Full text
PDF


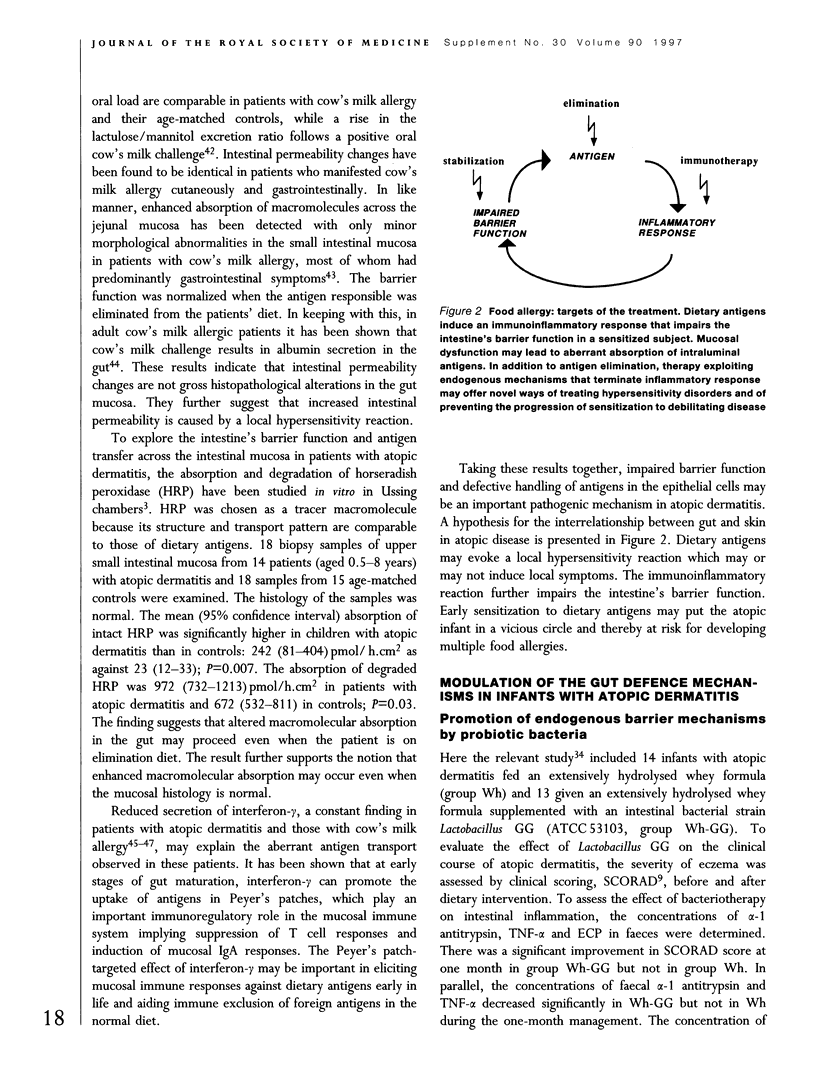


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agata H., Kondo N., Fukutomi O., Shinoda S., Orii T. Effect of elimination diets on food-specific IgE antibodies and lymphocyte proliferative responses to food antigens in atopic dermatitis patients exhibiting sensitivity to food allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1993 Feb;91(2):668–679. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(93)90273-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson U., Knutson T. W., Knutson L., Dannaeus A., Hällgren R., Ahlstedt S. Increased levels of hyaluronan and albumin after intestinal challenge in adult patients with cow's milk intolerance. Clin Exp Allergy. 1996 Jan;26(1):96–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1996.tb00061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman R., Trembath R. C., Harper J. I. Chromosome 11q13 and atopy underlying atopic eczema. Lancet. 1993 May 1;341(8853):1121–1122. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)93130-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerkinsky C. C., Nilsson L. A., Nygren H., Ouchterlony O., Tarkowski A. A solid-phase enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) assay for enumeration of specific antibody-secreting cells. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):109–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont C., Barau E., Molkhou P., Raynaud F., Barbet J. P., Dehennin L. Food-induced alterations of intestinal permeability in children with cow's milk-sensitive enteropathy and atopic dermatitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1989 May;8(4):459–465. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198905000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fargeas M. J., Theodorou V., More J., Wal J. M., Fioramonti J., Bueno L. Boosted systemic immune and local responsiveness after intestinal inflammation in orally sensitized guinea pigs. Gastroenterology. 1995 Jul;109(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90268-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fartasch M., Diepgen T. L. The barrier function in atopic dry skin. Disturbance of membrane-coating granule exocytosis and formation of epidermal lipids? Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh) 1992;176:26–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman M., Corthier G., Petit A., Meslin J. C., Moreau C., Desjeux J. F. Intestinal absorption of macromolecules during viral enteritis: an experimental study on rotavirus-infected conventional and germ-free mice. Pediatr Res. 1987 Jul;22(1):72–78. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198707000-00017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman M., Grasset E., Ducroc R., Desjeux J. F. Antigen absorption by the jejunal epithelium of children with cow's milk allergy. Pediatr Res. 1988 Aug;24(2):197–202. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198808000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. J., Ball G., Hosking C. S., Wood P. R. Gamma-interferon production in cow milk allergy. Allergy. 1993 Feb;48(2):75–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1993.tb00689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. J., Cameron D. J., Francis D. E., Gonzalez-Andaya A. M., Hosking C. S. Challenge confirmation of late-onset reactions to extensively hydrolyzed formulas in infants with multiple food protein intolerance. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995 Sep;96(3):386–394. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(95)70058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. J., Firer M. A., Shelton M. J., Hosking C. S. Manifestations of milk allergy in infancy: clinical and immunologic findings. J Pediatr. 1986 Aug;109(2):270–276. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80384-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. G. A potential vaccine strategy for asthma and allied atopic diseases during early childhood. Lancet. 1994 Aug 13;344(8920):456–458. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91776-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isolauri E., Majamaa H., Arvola T., Rantala I., Virtanen E., Arvilommi H. Lactobacillus casei strain GG reverses increased intestinal permeability induced by cow milk in suckling rats. Gastroenterology. 