Abstract
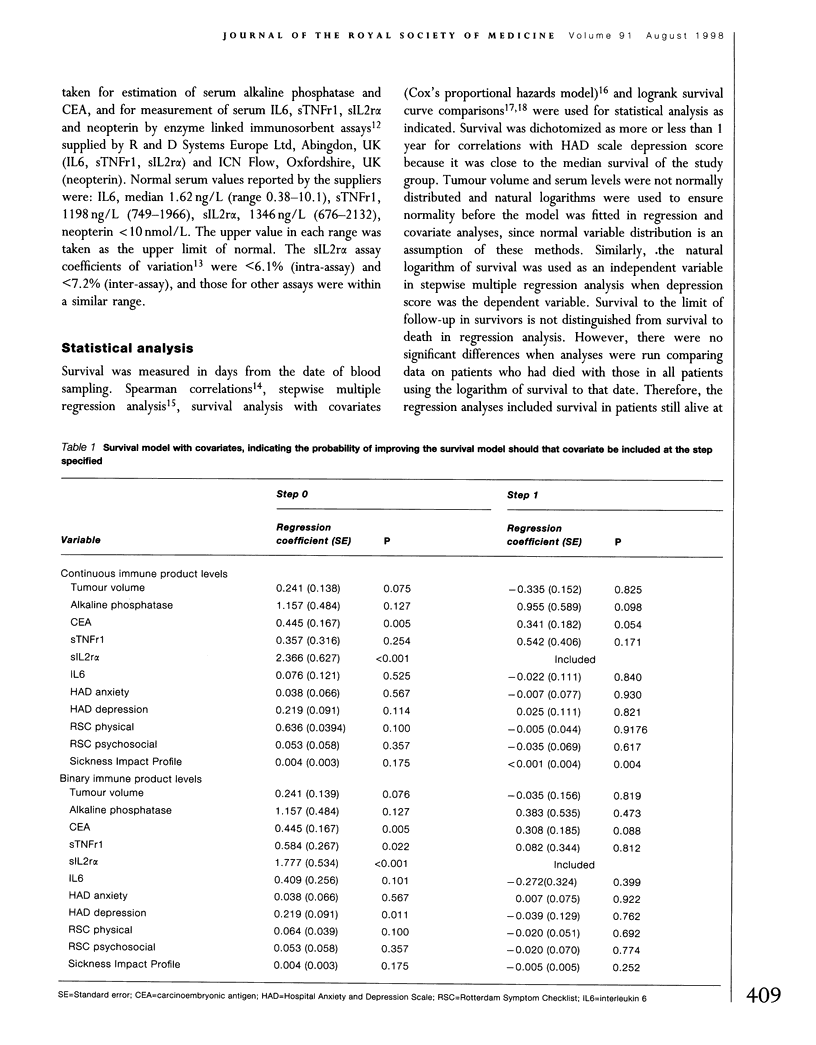
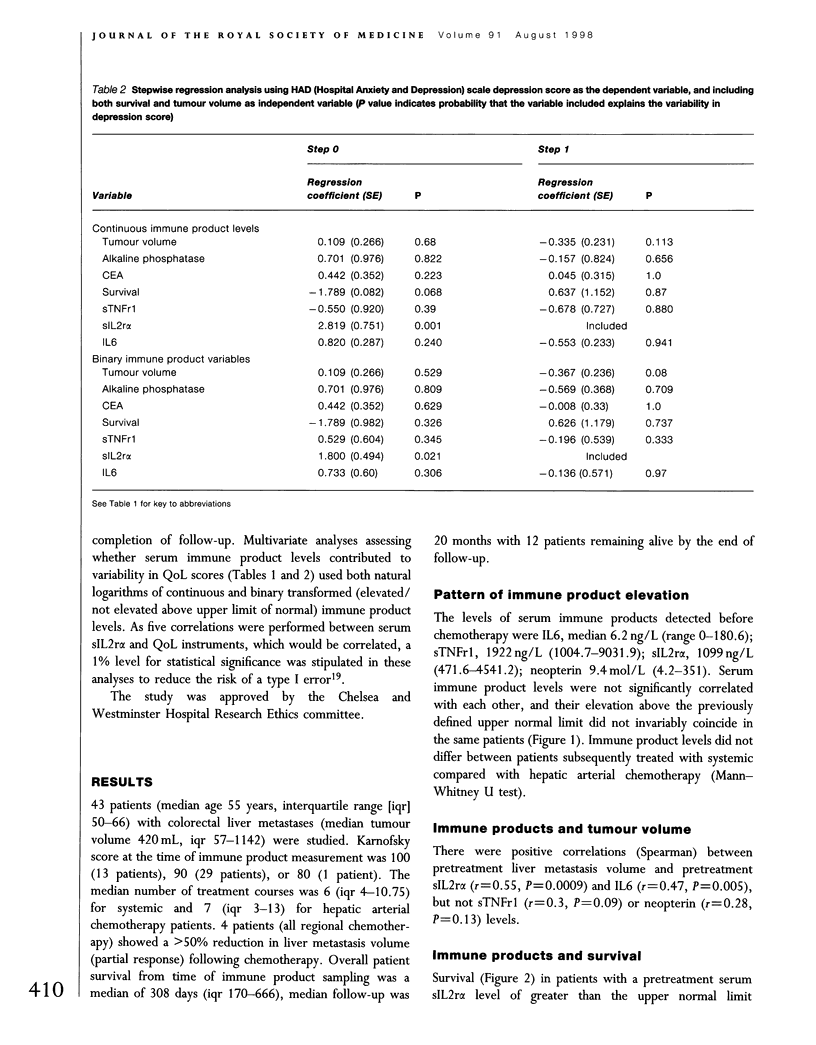
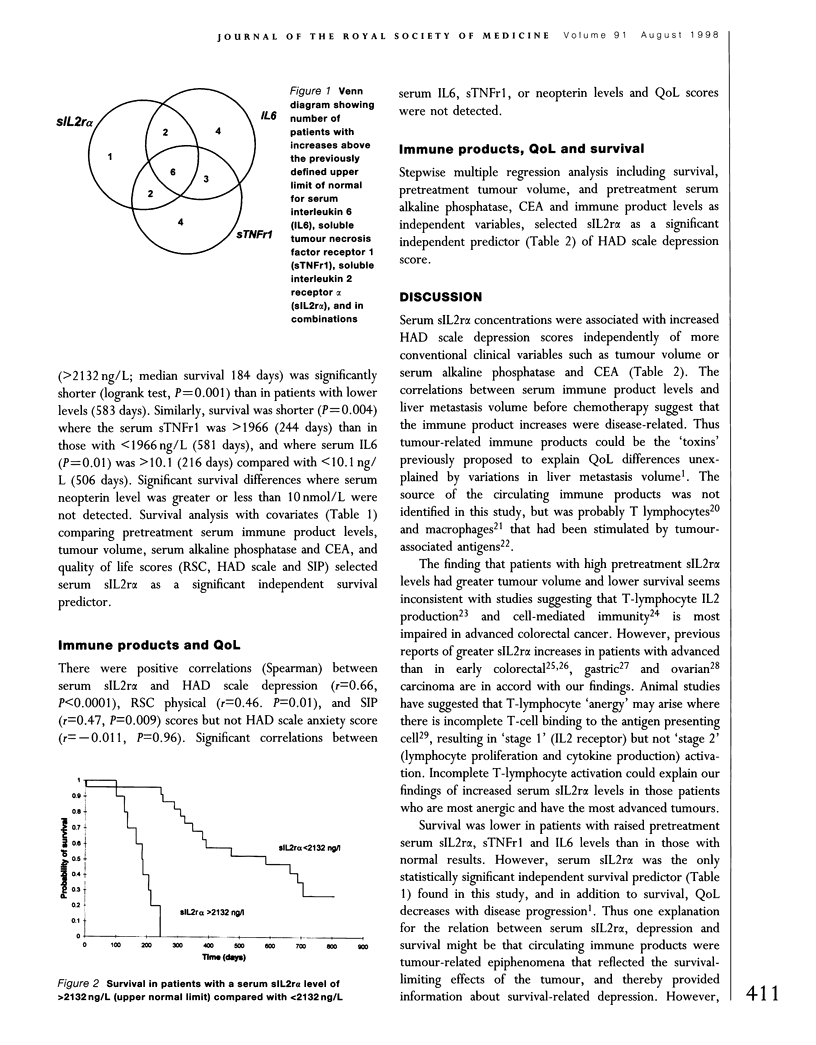
We have previously suggested that colorectal liver metastases might produce 'toxins' that reduce both quality of life (QoL) and survival. In this study we assessed whether QoL in patients with such metastases was related to immune activation, as determined by increased serum levels of interleukin 6 (IL6), soluble tumour necrosis factor receptor 1 (sTNFr1), soluble interleukin 2 receptor alpha (sIL2r alpha) or the interferon-gamma marker neopterin. Serum IL6, sTNFr1, sIL2r alpha, neopterin, alkaline phosphatase and carcinoembryonic antigen levels, liver metastasis volume, and QoL (Hospital Anxiety and Depression [HAD] scale, Rotterdam Symptom Checklist [RSC], and Sickness Impact Profile [SIP]) were measured in 43 patients. There were significant positive correlations between serum sIL2r alpha and HAD depression score (r = 0.66, P = 0.0001), RSC physical symptom score (r = 0.46, P < 0.01), and SIP score (r = 0.47, P = 0.009). Multiple regression analysis suggested that serum sIL2r alpha level was a significant independent predictor of HAD depression score. Although survival was shorter (logrank test P < 0.05) where sIL2r alpha, sTNFr1 and IL6 levels were higher, the ability of sIL2r alpha to predict HAD depression score was independent of survival.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton D. P., Blanchard D. K., Wells A. F., Nicosia S. V., Roberts W. S., Cavanagh D., Djeu J. Y. Expression of interleukin-2 receptor alpha (IL-2R alpha) mRNA and protein in advanced epithelial ovarian cancer. Anticancer Res. 1994 May-Jun;14(3A):761–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berghella A. M., Pellegrini P., Piancatelli D., Maccarone D., Del Beato T., Giubilei D., Pomidori A., Adorno D., Casciani C. U. Progression mechanisms in colon cancer: soluble interleukin-2 (IL-2) receptor, IL-2 plus anti-CD3 proliferative response and tumour stage correlations. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1994 Mar;38(3):160–166. doi: 10.1007/BF01525636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergner M., Bobbitt R. A., Carter W. B., Gilson B. S. The Sickness Impact Profile: development and final revision of a health status measure. Med Care. 1981 Aug;19(8):787–805. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198108000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Mahoney J., Le Trang N., Pekala P., Cerami A. Purification of cachectin, a lipoprotein lipase-suppressing hormone secreted by endotoxin-induced RAW 264.7 cells. