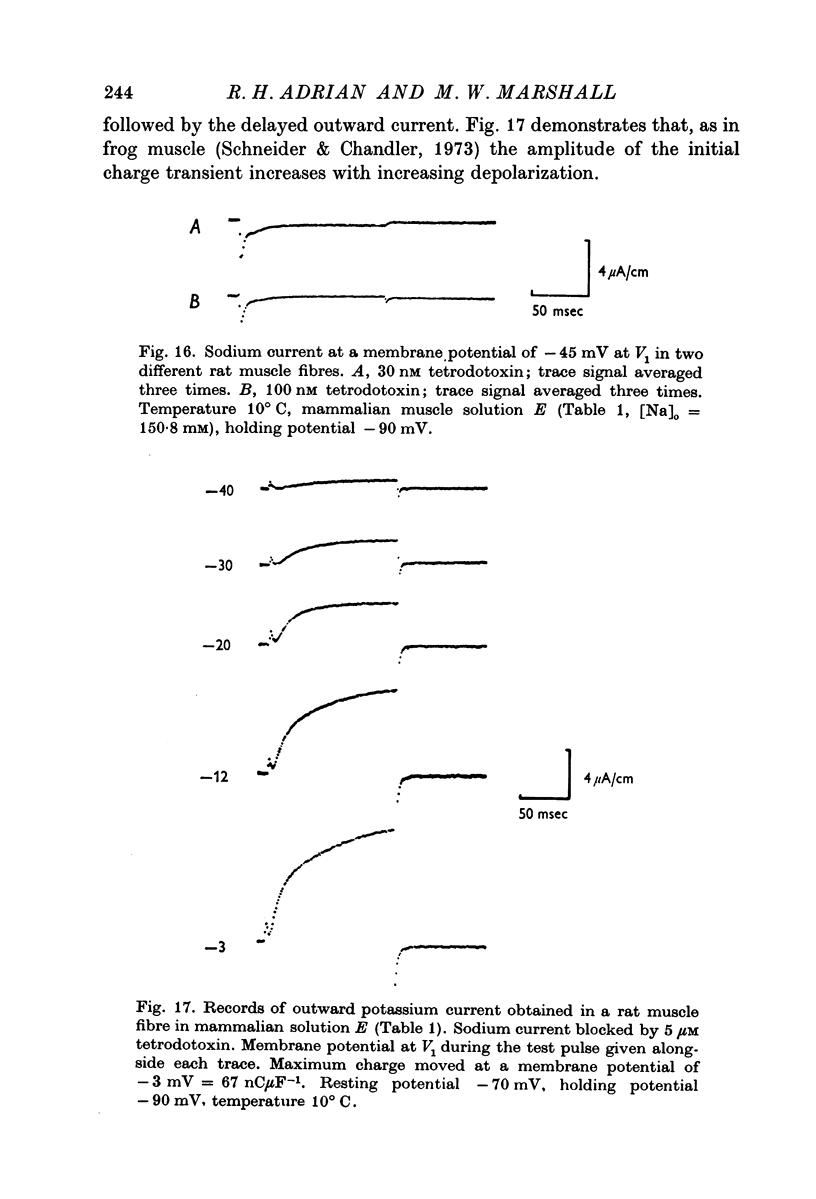
4. Delayed outward current and charge movement (Schneider & Chandler, 1973) are present in rat muscle.
5. Rat muscle fibres are more resistant than frog muscle fibres to the action of tetrodotoxin. Inward current is still detectable in rat muscle at 100 nM tetrodotoxin. We found no evidence to suggest the existence in rat muscle of two kinds of sodium channel, one sensitive and one less sensitive to tetrodotoxin.
