Abstract
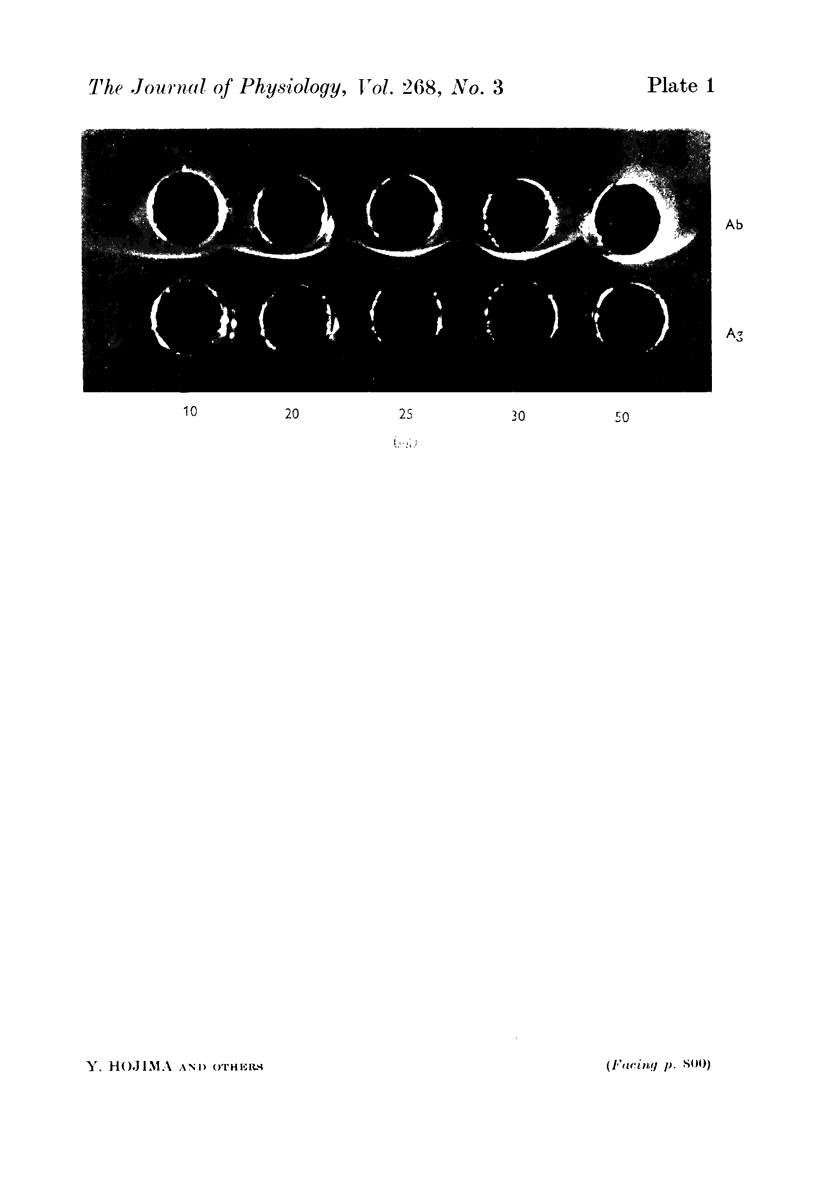
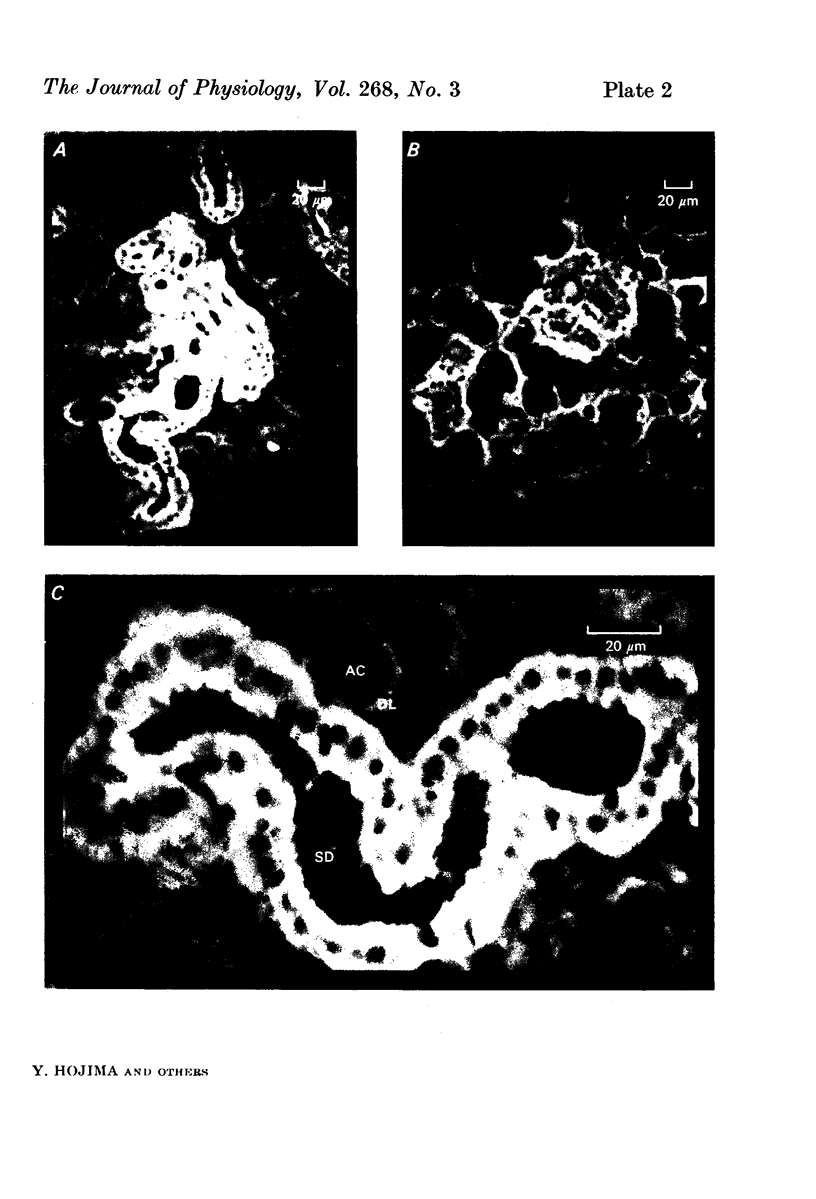
Kallikrein was located in the apical portion of the striated duct cells of the cat's submandibular gland by an immunohistochemical technique. This portion only of these cells showed an intense band of specific fluorescence. There was no evidence of specific fluorescence in the acinar and demilune cells nor in the interstitial tissue or blood besells. In some sections the collecting ducts showed a very fine fluorescent luminal rim.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aschoff J. Desynchronization and resynchronization of human circadian rhythms. Aerosp Med. 1969 Aug;40(8):844–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aschoff J., Pöppel E., Wever R. Circadiane Periodik des Menschen unter dem Einfluss von Licht-Dunkel-Wechseln unterschiedlicher Periode. Pflugers Arch. 1969;306(1):58–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00586611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barcroft J., Piper H. The gaseous metabolism of the submaxillary gland with reference especially to the effect of adrenalin and the time relation of the stimulus to the oxidation process. J Physiol. 1912 Jul 15;44(5-6):359–373. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1912.sp001520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton S., Sanders E. J., Schachter M., Uddin M. Autonomic nerve stimulation, kallikrein content anc acinar cell granules of the cat's submandibular gland. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):363–369. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beilenson S., Schachter M., Smaje L. H. Secretion of kallikrein and its role in vasodilatation in the submaxillary gland. J Physiol. 1968 Dec;199(2):303–317. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhoola K. D. Comparative study of the subcellular distribution of submaxillary kallikrein. Biochem Pharmacol. 1969 May;18(5):1252–1254. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(69)90134-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhoola K. D., Dorey G., Jones C. W. The influence of androgens on enzymes (chymotrypsin-and trypsin-like proteases, renin, kallikrein and amylase) and on cellular structure of the mouse submaxillary gland. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(2):503–522. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhoola K. D., Heap P. F. Properties of kallikrein-containing granules isolated from the submaxillary gland of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):421–432. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhoola K. D., Morley J., Schachter M., Smaje L. H. Vasodilatation in the submaxillary gland of the cat. J Physiol. 1965 Jul;179(1):172–184. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhoola K. D., Ogle C. W. The subcellular localization of kallikrein, amylase and acetylcholine in the submaxillary gland of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1966 Jun;184(3):663–672. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H. Fluorescent antibody methods. Gen Cytochem Methods. 1958;1:399–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang T. S., Erdös E. G., Miwa I., Tague L. L., Coalson J. J. Isolation from a salivary gland of granules containing renin and kallikrein. Circ Res. 1968 Oct;23(4):507–517. doi: 10.1161/01.res.23.4.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Revak S. D., Wuepper K. D. Activation of Hageman factor in solid and fluid phases. A critical role of kallikrein. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1564–1583. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzari C., Angeletti P. U., Lazar J., Orth H., Gross F. Separation of isorenin activity from nerve growth factor (NGF) activity in mouse submaxillary gland extracts. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Jun 1;22(11):1321–1327. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90306-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott A. L., Mills J. N., Minors D. S., Waterhouse J. M. The effect of real and simulated time-zone shifts upon the circadian rhythms of body temperature, plasma 11-hydroxycorticosteroids, and renal excretion in human subjects. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;221(1):227–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdös E. G., Tague L. L., Miwa I. Kallikrein in granules of the submaxillary gland. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 May;17(5):667–674. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia R., Boucher R., Genest J. Tonin activity in rat saliva: effect of sympathomimetic and parasympathomimetic drugs. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1976 Aug;54(4):443–445. doi: 10.1139/y76-063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett J. R., Kidd A. Effects of nerve stimulation and denervation on secretory material in submandibular striated duct cells of cats, and the possible role of these cells in the secretion of salivary kallikrein. Cell Tissue Res. 1975 Aug 1;161(1):71–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00222115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geipert F., Erdös E. G. Properties of granules that contain kallikrein and renin. Experientia. 1971 Aug;27(8):912–913. doi: 10.1007/BF02135739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman Y., Levy M., Shorr J. Renin-like activity of the rat submaxillary gland: characterization and the effect of several drugs and stimuli. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Jan;47(1):59–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08158.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILTON S. M., LEWIS G. P. The mechanism of the functional hyperaemia in the submandibular salivary gland. J Physiol. 1955 Aug 29;129(2):253–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halberg F., Katinas G. S. Chronobiologic glossary of the International Society for the Study of Biologic Rhythms. Int J Chronobiol. 1973;1(1):31–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenner F. A., Goodwin J. C., Sheridan M., Tauber I. J., Lobban M. C. The effect of an altered time regime on biological rhythms in a 48-hour periodic psychosis. Br J Psychiatry. 1968 Feb;114(507):215–224. doi: 10.1192/bjp.114.507.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEITMAN N., KLEITMAN E. Effect of non-twenty-four-hour routines of living on oral temperature and heart rate. J Appl Physiol. 1953 Nov;6(5):283–291. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1953.6.5.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpinski E., Barton S., Schachter M. Vasodilator nerve fibres to the submaxillary gland of the cat. Nature. 1971 Jul 9;232(5306):122–124. doi: 10.1038/232122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVI-MONTALCINI R., ANGELETTI P. U. Growth control of the sympathetic system by a specific protein factor. Q Rev Biol. 1961 Jun;36:99–108. doi: 10.1086/403331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVI-MONTALCINI R., HAMBURGER V. Selective growth stimulating effects of mouse sarcoma on the sensory and sympathetic nervous system of the chick embryo. J Exp Zool. 1951 Mar;116(2):321–361. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401160206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS P. R., LOBBAN M. C. Dissociation of diurnal rhythms in human subjects living on abnormal time routines. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1957 Oct;42(4):371–386. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1957.sp001281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS P. R., LOBBAN M. C. Patterns of electrolyte excretion in human subjects during a prolonged period of life on a 22-hour day. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):670–680. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS P. R., LOBBAN M. C., SHAW T. I. Patterns of urine flow in human subjects during a prolonged period of life on a 22-hour day. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):659–669. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS P. R., LOBBAN M. C. The effects of prolonged periods of life on abnormal time routines upon excretory rhythms in human subjects. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1957 Oct;42(4):356–371. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1957.sp001280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann H., Stiller S., Korz R. Biological balance of sodium and potassium: a control system with oscillating correcting variable. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Mar 30;362(2):135–139. doi: 10.1007/BF00583639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelakis A. M., Yoshida H., Menzie J., Murakami K., Inagami T. A radioimmunoassay for the direct measurement of renin in mice and its application to submaxillary gland and kidney studies. Endocrinology. 1974 Apr;94(4):1101–1105. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-4-1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. N., Minors D. S., Waterhouse J. M. Proceedings: Urinary and temperature rhythms on days of abnormal length. J Physiol. 1976 May;257(1):54P–55P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. N., Minors D. S., Waterhouse J. M. The circadian rhythms of human subjects without timepieces or indication of the alternation of day and night. J Physiol. 1974 Aug;240(3):567–594. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. N., Waterhouse J. M. Circadian rhythms over the course of a year in a man living alone. Int J Chronobiol. 1973;1(1):73–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minors D. S., Mills J. N., Waterhouse J. M. The circadian variations of the rates of excretion of urinary electrolytes and of deep body temperature. Int J Chronobiol. 1976;4(1):1–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriwaki C., Hojima Y., Schachter M. Purification of kallikrein from cat submaxillary gland. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1976;70(00):151–156. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3267-1_19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor W. J., Summerill R. A. The effect of a meal of meat on glomerular filtration rate in dogs at normal urine flows. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;256(1):81–91. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orstavik T. B., Brandtzaeg P., Nustad K., Halvorsen K. M. Cellular localization of kallikreins in rat submandibular and sublingual salivary glands: immunofluorescence tracing related to histological characteristics. Acta Histochem. 1975;54(2):183–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter M. Kallikreins and kinins. Physiol Rev. 1969 Jul;49(3):509–547. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1969.49.3.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson H. W., Lobban M. C. Effect of a 21-hour day on the human circadian excretory rhythms of 17-hydroxycorticosteroids and electrolytes. Aerosp Med. 1967 Dec;38(12):1205–1213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroud R. M. A family of protein-cutting proteins. Sci Am. 1974 Jul;231(1):74–88. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0774-74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERLE E., TRAUTSCHOLD I., SCHMAL A. UBER EIN ISO-ENZYM DES RENINS UND UEBER DIE ISOLIERUNG EINES BIOLOGISCH AKTIVEN SPALTPRODUKTES SEINES SUBSTRATES. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1963;332:79–87. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1963.332.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wever R. Internal phase-angle differences in human circadian rhythms: causes for changes and problems of determinations. Int J Chronobiol. 1973;1(4):371–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wever R. Virtual synchronization towards the limits of the range of entrainment. J Theor Biol. 1972 Jul;36(1):119–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(72)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]