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):984–995. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D., Fordy C., Earlam S. A., Allen-Mersh T. G. Hepatic arterial cannulation for regional chemotherapy is safe in patients with a liver metastasis volume of less than 1 litre. Br J Cancer. 1997;75(8):1213–1216. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1997.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durelli L., Bongioanni M. R., Cavallo R., Ferrero B., Ferri R., Ferrio M. F., Bradac G. B., Riva A., Vai S., Geuna M. Chronic systemic high-dose recombinant interferon alfa-2a reduces exacerbation rate, MRI signs of disease activity, and lymphocyte interferon gamma production in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 1994 Mar;44(3 Pt 1):406–413. doi: 10.1212/wnl.44.3_part_1.406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin M. J., Burke D., Earlam S., Fordy C., Allen-Mersh T. G. Measurement of response to treatment in colorectal liver metastases. Br J Cancer. 1995 Apr;71(4):873–876. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earlam S., Glover C., Davies M., Fordy C., Allen-Mersh T. G. Effect of regional and systemic fluorinated pyrimidine chemotherapy on quality of life in colorectal liver metastasis patients. J Clin Oncol. 1997 May;15(5):2022–2029. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1997.15.5.2022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earlam S., Glover C., Fordy C., Burke D., Allen-Mersh T. G. Relation between tumor size, quality of life, and survival in patients with colorectal liver metastases. J Clin Oncol. 1996 Jan;14(1):171–175. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1996.14.1.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsässer-Beile U., Gallati H., Weber W., Wild E. D., Schulte Mönting J., von Kleist S. Increased plasma concentrations for type I and II tumor necrosis factor receptors and IL-2 receptors in cancer patients. Tumour Biol. 1994;15(1):17–24. doi: 10.1159/000217869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough D. B., Heys S. D., Eremin O. Cancer cachexia: pathophysiological mechanisms. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1996 Apr;22(2):192–196. doi: 10.1016/s0748-7983(96)90905-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellström I., Hellström K. E., Shepard T. H. Cell-mediated immunity against antigens common to human colonic carcinomas and fetal gut epithelium. Int J Cancer. 