Full text
PDF






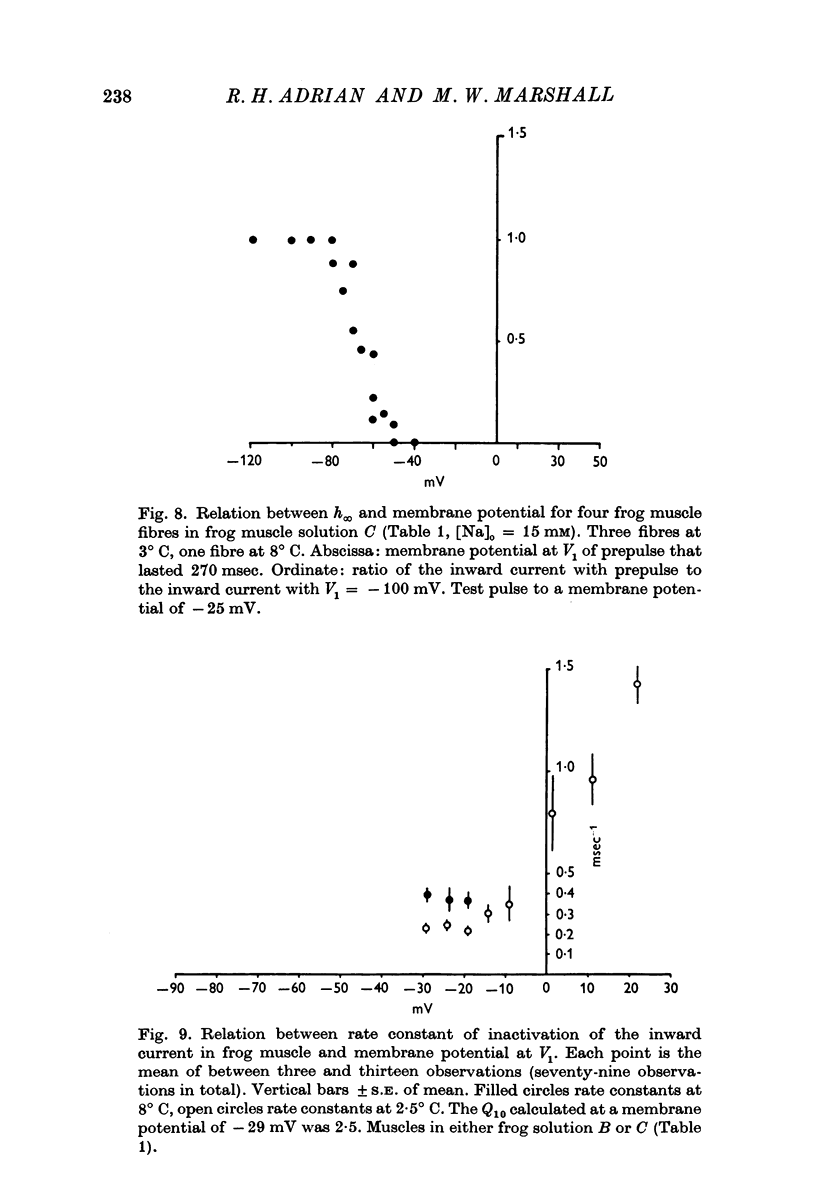
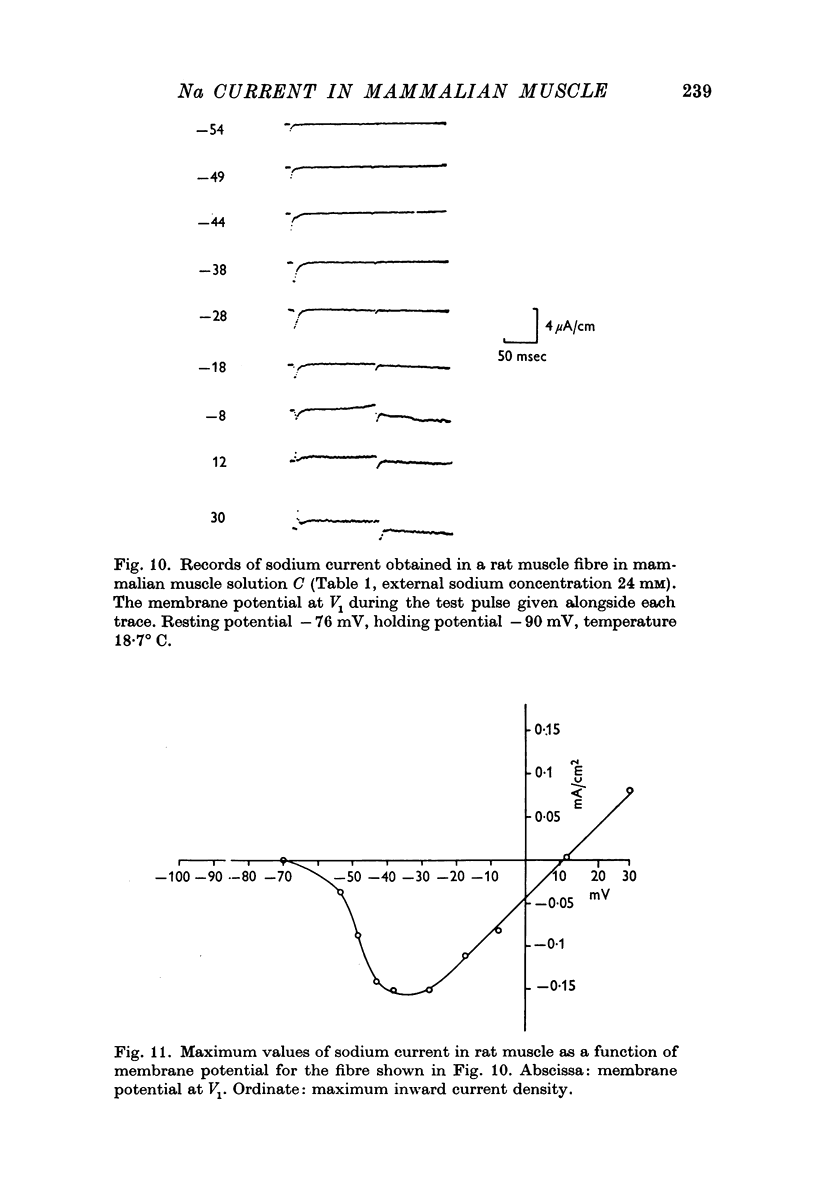

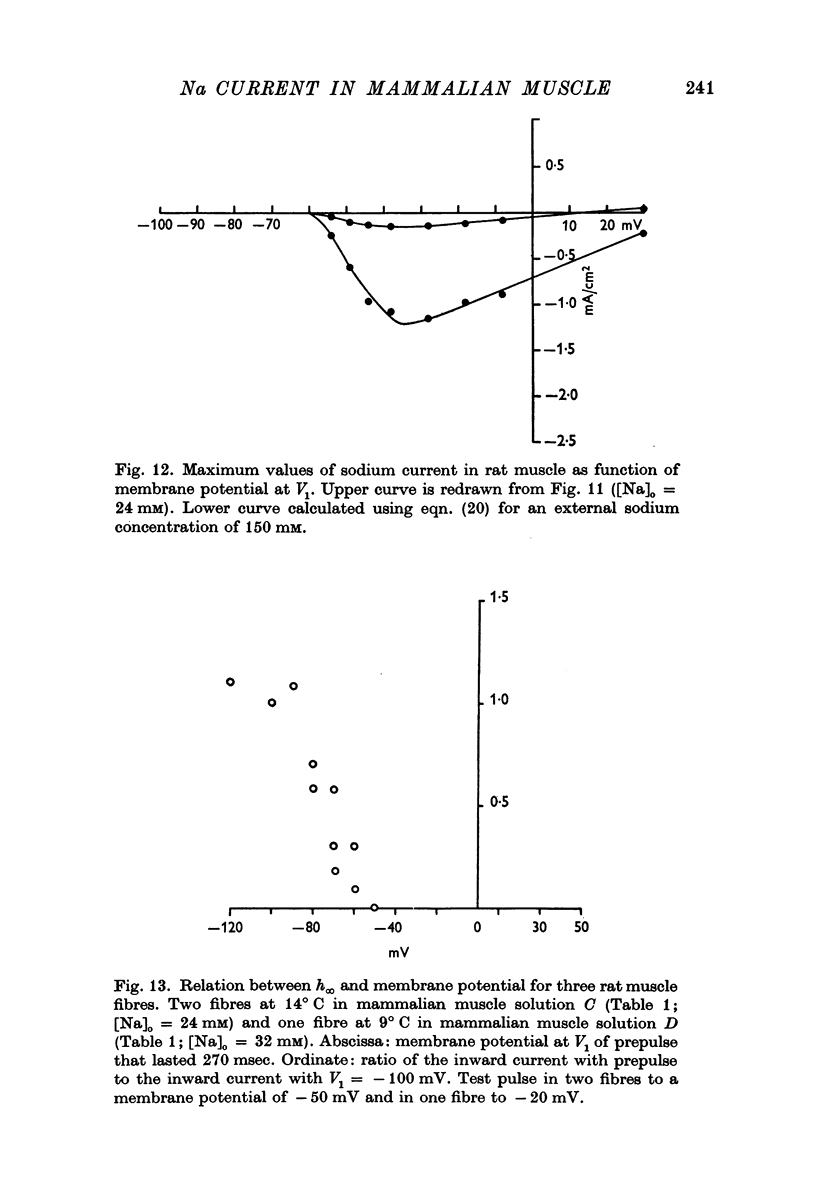
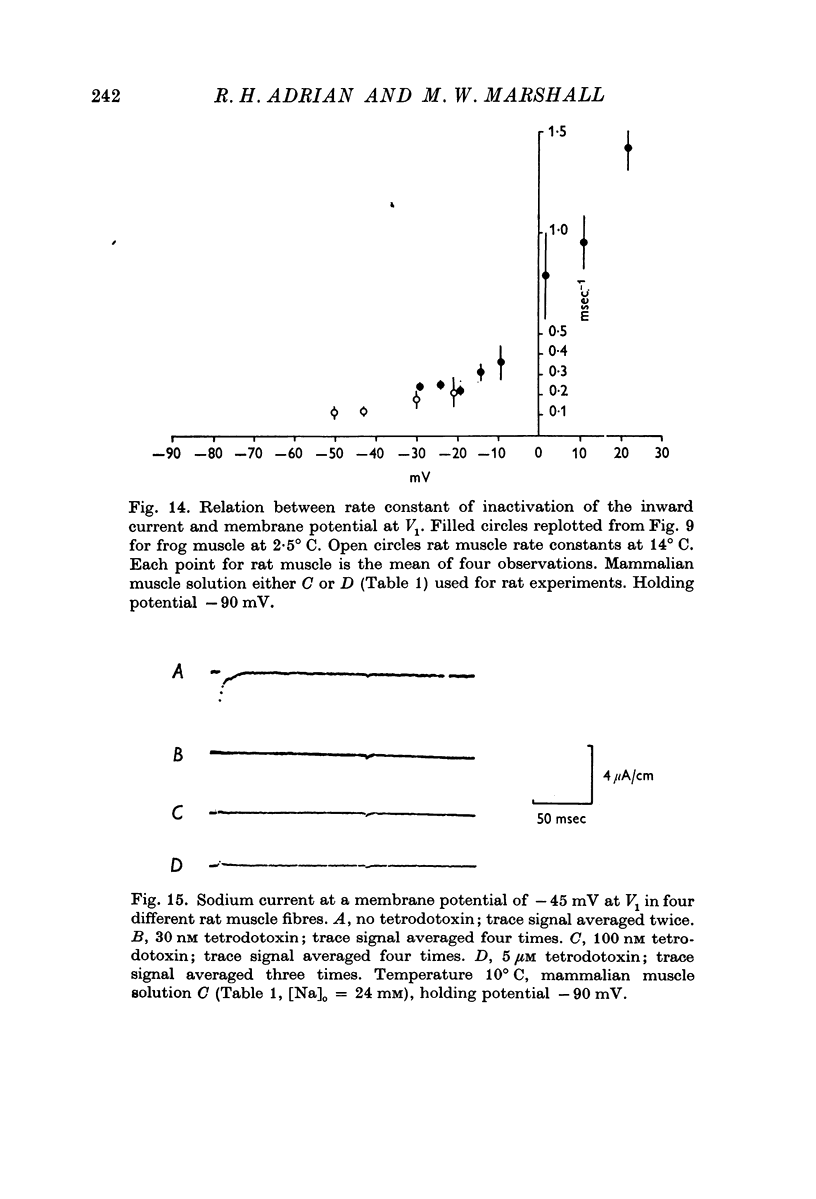







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Almers W. Membrane capacity measurements on frog skeletal muscle in media of low ion content. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(3):573–605. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Almers W. The voltage dependence of membrane capacity. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):317–338. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. Voltage clamp experiments in striated muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;208(3):607–644. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Marshall M. W. Action potentials reconstructed in normal and myotonic muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1976 Jun;258(1):125–143. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Peachey L. D. Reconstruction of the action potential of frog sartorius muscle. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;235(1):103–131. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaty G. N., Stefani E. Inward calcium current in twitch muscle fibres of the frog [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;260(2):27P–27P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. T., Hille B. Kinetic and pharmacological properties of the sodium channel of frog skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):309–323. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Rang H. P., Ritchie J. M. The binding of tetrodotoxin and alpha-bungarotoxin to normal and denervated mammalian muscle. J Physiol. 1974 Jul;240(1):199–226. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. An analysis of the end-plate potential recorded with an intracellular electrode. J Physiol. 1951 Nov 28;115(3):320–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D. E. POTENTIAL, IMPEDANCE, AND RECTIFICATION IN MEMBRANES. J Gen Physiol. 1943 Sep 20;27(1):37–60. doi: 10.1085/jgp.27.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIWARA S., WATANABE A. The effect of tetraethylammonium chloride on the muscle membrane examined with an intracellular microelectrode. J Physiol. 1955 Sep 28;129(3):513–527. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):449–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F. Ion movements during nerve activity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Aug 28;81:221–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb49311.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Campbell D. T. An improved vaseline gap voltage clamp for skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):265–293. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., Nakajima S. The effect of diameter on the electrical constants of frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;221(1):105–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ildefonse M., Rougier O. Voltage-clamp analysis of the early current in frog skeletal muscle fibre using the double sucrose-gap method. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(2):373–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ildefonse M., Roy G. Kinetic properties of the sodium current in striated muscle fibres on the basis of the Hodgkin-Huxley theory. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(2):419–431. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernan R. P., MacDermott M. Intracellular potassium concentrations and extracellular spaces in rat skeletal muscles immersed in normal, hypotonic and high-K modified Krebs fluid, determined by potassium-selective microelectrodes [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1976 Dec;263(1):158P–160P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyohara T., Sato M. Membrane constants of red and white muscle fibers in the rat. Jpn J Physiol. 1967 Dec 15;17(6):720–725. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.17.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Chandler W. K. Voltage dependent charge movement of skeletal muscle: a possible step in excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1973 Mar 23;242(5395):244–246. doi: 10.1038/242244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F. Linear electrical properties of the transverse tubules and surface membrane of skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Nov;56(5):640–671. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.5.640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R. The effect of the tetraethylammonium ion on the delayed currents of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;209(1):209–229. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zolovick A. J., Norman R. L., Fedde M. R. Membrane constants of muscle fibers of rat diaphragm. Am J Physiol. 1970 Sep;219(3):654–657. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.3.654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


