Abstract
Studies of school leadership suggest that visiting classrooms, emphasizing achievement and training, and supporting teachers are important indicators of the effectiveness of school principals. The utility of a behavior-analytic program to support the enhancement of these behaviors in 2 school principals and the impact of their involvement upon teachers' and students' performances in three classes were examined in two experiments, one at an elementary school and another at a secondary school. Treatment conditions consisted of helping the principal or teacher to schedule his or her time and to use goal setting, feedback, and praise. A withdrawal design (Experiment 1) and a multiple baseline across classrooms (Experiment 2) showed that the principal's and teacher's rates of praise, feedback, and goal setting increased during the intervention, and were associated with improvements in the academic performance of the students. In the future, school psychologists might analyze the impact of involving themselves in supporting the principal's involvement in improving students' and teachers' performances or in playing a similar leadership role themselves.
Keywords: performance management, feedback, public education, school principals, teacher behavior, academic skills
Full text
PDF




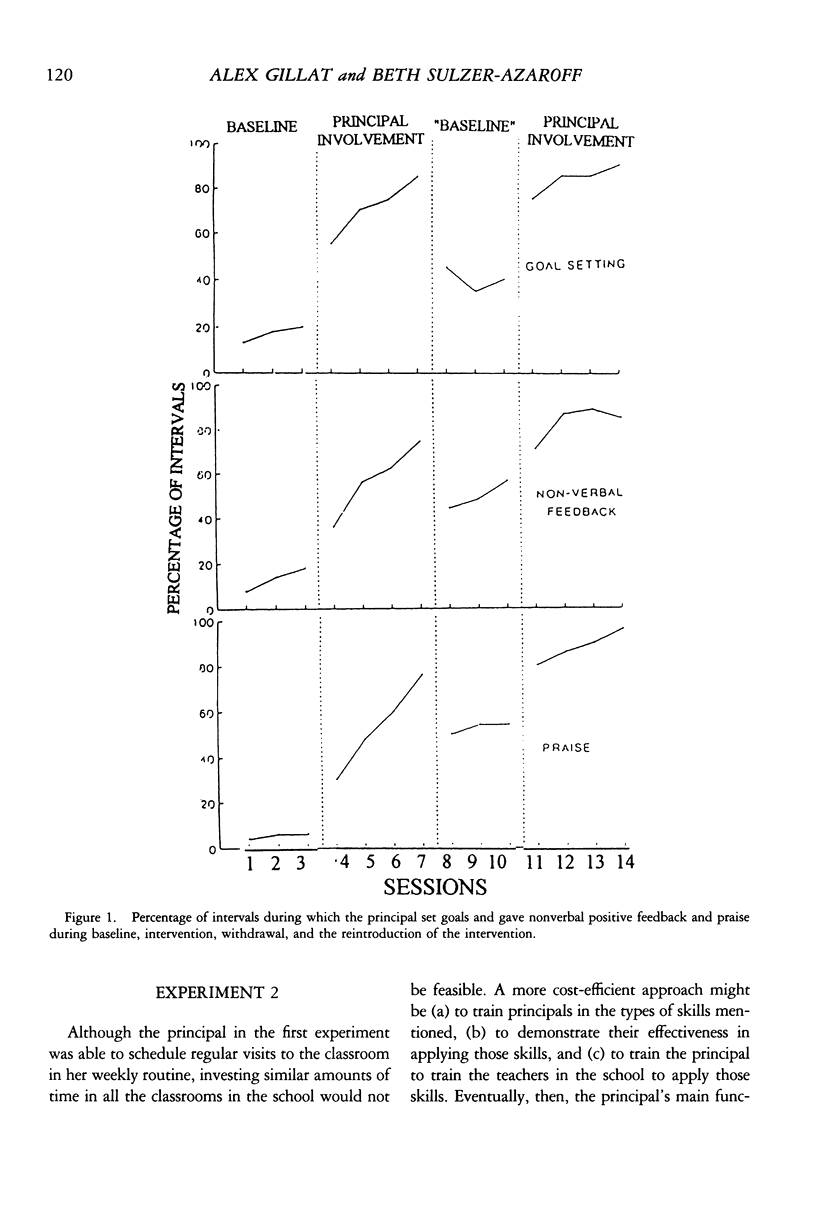
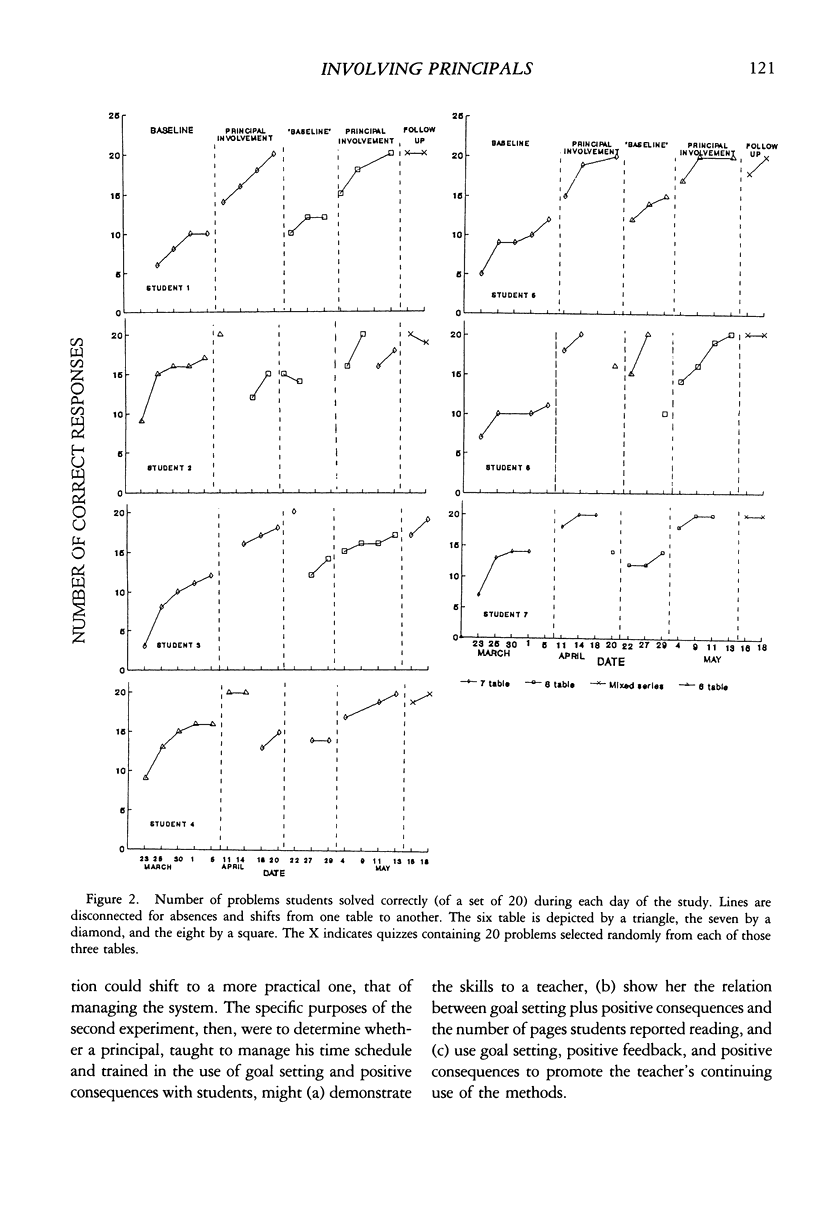



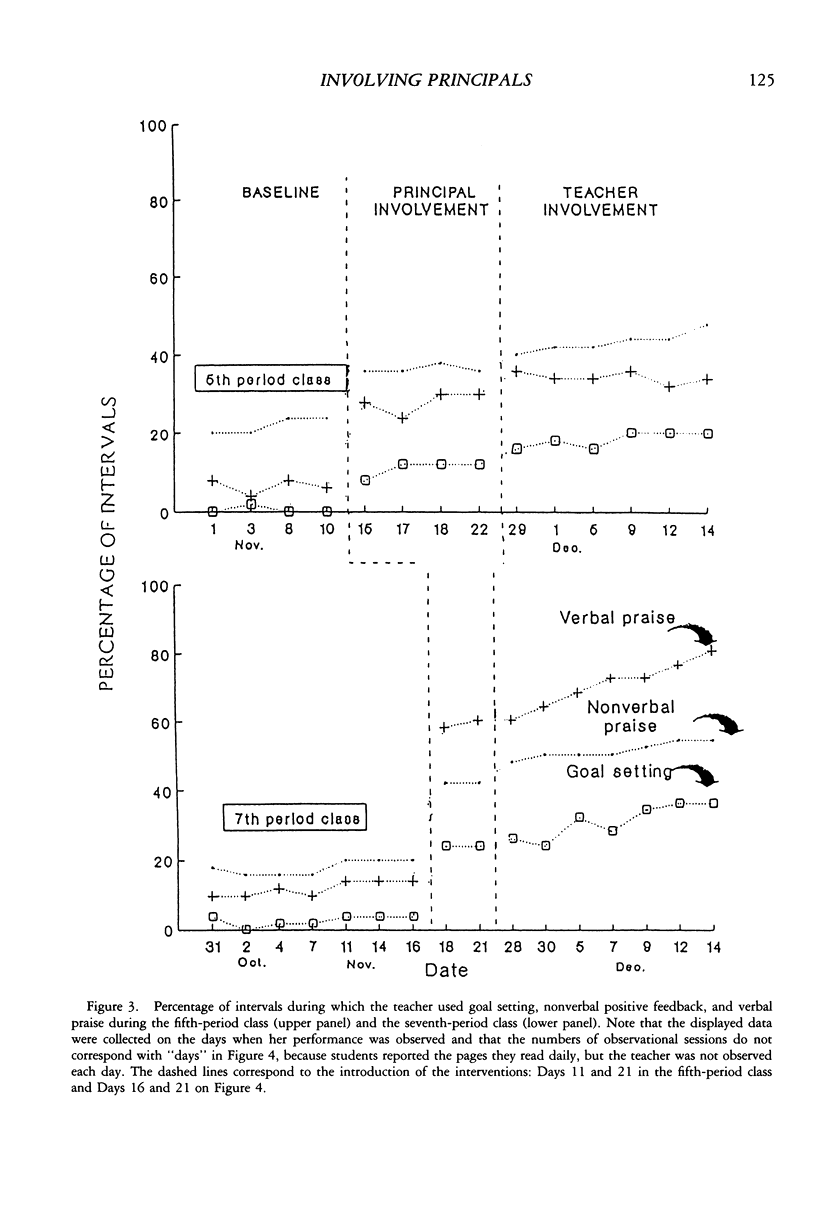
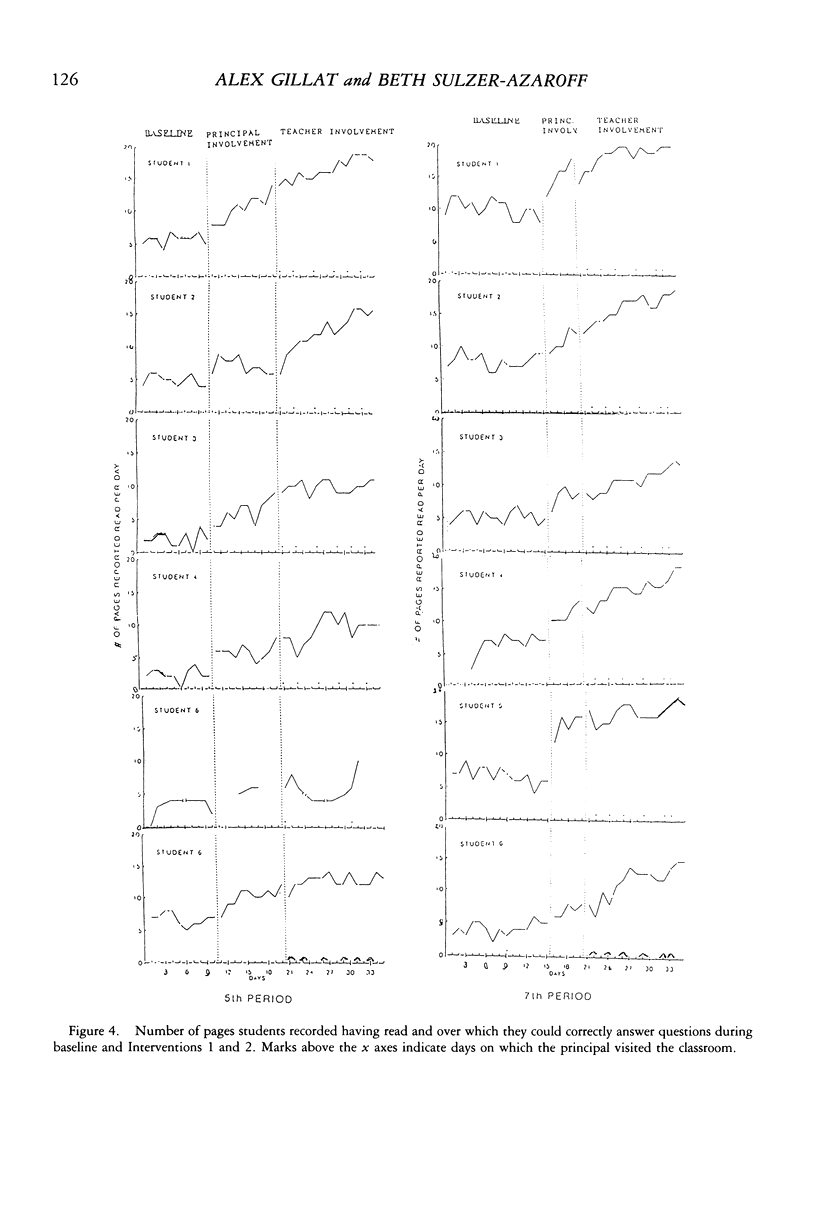



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballard K. D., Glynn T. Behavioral self-management in story writing with elementary school children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1975 Winter;8(4):387–398. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1975.8-387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broden M., Hall R. V., Mitts B. The effect of self-recording on the classroom behavior of two eighth-grade students. J Appl Behav Anal. 1971 Fall;4(3):191–199. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1971.4-191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland R. E., Brown R. E., Hall R. V. The effects of principal-implemented techniques on the behavior of pupils. J Appl Behav Anal. 1974 Spring;7(1):77–86. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1974.7-77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fixsen D. L., Phillips E. L., Wolf M. M. Achievement Place: the reliability of self-reporting and peer-reporting and their effects on behavior. J Appl Behav Anal. 1972 Spring;5(1):19–30. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1972.5-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn E. L., Thomas J. D., Shee S. M. Behavioral self-control of on-task behavior in an elementary classroom. J Appl Behav Anal. 1973 Spring;6(1):105–113. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1973.6-105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes S. C., Rosenfarb I., Wulfert E., Munt E. D., Korn Z., Zettle R. D. Self-reinforcement effects: An artifact of social standard setting? J Appl Behav Anal. 1985 Fall;18(3):201–214. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1985.18-201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins B. L. Comments on the future of applied behavior analysis. J Appl Behav Anal. 1987 Winter;20(4):339–346. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1987.20-339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. R., Layng T. V. Breaking the structuralist barrier. Literacy and numeracy with fluency. Am Psychol. 1992 Nov;47(11):1475–1490. doi: 10.1037//0003-066x.47.11.1475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