1970 Nov 15;6(3):346–351. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910060304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson D. C., Rippin J. J. Stimulus-dependent production of cytokines and pterins by peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Immunol Lett. 1995 Feb;45(1-2):29–34. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(94)00222-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson D. C., Sheldon J., Riches P., Hobbs J. R. Cytokine induction of neopterin production. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Mar;83(3):479–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05664.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J., Caplehorn J. R., Ross W. B., Morris D. L. High serum carcinoembryonic antigen concentration in patients with colorectal liver metastases is associated with poor cell-mediated immunity, which is predictive of survival. Br J Surg. 1997 Oct;84(10):1382–1385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maes M., Bosmans E., Meltzer H. Y. Immunoendocrine aspects of major depression. Relationships between plasma interleukin-6 and soluble interleukin-2 receptor, prolactin and cortisol. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1995;245(3):172–178. doi: 10.1007/BF02193091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meta-Analysis Group in Cancer. Piedbois P., Buyse M., Kemeny N., Rougier P., Carlson R., Allen-Mersh T., O'Connell M., Chang A., Sondak V. Reappraisal of hepatic arterial infusion in the treatment of nonresectable liver metastases from colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996 Mar 6;88(5):252–258. doi: 10.1093/jnci/88.5.252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monson J. R., Ramsden C., Guillou P. J. Decreased interleukin-2 production in patients with gastrointestinal cancer. Br J Surg. 1986 Jun;73(6):483–486. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800730620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami S., Satomi A., Ishida K., Murai H., Matsuki M., Hashimoto T. Serum-soluble interleukin-2 receptor concentrations in patients with gastric cancer. Cancer. 1994 Nov 15;74(10):2745–2748. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19941115)74:10<2745::aid-cncr2820741002>3.0.co;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami S., Satomi A., Ishida K., Murai H., Okamura Y. Serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor in colorectal cancer. Acta Oncol. 