1993 Dec;105(6):1643–1650. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)91059-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isolauri E., Suomalainen H., Kaila M., Jalonen T., Soppi E., Virtanen E., Arvilommi H. Local immune response in patients with cow milk allergy: follow-up of patients retaining allergy or becoming tolerant. J Pediatr. 1992 Jan;120(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)80589-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isolauri E., Sütas Y., Mäkinen-Kiljunen S., Oja S. S., Isosomppi R., Turjanmaa K. Efficacy and safety of hydrolyzed cow milk and amino acid-derived formulas in infants with cow milk allergy. J Pediatr. 1995 Oct;127(4):550–557. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(95)70111-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isolauri E., Turjanmaa K. Combined skin prick and patch testing enhances identification of food allergy in infants with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996 Jan;97(1 Pt 1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(96)70277-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isolauri E., Virtanen E., Jalonen T., Arvilommi H. Local immune response measured in blood lymphocytes reflects the clinical reactivity of children with cow's milk allergy. Pediatr Res. 1990 Dec;28(6):582–586. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199012000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalonen T. Identical intestinal permeability changes in children with different clinical manifestations of cow's milk allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991 Nov;88(5):737–742. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(91)90180-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaila M., Arvilommi H., Soppi E., Laine S., Isolauri E. A prospective study of humoral immune responses to cow milk antigens in the first year of life. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 1994 Aug;5(3):164–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3038.1994.tb00233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaila M. Immune defense to dietary cow milk in healthy infants. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 1993 Feb;4(1):41–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3038.1993.tb00064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. Y. Atopic dermatitis: the skin as a window into the pathogenesis of chronic allergic diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995 Sep;96(3):302–319. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(95)70049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majamaa H., Isolauri E. Evaluation of the gut mucosal barrier: evidence for increased antigen transfer in children with atopic eczema. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996 Apr;97(4):985–990. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(96)80074-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majamaa H., Miettinen A., Laine S., Isolauri E. Intestinal inflammation in children with atopic eczema: faecal eosinophil cationic protein and tumour necrosis factor-alpha as non-invasive indicators of food allergy. Clin Exp Allergy. 1996 Feb;26(2):181–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1996.tb00078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcucci F., Sensi L. G., Bizzarri G. Specific IgE to food and inhalant allergens in intestinal washings of children affected by atopic eczema. Clin Allergy. 1985 Jul;15(4):345–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1985.tb03002.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau M. C., Corthier G. Effect of the gastrointestinal microflora on induction and maintenance of oral tolerance to ovalbumin in C3H/HeJ mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2766–2768. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2766-2768.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pène J., Rivier A., Lagier B., Becker W. M., Michel F. B., Bousquet J. Differences in IL-4 release by PBMC are related with heterogeneity of atopy. Immunology. 1994 Jan;81(1):58–64. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romagnani S. Regulation of the development of type 2 T-helper cells in allergy. Curr Opin Immunol. 