Abstract
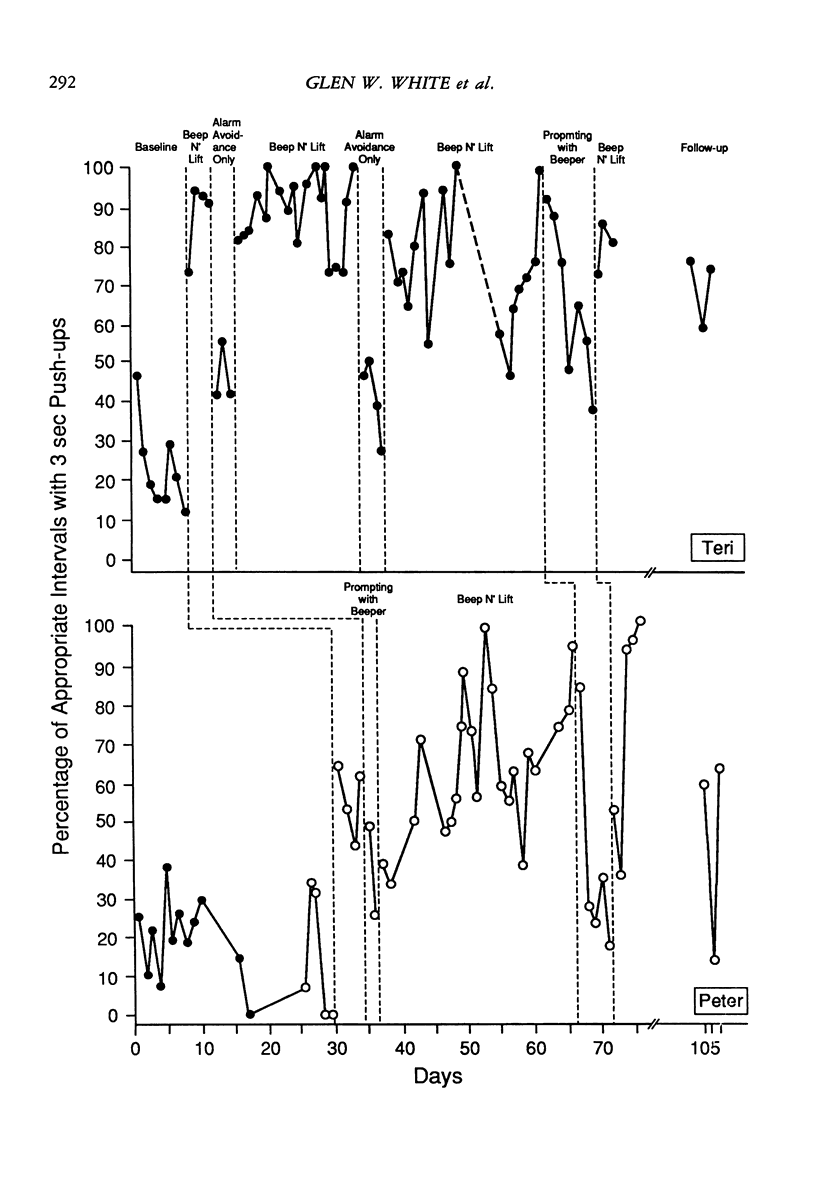
People who use wheelchairs are at risk for developing pressure sores. Regular pressure relief, in the form of a wheelchair push-up, is one way to reduce the likelihood of pressure sores. We examined the effects of antecedent (i.e., instructions, audible prompts) and consequent (i.e., alarm avoidance) events on wheelchair push-ups, using a multiple baseline analysis with 2 participants with spina bifida. Results suggest that the combined procedure was more effective than either antecedent or consequent events alone, and there is some evidence suggesting maintenance of effects over time.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cumming W. T., Tompkins W. J., Jones R. M., Margolis S. A. Microprocessor-based weight shift monitors for paraplegic patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1986 Mar;67(3):172–174. doi: 10.1016/0003-9993(86)90067-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinsdale S. M. Decubitus ulcers: role of pressure and friction in causation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1974 Apr;55(4):147–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. H., Cluss P. A. A behavioral medicine perspective on adherence to long-term medical regimens. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1982 Dec;50(6):950–971. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.50.6.950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finney J. W., Friman P. C., Rapoff M. A., Christophersen E. R. Improving compliance with antibiotic regimens for otitis media. Randomized clinical trial in a pediatric clinic. Am J Dis Child. 1985 Jan;139(1):89–95. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1985.02140030095041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. V., Patterson P. Long term pressure recordings under the ischial tuberosities of tetraplegics. Paraplegia. 1983 Apr;21(2):99–106. doi: 10.1038/sc.1983.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordyce W. E., Simons B. C. Automated training system for wheelchair pushups. Public Health Rep. 1968 Jun;83(6):527–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy D. J., Silver J. R. Major amputation in paraplegic and tetraplegic patients. Int Rehabil Med. 1984;6(4):162–165. doi: 10.3109/03790798409165951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. L., Millman A. A three-part system to combat pressure sores. Geriatr Nurs. 1986 Mar-Apr;7(2):78–82. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4572(86)80105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krouskop T. A., Noble P. C., Garber S. L., Spencer W. A. The effectiveness of preventive management in reducing the occurrence of pressure sores. J Rehabil R D. 1983 Jul;20(1):74–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malament I. R., Dunn M. E., Davis R. Pressure sores: an operant conditioning approach to prevention. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1975 Apr;56(4):161–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merbitz C. T., King R. B., Bleiberg J., Grip J. C. Wheelchair push-ups: measuring pressure relief frequency. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1985 Jul;66(7):433–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinchcofsky-Devin G. D., Kaminski M. V., Jr Correlation of pressure sores and nutritional status. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1986 Jun;34(6):435–440. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1986.tb03411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. H., Dinsdale S. M., Matthews R. E., Cole T. M. Modifying persistent undesirable behavior in a medical setting. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1969 Mar;50(3):147–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Loch E. Pressure sore prevention system: a new biofeedback approach. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1985 Jun;75(6):926–928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shea J. D. Pressure sores: classification and management. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1975 Oct;(112):89–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman B. Infection and pressure sores. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1985 Mar;66(3):177–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner U., Hall D. J. Pressure sores: a policy for prevention. Nurs Times. 1986 Apr 16;82(16):59–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M. M. Social validity: the case for subjective measurement or how applied behavior analysis is finding its heart. J Appl Behav Anal. 1978 Summer;11(2):203–214. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1978.11-203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