1994;33(1):19–21. doi: 10.3109/02841869409098369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray G. D. Statistical aspects of research methodology. Br J Surg. 1991 Jul;78(7):777–781. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800780704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peto R., Pike M. C., Armitage P., Breslow N. E., Cox D. R., Howard S. V., Mantel N., McPherson K., Peto J., Smith P. G. Design and analysis of randomized clinical trials requiring prolonged observation of each patient. II. analysis and examples. Br J Cancer. 1977 Jan;35(1):1–39. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1977.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J. H., Hank J., Storer B., Borchert A. A., Moore K. H., Albertini M., Bechhofer R., Wesley O., Brown R. R., Bastin A. M. A direct comparison of immunological and clinical effects of interleukin 2 with and without interferon-alpha in humans. Cancer Res. 1993 Mar 15;53(6):1286–1292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloan-Lancaster J., Evavold B. D., Allen P. M. Induction of T-cell anergy by altered T-cell-receptor ligand on live antigen-presenting cells. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):156–159. doi: 10.1038/363156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Shimada E., Urakawa T. Serum levels of cytokines in patients with colorectal cancer: possible involvement of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 in hematogenous metastasis. J Gastroenterol. 1994 Aug;29(4):423–429. doi: 10.1007/BF02361238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalcman S., Green-Johnson J. M., Murray L., Nance D. M., Dyck D., Anisman H., Greenberg A. H. Cytokine-specific central monoamine alterations induced by interleukin-1, -2 and -6. Brain Res. 1994 Apr 18;643(1-2):40–49. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond A. S., Snaith R. P. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1983 Jun;67(6):361–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1983.tb09716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haes J. C., van Knippenberg F. C., Neijt J. P. Measuring psychological and physical distress in cancer patients: structure and application of the Rotterdam Symptom Checklist. Br J Cancer. 1990 Dec;62(6):1034–1038. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1990.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