1994 Dec;6(6):838–846. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(94)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson H. A., McCaskill C. C. Food hypersensitivity and atopic dermatitis: evaluation of 113 patients. J Pediatr. 1985 Nov;107(5):669–675. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80390-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson I. R., Walker W. A. Uptake and transport of macromolecules by the intestine: possible role in clinical disorders (an update). Gastroenterology. 1993 Feb;104(2):622–639. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90436-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrander J. J., van den Bogart J. P., Forget P. P., Schrander-Stumpel C. T., Kuijten R. H., Kester A. D. Cow's milk protein intolerance in infants under 1 year of age: a prospective epidemiological study. Eur J Pediatr. 1993 Aug;152(8):640–644. doi: 10.1007/BF01955238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz Larsen F. Atopic dermatitis: a genetic-epidemiologic study in a population-based twin sample. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993 May;28(5 Pt 1):719–723. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(93)70099-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selbekk B. H. A comparison between in vitro jejunal mast cell degranulation and intragastric challenge in patients with suspected food intolerance. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1985 Apr;20(3):299–303. doi: 10.3109/00365528509091654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M., Pang K. Y., Walker W. A. Food proteins and gut mucosal barrier. II. Differential interaction of cow's milk proteins with the mucous coat and the surface membrane of adult and immature rat jejunum. Pediatr Res. 1984 Dec;18(12):1252–1257. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198412000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strachan D. P. Hay fever, hygiene, and household size. BMJ. 1989 Nov 18;299(6710):1259–1260. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6710.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suomalainen H., Soppi E., Laine S., Isolauri E. Immunologic disturbances in cow's milk allergy, 2: Evidence for defective interferon-gamma generation. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 1993 Nov;4(4):203–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3038.1993.tb00092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sütas Y., Hurme M., Isolauri E. Down-regulation of anti-CD3 antibody-induced IL-4 production by bovine caseins hydrolysed with Lactobacillus GG-derived enzymes. Scand J Immunol. 1996 Jun;43(6):687–689. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3083.1996.d01-258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sütas Y., Soppi E., Korhonen H., Syväoja E. L., Saxelin M., Rokka T., Isolauri E. Suppression of lymphocyte proliferation in vitro by bovine caseins hydrolyzed with Lactobacillus casei GG-derived enzymes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996 Jul;98(1):216–224. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(96)70245-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Friedman A., Miller A., Khoury S. J., al-Sabbagh A., Santos L., Sayegh M., Nussenblatt R. B., Trentham D. E., Hafler D. A. Oral tolerance: immunologic mechanisms and treatment of animal and human organ-specific autoimmune diseases by oral administration of autoantigens. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:809–837. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.004113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga E. A., Snoek M., Jansen H. M., Bos J. D., van Lier R. A., Kapsenberg M. L. Human atopen-specific types 1 and 2 T helper cell clones. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 1;147(9):2942–2949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijden F. L., Wierenga E. A., Bos J. D., Kapsenberg M. L. High frequency of IL-4-producing CD4+ allergen-specific T lymphocytes in atopic dermatitis lesional skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Sep;97(3):389–394. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12480966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


