Abstract
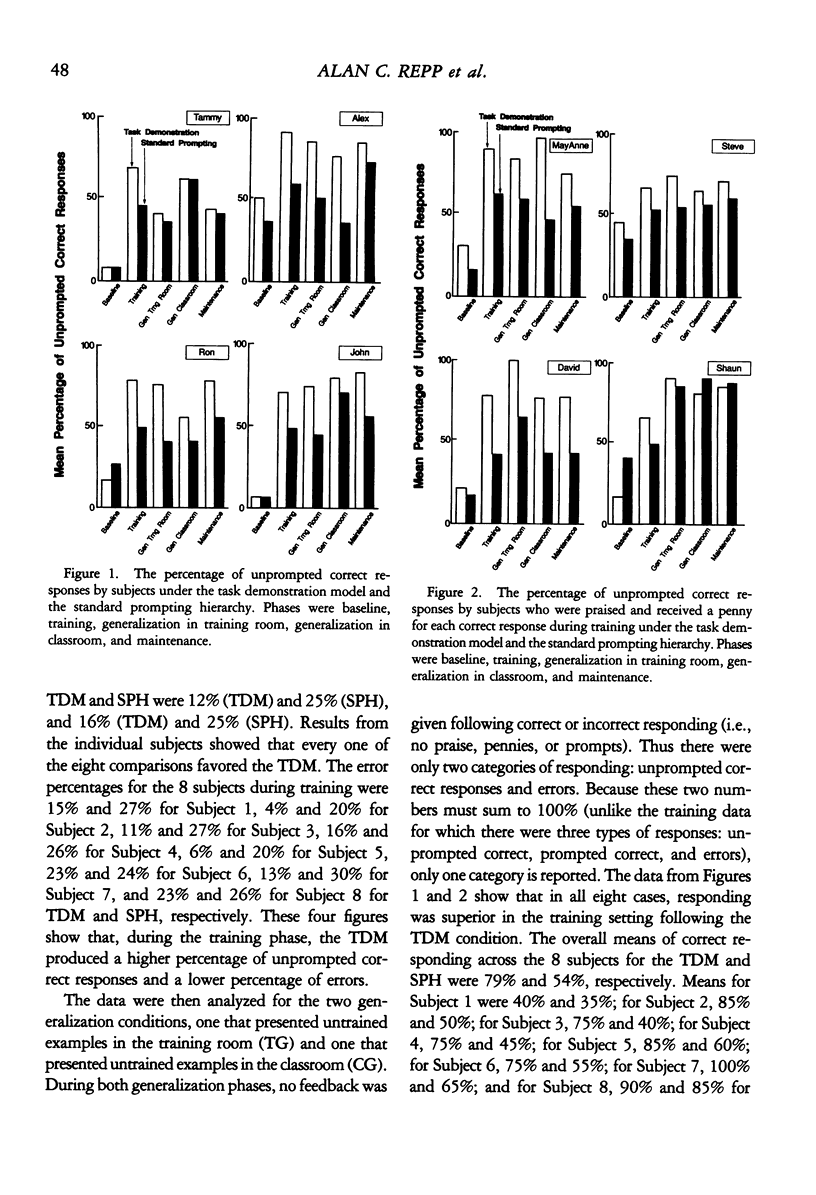
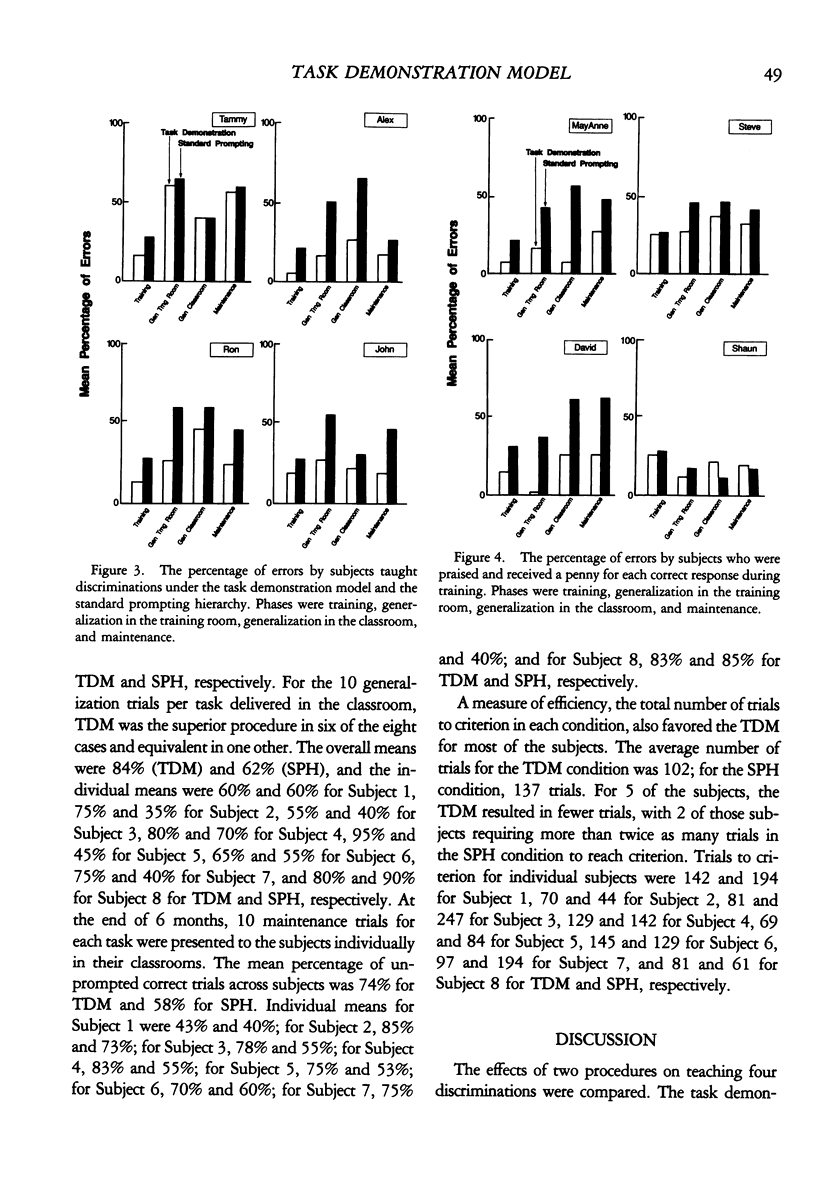
A comparison was made between two procedures for teaching persons with severe handicaps: (a) the task demonstration model, which is based upon a fading procedure and general case programming, and (b) the standard prompting hierarchy, a least-to-most intrusive prompting procedure commonly used to teach these individuals. Five phases were used in comparing the procedures: pretesting, training, two generalization tests, and a 6-month maintenance test. Eight students learned two discrimination tasks by each procedure, with each task involving two- or three-digit numbers. Results showed that under the task demonstration model all 8 subjects had more unprompted correct responses (about 1.5 times as many) in training, all 8 subjects had fewer errors (about 0.6 times as many) in training, all 8 subjects had more correct responding in the generalization test with untrained stimuli in the training room, 6 of 8 subjects had more correct responding with untrained stimuli in another room, a 7th had equivalent amounts, and 7 of 8 subjects had more correct responding on a 6-month maintenance test. Thus, the task demonstration model proved superior to the standard prompting hierarchy in 29 of 32 tests of correct responding. Results are discussed in terms of implications for stimulus control training strategies.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen K. D., Fuqua R. W. Eliminating selective stimulus control: a comparison of two procedures for teaching mentally retarded children to respond to compound stimuli. J Exp Child Psychol. 1985 Feb;39(1):55–71. doi: 10.1016/0022-0965(85)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow D. H., Hayes S. C. Alternating treatments design: one strategy for comparing the effects of two treatments in a single subject. J Appl Behav Anal. 1979 Summer;12(2):199–210. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1979.12-199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L., Bellamy T., Perlmutter L., Sackowitz P., Sontag E. The development of quality, quantity and durability in the work performance of retarded students in a public school prevocational workshop. Train Sch Bull (Vinel) 1972 Aug;69(2):58–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuvo A. J., Leaf R. B., Borakove L. S. Teaching janitorial skills to the mentally retarded: acquisition, generalization, and maintenance. J Appl Behav Anal. 1978 Fall;11(3):345–355. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1978.11-345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etzel B. C., LeBlanc J. M. The simplest treatment alternative: the law of parsimony applied to choosing appropriate instructional control and errorless-learning procedures for the difficult-to-teach child. J Autism Dev Disord. 1979 Dec;9(4):361–382. doi: 10.1007/BF01531445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. W. Stimulus factors in skill training of retarded adolescents on a complex assembly task: acquisition, transfer, and retention. Am J Ment Defic. 1972 Mar;76(5):517–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. W. Task analysis of a complex assembly task by the retarded blind. Except Child. 1976 Oct;43(2):78–84. doi: 10.1177/001440297604300203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koegel R. L., Rincover A. Some detrimental effects of using extra stimuli to guide learning in normal and autistic children. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1976;4(1):59–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00917605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koegel R. L., Wilhelm H. Selective responding to the components of multiple visual cues by autistic children. J Exp Child Psychol. 1973 Jun;15(3):442–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-0965(73)90094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koop S., Martin G., Yu D., Suthons E. Comparison of two reinforcement strategies in vocational-skill training of mentally retarded persons. Am J Ment Defic. 1980 May;84(6):616–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovaas O. I., Koegel R. L., Schreibman L. Stimulus overselectivity in autism: a review of research. Psychol Bull. 1979 Nov;86(6):1236–1254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovaas O. I., Schreibman L., Koegel R., Rehm R. Selective responding by autistic children to multiple sensory input. J Abnorm Psychol. 1971 Jun;77(3):211–222. doi: 10.1037/h0031015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosk M. D., Bucher B. Prompting and stimulus shaping procedures for teaching visual-motor skills to retarded children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1984 Spring;17(1):23–34. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1984.17-23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rincover A. Variables affecting stimulus fading and discriminative responding in psychotic children. J Abnorm Psychol. 1978 Oct;87(5):541–553. doi: 10.1037//0021-843x.87.5.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreibman L., Charlop M. H., Koegel R. L. Teaching autistic children to use extra-stimulus prompts. J Exp Child Psychol. 1982 Jun;33(3):475–491. doi: 10.1016/0022-0965(82)90060-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreibman L., Charlop M. H. S + versus S- fading in prompting procedures with autistic children. J Exp Child Psychol. 1981 Jun;31(3):508–520. doi: 10.1016/0022-0965(81)90033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreibman L. Effects of within-stimulus and extra-stimulus prompting on discrimination learning in autistic children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1975 Spring;8(1):91–112. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1975.8-91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman M., Stoddard L. T. The effectiveness of fading in programming a simultaneous form discrimination for retarded children. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Jan;10(1):3–15. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steege M. W., Wacker D. P., McMahon C. M. Evaluation of the effectiveness and efficiency of two stimulus prompt strategies with severely handicapped students. J Appl Behav Anal. 1987 Fall;20(3):293–299. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1987.20-293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRACE H. S. Discrimination learning with and without "errors". J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jan;6:1–27. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRACE H. S. Errorless transfer of a discrimination across two continua. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:223–232. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


